Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article shows you how to use Microsoft Entra ID for authentication with Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Note
Microsoft Entra ID was previously known as Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
Alternatively, you can also configure Microsoft Entra authentication for SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines.
Prerequisites
To use Microsoft Entra authentication with your Azure SQL resource, you need the following prerequisites:
- A Microsoft Entra tenant populated with users and groups.
- An existing Azure SQL resource, such as Azure SQL Database, or Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Create and populate a Microsoft Entra tenant
Before you can configure Microsoft Entra authentication for your Azure SQL resource, you need to create a Microsoft Entra tenant and populate it with users and groups. Microsoft Entra tenants can be managed entirely within Azure or used for the federation of an on-premises Active Directory Domain Service.
For more information, see:
- What is Microsoft Entra ID?
- Integrating your on-premises identities with Microsoft Entra ID
- Add your domain name to Microsoft Entra ID
- What is federation with Microsoft Entra ID?
- Directory synchronization with Microsoft Entra ID
- Manage Microsoft Entra ID using Windows PowerShell
- Hybrid Identity Required Ports and Protocols
Set Microsoft Entra admin
To use Microsoft Entra authentication with your resource, it needs to have the Microsoft Entra administrator set. While conceptually the steps are the same for Azure SQL Database, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Azure SQL Managed Instance, this section describes in detail the different APIs and portal experiences to do so per product.
The Microsoft Entra admin can also be configured when the Azure SQL resource is created. If a Microsoft Entra admin is already configured, skip this section.
Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics
Setting the Microsoft Entra admin enables Microsoft Entra authentication for your Logical server for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics. You can set a Microsoft Entra admin for your server by using the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST APIs.
In the Azure portal, you can find the logical server name
- In the server name field on the Overview page of Azure SQL Database.
- In the server name field on the Overview page of your standalone dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics.
- In the relevant SQL endpoint on the Overview page of your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
To set the Microsoft Entra admin for your logical server in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal Directories + subscriptions pane, choose the directory that contains your Azure SQL resource as the Current directory.
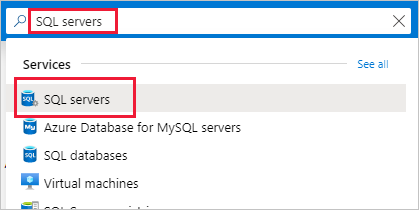
Search for SQL servers and then select the logical server for your database resource to open the SQL server pane.
On the SQL server pane for your logical server, select Microsoft Entra ID under Settings to open the Microsoft Entra ID pane.
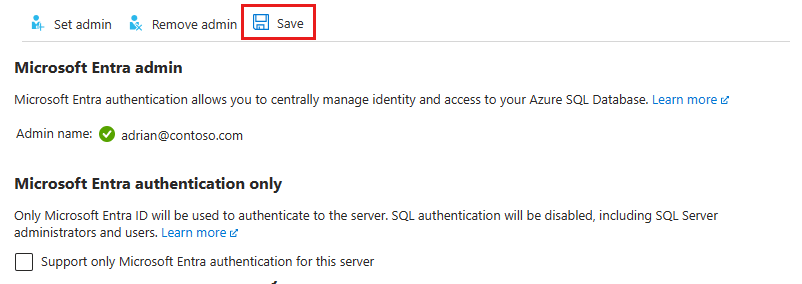
On the Microsoft Entra ID pane, select Set admin to open the Microsoft Entra ID pane.
The Microsoft Entra ID pane shows all users, groups, and applications in your current directory and allows you to search by name, alias, or ID. Find your desired identity for your Microsoft Entra admin and select it, then select Select to close the pane.
At the top of the Microsoft Entra ID page for your logical server, select Save.
The Object ID is displayed next to the admin name for Microsoft Entra users and groups. For applications (service principals), the Application ID is displayed.
The process of changing the administrator might take several minutes. Then the new administrator appears in the Microsoft Entra admin field.
To remove the admin, at the top of the Microsoft Entra ID page, select Remove admin, then select Save. Removing the Microsoft Entra admin disables Microsoft Entra authentication for your logical server.
Note
The Microsoft Entra admin is stored in the server's master database as a user (database principal). Since database principal names must be unique, the display name of the admin can't be the same as the name of any user in the server's master database. If a user with the name already exists, the Microsoft Entra admin setup fails and rolls back, indicating that the name is already in use.
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Setting the Microsoft Entra admin enables Microsoft Entra authentication for Azure SQL Managed Instance. You can set a Microsoft Entra admin for your SQL managed instance by using the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST APIs.
To grant your SQL managed instance read permissions to Microsoft Entra ID by using the Azure portal, sign in as a Privileged Role Administrator and follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, in the upper-right corner select your account, and then choose Switch directories to confirm which directory is your Current directory. Switch directories, if necessary.
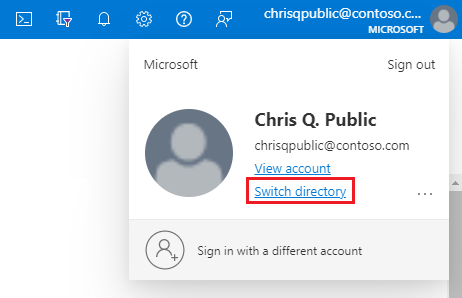
In the Azure portal Directories + subscriptions pane, choose the directory that contains your managed instance as the Current directory.```
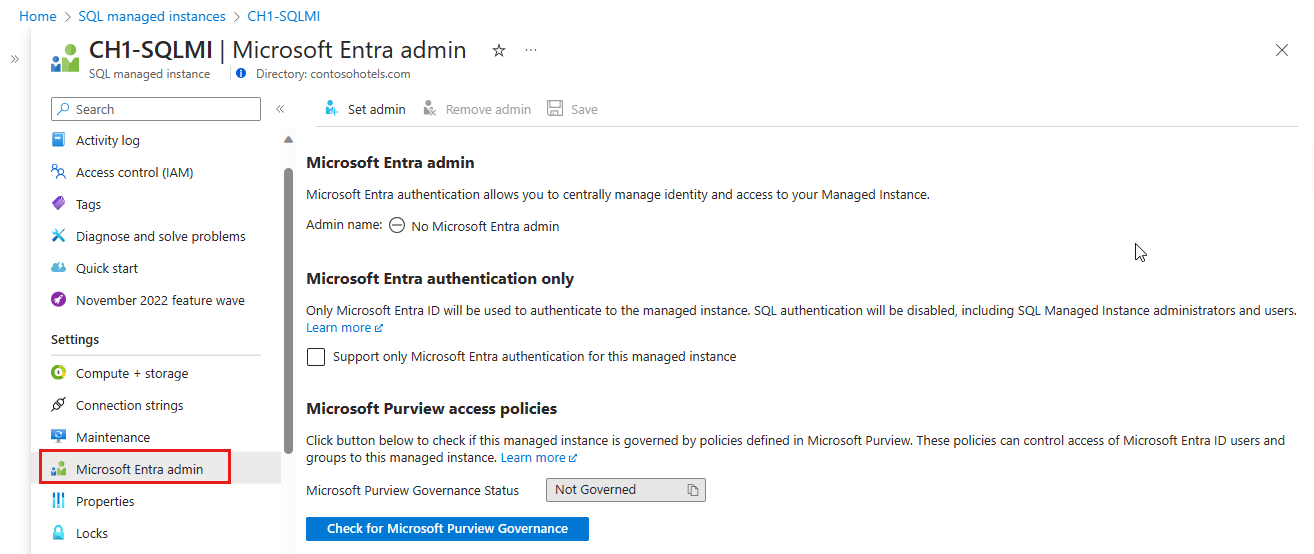
Search for SQL managed instances and then select your managed instance to open the SQL managed instance pane. Then, select Microsoft Entra ID under Settings to open the Microsoft Entra ID pane for your instance.
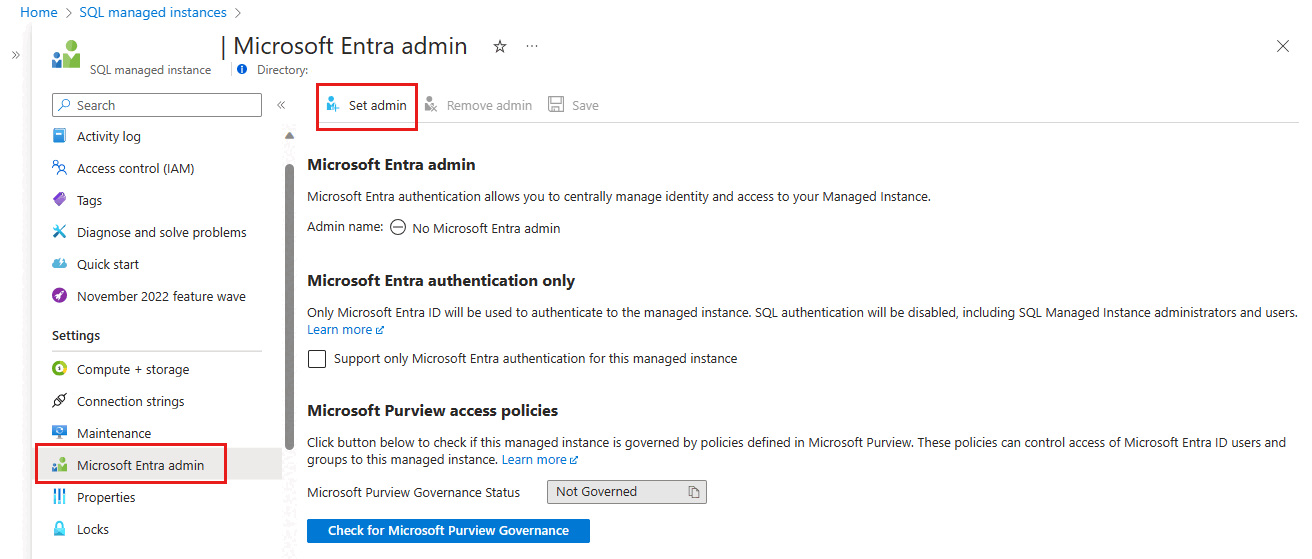
On the Microsoft Entra admin pane, select Set admin from the navigation bar to open the Microsoft Entra ID pane.
On the Microsoft Entra ID pane, search for a user, check the box next to the user or group to be an administrator, and then press Select to close the pane and go back to the Microsoft Entra admin page for your managed instance.
The Microsoft Entra ID pane shows all members and groups within your current directory. Grayed-out users or groups can't be selected because they aren't supported as Microsoft Entra administrators. Select the identity you want to assign as your administrator.
From the navigation bar of the Microsoft Entra admin page for your managed instance, select Save to confirm your Microsoft Entra administrator.
After the administrator change operation completes, the new administrator appears in the Microsoft Entra admin field.
The Object ID is displayed next to the admin name for Microsoft Entra users and groups. For applications (service principals), the Application ID is displayed.
Tip
To remove the admin, select Remove admin at the top of the Microsoft Entra ID page, then select Save.
Assign Microsoft Graph permissions
SQL Managed Instance needs permissions to read Microsoft Entra ID for scenarios like authorizing users who connect through security group membership and new user creation. For Microsoft Entra authentication to work, you need to assign the managed instance identity to the Directory Readers role. You can do this using the Azure portal or PowerShell.
For some operations, Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics also require permissions to query Microsoft Graph, explained in Microsoft Graph permissions. Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics support fine-grained Graph permissions for these scenarios, whereas SQL Managed Instance requires the Directory Readers role. Fine-grained permissions and their assignment are described in detail in enable service principals to create Microsoft Entra users.
Directory Readers role
The Microsoft Entra ID page for SQL Managed Instance in the Azure portal displays a convenient banner when the instance isn't assigned the Directory Reader permissions.
Select the banner on top of the Microsoft Entra ID page and grant permission to the system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity that represents your instance. Only a Privileged Role Administrator or higher role in your tenant can perform this operation.
When the operation succeeds, a Success notification shows in the top-right corner:

The Microsoft Entra admin can now be used to create Microsoft Entra server principals (logins) and database principals (users). For more information, see Microsoft Entra integration with Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Create Microsoft Entra principals in SQL
To connect to a database in SQL Database or Azure Synapse Analytics with Microsoft Entra authentication, a principal has to be configured on the database for that identity with at least the CONNECT permission.
Database user permissions
When a database user is created, it receives the CONNECT permission to the database by default. A database user also inherits permissions in two circumstances:
- If the user is a member of a Microsoft Entra group that's also assigned permissions on the server.
- If the user is created from a login, it inherits the server-assigned permissions of the login applicable on the database.
Managing permissions for server and database principals works the same regardless of the type of principal (Microsoft Entra ID, SQL authentication, etc.). We recommend granting permissions to database roles instead of directly granting permissions to users. Then users can be added to roles with appropriate permissions. This simplifies long-term permissions management and reduces the likelihood of an identity retaining access past when is appropriate.
For more information, see:
- Database engine permissions and examples
- Blog: Database Engine permission basics
- Managing special databases roles and logins in Azure SQL Database
Contained database users
A contained database user is a type of SQL user that isn't connected to a login in the master database. To create a Microsoft Entra contained database user, connect to the database with a Microsoft Entra identity that has at least the ALTER ANY USER** permission. The following T-SQL example creates a database principal Microsoft_Entra_principal_name from Microsoft Entra ID.
CREATE USER [<Microsoft_Entra_principal_name>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
To create a contained database user for a Microsoft Entra group, enter the display name of the group:
CREATE USER [ICU Nurses] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
To create a contained database user for a managed identity or service principal, enter the display name of the identity:
CREATE USER [appName] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
To create a contained database user for a Microsoft Entra user, enter the user principal name of the identity:
CREATE USER [adrian@contoso.com] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
Login based users
Note
Microsoft Entra server principals (logins) are currently in public preview for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics. Microsoft Entra logins are generally available for Azure SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server 2022.
Microsoft Entra server principals (or logins) are supported, which means contained database users aren't required. Database principals (users) can be created based off of a server principal, which means Microsoft Entra users can inherit server-level assigned permissions of a login.
CREATE USER [appName] FROM LOGIN [appName];
For more information, see SQL Managed Instance overview. For syntax on creating Microsoft Entra server principals (logins), see CREATE LOGIN.
External users
You can't directly create a database user for an identity managed in a different Microsoft Entra tenant than the one associated with your Azure subscription. However, users in other directories can be imported into the associated directory as external users. They can then be used to create contained database users that can access the database. External users can also gain access through membership in Microsoft Entra groups.
Examples: To create a contained database user representing a Microsoft Entra federated or managed domain user:
CREATE USER [alice@fabrikam.com] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
A federated domain user account that is imported into a managed domain as an external user, must use the managed domain identity.
Name considerations
Special characters like colon : or ampersand & when included as user names in the T-SQL CREATE LOGIN and CREATE USER statements aren't supported.
Microsoft Entra ID and Azure SQL diverge in their user management design in one key way: Microsoft Entra ID allows display names to be duplicated within a tenant, whereas Azure SQL requires all server principals on a server or instance and all database principals on a database to have a unique name. Because Azure SQL directly uses the Microsoft Entra display name of the identity when creating principals, this can result in errors when creating users. To solve this issue, Azure SQL has released the WITH OBJECT_ID enhancement currently in preview, which allows users to specify the Microsoft Entra object ID of the identity being added to the server or instance.
Microsoft Graph permissions
The CREATE USER ... FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER command requires Azure SQL access to Microsoft Entra ID (the "external provider") on behalf of the logged-in user. Sometimes, circumstances arise that cause Microsoft Entra ID to return an exception to Azure SQL.
- You might encounter SQL error 33134, which contains the Microsoft Entra ID-specific error message. The error usually says that access is denied, that the user must enroll in MFA to access the resource, or that access between first-party applications must be handled via preauthorization. In the first two cases, the issue is usually caused by Conditional Access policies that are set in the user's Microsoft Entra tenant: they prevent the user from accessing the external provider. Updating the Conditional Access policies to allow access to the application '00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000' (the application ID of the Microsoft Graph API) should resolve the issue. If the error says access between first-party applications must be handled via preauthorization, the issue is because the user is signed in as a service principal. The command should succeed if it's executed by a user instead.
- If you receive a Connection Timeout Expired, you might need to set the
TransparentNetworkIPResolutionparameter of the connection string to false. For more information, see Connection timeout issue with .NET Framework 4.6.1 - TransparentNetworkIPResolution.
For more information about creating contained database users based on Microsoft Entra identities, see CREATE USER.
Configure multifactor authentication
For improved security to your Azure SQL resource, consider configuring multifactor authentication (MFA), which prompts the user to use a second alternative method to authenticate to the database, such as a phone call or an authenticator app.
To use multifactor authentication with your Azure SQL resource, first enable multifactor authentication, and then use a Conditional access policy to enforce MFA for your Azure SQL resource.
Connect with Microsoft Entra
After Microsoft Entra authentication has been configured, you can use it to connect to your SQL resource with Microsoft tools like SQL Server Management Studio and SQL Server Data Tools, and configure client applications to connect using Microsoft Entra identities.
Troubleshoot Microsoft Entra authentication
For guidance on troubleshooting issues, see Blog: Troubleshooting problems related to Microsoft Entra authentication with Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse.
Related content
- Authorize database access to SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics
- Principals
- Database roles
- Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse IP firewall rules
- Create Microsoft Entra guest users and set them as a Microsoft Entra admin
- Tutorial: Create Microsoft Entra users using Microsoft Entra applications