Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure SQL
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics (dedicated SQL pools only)
Microsoft Entra-only authentication is a feature within Azure SQL that allows the service to only support Microsoft Entra authentication, and is supported for Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Note
Microsoft Entra ID was previously known as Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
Microsoft Entra-only authentication is also available for dedicated SQL pools (formerly SQL DW) in standalone servers. Microsoft Entra-only authentication can be enabled for the Azure Synapse workspace. For more information, see Microsoft Entra-only authentication with Azure Synapse workspaces.
SQL authentication is disabled when enabling Microsoft Entra-only authentication in the Azure SQL environment, including connections from SQL server administrators, logins, and users. Only users using Microsoft Entra authentication are authorized to connect to the server or database.
Microsoft Entra-only authentication can be enabled or disabled using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, PowerShell, or REST API. Microsoft Entra-only authentication can also be configured during server creation with an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
For more information on Azure SQL authentication, see Authentication and authorization.
Feature description
When enabling Microsoft Entra-only authentication, SQL authentication is disabled at the server or managed instance level and prevents any authentication based on any SQL authentication credentials. SQL authentication users won't be able to connect to the logical server for Azure SQL Database or managed instance, including all of its databases. Although SQL authentication is disabled, new SQL authentication logins and users can still be created by Microsoft Entra accounts with proper permissions. Newly created SQL authentication accounts won't be allowed to connect to the server. Enabling Microsoft Entra-only authentication doesn't remove existing SQL authentication login and user accounts. The feature only prevents these accounts from connecting to the server, and any database created for this server.
You can also force servers to be created with Microsoft Entra-only authentication enabled using Azure Policy. For more information, see Azure Policy for Microsoft Entra-only authentication.
Permissions
Microsoft Entra-only authentication can be enabled or disabled by Microsoft Entra users who are members of high privileged Microsoft Entra built-in roles, such as Azure subscription Owners, Contributors, and Global Administrators. Additionally, the role SQL Security Manager can also enable or disable the Microsoft Entra-only authentication feature.
The SQL Server Contributor and SQL Managed Instance Contributor roles won't have permissions to enable or disable the Microsoft Entra-only authentication feature. This is consistent with the Separation of Duties approach, where users who can create an Azure SQL server or create a Microsoft Entra admin, can't enable or disable security features.
Actions required
The following actions are added to the SQL Security Manager role to allow management of the Microsoft Entra-only authentication feature.
- Microsoft.Sql/servers/azureADOnlyAuthentications/*
- Microsoft.Sql/servers/administrators/read - required only for users accessing the Azure portal Microsoft Entra ID menu
- Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances/azureADOnlyAuthentications/*
- Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances/read
The above actions can also be added to a custom role to manage Microsoft Entra-only authentication. For more information, see Create and assign a custom role in Microsoft Entra ID.
Managing Microsoft Entra-only authentication using APIs
Important
The Microsoft Entra admin must be set before enabling Microsoft Entra-only authentication.
You must have Azure CLI version 2.14.2 or higher.
name corresponds to the prefix of the server or instance name (for example, myserver) and resource-group corresponds to the resource the server belongs to (for example, myresource).
Azure SQL Database
For more information, see az sql server ad-only-auth.
Enable or disable in SQL Database
Enable
az sql server ad-only-auth enable --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Disable
az sql server ad-only-auth disable --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Check the status in SQL Database
az sql server ad-only-auth get --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Azure SQL Managed Instance
For more information, see az sql mi ad-only-auth.
Enable
az sql mi ad-only-auth enable --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Disable
az sql mi ad-only-auth disable --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Check the status in SQL Managed Instance
az sql mi ad-only-auth get --resource-group myresource --name myserver
Checking Microsoft Entra-only authentication using T-SQL
The SERVERPROPERTY IsExternalAuthenticationOnly has been added to check if Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled for your server or managed instance. 1 indicates that the feature is enabled, and 0 represents the feature is disabled.
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('IsExternalAuthenticationOnly')
Remarks
- A SQL Server Contributor can set or remove a Microsoft Entra admin, but can't set the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting. The SQL Security Manager can't set or remove a Microsoft Entra admin, but can set the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting. Only accounts with higher Azure RBAC roles or custom roles that contain both permissions can set or remove a Microsoft Entra admin and set the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting. One such role is the Contributor role.
- After enabling or disabling Microsoft Entra authentication only in the Azure portal, an Activity log entry can be seen in the SQL server menu.
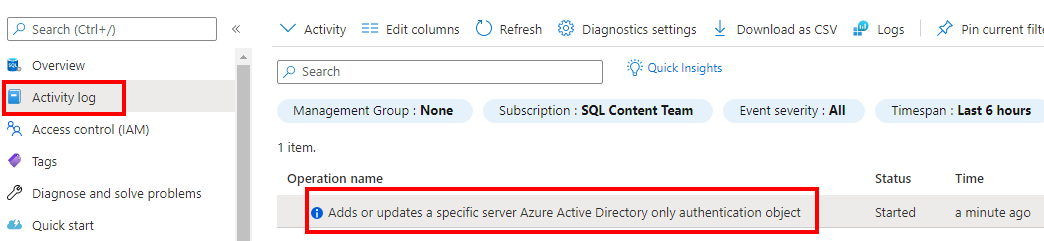
- The Microsoft Entra authentication only setting can only be enabled or disabled by users with the right permissions if the Microsoft Entra admin is specified. If the Microsoft Entra admin isn't set, the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting remains inactive and cannot be enabled or disabled. Using APIs to enable Microsoft Entra-only authentication will also fail if the Microsoft Entra admin hasn't been set.
- Changing a Microsoft Entra admin when Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled is supported for users with the appropriate permissions.
- Changing a Microsoft Entra admin and enabling or disabling Microsoft Entra-only authentication is allowed in the Azure portal for users with the appropriate permissions. Both operations can be completed with one Save in the Azure portal. The Microsoft Entra admin must be set in order to enable Microsoft Entra-only authentication.
- Removing a Microsoft Entra admin when the Microsoft Entra-only authentication feature is enabled isn't supported. Using an API to remove a Microsoft Entra admin will fail if Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled.
- If the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting is enabled, the Remove admin button is inactive in the Azure portal.
- Removing a Microsoft Entra admin and disabling the Microsoft Entra authentication only setting is allowed, but requires the right user permission to complete the operations. Both operations can be completed with one Save in the Azure portal.
- Microsoft Entra users with proper permissions can impersonate existing SQL users.
- Impersonation continues working between SQL authentication users even when the Microsoft Entra-only authentication feature is enabled.
Limitations for Microsoft Entra-only authentication in SQL Database
When Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled for SQL Database, the following features aren't supported:
- Azure SQL Database server roles are supported for Microsoft Entra server principals, but not if the Microsoft Entra login is a group.
- Elastic jobs
- SQL Data Sync
- Change data capture (CDC) - If you create a database in Azure SQL Database as a Microsoft Entra user and enable change data capture on it, a SQL user will not be able to disable or make changes to CDC artifacts. However, another Microsoft Entra user will be able to enable or disable CDC on the same database. Similarly, if you create an Azure SQL Database as a SQL user, enabling or disabling CDC as a Microsoft Entra user won't work
- Transactional replication - Since SQL authentication is required for connectivity between replication participants, when Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled, transactional replication is not supported for SQL Database for scenarios where transactional replication is used to push changes made in an Azure SQL Managed Instance, on-premises SQL Server, or an Azure VM SQL Server instance to a database in Azure SQL Database
- SQL Insights (preview)
- EXEC AS statement for Microsoft Entra group member accounts
Limitations for Microsoft Entra-only authentication in Managed Instance
When Microsoft Entra-only authentication is enabled for Managed Instance, the following features aren't supported:
- Transactional replication
- SQL Agent Jobs in Managed Instance supports Microsoft Entra-only authentication. However, the Microsoft Entra user who is a member of a Microsoft Entra group that has access to the managed instance cannot own SQL Agent Jobs
- SQL Insights (preview)
- EXEC AS statement for Microsoft Entra group member accounts
For more limitations, see T-SQL differences between SQL Server & Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for