Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
When you deploy a machine learning model to a managed online endpoint, you can secure communication with the online endpoint by using private endpoints. In this article, you learn how a private endpoint can secure inbound communication to a managed online endpoint. You also learn how a workspace managed virtual network can provide secure communication between deployments and resources.
You can secure inbound scoring requests from clients to an online endpoint and secure outbound communications between a deployment, the Azure resources it uses, and private resources. You configure security for inbound and outbound communication separately. For more information on endpoints and deployments, see What are endpoints and deployments.
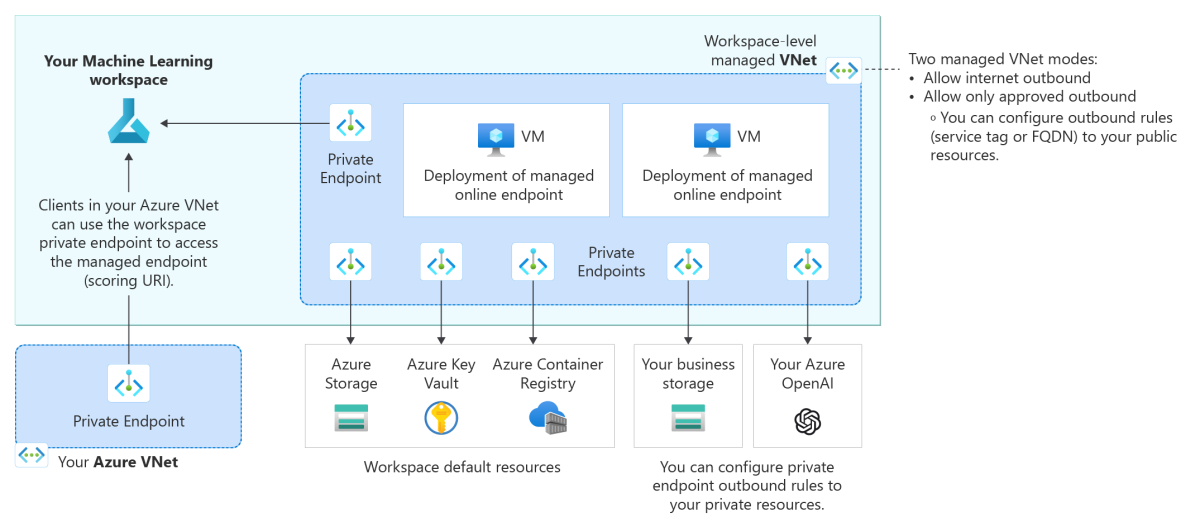
The following architecture diagram shows how communications flow through private endpoints to the managed online endpoint. Incoming scoring requests from a client's virtual network flow through the workspace's private endpoint to the managed online endpoint. Outbound communications from deployments to services are handled through private endpoints from the workspace's managed virtual network to those service instances.
Note
- This article focuses on network isolation by using the workspace's managed virtual network. For a description of the legacy method for network isolation, in which Azure Machine Learning creates a managed virtual network for each deployment in an endpoint, see the Appendix.
- Each deployment is isolated from other deployments, regardless of inbound and outbound communication discussed in this article. In other words, even with endpoints and deployments that allow internet inbound and outbound access, there's a network isolation between deployments, which blocks any deployment from directly connecting to other deployments.
Limitations
The
v1_legacy_modeflag must be set tofalseto turn off v1 legacy mode on your Azure Machine Learning workspace. If this setting is turned on, you can't create a managed online endpoint. For more information, see Network isolation change with our new API platform on Azure Resource Manager.If your Azure Machine Learning workspace has a private endpoint that was created before May 24, 2022, you must re-create that private endpoint before you configure your online endpoints to use private endpoints. For more information about creating a private endpoint for your workspace, see Configure a private endpoint for an Azure Machine Learning workspace.
Tip
To see the creation date of a workspace, you can check the workspace properties.
- In Azure Machine Learning studio, go to the upper-right corner and select the name of your workspace.
- In the Directory + Subscription + Workspace window, select View all properties in Azure portal.
- In the Azure portal Overview page, go to the upper-right corner and select JSON View.
- In the Resource JSON window, under API Versions, select the latest API version.
- In the
propertiessection of the JSON code, check thecreationTimevalue.
Alternatively, use one of the following methods:
- Python SDK:
Workspace.get(name=<workspace-name>, subscription_id=<subscription-ID>, resource_group=<resource-group-name>).get_details() - REST API:
curl https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subscription-ID>/resourceGroups/<resource-group-name>/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/?api-version=2023-10-01 -H "Authorization:Bearer <access-token>" - PowerShell:
Get-AzMLWorkspace -Name <workspace-name> -ResourceGroupName <resource-group-name>
When you use network isolation to help secure online endpoints, you can use workspace-associated resources from a different resource group than your workspace resource group. However, these resources must belong to the same subscription and tenant as your workspace. Resources that are associated with a workspace include Azure Container Registry, Azure Storage, Azure Key Vault, and Application Insights.
Note
This article describes network isolation that applies to data plane operations. These operations result from scoring requests, or model serving. Control plane operations, such as requests to create, update, delete, or retrieve authentication keys, are sent to Azure Resource Manager over the public network.
Secure inbound scoring requests
You can secure inbound communication from a client to a managed online endpoint by using a private endpoint for the Azure Machine Learning workspace. This private endpoint on the client's virtual network communicates with the workspace of the managed online endpoint and is the means by which the managed online endpoint receives incoming scoring requests from the client.
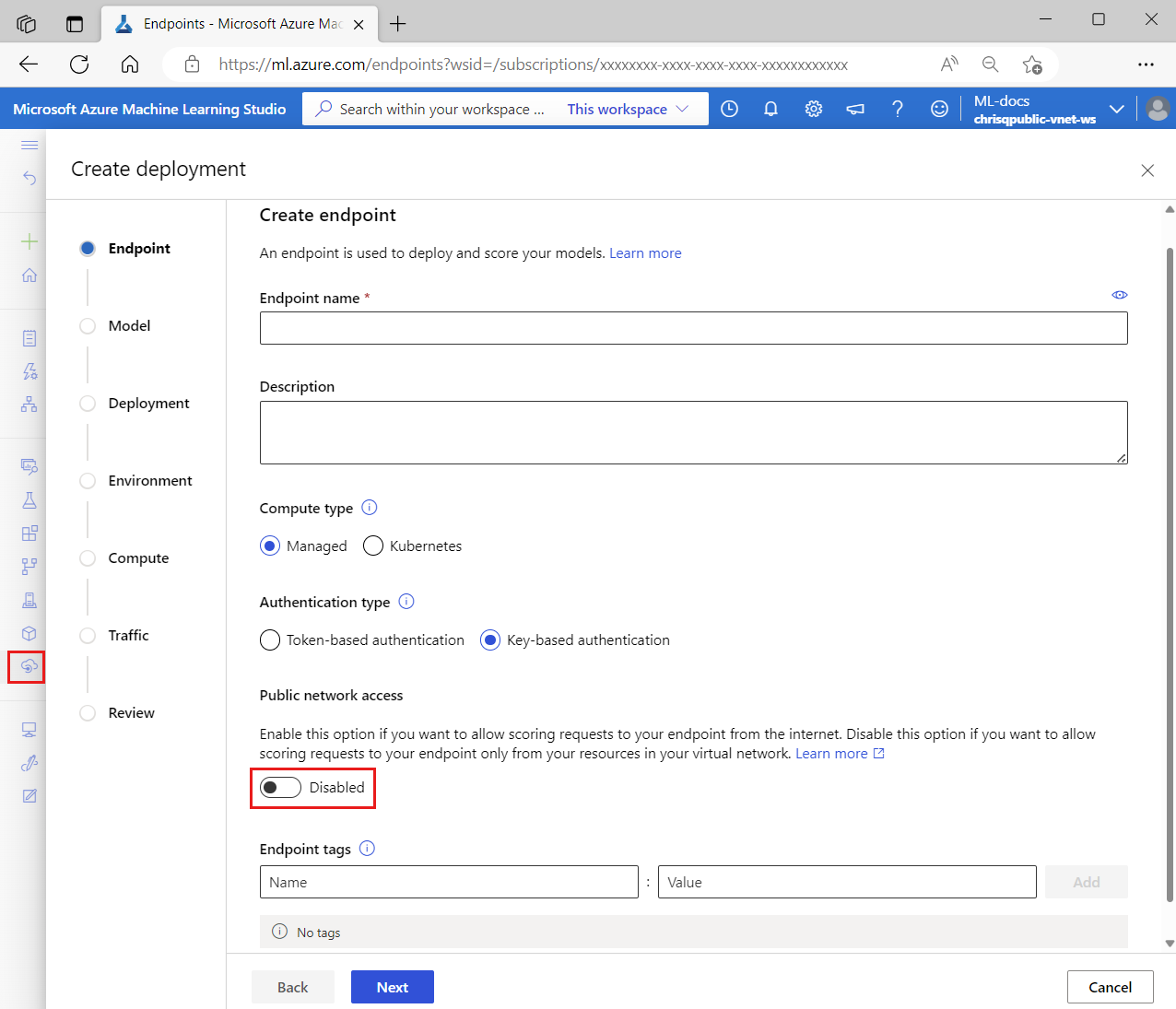
To secure scoring requests to the online endpoint, so that a client can access it only through the workspace's private endpoint, set the public_network_access flag for the endpoint to disabled. After you create the endpoint, you can update this setting to enable public network access if desired.
Set the endpoint's public_network_access flag to disabled:
Before you run the Azure CLI command:
- Make sure you have an
endpoint.ymlfile in your current working directory (either locally or in Azure Cloud Shell). - If you use Azure Cloud Shell, upload
endpoint.ymlor clone a repository that contains it into your Cloud Shell home directory. - If your default Azure Machine Learning workspace and resource group are not set, add the
--resource-groupand--workspace-nameparameters.
az ml online-endpoint create \
--file endpoint.yml \
--set public_network_access=disabled
# Optionally specify the workspace and resource group explicitly
az ml online-endpoint create \
--file endpoint.yml \
--resource-group <resource-group-name> \
--workspace-name <workspace-name> \
--set public_network_access=disabled
If you see a No such file or directory: endpoint.yml error, confirm that endpoint.yml exists in your current directory and that you run the command from that directory.
When you disable public_network_access, the workspace's private endpoint receives inbound scoring requests, and public networks can't reach the endpoint.
If you enable public_network_access, the endpoint can receive inbound scoring requests from the internet.
Secure inbound scoring with public network access from specific IP addresses
Azure Machine Learning workspace supports enabling public network access from specific IP addresses or address ranges. This feature has some interactions with the managed online endpoint's public_network_access flag that you should be aware of when using it with managed online endpoints. For more information, see Scenario: Managed online endpoints with access from specific IP addresses.
Secure outbound access with workspace managed virtual network
To secure outbound communication from a deployment to services, you need to enable managed virtual network isolation for your Azure Machine Learning workspace so that Azure Machine Learning can create a managed virtual network for the workspace. All managed online endpoints in the workspace (and managed compute resources for the workspace, such as compute clusters and compute instances) automatically use this workspace managed virtual network, and the deployments under the endpoints share the managed virtual network's private endpoints for communication with the workspace's resources.
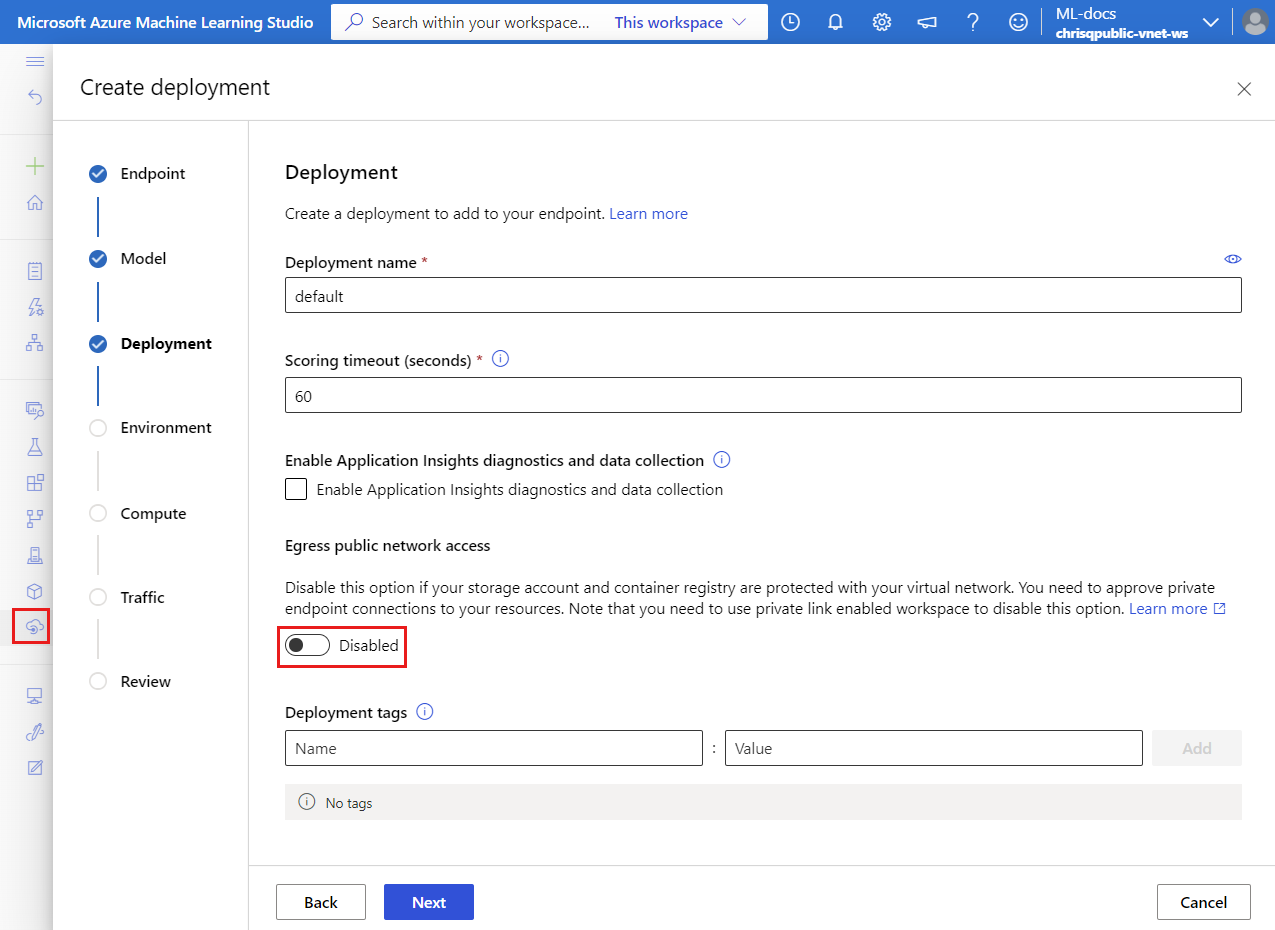
When you secure your workspace with a managed virtual network, the egress_public_access flag for managed online deployments no longer applies. Avoid setting this flag when creating the managed online deployment.
For outbound communication with a workspace managed virtual network, Azure Machine Learning:
- Creates private endpoints for the managed virtual network to use for communication with Azure resources that the workspace uses, such as Azure Storage, Azure Key Vault, and Azure Container Registry.
- Allows deployments to access the Microsoft Container Registry (MCR), which can be useful when you want to use curated environments or MLflow no-code deployment.
- Allows users to configure private endpoint outbound rules to private resources and configure outbound rules (service tag or FQDN) for public resources. For more information on how to manage outbound rules, see Manage outbound rules.
Furthermore, you can configure two isolation modes for outbound traffic from the workspace managed virtual network:
- Allow internet outbound, to allow all internet outbound traffic from the managed virtual network
- Allow only approved outbound, to control outbound traffic by using private endpoints, FQDN outbound rules, and service tag outbound rules.
For example, if your workspace's managed virtual network contains two deployments under a managed online endpoint, both deployments can use the workspace's private endpoints to communicate with:
- The Azure Machine Learning workspace
- The Azure Storage blob that's associated with the workspace
- The Azure Container Registry for the workspace
- The Azure Key Vault
- (Optional) additional private resources that support private endpoints.
To learn more about configurations for the workspace managed virtual network, see Managed virtual network architecture.
Scenarios for network isolation configuration
Your Azure Machine Learning workspace and managed online endpoint each have a public_network_access flag that you can use to configure their inbound communication. On the other hand, outbound communication from a deployment depends on the workspace's managed virtual network.
Communication with the managed online endpoint
Suppose a managed online endpoint has a deployment that uses an AI model, and you want to use an app to send scoring requests to the endpoint. You can decide what network isolation configuration to use for the managed online endpoint as follows:
For inbound communication:
If the app is publicly available on the internet, then you need to enable public_network_access for the endpoint so that it can receive inbound scoring requests from the app.
However, if the app is private, such as an internal app within your organization, you want the AI model to be used only within your organization rather than expose it to the internet. Therefore, you need to disable the endpoint's public_network_access so that it can receive inbound scoring requests only through its workspace's private endpoint.
For outbound communication (deployment):
Suppose your deployment needs to access private Azure resources (such as the Azure Storage blob, ACR, and Azure Key Vault), or it's unacceptable for the deployment to access the internet. In this case, you need to enable the workspace's managed virtual network with the allow only approved outbound isolation mode. This isolation mode allows outbound communication from the deployment to approved destinations only, thereby protecting against data exfiltration. Furthermore, you can add outbound rules for the workspace, to allow access to more private or public resources. For more information, see Configure a managed virtual network to allow only approved outbound.
However, if you want your deployment to access the internet, you can use the workspace's managed virtual network with the allow internet outbound isolation mode. Apart from being able to access the internet, you'll be able to use the private endpoints of the managed virtual network to access private Azure resources that you need.
Finally, if your deployment doesn't need to access private Azure resources and you don't need to control access to the internet, then you don't need to use a workspace managed virtual network.
Inbound communication to the Azure Machine Learning workspace
You can use the public_network_access flag of your Azure Machine Learning workspace to enable or disable inbound workspace access.
Typically, if you secure inbound communication to your workspace (by disabling the workspace's public_network_access flag) you also want to secure inbound communication to your managed online endpoint.
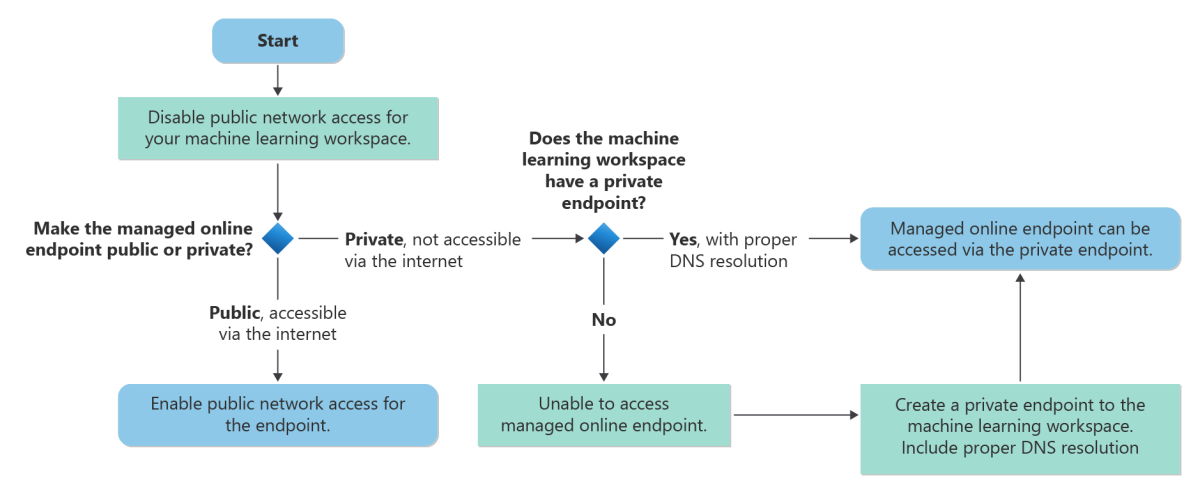
The following chart shows a typical workflow for securing inbound communication to your Azure Machine Learning workspace and your managed online endpoint. For best security, we recommend that you disable the public_network_access flags for the workspace and the managed online endpoint to ensure that both can't be accessed via the public internet. If the workspace doesn't have a private endpoint, you can create one, making sure to include proper DNS resolution. You can then access the managed online endpoint by using the workspace's private endpoint.
Note
Managed online endpoints share the workspace's private endpoint. If you're manually adding DNS records to the private DNS zone privatelink.api.azureml.ms, an A record with wildcard
*.<per-workspace globally-unique identifier>.inference.<region>.privatelink.api.azureml.ms should be added to route all endpoints under the workspace to the private endpoint.
For more information on DNS resolution for your workspace and private endpoint, see How to use your workspace with a custom DNS server.
Appendix
Secure outbound access with legacy network isolation method
For managed online endpoints, you can secure outbound communication between deployments and resources by using an Azure Machine Learning managed virtual network for each deployment in the endpoint. The secure outbound communication is also handled by using private endpoints to those service instances.
Note
We strongly recommend that you use the approach described in Secure outbound access with workspace managed virtual network instead of this legacy method.
To restrict communication between a deployment and external resources, including the Azure resources it uses, you should ensure that:
The deployment's
egress_public_network_accessflag isdisabled. This flag ensures that the download of the model, code, and images needed by the deployment are secured with a private endpoint. Once you create the deployment, you can't update (enable or disable) theegress_public_network_accessflag. Attempting to change the flag while updating the deployment fails with an error.The workspace has a private link that allows access to Azure resources via a private endpoint.
The workspace has a
public_network_accessflag that you can enable or disable. If you plan on using a managed online deployment that uses public outbound, then you must also configure the workspace to allow public access. This requirement exists because outbound communication from the online deployment is to the workspace API. When you configure the deployment to use public outbound, the workspace must be able to accept that public communication (allow public access).
When you have multiple deployments, and you configure the egress_public_network_access to disabled for each deployment in a managed online endpoint, each deployment has its own independent Azure Machine Learning managed virtual network. For each virtual network, Azure Machine Learning creates three private endpoints for communication to the following services:
- The Azure Machine Learning workspace
- The Azure Storage blob that's associated with the workspace
- The Azure Container Registry for the workspace
For example, if you set the egress_public_network_access flag to disabled for two deployments of a managed online endpoint, a total of six private endpoints are created. Each deployment uses three private endpoints to communicate with the workspace, blob, and container registry.
Important
Azure Machine Learning doesn't support peering between a deployment's managed virtual network and your client's virtual network. For secure access to resources needed by the deployment, we use private endpoints to communicate with the resources.
The following diagram shows incoming scoring requests from a client's virtual network flowing through the workspace's private endpoint to the managed online endpoint. The diagram also shows two online deployments, each in its own Azure Machine Learning managed virtual network. Each deployment's virtual network has three private endpoints for outbound communication with the Azure Machine Learning workspace, the Azure Storage blob associated with the workspace, and the Azure Container Registry for the workspace.
To disable the egress_public_network_access and create the private endpoints:
az ml online-deployment create -f deployment.yml --set egress_public_network_access=disabled
To confirm the creation of the private endpoints, first check the storage account and container registry associated with the workspace (see Download a configuration file), find each resource from the Azure portal, and check the Private endpoint connections tab under the Networking menu.
Important
- As mentioned earlier, outbound communication from managed online endpoint deployment is to the workspace API. When the endpoint is configured to use public outbound (in other words,
public_network_accessflag for the endpoint is set toenabled), then the workspace must be able to accept that public communication (public_network_accessflag for the workspace set toenabled). - When online deployments are created with
egress_public_network_accessflag set todisabled, they have access to the secured resources (workspace, blob, and container registry) only. For instance, if the deployment uses model assets uploaded to other storage accounts, the model download fails. Ensure model assets are on the storage account associated with the workspace. - When
egress_public_network_accessis set todisabled, the deployment can only access the workspace-associated resources secured in the virtual network. On the contrary, whenegress_public_network_accessis set toenabled, the deployment can only access the resources with public access, which means it can't access the resources secured in the virtual network.
The following table lists the supported configurations when configuring inbound and outbound communications for an online endpoint:
| Configuration | Inbound (Endpoint property) |
Outbound (Deployment property) |
Supported? |
|---|---|---|---|
| secure inbound with secure outbound | public_network_access is disabled |
egress_public_network_access is disabled |
Yes |
| secure inbound with public outbound | public_network_access is disabled |
egress_public_network_access is enabledThe workspace must also allow public access as the deployment outbound is to the workspace API. |
Yes |
| public inbound with secure outbound | public_network_access is enabled |
egress_public_network_access is disabled |
Yes |
| public inbound with public outbound | public_network_access is enabled |
egress_public_network_access is enabledThe workspace must also allow public access as the deployment outbound is to the workspace API. |
Yes |