Copy and transform data in Azure Blob Storage by using Azure Data Factory or Azure Synapse Analytics
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the Copy activity in Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse pipelines to copy data from and to Azure Blob Storage. It also describes how to use the Data Flow activity to transform data in Azure Blob Storage. To learn more, read the Azure Data Factory and the Azure Synapse Analytics introduction articles.
Tip
To learn about a migration scenario for a data lake or a data warehouse, see the article Migrate data from your data lake or data warehouse to Azure.
Supported capabilities
This Azure Blob Storage connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR | Managed private endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ① ② | ✓ Exclude storage account V1 |
| Mapping data flow (source/sink) | ① | ✓ Exclude storage account V1 |
| Lookup activity | ① ② | ✓ Exclude storage account V1 |
| GetMetadata activity | ① ② | ✓ Exclude storage account V1 |
| Delete activity | ① ② | ✓ Exclude storage account V1 |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For the Copy activity, this Blob storage connector supports:
- Copying blobs to and from general-purpose Azure storage accounts and hot/cool blob storage.
- Copying blobs by using an account key, a service shared access signature (SAS), a service principal, or managed identities for Azure resource authentications.
- Copying blobs from block, append, or page blobs and copying data to only block blobs.
- Copying blobs as is, or parsing or generating blobs with supported file formats and compression codecs.
- Preserving file metadata during copy.
Get started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
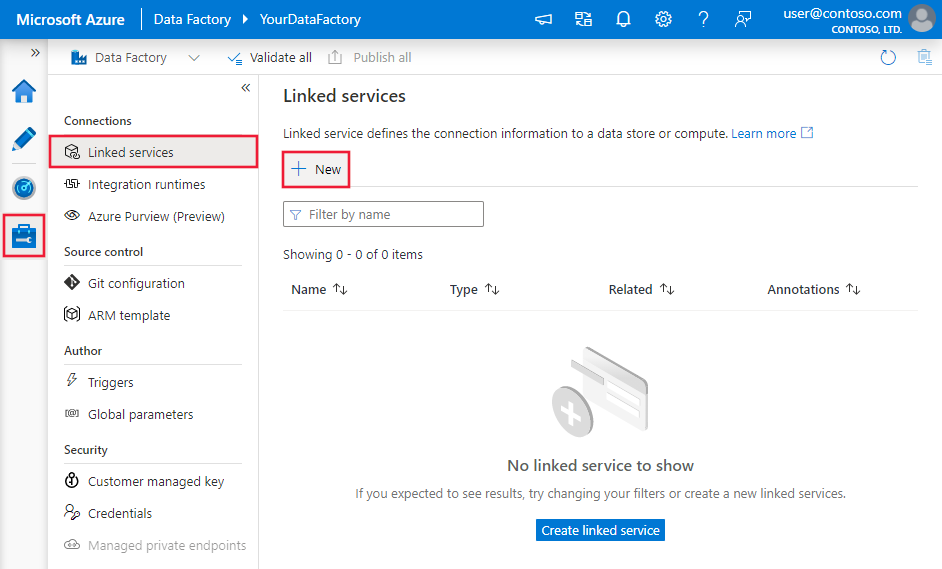
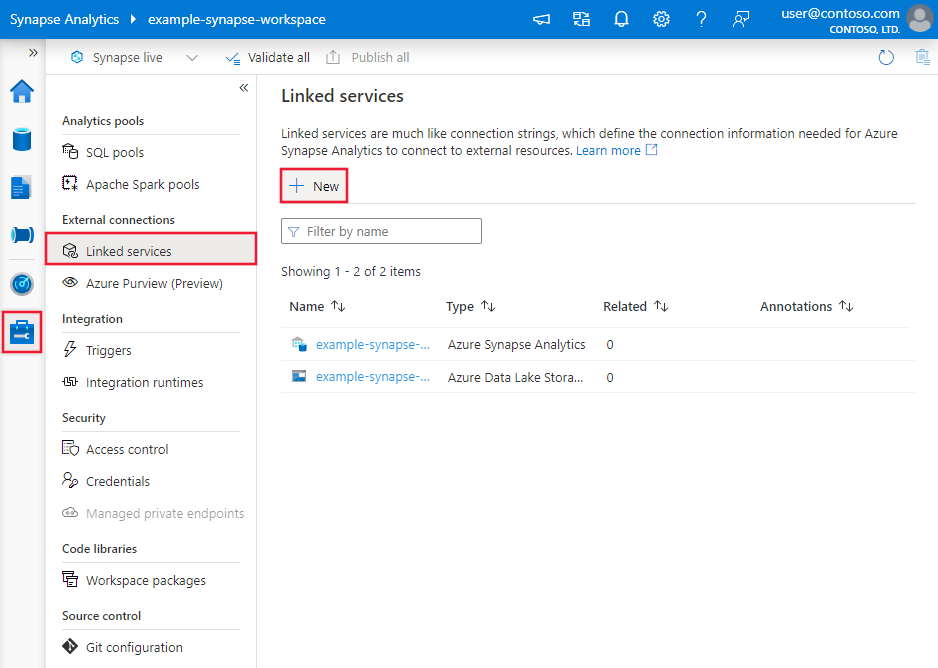
Create an Azure Blob Storage linked service using UI
Use the following steps to create an Azure Blob Storage linked service in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then select New:
Search for blob and select the Azure Blob Storage connector.

Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
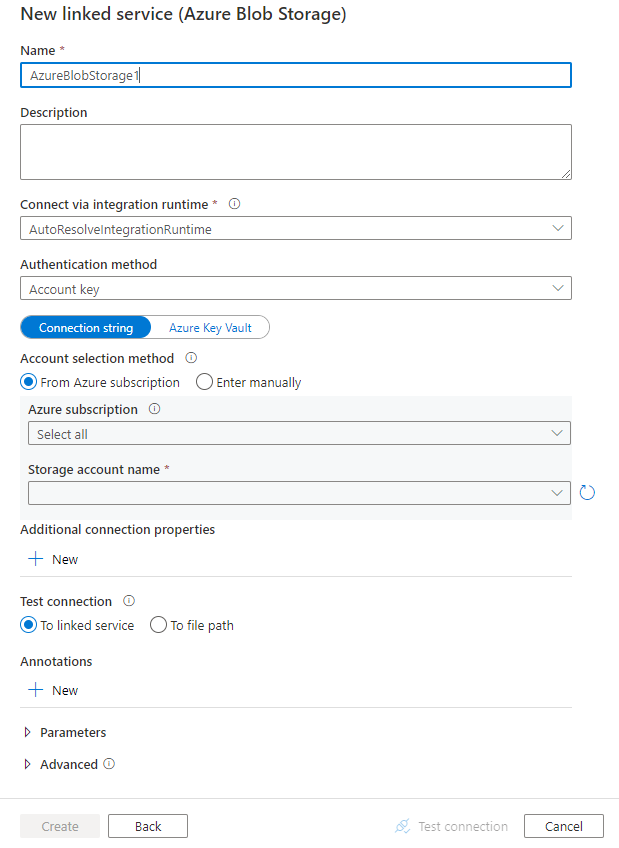
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory and Synapse pipeline entities specific to Blob storage.
Linked service properties
This Blob storage connector supports the following authentication types. See the corresponding sections for details.
- Anonymous authentication
- Account key authentication
- Shared access signature authentication
- Service principal authentication
- System-assigned managed identity authentication
- User-assigned managed identity authentication
Note
- If want to use the public Azure integration runtime to connect to your Blob storage by leveraging the Allow trusted Microsoft services to access this storage account option enabled on Azure Storage firewall, you must use managed identity authentication. For more information about the Azure Storage firewalls settings, see Configure Azure Storage firewalls and virtual networks.
- When you use PolyBase or COPY statement to load data into Azure Synapse Analytics, if your source or staging Blob storage is configured with an Azure Virtual Network endpoint, you must use managed identity authentication as required by Azure Synapse. See the Managed identity authentication section for more configuration prerequisites.
Note
Azure HDInsight and Azure Machine Learning activities only support authentication that uses Azure Blob Storage account keys.
Anonymous authentication
The following properties are supported for storage account key authentication in Azure Data Factory or Synapse pipelines:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage (suggested) or AzureStorage (see the following notes). |
Yes |
| containerUri | Specify the Azure Blob container URI that has enabled Anonymous read access by taking this format https://<AccountName>.blob.core.windows.net/<ContainerName> and Configure anonymous public read access for containers and blobs |
Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageAnonymous",
"properties": {
"annotations": [],
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"containerUri": "https:// <accountname>.blob.core.windows.net/ <containername>",
"authenticationType": "Anonymous"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Examples UI:
The UI experience is as described in the following image. This sample uses the Azure open dataset as the source. If you want to get the open dataset bing_covid-19_data.csv, you just need to choose Authentication type as Anonymous and fill in Container URI with https://pandemicdatalake.blob.core.windows.net/public.
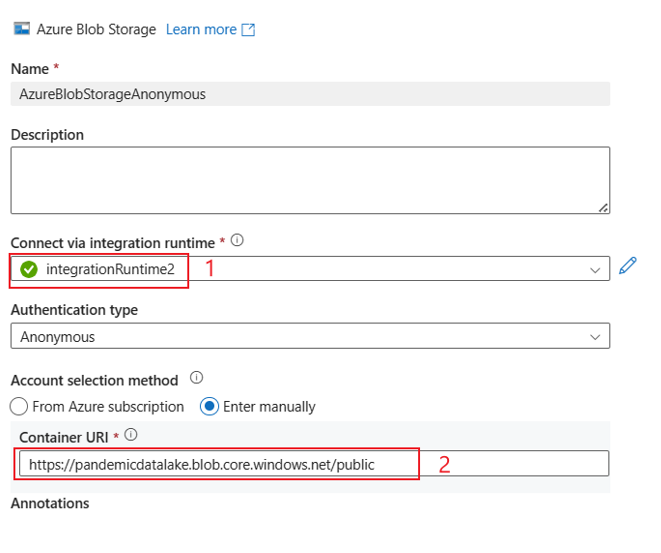
Account key authentication
The following properties are supported for storage account key authentication in Azure Data Factory or Synapse pipelines:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage (suggested) or AzureStorage (see the following notes). |
Yes |
| connectionString | Specify the information needed to connect to Storage for the connectionString property. You can also put the account key in Azure Key Vault and pull the accountKey configuration out of the connection string. For more information, see the following samples and the Store credentials in Azure Key Vault article. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Note
A secondary Blob service endpoint isn't supported when you're using account key authentication. You can use other authentication types.
Note
If you're using the AzureStorage type linked service, it's still supported as is. But we suggest that you use the new AzureBlobStorage linked service type going forward.
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=<accountname>;AccountKey=<accountkey>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store the account key in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=<accountname>;",
"accountKey": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Shared access signature authentication
A shared access signature provides delegated access to resources in your storage account. You can use a shared access signature to grant a client limited permissions to objects in your storage account for a specified time.
You don't have to share your account access keys. The shared access signature is a URI that encompasses in its query parameters all the information necessary for authenticated access to a storage resource. To access storage resources with the shared access signature, the client only needs to pass in the shared access signature to the appropriate constructor or method.
For more information about shared access signatures, see Shared access signatures: Understand the shared access signature model.
Note
- The service now supports both service shared access signatures and account shared access signatures. For more information about shared access signatures, see Grant limited access to Azure Storage resources using shared access signatures.
- In later dataset configurations, the folder path is the absolute path starting from the container level. You need to configure one aligned with the path in your SAS URI.
The following properties are supported for using shared access signature authentication:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage (suggested) or AzureStorage (see the following note). |
Yes |
| sasUri | Specify the shared access signature URI to the Storage resources such as blob or container. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely. You can also put the SAS token in Azure Key Vault to use auto-rotation and remove the token portion. For more information, see the following samples and Store credentials in Azure Key Vault. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Note
If you're using the AzureStorage type linked service, it's still supported as is. But we suggest that you use the new AzureBlobStorage linked service type going forward.
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"sasUri": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<SAS URI of the Azure Storage resource e.g. https://<accountname>.blob.core.windows.net/?sv=<storage version>&st=<start time>&se=<expire time>&sr=<resource>&sp=<permissions>&sip=<ip range>&spr=<protocol>&sig=<signature>>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store the account key in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"sasUri": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<SAS URI of the Azure Storage resource without token e.g. https://<accountname>.blob.core.windows.net/>"
},
"sasToken": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName with value of SAS token e.g. ?sv=<storage version>&st=<start time>&se=<expire time>&sr=<resource>&sp=<permissions>&sip=<ip range>&spr=<protocol>&sig=<signature>>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
When you create a shared access signature URI, consider the following points:
- Set appropriate read/write permissions on objects based on how the linked service (read, write, read/write) is used.
- Set Expiry time appropriately. Make sure that the access to Storage objects doesn't expire within the active period of the pipeline.
- The URI should be created at the right container or blob based on the need. A shared access signature URI to a blob allows the data factory or Synapse pipeline to access that particular blob. A shared access signature URI to a Blob storage container allows the data factory or Synapse pipeline to iterate through blobs in that container. To provide access to more or fewer objects later, or to update the shared access signature URI, remember to update the linked service with the new URI.
Service principal authentication
For general information about Azure Storage service principal authentication, see Authenticate access to Azure Storage using Microsoft Entra ID.
To use service principal authentication, follow these steps:
Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. To learn how, see Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. Make note of these values, which you use to define the linked service:
- Application ID
- Application key
- Tenant ID
Grant the service principal proper permission in Azure Blob Storage. For more information on the roles, see Use the Azure portal to assign an Azure role for access to blob and queue data.
- As source, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Reader role.
- As sink, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Contributor role.
These properties are supported for an Azure Blob Storage linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage. | Yes |
| serviceEndpoint | Specify the Azure Blob Storage service endpoint with the pattern of https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/. |
Yes |
| accountKind | Specify the kind of your storage account. Allowed values are: Storage (general purpose v1), StorageV2 (general purpose v2), BlobStorage, or BlockBlobStorage. When using Azure Blob linked service in data flow, managed identity or service principal authentication isn't supported when account kind is empty or "Storage". Specify the proper account kind, choose a different authentication, or upgrade your storage account to general purpose v2. |
No |
| servicePrincipalId | Specify the application's client ID. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalCredentialType | The credential type to use for service principal authentication. Allowed values are ServicePrincipalKey and ServicePrincipalCert. | Yes |
| servicePrincipalCredential | The service principal credential. When you use ServicePrincipalKey as the credential type, specify the application's key. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. When you use ServicePrincipalCert as the credential, reference a certificate in Azure Key Vault, and ensure the certificate content type is PKCS #12. |
Yes |
| tenant | Specify the tenant information (domain name or tenant ID) under which your application resides. Retrieve it by hovering over the upper-right corner of the Azure portal. | Yes |
| azureCloudType | For service principal authentication, specify the type of Azure cloud environment, to which your Microsoft Entra application is registered. Allowed values are AzurePublic, AzureChina, AzureUsGovernment, and AzureGermany. By default, the data factory or Synapse pipeline's cloud environment is used. |
No |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Note
- If your blob account enables soft delete, service principal authentication isn't supported in Data Flow.
- If you access the blob storage through private endpoint using Data Flow, note when service principal authentication is used Data Flow connects to the ADLS Gen2 endpoint instead of Blob endpoint. Make sure you create the corresponding private endpoint in your data factory or Synapse workspace to enable access.
Note
Service principal authentication is supported only by the "AzureBlobStorage" type linked service, not the previous "AzureStorage" type linked service.
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"serviceEndpoint": "https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/",
"accountKind": "StorageV2",
"servicePrincipalId": "<service principal id>",
"servicePrincipalKey": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<service principal key>"
},
"tenant": "<tenant info, e.g. microsoft.onmicrosoft.com>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
System-assigned managed identity authentication
A data factory or Synapse pipeline can be associated with a system-assigned managed identity for Azure resources, which represents that resource for authentication to other Azure services. You can directly use this system-assigned managed identity for Blob storage authentication, which is similar to using your own service principal. It allows this designated resource to access and copy data from or to Blob storage. To learn more about managed identities for Azure resources, see Managed identities for Azure resources
For general information about Azure Storage authentication, see Authenticate access to Azure Storage using Microsoft Entra ID. To use managed identities for Azure resource authentication, follow these steps:
Retrieve system-assigned managed identity information by copying the value of the system-assigned managed identity object ID generated along with your factory or Synapse workspace.
Grant the managed identity permission in Azure Blob Storage. For more information on the roles, see Use the Azure portal to assign an Azure role for access to blob and queue data.
- As source, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Reader role.
- As sink, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Contributor role.
These properties are supported for an Azure Blob Storage linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage. | Yes |
| serviceEndpoint | Specify the Azure Blob Storage service endpoint with the pattern of https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/. |
Yes |
| accountKind | Specify the kind of your storage account. Allowed values are: Storage (general purpose v1), StorageV2 (general purpose v2), BlobStorage, or BlockBlobStorage. When using Azure Blob linked service in data flow, managed identity or service principal authentication isn't supported when account kind is empty or "Storage". Specify the proper account kind, choose a different authentication, or upgrade your storage account to general purpose v2. |
No |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"serviceEndpoint": "https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/",
"accountKind": "StorageV2"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
User-assigned managed identity authentication
A data factory can be assigned with one or multiple user-assigned managed identities. You can use this user-assigned managed identity for Blob storage authentication, which allows to access and copy data from or to Blob storage. To learn more about managed identities for Azure resources, see Managed identities for Azure resources
For general information about Azure storage authentication, see Authenticate access to Azure Storage using Microsoft Entra ID. To use user-assigned managed identity authentication, follow these steps:
Create one or multiple user-assigned managed identities and grant permission in Azure Blob Storage. For more information on the roles, see Use the Azure portal to assign an Azure role for access to blob and queue data.
- As source, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Reader role.
- As sink, in Access control (IAM), grant at least the Storage Blob Data Contributor role.
Assign one or multiple user-assigned managed identities to your data factory and create credentials for each user-assigned managed identity.
These properties are supported for an Azure Blob Storage linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to AzureBlobStorage. | Yes |
| serviceEndpoint | Specify the Azure Blob Storage service endpoint with the pattern of https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/. |
Yes |
| accountKind | Specify the kind of your storage account. Allowed values are: Storage (general purpose v1), StorageV2 (general purpose v2), BlobStorage, or BlockBlobStorage. When using Azure Blob linked service in data flow, managed identity or service principal authentication isn't supported when account kind as empty or "Storage". Specify the proper account kind, choose a different authentication, or upgrade your storage account to general purpose v2. |
No |
| credentials | Specify the user-assigned managed identity as the credential object. | Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. You can use the Azure integration runtime or the self-hosted integration runtime (if your data store is in a private network). If this property isn't specified, the service uses the default Azure integration runtime. | No |
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobStorageLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorage",
"typeProperties": {
"serviceEndpoint": "https://<accountName>.blob.core.windows.net/",
"accountKind": "StorageV2",
"credential": {
"referenceName": "credential1",
"type": "CredentialReference"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Important
If you use PolyBase or COPY statement to load data from Blob storage (as a source or as staging) into Azure Synapse Analytics, when you use managed identity authentication for Blob storage, make sure you also follow steps 1 to 3 in this guidance. Those steps will register your server with Microsoft Entra ID and assign the Storage Blob Data Contributor role to your server. Data Factory handles the rest. If you configure Blob storage with an Azure Virtual Network endpoint, you also need to have Allow trusted Microsoft services to access this storage account turned on under Azure Storage account Firewalls and Virtual networks settings menu as required by Azure Synapse.
Note
- If your blob account enables soft delete, system-assigned/user-assigned managed identity authentication isn't supported in Data Flow.
- If you access the blob storage through private endpoint using Data Flow, note when system-assigned/user-assigned managed identity authentication is used Data Flow connects to the ADLS Gen2 endpoint instead of Blob endpoint. Make sure you create the corresponding private endpoint in ADF to enable access.
Note
System-assigned/user-assigned managed identity authentication is supported only by the "AzureBlobStorage" type linked service, not the previous "AzureStorage" type linked service.
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the Datasets article.
Azure Data Factory supports the following file formats. Refer to each article for format-based settings.
- Avro format
- Binary format
- Delimited text format
- Excel format
- JSON format
- ORC format
- Parquet format
- XML format
The following properties are supported for Azure Blob Storage under location settings in a format-based dataset:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the location in the dataset must be set to AzureBlobStorageLocation. | Yes |
| container | The blob container. | Yes |
| folderPath | The path to the folder under the given container. If you want to use a wildcard to filter the folder, skip this setting and specify that in activity source settings. | No |
| fileName | The file name under the given container and folder path. If you want to use wildcard to filter files, skip this setting and specify that in activity source settings. | No |
Example:
{
"name": "DelimitedTextDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "DelimitedText",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob Storage linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"schema": [ < physical schema, optional, auto retrieved during authoring > ],
"typeProperties": {
"location": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorageLocation",
"container": "containername",
"folderPath": "folder/subfolder"
},
"columnDelimiter": ",",
"quoteChar": "\"",
"firstRowAsHeader": true,
"compressionCodec": "gzip"
}
}
}
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties that the Blob storage source and sink support.
Blob storage as a source type
Azure Data Factory supports the following file formats. Refer to each article for format-based settings.
- Avro format
- Binary format
- Delimited text format
- Excel format
- JSON format
- ORC format
- Parquet format
- XML format
The following properties are supported for Azure Blob Storage under storeSettings settings in a format-based copy source:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property under storeSettings must be set to AzureBlobStorageReadSettings. |
Yes |
| Locate the files to copy: | ||
| OPTION 1: static path |
Copy from the given container or folder/file path specified in the dataset. If you want to copy all blobs from a container or folder, additionally specify wildcardFileName as *. |
|
| OPTION 2: blob prefix - prefix |
Prefix for the blob name under the given container configured in a dataset to filter source blobs. Blobs whose names start with container_in_dataset/this_prefix are selected. It utilizes the service-side filter for Blob storage, which provides better performance than a wildcard filter.When you use prefix and choose to copy to file-based sink with preserving hierarchy, note the sub-path after the last "/" in prefix is preserved. For example, you have source container/folder/subfolder/file.txt, and configure prefix as folder/sub, then the preserved file path is subfolder/file.txt. |
No |
| OPTION 3: wildcard - wildcardFolderPath |
The folder path with wildcard characters under the given container configured in a dataset to filter source folders. Allowed wildcards are: * (matches zero or more characters) and ? (matches zero or single character). Use ^ to escape if your folder name has wildcard or this escape character inside. See more examples in Folder and file filter examples. |
No |
| OPTION 3: wildcard - wildcardFileName |
The file name with wildcard characters under the given container and folder path (or wildcard folder path) to filter source files. Allowed wildcards are: * (matches zero or more characters) and ? (matches zero or single character). Use ^ to escape if your file name has a wildcard or this escape character inside. See more examples in Folder and file filter examples. |
Yes |
| OPTION 4: a list of files - fileListPath |
Indicates to copy a given file set. Point to a text file that includes a list of files you want to copy, one file per line, which is the relative path to the path configured in the dataset. When you're using this option, don't specify a file name in the dataset. See more examples in File list examples. |
No |
| Additional settings: | ||
| recursive | Indicates whether the data is read recursively from the subfolders or only from the specified folder. Note that when recursive is set to true and the sink is a file-based store, an empty folder or subfolder isn't copied or created at the sink. Allowed values are true (default) and false. This property doesn't apply when you configure fileListPath. |
No |
| deleteFilesAfterCompletion | Indicates whether the binary files will be deleted from source store after successfully moving to the destination store. The file deletion is per file. Therefore, when the copy activity fails, you'll see some files have already been copied to the destination and deleted from source, while others are still remaining on the source store. This property is only valid in binary files copy scenario. The default value: false. |
No |
| modifiedDatetimeStart | Files are filtered based on the attribute: last modified. The files will be selected if their last modified time is greater than or equal to modifiedDatetimeStart and less than modifiedDatetimeEnd. The time is applied to a UTC time zone in the format of "2018-12-01T05:00:00Z". The properties can be NULL, which means no file attribute filter will be applied to the dataset. When modifiedDatetimeStart has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeEnd is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is greater than or equal to the datetime value will be selected. When modifiedDatetimeEnd has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeStart is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is less than the datetime value will be selected.This property doesn't apply when you configure fileListPath. |
No |
| modifiedDatetimeEnd | Same as the previous property. | No |
| enablePartitionDiscovery | For files that are partitioned, specify whether to parse the partitions from the file path and add them as extra source columns. Allowed values are false (default) and true. |
No |
| partitionRootPath | When partition discovery is enabled, specify the absolute root path in order to read partitioned folders as data columns. If it isn't specified, by default, - When you use file path in dataset or list of files on source, partition root path is the path configured in dataset. - When you use wildcard folder filter, partition root path is the sub-path before the first wildcard. - When you use prefix, partition root path is sub-path before the last "/". For example, assuming you configure the path in dataset as "root/folder/year=2020/month=08/day=27": - If you specify partition root path as "root/folder/year=2020", copy activity will generate two more columns month and day with value "08" and "27" respectively, in addition to the columns inside the files.- If partition root path isn't specified, no extra column will be generated. |
No |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
Note
For Parquet/delimited text format, the BlobSource type for the Copy activity source mentioned in the next section is still supported as is for backward compatibility. We suggest that you use the new model until the authoring UI has switched to generating these new types.
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromBlob",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Delimited text input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "DelimitedTextSource",
"formatSettings":{
"type": "DelimitedTextReadSettings",
"skipLineCount": 10
},
"storeSettings":{
"type": "AzureBlobStorageReadSettings",
"recursive": true,
"wildcardFolderPath": "myfolder*A",
"wildcardFileName": "*.csv"
}
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Note
The $logs container, which is automatically created when Storage Analytics is enabled for a storage account, isn't shown when a container listing operation is performed via the UI. The file path must be provided directly for your data factory or Synapse pipeline to consume files from the $logs container.
Blob storage as a sink type
Azure Data Factory supports the following file formats. Refer to each article for format-based settings.
The following properties are supported for Azure Blob Storage under storeSettings settings in a format-based copy sink:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property under storeSettings must be set to AzureBlobStorageWriteSettings. |
Yes |
| copyBehavior | Defines the copy behavior when the source is files from a file-based data store. Allowed values are: - PreserveHierarchy (default): Preserves the file hierarchy in the target folder. The relative path of the source file to the source folder is identical to the relative path of the target file to the target folder. - FlattenHierarchy: All files from the source folder are in the first level of the target folder. The target files have autogenerated names. - MergeFiles: Merges all files from the source folder to one file. If the file or blob name is specified, the merged file name is the specified name. Otherwise, it's an autogenerated file name. |
No |
| blockSizeInMB | Specify the block size, in megabytes, used to write data to block blobs. Learn more about Block Blobs. Allowed value is between 4 MB and 100 MB. By default, the service automatically determines the block size based on your source store type and data. For nonbinary copy into Blob storage, the default block size is 100 MB so it can fit in (at most) 4.95 TB of data. It might be not optimal when your data isn't large, especially when you use the self-hosted integration runtime with poor network connections that result in operation timeout or performance issues. You can explicitly specify a block size, while ensuring that blockSizeInMB*50000 is large enough to store the data. Otherwise, the Copy activity run will fail. |
No |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
| metadata | Set custom metadata when copy to sink. Each object under the metadata array represents an extra column. The name defines the metadata key name, and the value indicates the data value of that key. If preserve attributes feature is used, the specified metadata will union/overwrite with the source file metadata.Allowed data values are: - $$LASTMODIFIED: a reserved variable indicates to store the source files' last modified time. Apply to file-based source with binary format only.- Expression - Static value |
No |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromBlob",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Parquet output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "ParquetSink",
"storeSettings":{
"type": "AzureBlobStorageWriteSettings",
"copyBehavior": "PreserveHierarchy",
"metadata": [
{
"name": "testKey1",
"value": "value1"
},
{
"name": "testKey2",
"value": "value2"
},
{
"name": "lastModifiedKey",
"value": "$$LASTMODIFIED"
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
Folder and file filter examples
This section describes the resulting behavior of the folder path and file name with wildcard filters.
| folderPath | fileName | recursive | Source folder structure and filter result (files in bold are retrieved) |
|---|---|---|---|
container/Folder* |
(empty, use default) | false | container FolderA File1.csv File2.json Subfolder1 File3.csv File4.json File5.csv AnotherFolderB File6.csv |
container/Folder* |
(empty, use default) | true | container FolderA File1.csv File2.json Subfolder1 File3.csv File4.json File5.csv AnotherFolderB File6.csv |
container/Folder* |
*.csv |
false | container FolderA File1.csv File2.json Subfolder1 File3.csv File4.json File5.csv AnotherFolderB File6.csv |
container/Folder* |
*.csv |
true | container FolderA File1.csv File2.json Subfolder1 File3.csv File4.json File5.csv AnotherFolderB File6.csv |
File list examples
This section describes the resulting behavior of using a file list path in the Copy activity source.
Assume that you have the following source folder structure and want to copy the files in bold:
| Sample source structure | Content in FileListToCopy.txt | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| container FolderA File1.csv File2.json Subfolder1 File3.csv File4.json File5.csv Metadata FileListToCopy.txt |
File1.csv Subfolder1/File3.csv Subfolder1/File5.csv |
In dataset: - Container: container- Folder path: FolderAIn Copy activity source: - File list path: container/Metadata/FileListToCopy.txt The file list path points to a text file in the same data store that includes a list of files you want to copy. It includes one file per line, with the relative path to the path configured in the dataset. |
Some recursive and copyBehavior examples
This section describes the resulting behavior of the Copy operation for different combinations of recursive and copyBehavior values.
| recursive | copyBehavior | Source folder structure | Resulting target |
|---|---|---|---|
| true | preserveHierarchy | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the same structure as the source: Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
| true | flattenHierarchy | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the following structure: Folder1 autogenerated name for File1 autogenerated name for File2 autogenerated name for File3 autogenerated name for File4 autogenerated name for File5 |
| true | mergeFiles | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the following structure: Folder1 File1 + File2 + File3 + File4 + File5 contents are merged into one file with an autogenerated file name. |
| false | preserveHierarchy | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the following structure: Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 with File3, File4, and File5 isn't picked up. |
| false | flattenHierarchy | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the following structure: Folder1 autogenerated name for File1 autogenerated name for File2 Subfolder1 with File3, File4, and File5 isn't picked up. |
| false | mergeFiles | Folder1 File1 File2 Subfolder1 File3 File4 File5 |
The target folder, Folder1, is created with the following structure: Folder1 File1 + File2 contents are merged into one file with an autogenerated file name. autogenerated name for File1 Subfolder1 with File3, File4, and File5 isn't picked up. |
Preserving metadata during copy
When you copy files from Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 or Azure Blob Storage, you can choose to preserve the file metadata along with data. Learn more from Preserve metadata.
Mapping data flow properties
When you're transforming data in mapping data flows, you can read and write files from Azure Blob Storage in the following formats:
Format specific settings are located in the documentation for that format. For more information, see Source transformation in mapping data flow and Sink transformation in mapping data flow.
Source transformation
In source transformation, you can read from a container, folder, or individual file in Azure Blob Storage. Use the Source options tab to manage how the files are read.

Wildcard paths: Using a wildcard pattern will instruct the service to loop through each matching folder and file in a single source transformation. This is an effective way to process multiple files within a single flow. Add multiple wildcard matching patterns with the plus sign that appears when you hover over your existing wildcard pattern.
From your source container, choose a series of files that match a pattern. Only a container can be specified in the dataset. Your wildcard path must therefore also include your folder path from the root folder.
Wildcard examples:
*Represents any set of characters.**Represents recursive directory nesting.?Replaces one character.[]Matches one or more characters in the brackets./data/sales/**/*.csvGets all .csv files under /data/sales./data/sales/20??/**/Gets all files in the 20th century./data/sales/*/*/*.csvGets .csv files two levels under /data/sales./data/sales/2004/*/12/[XY]1?.csvGets all .csv files in December 2004 starting with X or Y prefixed by a two-digit number.
Partition root path: If you have partitioned folders in your file source with a key=value format (for example, year=2019), then you can assign the top level of that partition folder tree to a column name in your data flow's data stream.
First, set a wildcard to include all paths that are the partitioned folders plus the leaf files that you want to read.
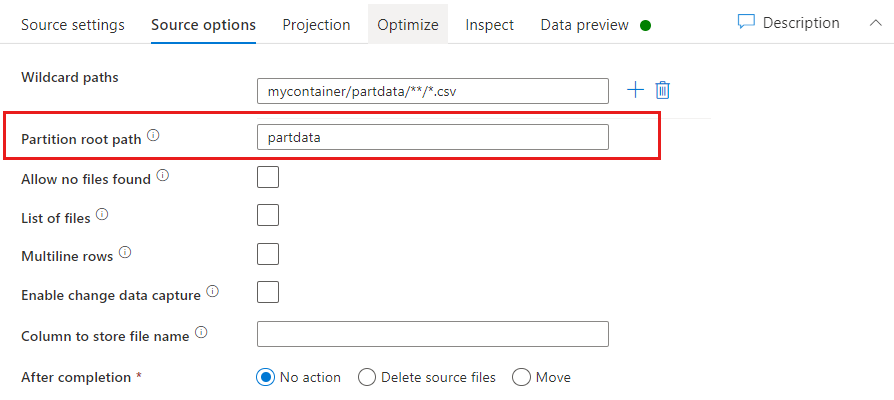
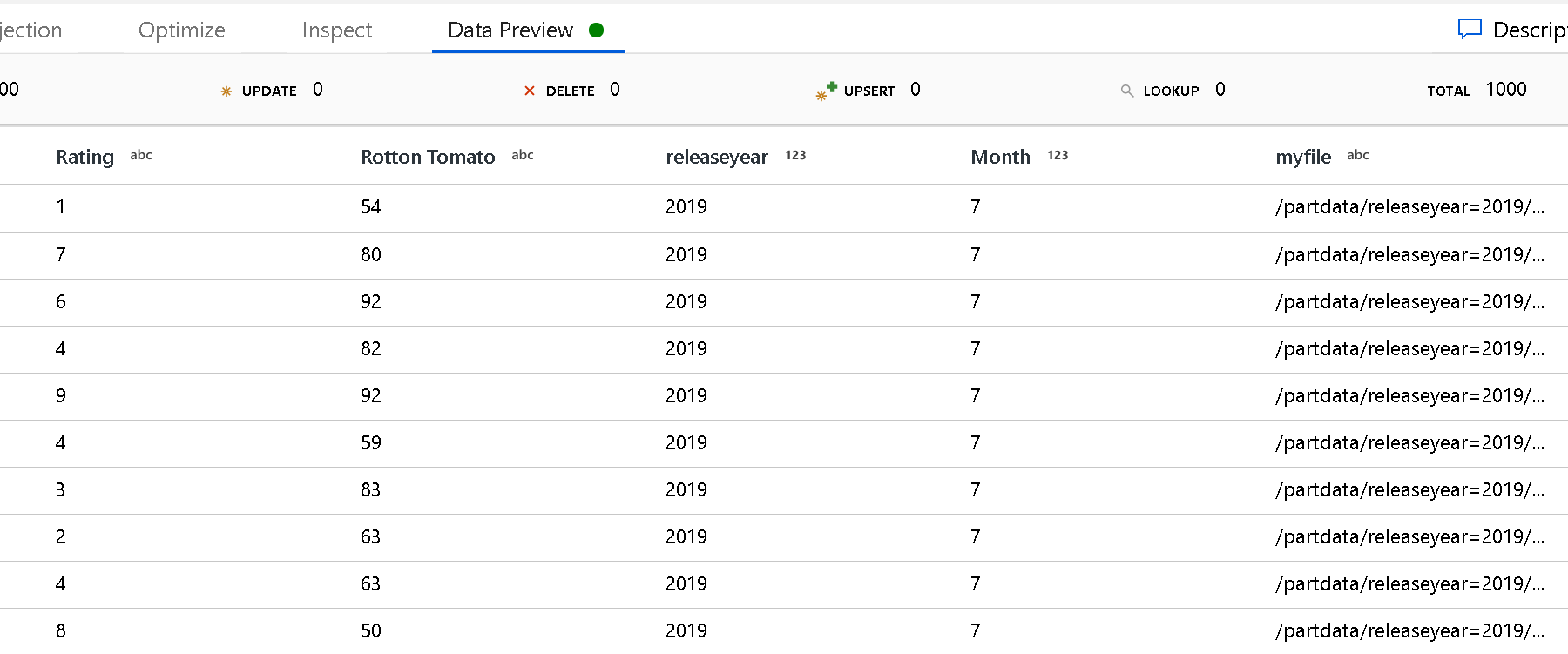
Use the Partition root path setting to define what the top level of the folder structure is. When you view the contents of your data via a data preview, you'll see that the service adds the resolved partitions found in each of your folder levels.
List of files: This is a file set. Create a text file that includes a list of relative path files to process. Point to this text file.
Column to store file name: Store the name of the source file in a column in your data. Enter a new column name here to store the file name string.
After completion: Choose to do nothing with the source file after the data flow runs, delete the source file, or move the source file. The paths for the move are relative.
To move source files to another location post-processing, first select "Move" for file operation. Then, set the "from" directory. If you're not using any wildcards for your path, then the "from" setting will be the same folder as your source folder.
If you have a source path with wildcard, your syntax is as follows:
/data/sales/20??/**/*.csv
You can specify "from" as:
/data/sales
And you can specify "to" as:
/backup/priorSales
In this case, all files that were sourced under /data/sales are moved to /backup/priorSales.
Note
File operations run only when you start the data flow from a pipeline run (a pipeline debug or execution run) that uses the Execute Data Flow activity in a pipeline. File operations don't run in Data Flow debug mode.
Filter by last modified: You can filter the files to be processed by specifying a date range of when they were last modified. All datetimes are in UTC.
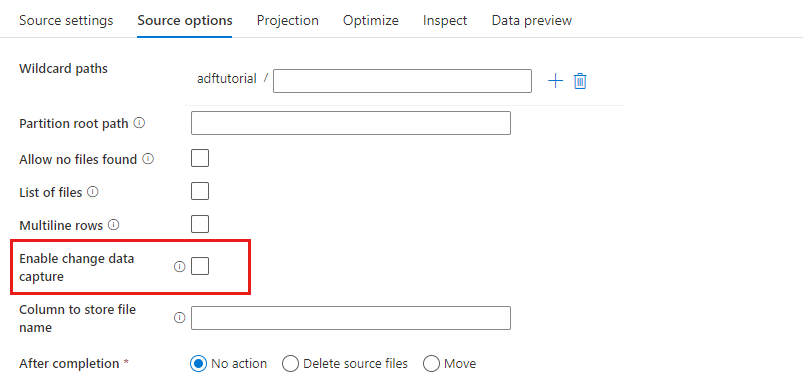
Enable change data capture: If true, you'll get new or changed files only from the last run. Initial load of full snapshot data will always be gotten in the first run, followed by capturing new or changed files only in next runs.
Sink properties
In the sink transformation, you can write to either a container or a folder in Azure Blob Storage. Use the Settings tab to manage how the files get written.

Clear the folder: Determines whether or not the destination folder gets cleared before the data is written.
File name option: Determines how the destination files are named in the destination folder. The file name options are:
- Default: Allow Spark to name files based on PART defaults.
- Pattern: Enter a pattern that enumerates your output files per partition. For example,
loans[n].csvcreatesloans1.csv,loans2.csv, and so on. - Per partition: Enter one file name per partition.
- As data in column: Set the output file to the value of a column. The path is relative to the dataset container, not the destination folder. If you have a folder path in your dataset, it is overridden.
- Output to a single file: Combine the partitioned output files into a single named file. The path is relative to the dataset folder. Be aware that the merge operation can possibly fail based on node size. We don't recommend this option for large datasets.
Quote all: Determines whether to enclose all values in quotation marks.
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
GetMetadata activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check GetMetadata activity.
Delete activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Delete activity.
Legacy models
Note
The following models are still supported as is for backward compatibility. We suggest that you use the new model mentioned earlier. The authoring UI has switched to generating the new model.
Legacy dataset model
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to AzureBlob. |
Yes |
| folderPath | Path to the container and folder in Blob storage. A wildcard filter is supported for the path, excluding container name. Allowed wildcards are: * (matches zero or more characters) and ? (matches zero or single character). Use ^ to escape if your folder name has a wildcard or this escape character inside. An example is: myblobcontainer/myblobfolder/. See more examples in Folder and file filter examples. |
Yes for the Copy or Lookup activity, No for the GetMetadata activity |
| fileName | Name or wildcard filter for the blobs under the specified folderPath value. If you don't specify a value for this property, the dataset points to all blobs in the folder. For the filter, allowed wildcards are: * (matches zero or more characters) and ? (matches zero or single character).- Example 1: "fileName": "*.csv"- Example 2: "fileName": "???20180427.txt"Use ^ to escape if your file name has a wildcard or this escape character inside.When fileName isn't specified for an output dataset and preserveHierarchy isn't specified in the activity sink, the Copy activity automatically generates the blob name with the following pattern: "Data.[activity run ID GUID].[GUID if FlattenHierarchy].[format if configured].[compression if configured]". For example: "Data.0a405f8a-93ff-4c6f-b3be-f69616f1df7a.txt.gz". If you copy from a tabular source by using a table name instead of a query, the name pattern is [table name].[format].[compression if configured]. For example: "MyTable.csv". |
No |
| modifiedDatetimeStart | Files are filtered based on the attribute: last modified. The files will be selected if their last modified time is greater than or equal to modifiedDatetimeStart and less than modifiedDatetimeEnd. The time is applied to the UTC time zone in the format of "2018-12-01T05:00:00Z". Be aware that enabling this setting affects the overall performance of data movement when you want to filter huge amounts of files. The properties can be NULL, which means no file attribute filter will be applied to the dataset. When modifiedDatetimeStart has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeEnd is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is greater than or equal to the datetime value will be selected. When modifiedDatetimeEnd has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeStart is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is less than the datetime value will be selected. |
No |
| modifiedDatetimeEnd | Files are filtered based on the attribute: last modified. The files will be selected if their last modified time is greater than or equal to modifiedDatetimeStart and less than modifiedDatetimeEnd. The time is applied to the UTC time zone in the format of "2018-12-01T05:00:00Z". Be aware that enabling this setting affects the overall performance of data movement when you want to filter huge amounts of files. The properties can be NULL, which means no file attribute filter will be applied to the dataset. When modifiedDatetimeStart has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeEnd is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is greater than or equal to the datetime value will be selected. When modifiedDatetimeEnd has a datetime value but modifiedDatetimeStart is NULL, the files whose last modified attribute is less than the datetime value will be selected. |
No |
| format | If you want to copy files as is between file-based stores (binary copy), skip the format section in both the input and output dataset definitions. If you want to parse or generate files with a specific format, the following file format types are supported: TextFormat, JsonFormat, AvroFormat, OrcFormat, and ParquetFormat. Set the type property under format to one of these values. For more information, see the Text format, JSON format, Avro format, Orc format, and Parquet format sections. |
No (only for binary copy scenario) |
| compression | Specify the type and level of compression for the data. For more information, see Supported file formats and compression codecs. Supported types are GZip, Deflate, BZip2, and ZipDeflate. Supported levels are Optimal and Fastest. |
No |
Tip
To copy all blobs under a folder, specify folderPath only.
To copy a single blob with a given name, specify folderPath for the folder part and fileName for the file name.
To copy a subset of blobs under a folder, specify folderPath for the folder part and fileName with a wildcard filter.
Example:
{
"name": "AzureBlobDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "AzureBlob",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob Storage linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"typeProperties": {
"folderPath": "mycontainer/myfolder",
"fileName": "*",
"modifiedDatetimeStart": "2018-12-01T05:00:00Z",
"modifiedDatetimeEnd": "2018-12-01T06:00:00Z",
"format": {
"type": "TextFormat",
"columnDelimiter": ",",
"rowDelimiter": "\n"
},
"compression": {
"type": "GZip",
"level": "Optimal"
}
}
}
}
Legacy source model for the Copy activity
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy activity source must be set to BlobSource. |
Yes |
| recursive | Indicates whether the data is read recursively from the subfolders or only from the specified folder. When recursive is set to true and the sink is a file-based store, an empty folder or subfolder isn't copied or created at the sink.Allowed values are true (default) and false. |
No |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromBlob",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "BlobSource",
"recursive": true
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Legacy sink model for the Copy activity
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the Copy activity sink must be set to BlobSink. |
Yes |
| copyBehavior | Defines the copy behavior when the source is files from a file-based data store. Allowed values are: - PreserveHierarchy (default): Preserves the file hierarchy in the target folder. The relative path of source file to source folder is identical to the relative path of target file to target folder. - FlattenHierarchy: All files from the source folder are in the first level of the target folder. The target files have autogenerated names. - MergeFiles: Merges all files from the source folder to one file. If the file or blob name is specified, the merged file name is the specified name. Otherwise, it's an autogenerated file name. |
No |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyToBlob",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Azure Blob output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "BlobSink",
"copyBehavior": "PreserveHierarchy"
}
}
}
]
Change data capture
Azure Data Factory can get new or changed files only from Azure Blob Storage by enabling **Enable change data capture ** in the mapping data flow source transformation. With this connector option, you can read new or updated files only and apply transformations before loading transformed data into destination datasets of your choice. Please refer to Change Data Capture for details.
Related content
For a list of data stores that the Copy activity supports as sources and sinks, see Supported data stores.