Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for servers
- Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2
This article describes how to migrate your servers from Defender for Endpoint to Defender for Servers.
Defender for Endpoint is an enterprise endpoint security platform designed to help organizations prevent, detect, investigate, and respond to advanced threats. The Defender for Endpoint for servers license enables you to onboard a server to Defender for Endpoint.
Defender for Servers is part of the Microsoft Defender for Cloud offering, a solution for cloud security posture management (CSPM) and cloud workload protection (CWP) that finds weak spots across your cloud configuration. Defender for Cloud also helps strengthen the overall security posture of your environment, and can protect workloads across multicloud and hybrid environments from evolving threats.
While both Defender for Endpoint for servers and Defender for Servers offer server protection capabilities, Defender for Servers is our primary solution to protect servers.
How do I migrate my servers from Defender for Endpoint to Defender for Cloud?
If you have servers onboarded to Defender for Endpoint, the migration process varies depending on machine type, but there's a set of shared prerequisites. Defender for Cloud is a subscription-based service in the Microsoft Azure portal. Therefore, Defender for Cloud and underlying plans like Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2 need to be enabled on Azure subscriptions.
Before you enable Defender for Cloud
Before you enable Defender for Cloud, it's important to know how to manage antivirus policies and define any needed exclusions. See the following articles:
- Use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Settings Management to manage Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Manage Microsoft Defender Antivirus in your business
- Defender for Endpoint exclusions
- Managing exclusions reference
- Troubleshoot performance issues related to real-time protection
- Review event logs and error codes to troubleshoot issues with Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Enable Defender for Servers for Azure VMs and non-Azure machines
To enable Defender for Servers for Azure VMs and non-Azure servers connected through Azure Arc-enabled servers, follow this guidance:
If you aren't already using Azure, plan your environment following the Azure Well-Architected Framework.
Enable Defender for Cloud on your subscription.
Enable a Defender for Servers plan on your subscription. In case you're using Defender for Servers Plan 2, make sure to also enable it on the Log Analytics workspace your machines are connected to. It enables you to use optional features, like File Integrity Monitoring.
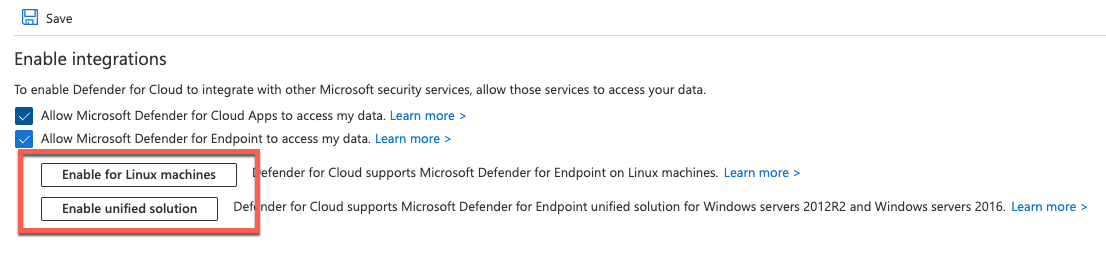
Make sure the Defender for Endpoint integration is enabled on your subscription. If you have preexisting Azure subscriptions, you might see one or both of the two opt-in buttons shown in the following image:
If you have either of these buttons in your environment, make sure to enable integration for both. On new subscriptions, both options are enabled by default, and you don't see these buttons in your environment.
If you're planning to use Azure Arc, make sure the connectivity requirements are met. Defender for Cloud requires all on-premises and non-Azure machines to be connected using the Azure Arc agent. In addition, Azure Arc doesn't support all Defender for Endpoint supported operating systems. For help with your planning process, see Azure Arc deployments.
(Recommended) If you want to see vulnerability findings in Defender for Cloud, make sure to enable vulnerability assessment in Defender for Cloud.
How do I migrate existing Azure VMs to Defender for Cloud?
For Azure VMs, no extra steps are required. These devices are automatically onboarded to Defender for Cloud because of the native integration between the Azure platform and Defender for Cloud.
See Connect your non-Azure machines to Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Defender for Endpoint.
How do I migrate on-premises machines to Defender for Servers?
You have several options.
- Use direct onboarding in Defender for Cloud. See Connect your non-Azure machines to Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Defender for Endpoint.
- Create a connection to Azure using Azure Arc. See Connect your non-Azure machines to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
How do I migrate VMs from AWS or GCP environments?
If you're using Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), follow these steps to migrate those VMs:
Create a new multicloud connector on your subscription. For more information about this connector, see AWS accounts or GCP projects.
On your multicloud connector, enable Defender for Servers on AWS or GCP connectors.
Enable autoprovisioning on the multicloud connector for the Azure Arc agent, Defender for Endpoint extension, and Vulnerability Assessment. For Defender for Servers Plan 2, enable agentless machine scanning.
For more information, see the following resources:
- Defender for Cloud's multicloud capabilities
- Connect your non-Azure machines to Microsoft Defender for Cloud
What happens once all migration steps are completed?
After you complete the relevant migration steps, Defender for Cloud deploys the MDE.Windows or MDE.Linux extension to your Azure VMs and non-Azure machines connected through Azure Arc (including VMs in AWS and GCP compute).
The extension acts as a management and deployment interface, which orchestrates and wraps the Defender for Endpoint installation scripts inside the operating system and reflects its provisioning state to the Azure management plane. The installation process recognizes an existing Defender for Endpoint installation and connects it to Defender for Cloud by automatically adding Defender for Endpoint service tags.
In case you have devices running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016, and those devices are provisioned with the legacy, Log Analytics-based Defender for Endpoint solution, Defender for Cloud's deployment process deploys the Defender for Endpoint unified solution. After successful deployment, it stops and disables the legacy Defender for Endpoint process (MsSense.exe) on these machines.
See also
- Defender for Cloud: Enable Defender for Endpoint integration
- Defender for Cloud: Agentless machine scanning
- Defender for Cloud: Remediate Defender for Endpoint misconfigurations (agentless)
- Onboard servers through Microsoft Defender for Endpoint's onboarding experience
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.