Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Migrating workloads from mainframe environments to the cloud enables you to modernize your infrastructure and often save on costs. Many workloads can be transferred to Azure with only minor code changes, such as updating the names of databases.
Generally speaking, the term mainframe means a large computer system. Specifically, the vast majority currently in use are IBM System Z servers or IBM plug-compatible systems that run MVS, DOS, VSE, OS/390, or z/OS.
An Azure virtual machine (VM) is used to isolate and manage the resources for a specific application on a single instance. Mainframes such as IBM z/OS use Logical Partitions (LPARS) for this purpose. A mainframe might use one LPAR for a CICS region with associated COBOL programs, and a separate LPAR for IBM Db2 database. A typical n-tier application on Azure deploys Azure VMs into a virtual network that can be segmented into subnets for each tier.
Azure VMs can run mainframe emulation environments and compilers that support lift-and-shift scenarios. Development and testing are often among the first workloads to migrate from a mainframe to an Azure dev/test environment. Common server components that you can emulate include online transaction process (OLTP), batch, and data ingestion systems as the following figure shows.
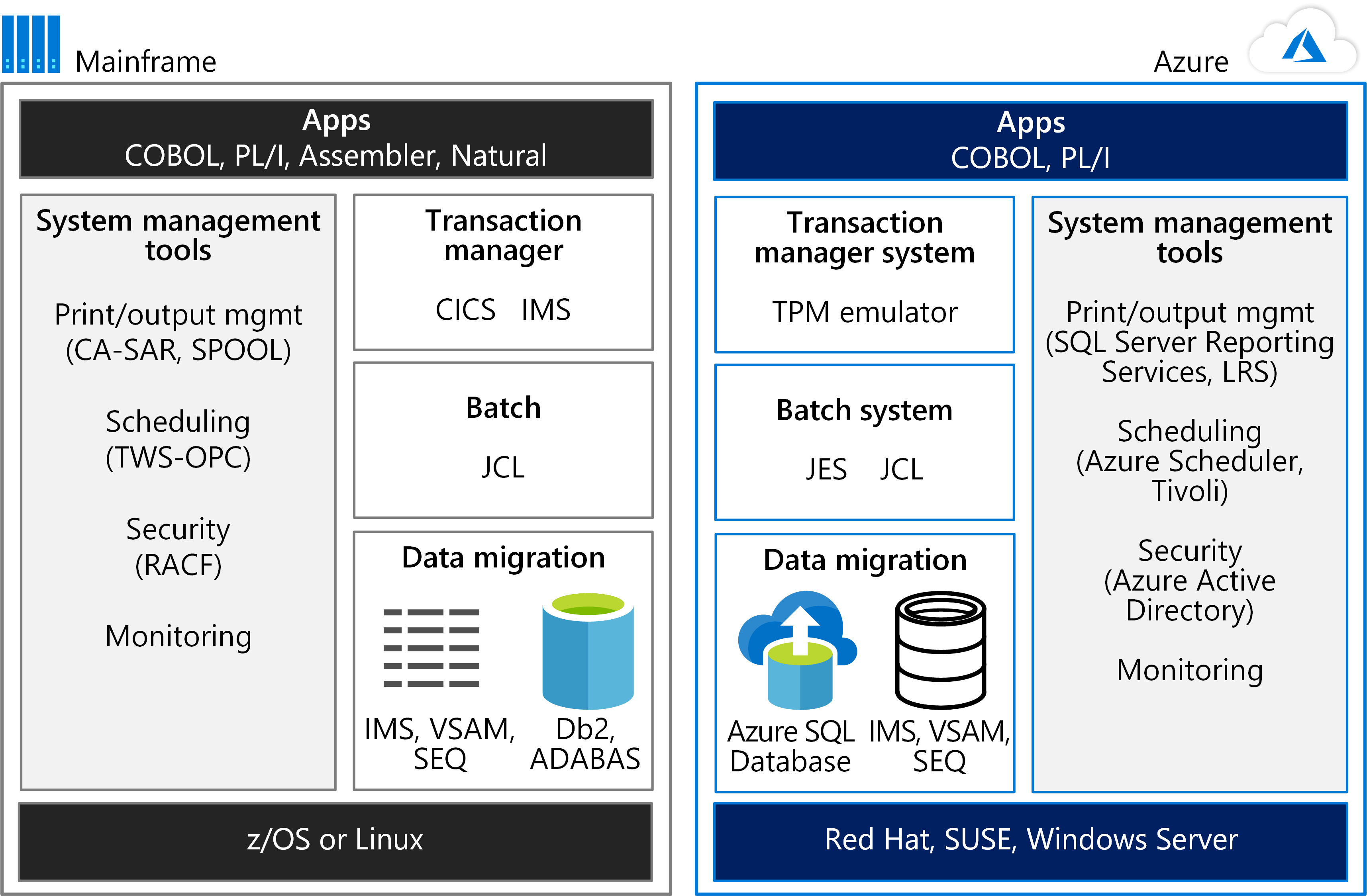
Some mainframe workloads can be migrated to Azure with relative ease, while others can be rehosted on Azure using a partner solution. For detailed guidance about choosing a partner solution, the Azure Mainframe Migration center can help.
Mainframe migration
Rehost, rebuild, replace, or retire? IaaS or PaaS? To determine the right migration strategy for your mainframe application, see the Mainframe migration guide in the Azure Architecture Center.
Micro Focus rehosting platform
Micro Focus Enterprise Server is one of the largest mainframe rehosting platforms available. You can use it run your z/OS workloads on a less expensive x86 platform on Azure.
To get started:
- Install Enterprise Server and Enterprise Developer on Azure
- Set up CICS BankDemo for Enterprise Developer on Azure
- Run Enterprise Server in a Docker Container on Azure
TmaxSoft OpenFrame on Azure
TmaxSoft OpenFrame is a popular mainframe rehosting solution used in lift-and-shift scenarios. An OpenFrame environment on Azure is suitable for development, demos, testing, or production workloads.
To get started:
IBM zD&T 12.0
IBM Z Development and Test Environment (IBM zD&T) sets up a non-production environment on Azure that you can use for development, testing, and demos of z/OS-based applications.
The emulation environment on Azure can host different kinds of Z instances through Application Developers Controlled Distributions (ADCDs). You can run zD&T Personal Edition, zD&T Parallel Sysplex, and zD&T Enterprise Edition on Azure and Azure Stack.
To get started:
IBM DB2 pureScale on Azure
The IBM DB2 pureScale environment provides a database cluster for Azure. It's not identical to the original environment, but it delivers similar availability and scale as IBM DB2 for z/OS running in a Parallel Sysplex setup.
To get started, see IBM DB2 pureScale on Azure.
Considerations
When you migrate mainframe workloads to Azure infrastructure as a service (IaaS), you can choose from several types of on-demand, scalable computing resources, including Azure VMs. Azure offers a range of Linux and Windows VMs.
Compute
Azure compute power compares favorably to a mainframe’s capacity. If you're thinking of moving a mainframe workload to Azure, compare the mainframe metric of one million instructions per second (MIPS) to virtual CPUs.
Learn how to move mainframe compute to Azure.
High availability and failover
Azure offers commitment-based service-level agreements (SLAs). Multiple-nines availability is the default, and SLAs can be optimized with local or geo-based replication of services. The full Azure SLA explains the guaranteed availability of Azure as a whole.
With Azure IaaS such as a VM, specific system functions provide failover support—for example, failover clustering instances and availability sets. When you use Azure platform as a service (PaaS) resources, the platform handles failover automatically. Examples include Azure SQL Database and Azure Cosmos DB.
Scalability
Mainframes typically scale up, while cloud environments scale out. Azure offers a range of Linux and Windows sizes to meet your needs. The cloud also scales up or down to match exact user specifications. Compute power, storage, and services scale on demand under a usage-based billing model.
Storage
In the cloud, you have a range of flexible, scalable storage options, and you pay only for what you need. Azure Storage offers a massively scalable object store for data objects, a file system service for the cloud, a reliable messaging store, and a NoSQL store. For VMs, managed and unmanaged disks provide persistent, secure disk storage.
Learn how to move mainframe storage to Azure.
Backup and recovery
Maintaining your own disaster recovery site can be an expensive proposition. Azure has easy-to-implement and cost-effective options for backup, recovery, and redundancy at local or regional levels, or via geo-redundancy.
Azure Government for mainframe migrations
Many public sector entities would love to move their mainframe applications to a more modern, flexible platform. Microsoft Azure Government is a physically separated instance of the global Microsoft Azure platform—packaged for federal, state, and local government systems. It provides world-class security, protection, and compliance services specifically for United States government agencies and their partners.
Azure Government earned a Provisional Authority to Operate (P-ATO) for FedRAMP High Impact for systems that need this type of environment.
Next steps
Ask our partners to help you migrate or rehost your mainframe applications.
See also: