Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This article outlines best practices when using the Managed Instance link to replicate data between Azure SQL Managed Instance and your SQL Server instances hosted anywhere, providing near real-time data replication between the linked replicas.
Take log backups regularly
If SQL Server is your initial primary, it's important to take the first log backup on SQL Server after initial seeding completes, when the database is no longer in the Restoring... state on Azure SQL Managed Instance. Then take SQL Server transaction log backups regularly to maintain a healthy transaction log file size while SQL Server is in the primary role.
The link feature replicates data using the distributed availability groups technology based on Always On availability groups. Data replication with distributed availability groups is based on replicating transaction log records. No transaction log records can be truncated from the database on the primary SQL Server instance until they're replicated to the database on the secondary replica. If transaction log record replication is slow or blocked due to network connection issues, the log file keeps growing on the primary instance. Growth speed depends on the intensity of workload and the network speed. If there's a prolonged network connection outage and heavy workload on primary instance, the log file can take all available storage space.
Taking regular transaction log backups truncates the transaction log and minimizes the risk of running out of space on the primary SQL Server instance due to log file growth. No extra action is necessary when SQL Managed Instance is the primary since log backups are already taken automatically. By taking log backups regularly on your SQL Server primary, you make your database more resilient to unplanned log growth events. Consider scheduling daily log backup tasks by using a SQL Server Agent job.
You can use a Transact-SQL (T-SQL) script to back up the log file, such as the sample provided in this section. Replace the placeholders in the sample script with name of your database, name and path of the backup file, and the description.
To back up your transaction log, use the following sample Transact-SQL (T-SQL) script on SQL Server:
-- Execute on SQL Server
-- Take log backup
BACKUP LOG [<DatabaseName>]
TO DISK = N'<DiskPathandFileName>'
WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT,
NAME = N'<Description>', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, COMPRESSION, STATS = 1
Use the following Transact-SQL (T-SQL) command to check the log spaced used by your database on SQL Server:
-- Execute on SQL Server
DBCC SQLPERF(LOGSPACE);
The query output looks like the following example for sample database tpcc:
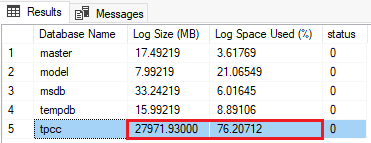
In this example, the database has used 76% of the available log, with an absolute log file size of approximately 27 GB (27,971 MB). The thresholds for action vary based on your workload. In the previous example, the transaction log size and the percentage of use of the log is typically an indication that you should take a transaction log backup to truncate the log file and free up some space, or, you should take more frequent log backups. It could also be an indication that the transaction log truncation is being blocked by open transactions. For more on troubleshooting a transaction log in SQL Server, see Troubleshoot a Full Transaction Log (SQL Server Error 9002). For more on troubleshooting a transaction log in Azure SQL Managed Instance, see Troubleshoot transaction log errors with Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Note
When participating in a link, automated full and transaction log backups are taken from SQL Managed Instance whether or not it's the primary replica. Differential backups aren't taken, which can lead to longer restore times.
Match performance capacity between replicas
When you're using the link feature, it's important to match performance capacity between SQL Server and SQL Managed Instance to avoid performance issues if the secondary replica can't keep up with replication from the primary replica, or after failover. Performance capacity includes CPU cores (or vCores in Azure), memory, and I/O throughput.
You can check the performance of replication with the redo queue size on the secondary replica. The redo queue size indicates the number of log records that are waiting to be redone on the secondary replica. A consistently high redo queue size indicates that the secondary replica can't keep up with the primary replica. You can check the redo queue size in the following ways:
- The
redo_queue_sizevalue in the sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states dynamic management view on the primary replica. - The
InstanceRedoLagReplicationSecondsvalue in Get-AzSqlInstanceLink on the primary replica.
If the redo queue size is consistently high, consider increasing resources on the secondary replica.
Rotate certificate
You might need to manually rotate the certificate used to secure the database mirroring endpoint on SQL Server. Since the certificate used to secure the database mirroring endpoint on SQL Managed Instance is managed by the service and rotated automatically, you don't need to manually rotate it yourself.
SQL Server
It's possible for the certificate that you use to secure the database mirroring endpoint on SQL Server to expire, which can lead to the degradation of the link. To prevent this issue, rotate the certificate before it expires.
Use the following Transact-SQL (T-SQL) command to check the expiration date of the current certificate:
-- Run on SQL Server
USE MASTER
GO
SELECT * FROM sys.certificates WHERE pvt_key_encryption_type = 'MK'
If your certificate is about to expire, or has already expired, you can create a new certificate, and then alter the existing endpoint to replace the current certificate.
Once the endpoint is configured to use the new certificate, you can drop the expired certificate.
SQL Managed Instance
The database mirroring endpoint certificate on SQL Managed Instance is automatically rotated periodically. Monitoring the expiration date for the database mirroring endpoint certificate on SQL Managed Instance is not necessary, as long as you can validate the certificate chain on SQL Server successfully.
Validate the certificate chain on SQL Server
Note
The certificate chain should be periodically validated for existing links, or to troubleshoot issues with a degraded link. Skip this section if you're configuring a new link or have recently completed the steps in sections Get the certificate public key from SQL Managed Instance and import it to SQL Server and Import Azure-trusted root certificate authority keys to SQL Server.
Issues with the certificate chain can degrade the link. To prevent this issue, validate the certificate chain on SQL Server regularly.
The following scenarios can cause issues with the certificate chain on SQL Server:
- Scheduled certificate rotation on SQL Managed Instance.
- Unintentional or accidental changes to the certificates on SQL Server, such as dropping or altering the certificate used to secure the database mirroring endpoint.
First, determine the certificate_id of the imported MI endpoint certificate by replacing the value of <ManagedInstanceFQDN> and then running the following query on SQL Server:
-- Run on SQL Server
USE master
SELECT name, subject, certificate_id, start_date, expiry_date
FROM sys.certificates
WHERE issuer_name LIKE '%Microsoft Corporation%' AND name = '<ManagedInstanceFQDN>'
GO
Next, validate the certificate by replacing the value of <certificate_id> from the result of the previous query and then running the following query on SQL Server:
-- Run on SQL Server
USE master
EXEC sp_validate_certificate_ca_chain <certificate_id>
GO
A response of Commands completed successfully. Completion time: … indicates the MI endpoint certificate has been successfully validated.
Important
The stored procedure sp_validate_certificate_ca_chain relies on host OS services to perform certificate validation, which might involve an online certificate revocation check. If the host OS is not configured to access the internet, the execution fails even if the certificate chain is valid.
If you encounter an error, the most reliable mitigation is to restore the certificate chain by first dropping all certificates created in sections Get the certificate public key from SQL Managed Instance and import it to SQL Server and Import Azure-trusted root certificate authority keys to SQL Server, and then reimporting them again.
Add startup trace flags
In SQL Server, there are two trace flags (-T1800 and -T9567) that, when added as startup parameters, can optimize the performance of data replication through the link. See Enable startup trace flags to learn more.
Related content
To use the link:
- Prepare environment for the Managed Instance link
- Configure link between SQL Server and SQL Managed instance with SSMS
- Configure link between SQL Server and SQL Managed instance with scripts
- Fail over the link
- Migrate with the link
- Troubleshoot issues with the link
To learn more about the link:
- Managed Instance link overview
- Disaster recovery with Managed Instance link
- Best practices for maintaining the link
For other replication and migration scenarios, consider: