Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
With Azure Communication Services, you can receive real-time event notifications in a dependable, expandable, and safe way by integrating it with Azure Event Grid. This integration can be used to build a notification system that sends push notifications to your users on mobile devices. To achieve it, create an Event Grid subscription that triggers an Azure Function or webhook.
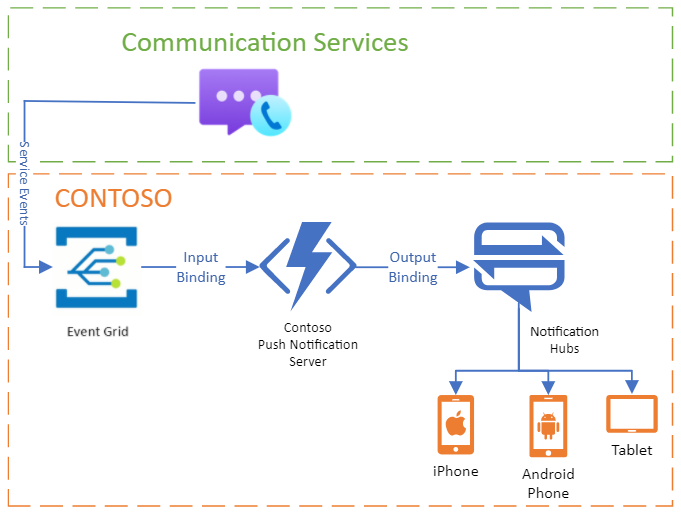
In this tutorial, we explore how to implement Azure Communication Services Calling with Azure Event Grid to receive push notifications on native platforms. Azure Event Grid is a serverless event routing service that makes it easy to build event-driven applications. This tutorial helps you set up and understand how to receive push notifications for incoming calls.
You can take a look at voice and video calling events available using Event Grid.
Current limitations with the Push Notification model
The current limitations of using the Native Calling SDK and Push Notifications are:
- The maximum value for time to live (TTL) is 180 days (15,552,000 seconds), and the min value is 5 minutes (300 seconds). For CTE (Custom Teams Endpoint) the max TTL value is 24 hrs (86,400 seconds).
- Can't deliver push notifications using Baidu or any other notification types supported by Azure Notification Hub but not yet supported in the Calling SDK.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource.
- A
User Access Tokento enable the call client. For more information on how to get aUser Access Token - The Azure Event Grid topic: Create an Azure Event Grid topic in your Azure subscription, it's used to send events when incoming calls occur.
- Optional: Complete the quickstart for getting started with adding calling to your application
- Optional Azure Functions extension to build your own serverless applications. For example, you can host your authentication application in Azure Functions.
- Optional, review the quickstart to learn how to handle voice and video calling events.
Consider a scenario where you want to notify users on their mobile devices (iOS and Android) when they receive an incoming call through Azure Communication Services. We use Azure Event Grid to achieve.
Implementation steps
Setup for register events into Event Grid
Azure functions to handle device information
Use Azure functions to handle device registration data. Create three separate webhook endpoints for each registration task.
- Store the device endpoint information.
- Delete the device endpoint information.
- Get the device endpoint information for a given
CommunicationIdentifier.
You should use a database to store device information. In this example, we're using MongoDB for simplicity. However, feel free to use any database you feel comfortable with.
You can use the code from the class Azure Communication Services Calling Event Grid - Calling Native Device Token Registrar.
Azure function to deliver the notifications
// Read all the required settings.
var anhHubConnectionString = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ANH_Hub_Connection_String");
var anhHubName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ANH_Hub_Name");
var anhHubUrl = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ANH_Hub_URL");
var anhHubApiVersion = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("ANH_Hub_Api_Version") ?? Defaults.ANH_DEFAULT_REST_API_VERSION;
// Generate the SAS token for making the REST API to Azure Notification Hub
var authorization = GenerateToken(anhHubConnectionString, anhHubName);
// Create the payload to sent to ANH.
PushNotificationInfo? pushNotificationInfo = Helpers.ConvertToPNInfo(input, logger) ?? throw new Exception("Could not extract PN info");
var body = new RootPayloadBody(pushNotificationInfo);
// Send the payload to all the devices registered.
// You can get the device info data from the database
using var client = new HttpClient();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Accept", "application/json");
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Authorization", authorization);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("ServiceBusNotification-Format", deviceInfo.platform);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("ServiceBusNotification-Type", deviceInfo.platform);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("ServiceBusNotification-DeviceHandle", deviceInfo.deviceToken);
if (deviceInfo.platform.Equals(Platform.apple.ToString()))
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("ServiceBusNotification-Apns-Push-Type", "voip");
}
var payload = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(The Event Grid payload model);
using var httpContent = new StringContent(payload, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
var httpResponse = await client.PostAsync(new Uri(anhHubUrl), httpContent).ConfigureAwait(false);
You can use the code from the class Azure Communication Services Calling Event Grid - Incoming Call Event Handler.
Azure function to handle Event Grid Trigger
After deploying the Azure functions, configure the Event Grid and Azure Communication Services resource to listen for IncomingCall event. You can follow these steps to easily configure your resources.
Register the Push Notifications
In your Calling native app; instead of calling the API CallAgent.registerPushNotifications (iOS SDK) with device token when the application starts, send the device token to the Azure function app, send a POST request to the AddDeviceToken function (register endpoint one).
Test your implementation
Test your implementation by placing calls to your Azure Communication Services application. Ensure that push notifications are received on your iOS and Android devices when incoming calls occur.
Summary workflow
- When there's an incoming call for an Azure Communication Services user; Azure Communication calling resource triggers the
EventGridTrigger, and the Azure function with the incoming call payload be executed. - The Azure function gets the device token information from the database.
- Convert the payload to the VOIP push notification payload is required
PushNotificationInfo.fromDictionary(iOS SDK). - The Azure function sends the push payload using the REST API provided by Azure Notification Hub.
- The push is successfully delivered to the device and
CallAgent.handlePushAPI should be called.
This article described how to implement Azure Communication Services Calling with Azure Event Grid for push notifications. By integrating Calling with Event Grid and handling events in your native platform apps, you can notify users about incoming calls in real-time. The Azure Event Grid can enhance the user experience and improve communication within your application.
Sample
The following sample works for any Native platforms (iOS, Android, Windows). Code sample is provided on GitHub at Use Event Grid to deliver VOIP push to devices.