Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Azure Maps Web SDK provides a Map Control that enables the customization of interactive maps with your own content and imagery for display in your web or mobile applications. This module is a helper library that makes it easy to use the Azure Maps REST services in web or Node.js applications by using JavaScript or TypeScript.
Note
Azure Maps Web SDK Map Control v1 retirement
Version 1 of the Web SDK Map Control is now deprecated and will be retired on 9/19/26. To avoid service disruptions, migrate to version 3 of the Web SDK Map Control by 9/19/26. Version 3 is backwards compatible and has several benefits including WebGL 2 Compatibility, increased performance and support for 3D terrain tiles. For more information, see The Azure Maps Web SDK v1 migration guide.
Prerequisites
To use the Map Control in a web page, you must have one of the following prerequisites:
- An Azure Maps account
- A subscription key or Microsoft Entra credentials. For more information, see authentication options.
Create a new map in a web page
You can embed a map in a web page by using the Map Control client-side JavaScript library.
Create a new HTML file.
Load in the Azure Maps Web SDK. You can choose one of two options:
Use the globally hosted CDN version of the Azure Maps Web SDK by adding references to the JavaScript and
stylesheetin the<head>element of the HTML file:<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css" type="text/css"> <script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.js"></script>Load the Azure Maps Web SDK source code locally using the azure-maps-control npm package and host it with your app. This package also includes TypeScript definitions.
npm install azure-maps-control
Then add references to the Azure Maps
stylesheetto the<head>element of the file:<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css" type="text/css" />Note
TypeScript definitions can be imported into your application by adding the following code:
import * as atlas from 'azure-maps-control';To render the map so that it fills the full body of the page, add the following
<style>element to the<head>element.<style> html, body { margin: 0; } #myMap { height: 100vh; width: 100vw; } </style>In the body of the page, add a
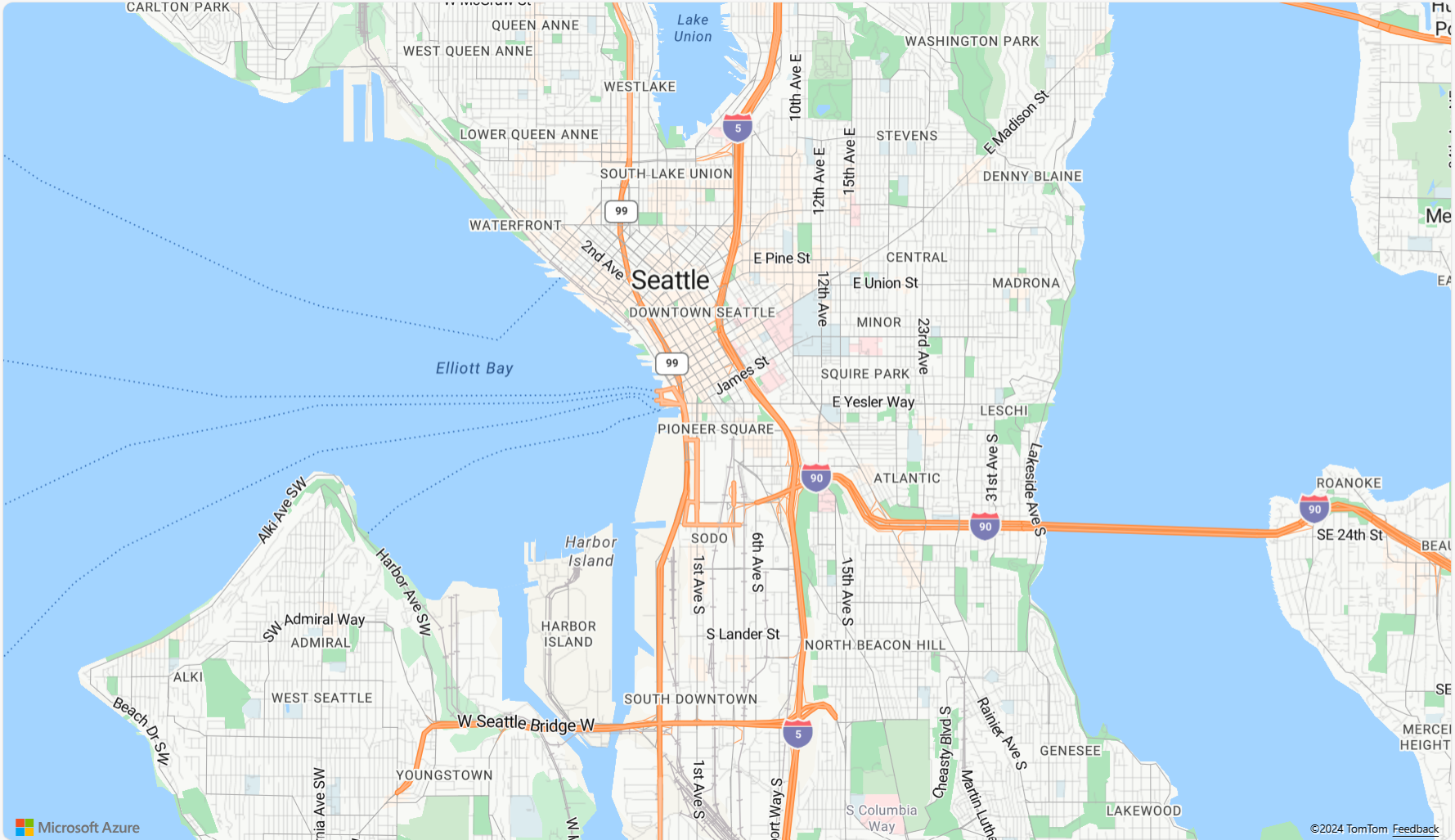
<div>element and give it anidof myMap.<body onload="InitMap()"> <div id="myMap"></div> </body>Next, initialize the map control. In order to authenticate the control, use an Azure Maps subscription key or Microsoft Entra credentials with authentication options.
If you're using a subscription key for authentication, copy and paste the following script element inside the
<head>element, and below the first<script>element. Replace<Your Azure Maps Key>with your Azure Maps subscription key.<script type="text/javascript"> function InitMap() { var map = new atlas.Map('myMap', { center: [-122.33, 47.6], zoom: 12, language: 'en-US', authOptions: { authType: 'subscriptionKey', subscriptionKey: '<Your Azure Maps Key>' } }); } </script>If you're using Microsoft Entra ID for authentication, copy and paste the following script element inside the
<head>element, and below the first<script>element.<script type="text/javascript"> function InitMap() { var map = new atlas.Map('myMap', { center: [-122.33, 47.6], zoom: 12, language: 'en-US', authOptions: { authType: 'aad', clientId: '<Your Microsoft Entra Client ID>', aadAppId: '<Your Microsoft Entra App ID>', aadTenant: '<Your Microsoft Entra tenant ID>' } }); } </script>For more information about authentication with Azure Maps, see the Authentication with Azure Maps document. For a list of samples showing how to integrate Azure AD with Azure Maps, see Azure Maps & Azure Active Directory Samples in GitHub.
Tip
In this example, we've passed in the
idof the map<div>. Another way to do this is to pass in theHTMLElementobject by passingdocument.getElementById('myMap')as the first parameter.Optionally, you may find it helpful to add the following
metaelements to theheadelement of the page:<!-- Ensures that Internet Explorer and Edge uses the latest version and doesn't emulate an older version --> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=Edge"> <!-- Ensures the web page looks good on all screen sizes. --> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">Your HTML file should now look something like the following code snippet:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title></title> <meta charset="utf-8"> <!-- Ensures that Internet Explorer and Edge uses the latest version and doesn't emulate an older version --> <meta http-equiv="x-ua-compatible" content="IE=Edge"> <!-- Ensures the web page looks good on all screen sizes. --> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"> <!-- Add references to the Azure Maps Map control JavaScript and CSS files. --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css" type="text/css"> <script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> //Create an instance of the map control and set some options. function InitMap() { var map = new atlas.Map('myMap', { center: [-122.33, 47.6], zoom: 12, language: 'en-US', authOptions: { authType: 'subscriptionKey', subscriptionKey: '<Your Azure Maps Key>' } }); } </script> <style> html, body { margin: 0; } #myMap { height: 100vh; width: 100vw; } </style> </head> <body onload="InitMap()"> <div id="myMap"></div> </body> </html>Open the file in your web browser and view the rendered map. It should look like the following image:
Localizing the map
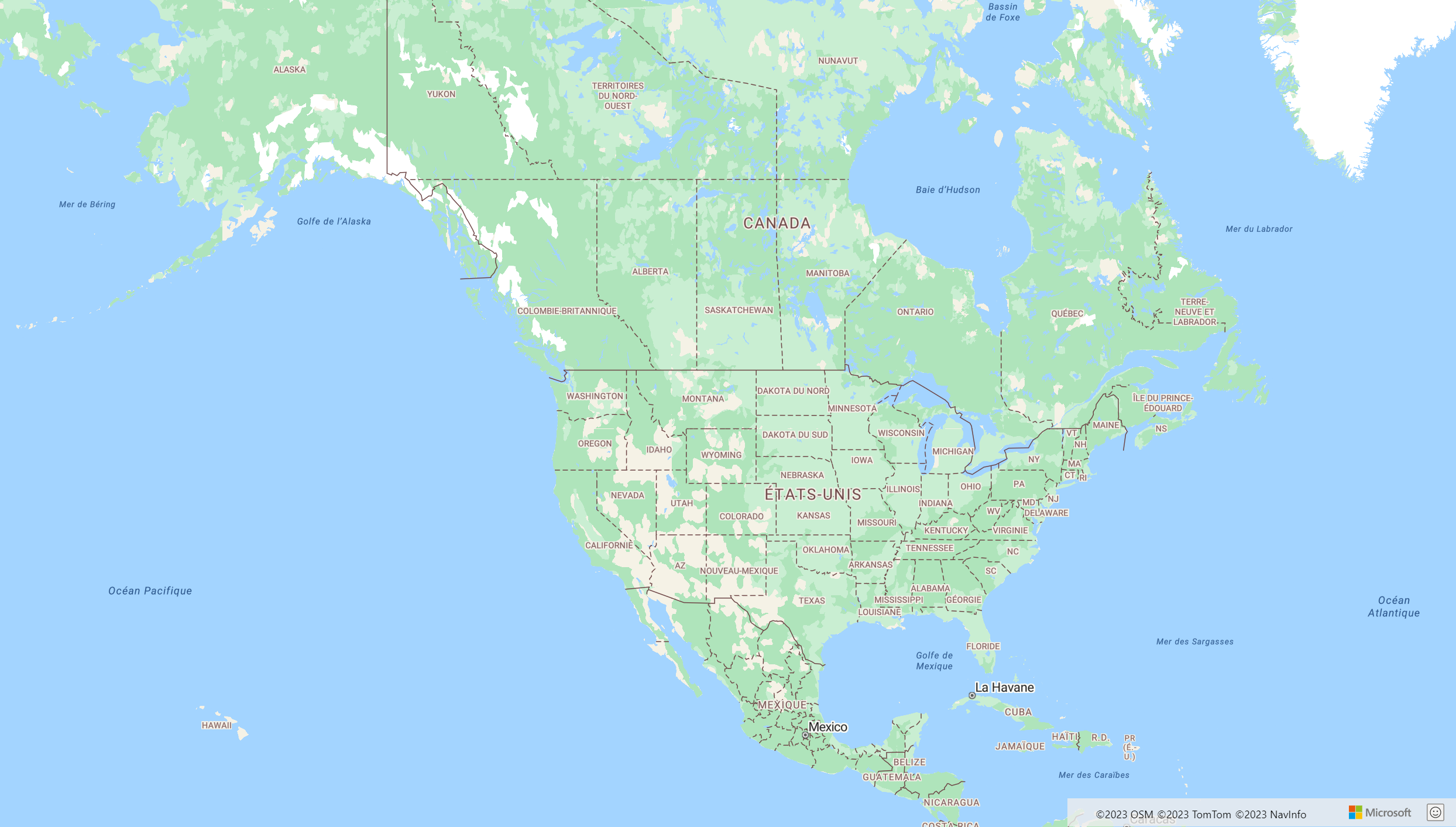
Azure Maps provides two different ways of setting the language and regional view for the rendered map. The first option is to add this information to the global atlas namespace, which results in all map control instances in your app defaulting to these settings. The following sets the language to French ("fr-FR") and the regional view to "Auto":
atlas.setLanguage('fr-FR');
atlas.setView('Auto');
The second option is to pass this information into the map options when loading the map like this:
map = new atlas.Map('myMap', {
language: 'fr-FR',
view: 'Auto',
authOptions: {
authType: 'aad',
clientId: '<Your AAD Client ID>',
aadAppId: '<Your AAD App ID>',
aadTenant: '<Your AAD Tenant ID>'
}
});
Note
It is possible to load multiple map instances on the same page with different language and region settings. Additionally, these settings can be updated after the map loads using the setStyle function of the map.
Here's an example of Azure Maps with the language set to "fr-FR" and the regional view set to Auto.
For a list of supported languages and regional views, see Localization support in Azure Maps.
WebGL 2 Compatibility
Beginning with Azure Maps Web SDK 3.0, the Web SDK includes full compatibility with WebGL 2, a powerful graphics technology that enables hardware-accelerated rendering in modern web browsers. By using WebGL 2, developers can harness the capabilities of modern GPUs to render complex maps and visualizations more efficiently, resulting in improved performance and visual quality.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no" />
<title>WebGL2 - Azure Maps Web SDK Samples</title>
<link href=https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css rel="stylesheet"/>
<script src=https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.js></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/deck.gl@^8/dist.min.js"></script>
<style>
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
#map {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script>
var map = new atlas.Map("map", {
center: [-122.44, 37.75],
bearing: 36,
pitch: 45,
zoom: 12,
style: "grayscale_light",
// Get an Azure Maps key at https://azuremaps.com/.
authOptions: {
authType: "subscriptionKey",
subscriptionKey: " <Your Azure Maps Key> "
}
});
// Wait until the map resources are ready.
map.events.add("ready", (event) => {
// Create a custom layer to render data points using deck.gl
map.layers.add(
new DeckGLLayer({
id: "grid-layer",
data: "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/visgl/deck.gl-data/master/website/sf-bike-parking.json",
cellSize: 200,
extruded: true,
elevationScale: 4,
getPosition: (d) => d.COORDINATES,
// GPUGridLayer leverages WebGL2 to perform aggregation on the GPU.
// For more details, see https://deck.gl/docs/api-reference/aggregation-layers/gpu-grid-layer
type: deck.GPUGridLayer
})
);
});
// A custom implementation of WebGLLayer
class DeckGLLayer extends atlas.layer.WebGLLayer {
constructor(options) {
super(options.id);
// Create an instance of deck.gl MapboxLayer which is compatible with Azure Maps
// https://deck.gl/docs/api-reference/mapbox/mapbox-layer
this._mbLayer = new deck.MapboxLayer(options);
// Create a renderer
const renderer = {
renderingMode: "3d",
onAdd: (map, gl) => {
this._mbLayer.onAdd?.(map["map"], gl);
},
onRemove: (map, gl) => {
this._mbLayer.onRemove?.(map["map"], gl);
},
prerender: (gl, matrix) => {
this._mbLayer.prerender?.(gl, matrix);
},
render: (gl, matrix) => {
this._mbLayer.render(gl, matrix);
}
};
this.setOptions({ renderer });
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
3D terrain tiles
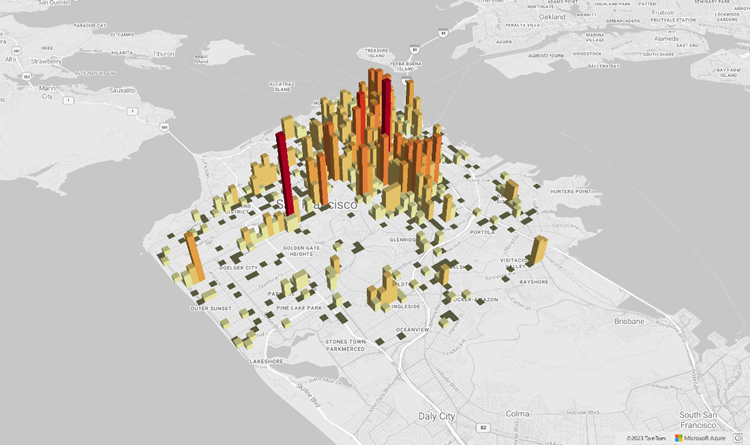
Beginning with Azure Maps Web SDK 3.0, developers can take advantage of 3D terrain visualizations. This feature allows you to incorporate elevation data into your maps, creating a more immersive experience for your users. Whether it's visualizing mountain ranges, valleys, or other geographical features, the 3D terrain support brings a new level of realism to your mapping applications.
The following code example demonstrates how to implement 3D terrain tiles.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no" />
<title>Elevation - Azure Maps Web SDK Samples</title>
<link href="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.css rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://atlas.microsoft.com/sdk/javascript/mapcontrol/3/atlas.min.js></script>
<style>
html,
body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
#map {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map"></div>
<script>
var map = new atlas.Map("map", {
center: [-121.7269, 46.8799],
maxPitch: 85,
pitch: 60,
zoom: 12,
style: "road_shaded_relief",
// Get an Azure Maps key at https://azuremaps.com/.
authOptions: {
authType: "subscriptionKey",
subscriptionKey: "<Your Azure Maps Key>"
}
});
// Create a tile source for elevation data. For more information on creating
// elevation data & services using open data, see https://aka.ms/elevation
var elevationSource = new atlas.source.ElevationTileSource("elevation", {
url: "<tileSourceUrl>"
});
// Wait until the map resources are ready.
map.events.add("ready", (event) => {
// Add the elevation source to the map.
map.sources.add(elevationSource);
// Enable elevation on the map.
map.enableElevation(elevationSource);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Azure Government cloud support
The Azure Maps Web SDK supports the Azure Government cloud. All JavaScript and CSS URLs used to access the Azure Maps Web SDK remain the same. The following tasks need to be done to connect to the Azure Government cloud version of the Azure Maps platform.
When using the interactive map control, add the following line of code before creating an instance of the Map class.
atlas.setDomain('atlas.azure.us');
Be sure to use Azure Maps authentication details from the Azure Government cloud platform when authenticating the map and services.
JavaScript frameworks
If developing using a JavaScript framework, one of the following open-source projects may be useful:
- ng-azure-maps - Angular 10 wrapper around Azure Maps.
- AzureMapsControl.Components - An Azure Maps Blazor component.
- Azure Maps React Component - A react wrapper for the Azure Maps control.
- Vue Azure Maps - An Azure Maps component for Vue application.
Next steps
Learn how to create and interact with a map:
Learn how to style a map:
Learn best practices and see samples:
For a list of samples showing how to integrate Microsoft Entra ID with Azure Maps, see: