Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
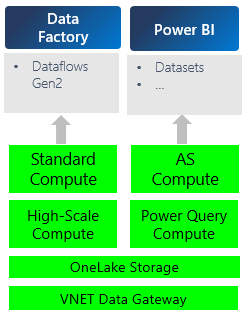
The virtual network (VNet) data gateway consumes the capacity of a Power BI Premium or Fabric capacity. The virtual network data gateway is infrastructure that supports many different artifacts, like Dataflow Gen2, semantic models, and so on. The gateway consumes capacity for the time that it's up and running. As a consequence, the gateway's capacity consumption is consistent regardless of which artifact uses it.
To learn more and get started using the VNet data gateway, refer to virtual network data gateways.
Understand how and where the virtual network consumes capacity
The virtual network data gateway charge is according to the uptime of the virtual network data gateway; uptime is anytime the virtual network data gateway is on.
The virtual network data gateway consumes the capacity of a Power BI Premium or Fabric capacity. Capacities are billed by capacity unit hours, or CU hours. To learn more about CUs, go to the Fabric operations page. The VNet data gateway charges with a fixed CU consumption rate of 4CUs per gateway member (a member is a single gateway node in a cluster).
Your bill is automatically charged to the capacity linked to your virtual network data gateway. When you signed up for your capacity, you paid for some capacity unit hours. When you use your virtual network, this prepaid amount is consumed. This side of the metrics can only be seen from the consumption metrics app.
- Consumption Unit (CU) consumption rate per gateway member: 4 CUs
- Number of gateway members is the number of nodes deployed in your cluster. You can check this number in the advanced settings of your virtual network data gateway.
- To reduce costs, you can actively manage the time to live on your virtual network data gateway in settings. For more information, go to Manage settings.
Capacity consumption in CU seconds = (CU Consumption rate) * (Uptime in seconds) * (Number of gateway members)
Note
The CU consumption rate is fixed at 4CUs per gateway member. The billing model bills per minute and doesn't round up. This means that if you use the gateway for a short duration, you're only charged for what you use.
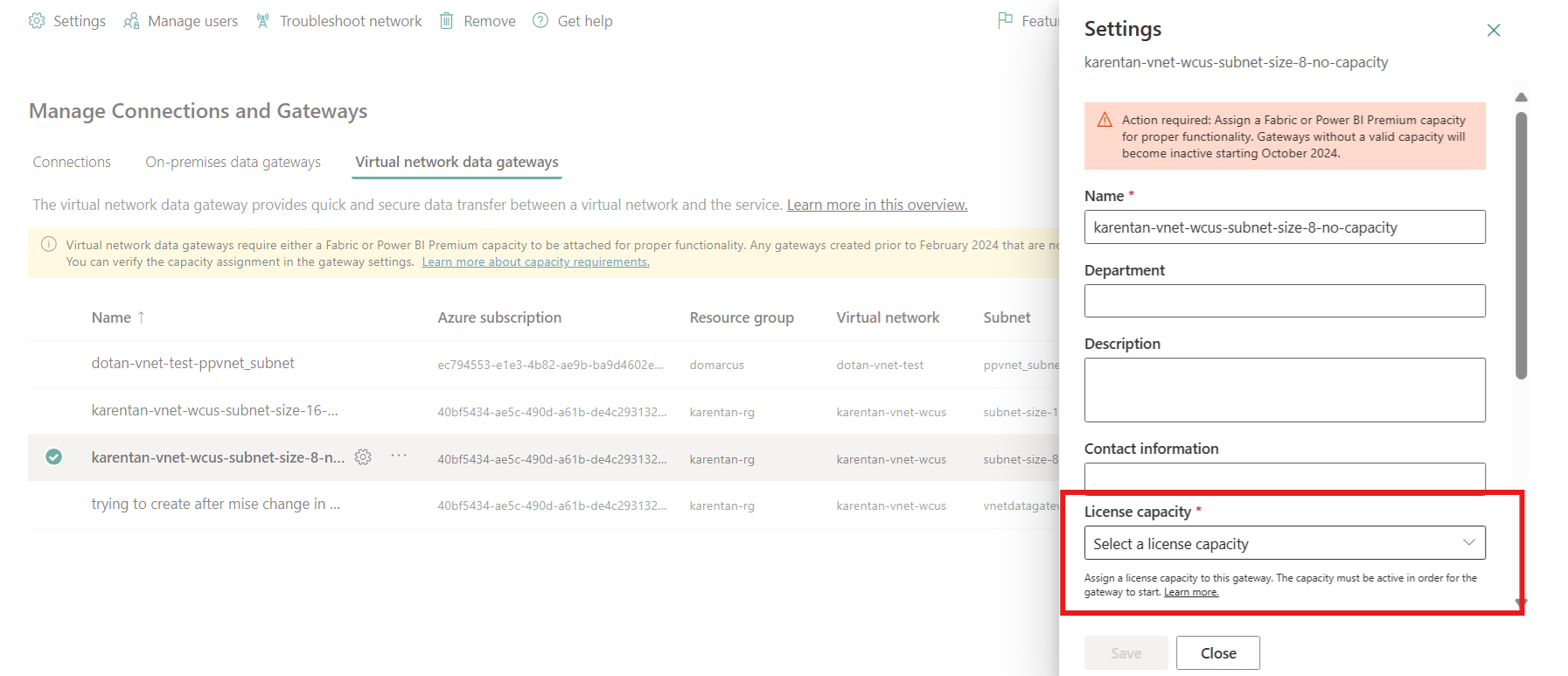
Assign a valid capacity to virtual network data gateway
Each virtual network data gateway must be attached to a valid capacity, such as Power BI Premium or Fabric capacity. If your virtual network data gateway lacks a valid capacity, you can select an existing one from the settings page.
Best practices to manage costs
- You can set up your virtual network data gateways and connections on the gateway for free. We start to bill when your first query runs or you run a test connection.
- Configure your queries to run concurrently. Each gateway member can run six queries concurrently.
- Maintain a minimum number of gateway members for your needs. The number of gateway members is the number of nodes deployed in your cluster. You can check and configure this number in the advanced settings of your virtual network data gateway.
- To reduce costs, reduce the time to live on your virtual network data gateway in settings. Whenever there's a new query execution, the virtual network data gateway is automatically turned on. For more information, go to Manage settings.
View and manage your bill
To view your bill, use the Fabric Capacity Metrics app.
You see three line items:
| Item Kind | Item Name | Operation | Utilization Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual network data gateway | Virtual network data gateway | Virtual network data gateway uptime | Background |
| Dataset | Global revenue analytics | Virtual network data gateway | Background |
| Dataset | Global revenue analytics | Dataset on-demand refresh | Background |
Description of each line item by Operation name:
- Virtual network data gateway uptime The charge from using the virtual network data gateway. This uptime is billed at 4 CUs/hour and is consistent across all artifacts.
- (Dataset) Virtual network data gateway The charge for compute from executing queries on the M Engine. The Virtual network data gateway hosts the M Engine and reports its usage to the semantic model artifact.
- (Dataset) Dataset on-demand refresh The charge for compute from using the Analysis Services engine to execute the semantic model.
The charges from the item kind dataset are the same as they would be without using the virtual network data gateway.
The following diagram illustrates how the cost model works. For example, under semantic models there are two compute engines. The Analysis Services and Power Query Mashup Engine compute costs are each infrastructure items that incur costs over the virtual network data gateway. If you use OneLake for storage, you would be billed for that extra cost too.