Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, learn how to turn on public IP addresses on a VMware NSX Edge node to run VMware NSX for your instance of Azure VMware Solution.
Tip
Before you turn on internet access to your instance of Azure VMware Solution, review Internet connectivity design considerations.
Public IP addresses to an NSX Edge node for NSX is a feature in Azure VMware Solution that turns on inbound and outbound internet access for your Azure VMware Solution environment.
Important
IPv4 public IP address usage can be consumed directly in Azure VMware Solution and charged based on the IPv4 public IP address prefix that's shown in Pricing - Virtual machine IP addresses. No charges for data ingress or egress are related to this service.
The public IP address range is configured in Azure VMware Solution through the Azure portal and the NSX interface within your Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
With this capability, you have the following features:
- A cohesive and simplified experience for reserving and using a public IP address to the NSX Edge node.
- The ability to receive 1,000 or more public IP addresses. Turn on internet access at scale.
- Inbound and outbound internet access for your workload VMs.
- Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) security protection against network traffic to and from the internet.
- VMware HCX migration support over the public internet.
Important
You can set up a maximum of 64 total public IP addresses across these network blocks. If you want to configure more than 64 public IP addresses, please submit a support ticket that indicates the number of addresses you need.
Prerequisites
- An Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
- A DNS server set up for your instance of NSX.
Reference architecture
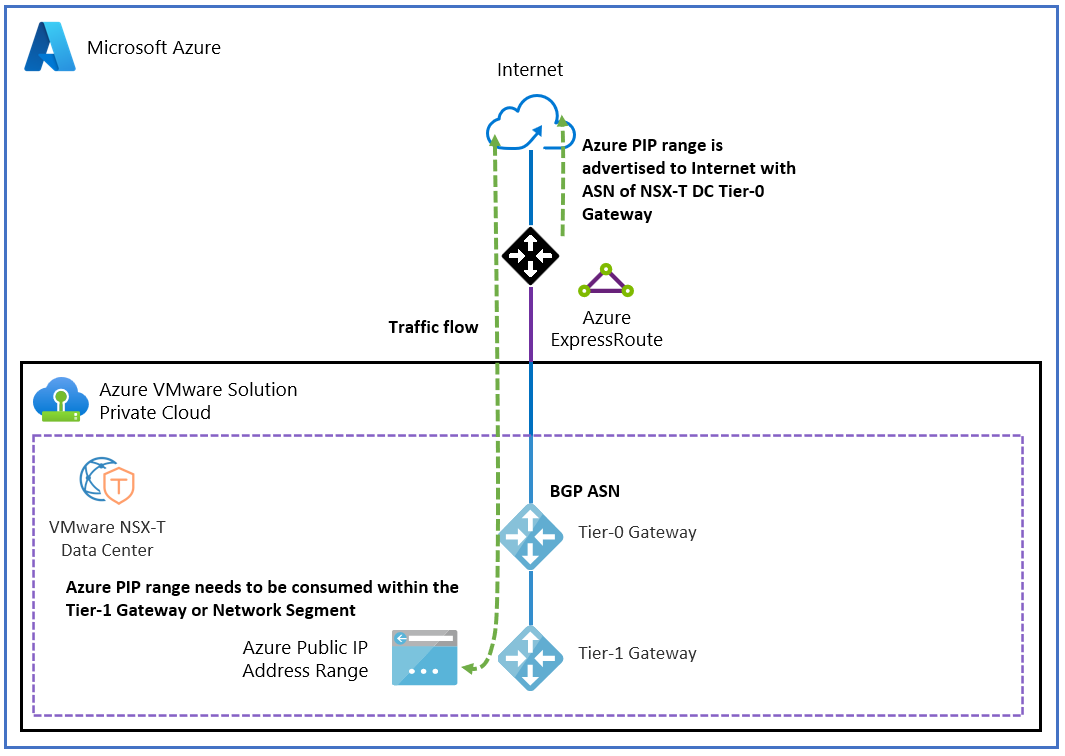
The following figure shows internet access to and from your Azure VMware Solution private cloud via a public IP address directly to the NSX Edge node for NSX.
Important
When using a Public IP on NSX the Public IP address(es) will not be advertised via the Private Cloud ExpressRoute. For customers advertising public IP space from on premises to Azure VMware Solution via Express Route this will cause asymmetric routing when accessing a Public IP address assigned in NSX from an IP address that is within the range(s) advertised from on-premises.
Also, using a public IP address at the NSX Edge node for NSX is not compatible with reverse DNS lookup. If you use this scenario, you can't host a mail server in the Azure VMware Solution.
Set up a public IP address or range
To set up a public IP address or range, use the Azure portal:
Sign in to the Azure portal, and then go to your Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
On the resource menu under Workload networking, select Internet connectivity.
Select the Connect using Public IP down to the NSX Edge checkbox.
Important
Before you select a public IP address, ensure that you understand the implications to your existing environment. For more information, see Internet connectivity design considerations. Considerations should include a risk mitigation review with your relevant networking and security governance and compliance teams.
Select Public IP.
Enter a value for Public IP name. In the Address space dropdown list, select a subnet size. Then, select Configure.
This public IP address is available within approximately 20 minutes.
Check that the subnet is listed. If you don't see the subnet, refresh the list. If the refresh fails to display the subnet, try the configuration again.

After you set the public IP address, select the Connect using the public IP down to the NSX Edge checkbox to turn off all other internet options.
Select Save.
You successfully turned on internet connectivity for your Azure VMware Solution private cloud and reserved a Microsoft-allocated public IP address. You can now set this public IP address to the NSX Edge node for NSX to use for your workloads. NSX is used for all virtual machine (VM) communication.
You have three options for configuring your reserved public IP address to the NXS Edge node for NSX:
- Outbound internet access for VMs
- Inbound internet access for VMs
- A gateway firewall to filter traffic to VMs at T1 gateways
Outbound internet access for VMs
A Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) service with Port Address Translation (PAT) is used to allow many VMs to use one SNAT service. Using this type of connection means that you can provide internet connectivity for many VMs.
Important
To enable SNAT for your specified address ranges, you must configure a gateway firewall rule and SNAT for the specific address ranges that you want to use. If you don't want SNAT turned on for specific address ranges, you must create a No-NAT rule for address ranges to exclude from Network Address Translation (NAT). For your SNAT service to work as expected, the No-NAT rule should be a lower priority than the SNAT rule.
Create a SNAT rule
In your Azure VMware Solution private cloud, select VMware credentials.
Locate your NSX Manager URL and credentials.
Sign in to VMware NSX Manager.
Go to NAT Rules.
Select the T1 router.
Select Add NAT Rule.
Enter a name for the rule.
Select SNAT.
Optionally, enter a source, such as a subnet to SNAT or a destination.
Enter the translated IP address. This IP address is from the range of public IP addresses that you reserved in the Azure VMware Solution portal.
Optionally, give the rule a higher-priority number. This prioritization moves the rule further down the rule list to ensure that more specific rules are matched first.
Select Save.
Logging is turned on via the logging slider.
For more information on VMware NSX NAT configuration and options, see the NSX Data Center NAT Administration Guide.
Create a No-NAT rule
You can create a No-NAT or No-SNAT rule in NSX Manager to exclude certain matches from performing NAT. This policy can be used to allow private IP address traffic to bypass existing network translation rules.
- In your Azure VMware Solution private cloud, select VMware credentials.
- Locate your NSX Manager URL and credentials.
- Sign in to NSX Manager, and then select NAT Rules.
- Select the T1 router, and then select Add NAT Rule.
- Select No SNAT rule as the type of NAT rule.
- Select the Source IP value as the range of addresses that you don't want to be translated. The Destination IP value should be any internal addresses that you're reaching from the range of source IP address ranges.
- Select Save.
Inbound internet access for VMs
A Destination Network Translation (DNAT) service is used to expose a VM on a specific public IP address or on a specific port. This service provides inbound internet access to your workload VMs.
Create a DNAT rule
In your Azure VMware Solution private cloud, select VMware credentials.
Locate your NSX Manager URL and credentials.
Sign in to NSX Manager, and then select NAT Rules.
Select the T1 router, and then select Add DNAT Rule.
Enter a name for the rule.
Select DNAT as the action.
For the destination match, enter the reserved public IP address. This IP address is from the range of public IP addresses that are reserved in the Azure VMware Solution portal.
For the translated IP, enter the VM private IP address.
Select Save.
Optionally, configure the translated port or the source IP address for more specific matches.
The VM is now exposed to the internet on the specific public IP address or on specific ports.
Set up a gateway firewall to filter traffic to VMs at T1 gateways
You can provide security protection for your network traffic in and out of the public internet through your gateway firewall.
In your Azure VMware Solution private cloud, select VMware credentials.
Locate your NSX Manager URL and credentials.
Sign in to NSX Manager.
On the NSX overview page, select Gateway Policies.
Select Gateway Specific Rules, choose the T1 gateway, and then select Add Policy.
Select New Policy and enter a policy name.
Select the policy and select Add Rule.
Configure the rule:
- Select New Rule.
- Enter a descriptive name.
- Configure the source, destination, services, and action.
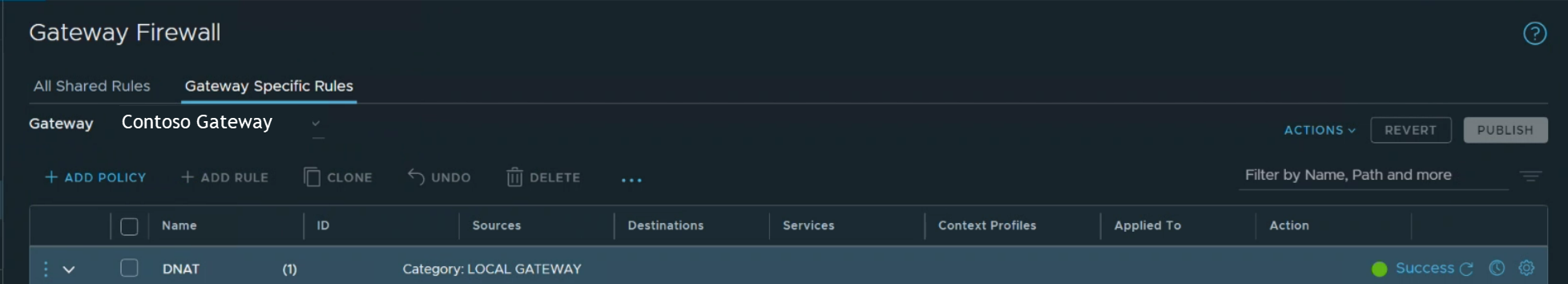
Select Match External Address to apply firewall rules to the external address of a NAT rule.
For example, the following rule is set to Match External Address. The setting allows Secure Shell (SSH) traffic inbound to the public IP address.
If Match Internal Address was specified, the destination is the internal or private IP address of the VM.
For more information on the NSX gateway firewall, see the NSX Gateway Firewall Administration Guide. The distributed firewall can be used to filter traffic to VMs. For more information, see NSX Distributed Firewall Administration Guide.