Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Defender for Endpoint extends support to include down-level operating systems, providing advanced attack detection and investigation capabilities on supported Windows versions.
To onboard down-level Windows client endpoints to Defender for Endpoint, you can:
Use the Defender deployment tool to deploy Defender endpoint security
or
Install and configure Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA) and Configure and update System Center Endpoint Protection (SCEP) clients
Tip
After onboarding the device, you can choose to run a detection test to verify that it's properly onboarded to the service. For more information, see Run a detection test on a newly onboarded Defender for Endpoint endpoint.
Supported operating systems
Defender endpoint security solution
- Windows 7 SP1 Pro
- Windows 7 SP1 Enterprise
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
MMA/SCEP
- Windows 7 SP1 Pro
- Windows 7 SP1 Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 Pro
- Windows 8.1
- Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
Use the Defender deployment tool to deploy Defender endpoint security
A Microsoft Defender for endpoint security solution (preview) is available for legacy Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 devices. The solution provides advanced protection capabilities and improved functionality for those devices compared to other solutions. The following table outlines the solution's currently supported functionality.
| Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Advanced Hunting | Hunt across events with Kusto Query Language |
| Antivirus in Passive Mode | Allows for coexistence with non-Microsoft anti-malware solutions. |
| Custom file indicators | Allow, block, quarantine files based on hash or certificate information |
| Device and file response capabilities | Isolate device, block and get files, collect investigation packages, run antivirus scan Note: other response capabilities aren't supported |
| Next-generation protection | Defender Antivirus with real-time behavior monitoring, cloud-delivered, and definition-based malware blocking and remediation. Scheduled and manually triggered scans. Note: Network Protection, Attack Surface Reduction Rules, Controlled Folder Access, and related functionality including IP and URL indicators aren't supported. |
| Operating system and software vulnerability assessments | Defender Vulnerability Management provides insights into vulnerabilities for Windows and installed software. Note: The following functionality isn't available for Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2: - Security configuration assessment - "Pending reboot" experience - Premium capabilities: security baseline assessment, browser extensions, certificate and application blocking |
| Security Settings Management | Policy enforcement for Defender Antivirus capabilities. Note that only settings for available features will take effect. |
| Sense detection sensor | Rich detection events for use in device timeline, hunting, and to generate alerts based on indicators of compromise and attack. |
| Attack Disruption: contain device/IP | Automated attack disruption to shut down attacks leveraging lateral movement. |
| (Automatic) updates | Regular updates for anti-malware and detection components. |
The solution can be downloaded and installed using the Defender deployment tool, a lightweight, self-updating application that streamlines onboarding for all Windows versions supported by Defender for Endpoint. The deployment tool takes care of prerequisites, automates migrations from older solutions, and removes the need for complex onboarding scripts, separate downloads, and manual installations. For information about the tool and how to use it, see Deploy Microsoft Defender endpoint security to Windows devices using the Defender deployment tool (preview).
Install and configure Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA)
Before you begin
Review the following details to verify minimum system requirements:
Install the February 2018 monthly update rollup - Direct download link from the Windows Update catalog is available here
Install the March 12, 2019 (or later) Servicing stack update - Direct download link from the Windows Update catalog is available here
Install the SHA-2 code signing support update - Direct download link from the Windows Update catalog is available here
Note
Only applicable for Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7 SP1 Enterprise, and Windows 7 SP1 Pro.
Install the Update for customer experience and diagnostic telemetry
Install Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later
Note
Installation of .NET 4.5 might require you to restart your computer after installation.
Meet the Azure Log Analytics agent minimum system requirements. For more information, see Collect data from computers in your environment with Log Analytics
Installation steps
Download the agent setup file: Windows 64-bit agent or Windows 32-bit agent.
Note
Due to the deprecation of SHA-1 support by the MMA agent, the MMA agent needs to be version 10.20.18029 or newer.
Obtain the workspace ID:
- In the Defender for Endpoint navigation pane, select Settings > Device management > Onboarding.
- Select the operating system.
- Copy the workspace ID and workspace key.
Using the Workspace ID and Workspace key choose any of the following installation methods to install the agent:
Manually install the agent using setup.
On the Agent Setup Options page, select Connect the agent to Azure Log Analytics (OMS)
Note
If you're a US Government customer, under "Azure Cloud", you need to choose "Azure US Government" if using the setup wizard, or if using a command line or a script - set the "OPINSIGHTS_WORKSPACE_AZURE_CLOUD_TYPE" parameter to 1.
If you're using a proxy to connect to the Internet see the Configure proxy and Internet connectivity settings section.
Once completed, you should see onboarded endpoints in the portal within an hour.
Configure and update System Center Endpoint Protection clients
Defender for Endpoint integrates with System Center Endpoint Protection to provide visibility to malware detections and to stop propagation of an attack in your organization by banning potentially malicious files or suspected malware.
The following steps are required to enable this integration:
- Install the January 2017 anti-malware platform update for Endpoint Protection clients
- Configure the SCEP client Cloud Protection Service membership to the Advanced setting
- Configure your network to allow connections to the Microsoft Defender Antivirus cloud. For more information, see Configure and validate Microsoft Defender Antivirus network connections
Configure proxy and Internet connectivity settings
If your servers need to use a proxy to communicate with Defender for Endpoint, use one of the following methods to configure the MMA to use the proxy server:
If a proxy or firewall is in use, ensure that servers can access all of the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint service URLs directly and without SSL interception. For more information, see enable access to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint service URLs. Use of SSL interception prevents the system from communicating with the Defender for Endpoint service.
Once completed, you should see onboarded Windows servers in the portal within an hour.
Onboard Windows servers through Microsoft Defender for Cloud
In the Microsoft Defender XDR navigation pane, select Settings > Endpoints > Device management > Onboarding.
Select Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 as the operating system.
Select Onboard Servers in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Follow the onboarding instructions in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Microsoft Defender for Cloud and If you're using Azure ARC, follow the onboarding instructions in Enabling the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integration.
After completing the onboarding steps, you'll need to Configure and update System Center Endpoint Protection clients.
Note
- For onboarding via Microsoft Defender for servers to work as expected, the server must have an appropriate workspace and key configured within the Microsoft Monitoring Agent (MMA) settings.
- Once configured, the appropriate cloud management pack is deployed on the machine and the sensor process (MsSenseS.exe) will be deployed and started.
- This is also required if the server is configured to use an OMS Gateway server as proxy.
Verify onboarding
Verify that Microsoft Defender Antivirus and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint are running.
Note
Running Microsoft Defender Antivirus isn't required but it's recommended. If another antivirus vendor product is the primary endpoint protection solution, you can run Defender Antivirus in Passive mode. You can only confirm that passive mode is on after verifying that Microsoft Defender for Endpoint sensor (SENSE) is running.
Note
As Microsoft Defender Antivirus is only supported for Windows 10 and Windows 11, step 1 doesn't apply when running Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1.
Run the following command to verify that Microsoft Defender Antivirus is installed:
sc.exe query WindefendIf the result is 'The specified service doesn't exist as an installed service', then you'll need to install Microsoft Defender Antivirus. For more information, see Microsoft Defender Antivirus in Windows 10.
For information on how to use Group Policy to configure and manage Microsoft Defender Antivirus on your Windows servers, see Use Group Policy settings to configure and manage Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
If you encounter issues with onboarding, see Troubleshoot onboarding.
Run a detection test
Follow the steps in Run a detection test on a newly onboarded device to verify that the server is reporting to Defender for the Endpoint service.
Onboarding endpoints with no management solution
Using Group Policy
Step 1: Download the corresponding update for your endpoint.
Navigate to c:\windows\sysvol\domain\scripts (Change control could be needed on one of the domain controllers.)
Create a folder named MMA.
Download the following and place them in the MMA folder:
- Update for customer experience and diagnostic telemetry:
For Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, following updates are also required:
February 2018 Monthly Roll up - KB4074598 (Windows Server 2008 R2)
Download updates for Windows Server 2008 R2 x64
.NET Framework 3.5.1 (KB315418)
Note
This article assumes you're using x64-based servers (MMA Agent .exe x64 New SHA-2 compliant version).
Step 2: Create a file named DeployMMA.cmd (using notepad) Add the following lines to the cmd file. Note that you'll need your WORKSPACE ID and KEY.
The following command is an example. Replace the following values:
- KB - Use the applicable KB relevant to the endpoint you're onboarding
- Workspace ID and KEY - Use your ID and key
@echo off
cd "C:"
IF EXIST "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Monitoring Agent\Agent\MonitoringHost.exe" (
exit
) ELSE (
wusa.exe C:\Windows\MMA\Windows6.1-KB3080149-x64.msu /quiet /norestart
wusa.exe C:\Windows\MMA\Windows6.1-KB4074598-x64.msu /quiet /norestart
wusa.exe C:\Windows\MMA\Windows6.1-KB3154518-x64.msu /quiet /norestart
wusa.exe C:\Windows\MMA\Windows8.1-KB3080149-x64.msu /quiet /norestart
"c:\windows\MMA\MMASetup-AMD64.exe" /c /t:"C:\Windows\MMA"
c:\windows\MMA\setup.exe /qn NOAPM=1 ADD_OPINSIGHTS_WORKSPACE=1 OPINSIGHTS_WORKSPACE_ID="<your workspace ID>" OPINSIGHTS_WORKSPACE_KEY="<your workspace key>" AcceptEndUserLicenseAgreement=1
)
Group Policy Configuration
Create a new group policy specifically for onboarding devices such as "Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Onboarding".
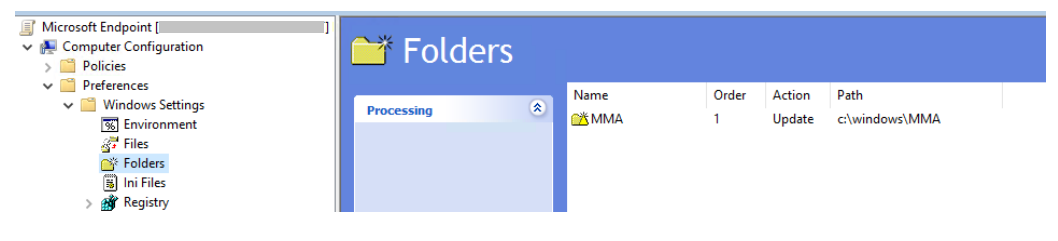
Create a Group Policy Folder named "c:\windows\MMA"
This will add a new folder on every server that gets the GPO applied, called MMA, and will be stored in c:\windows. This will contain the installation files for the MMA, prerequisites, and install script.
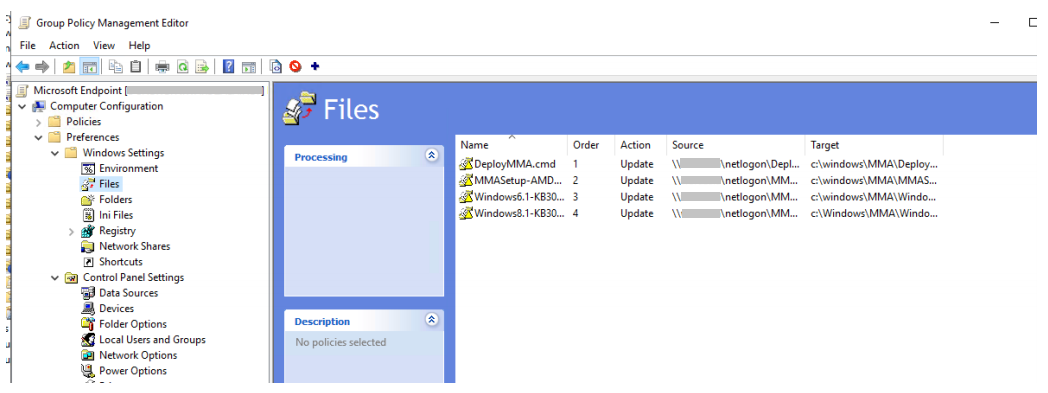
Create a Group Policy Files preference for each of the files stored in Net logon.
It copies the files from DOMAIN\NETLOGON\MMA\filename to C:\windows\MMA\filename - so the installation files are local to the server:
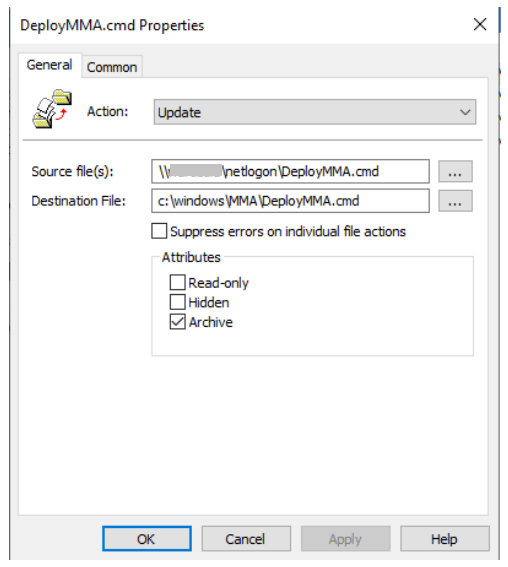
Repeat the process but create item level targeting on the COMMON tab, so the file only gets copied to the appropriate platform/Operating system version in scope:
For Windows Server 2008 R2 you'll need (and it will only copy down) the following:
- Windows6.1-KB3080149-x64.msu
- Windows6.1-KB3154518-x64.msu
- Windows6.1-KB4075598-x64.msu
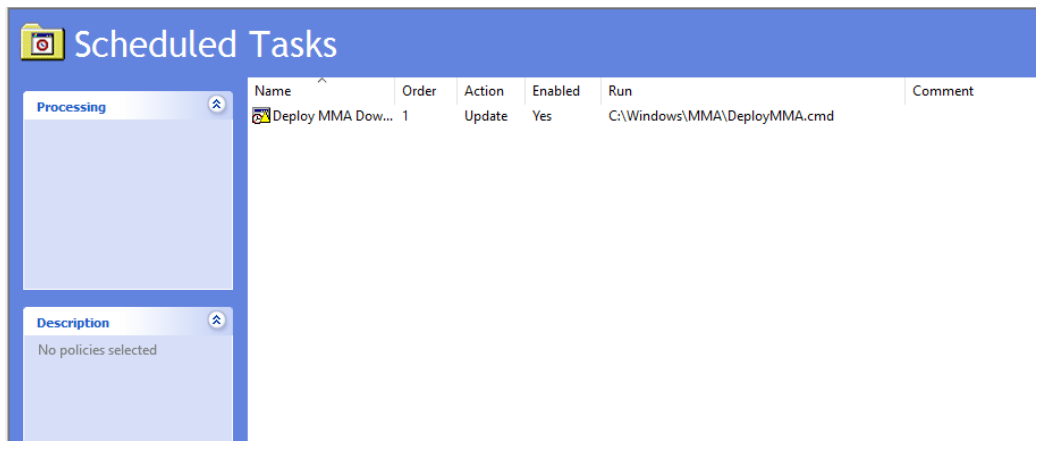
Once this is done, you'll need to create a start-up script policy:
The name of the file to run here's c:\windows\MMA\DeployMMA.cmd. Once the server is restarted as part of the start-up process it will install the Update for customer experience and diagnostic telemetry KB, and then install the MMA Agent, while setting the Workspace ID and Key, and the server will be onboarded.
You could also use an immediate task to run the deployMMA.cmd if you don't want to reboot all the servers.
This could be done in two phases. First create the files and the folder in GPO - Give the system time to ensure the GPO has been applied, and all the servers have the install files. Then, add the immediate task. This will achieve the same result without requiring a reboot.
As the Script has an exit method and won't rerun if the MMA is installed, you could also use a daily scheduled task to achieve the same result. Similar to a Configuration Manager compliance policy, it will check daily to ensure the MMA is present.
As mentioned in the onboarding documentation for Server specifically around Server 2008 R2 please see below: For Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, ensure that you fulfill the following requirements:
- Install the February 2018 monthly update rollup
- Install either .NET framework 4.5 (or later) or KB3154518
Check the KBs are present before onboarding Windows Server 2008 R2. This process allows you to onboard all the servers if you don't have Configuration Manager managing Servers.
Offboard endpoints
You have two options to offboard Windows endpoints from the service:
- Uninstall the MMA agent
- Remove the Defender for Endpoint workspace configuration
Note
Offboarding causes the Windows endpoint to stop sending sensor data to the portal but data from the endpoint, including reference to any alerts it has had will be retained for up to six months.
Uninstall the MMA agent
To offboard the Windows endpoint, you can uninstall the MMA agent or detach it from reporting to your Defender for Endpoint workspace. After offboarding the agent, the endpoint will no longer send sensor data to Defender for Endpoint. For more information, see To disable an agent.
Remove the Defender for Endpoint workspace configuration
You can use either of the following methods:
- Remove the Defender for Endpoint workspace configuration from the MMA agent
- Run a PowerShell command to remove the configuration
Remove the Defender for Endpoint workspace configuration from the MMA agent
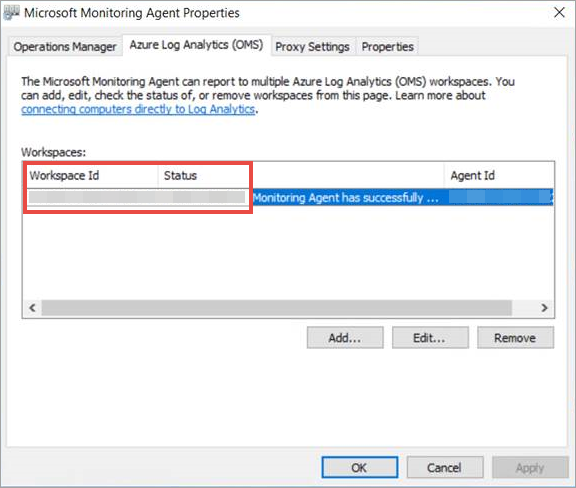
In the Microsoft Monitoring Agent Properties, select the Azure Log Analytics (OMS) tab.
Select the Defender for Endpoint workspace, and select Remove.
Run a PowerShell command to remove the configuration
Get your Workspace ID:
- In the navigation pane, select Settings > Onboarding.
- Select the relevant operating system and get your Workspace ID.
Open an elevated PowerShell and run the following command. Use the Workspace ID you obtained and replacing
WorkspaceID:$AgentCfg = New-Object -ComObject AgentConfigManager.MgmtSvcCfg # Remove OMS Workspace $AgentCfg.RemoveCloudWorkspace("WorkspaceID") # Reload the configuration and apply changes $AgentCfg.ReloadConfiguration()
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.