Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Agentless machine scanning in Microsoft Defender for Cloud improves the security posture of machines connected to Defender for Cloud.
Agentless scanning doesn't need any installed agents or network connectivity, and doesn't affect machine performance. Agentless machine scanning:
- Scans endpoint detection and response (EDR) settings: Scan machines to assess whether they're running an EDR solution, and whether settings are correct if machines integrate with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Learn more
- Scans software inventory: Scan your software inventory with integrated Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management.
- Scans for vulnerabilities: Assess machines for vulnerabilities using integrated Defender Vulnerability Management.
- Scans for secrets on machines: Locate plain text secrets in your compute environment with agentless secrets scanning.
- Scans for malware: Scan machines for malware and viruses using Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
- Scans VMs running as Kubernetes nodes: Vulnerability assessment and malware scanning is available for VMs running as Kubernetes nodes when Defender for Servers Plan 2 or the Defender for Containers plan is enabled. Available in commercial clouds only.
Agentless scanning is available in the following Defender for Cloud plans:
- Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM).
- Defender for Servers Plan 2.
- Malware scanning is only available in Defender for Servers Plan 2.
- Agentless scanning is available for Azure VMs, AWS EC2 and GCP compute instances connected to Defender for Cloud.
Agentless scanning architecture
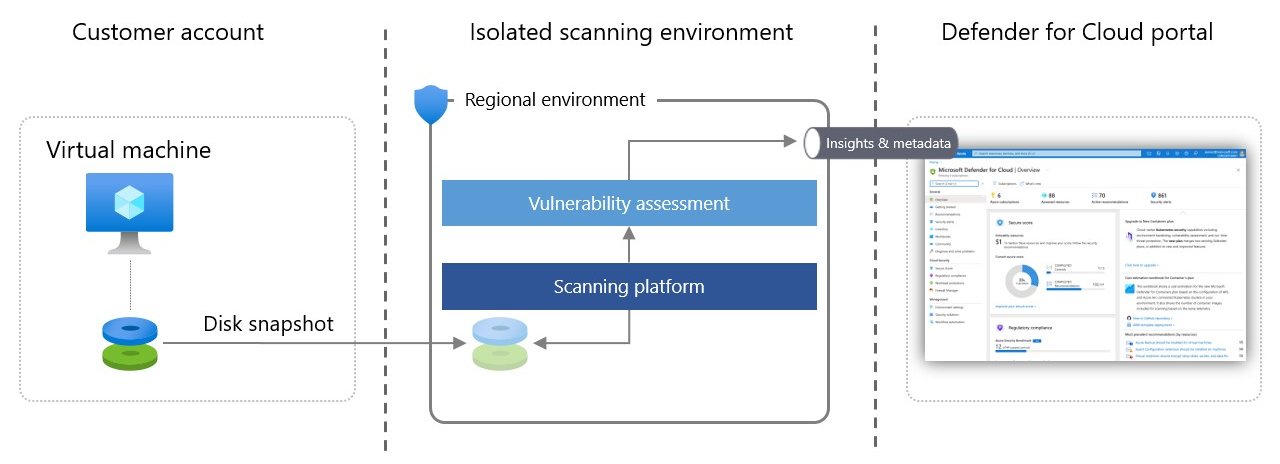
Here's how agentless scanning works:
Defender for Cloud takes snapshots of VM disks and performs an out-of-band, deep analysis of the operating system configuration and file system stored in the snapshot.
- The copied snapshot remains in the same region as the VM.
- The scan doesn't affect the VM.
After Defender for Cloud gets the necessary metadata from the copied disk, it immediately deletes the copied snapshot of the disk and sends the metadata to relevant Microsoft engines to detect configuration gaps and potential threats. For example, in vulnerability assessment, the analysis is done by Defender Vulnerability Management.
Defender for Cloud displays scanning results, which consolidates both the agent-based and agentless results on the Security alerts page.
Defender for Cloud analyses disks in a scanning environment that's regional, volatile, isolated, and highly secure. Disk snapshots and data unrelated to the scan aren't stored longer than is necessary to collect the metadata, typically a few minutes.
Permissions used by agentless scanning
Defender for Cloud used specific roles and permissions to perform agentless scanning.
- In Azure, these permissions are automatically added to your subscriptions when you enable agentless scanning.
- In AWS, these permissions are added to the CloudFormation stack in your AWS connector.
- In GCP, these permissions are added to the onboarding script in your GCP connector.
Azure permissions
The built-in role VM scanner operator has read-only permissions for VM disks that are required for the snapshot process. The detailed list of permissions is:
Microsoft.Compute/disks/readMicrosoft.Compute/disks/beginGetAccess/actionMicrosoft.Compute/disks/diskEncryptionSets/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachines/instanceView/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachines/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/instanceView/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/virtualMachines/readMicrosoft.Compute/virtualMachineScaleSets/virtualMachines/instanceView/read
When coverage for CMK encrypted disks is enabled, more permissions are required:
Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/readMicrosoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/wrap/actionMicrosoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/unwrap/action
AWS permissions
The role VmScanner is assigned to the scanner when you enable agentless scanning. This role has the minimal permission set to create and clean up snapshots (scoped by tag) and to verify the current state of the VM. The detailed permissions are:
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerDeleteSnapshotAccess |
| Actions | ec2:DeleteSnapshot |
| Conditions | "StringEquals":{"ec2:ResourceTag/CreatedBy”:<br>"Microsoft Defender for Cloud"} |
| Resources | arn:aws:ec2:::snapshot/ |
| Effect | Allow |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerAccess |
| Actions | ec2:ModifySnapshotAttribute ec2:DeleteTags ec2:CreateTags ec2:CreateSnapshots ec2:CopySnapshots ec2:CreateSnapshot |
| Conditions | None |
| Resources | arn:aws:ec2:::instance/ arn:aws:ec2:::snapshot/ arn:aws:ec2:::volume/ |
| Effect | Allow |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerVerificationAccess |
| Actions | ec2:DescribeSnapshots ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus |
| Conditions | None |
| Resources | * |
| Effect | Allow |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerEncryptionKeyCreation |
| Actions | kms:CreateKey |
| Conditions | None |
| Resources | * |
| Effect | Allow |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerEncryptionKeyManagement |
| Actions | kms:TagResource kms:GetKeyRotationStatus kms:PutKeyPolicy kms:GetKeyPolicy kms:CreateAlias kms:ListResourceTags |
| Conditions | None |
| Resources | arn:aws:kms::${AWS::AccountId}: key/ <br> arn:aws:kms:*:${AWS::AccountId}:alias/DefenderForCloudKey |
| Effect | Allow |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| SID | VmScannerEncryptionKeyUsage |
| Actions | kms:GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlaintext kms:DescribeKey kms:RetireGrant kms:CreateGrant kms:ReEncryptFrom |
| Conditions | None |
| Resources | arn:aws:kms::${AWS::AccountId}: key/ |
| Effect | Allow |
GCP permissions
During onboarding, a new custom role is created with minimal permissions required to get instances status and create snapshots.
In addition, permissions to an existing GCP KMS role are granted to support scanning disks that are encrypted with CMEK. The roles are:
- roles/MDCAgentlessScanningRole granted to Defender for Cloud’s service account with permissions: compute.disks.createSnapshot, compute.instances.get
- roles/cloudkms.cryptoKeyEncrypterDecrypter granted to Defender for Cloud’s compute engine service agent