Cluster autoscaler
To respond to changing pod demands, the Kubernetes cluster autoscaler adjusts the number of nodes based on the requested compute resources in the node pool. By default, the cluster autoscaler checks the Metrics API server every 10 seconds for any required changes in node count.
If the cluster autoscaler determines that a change is required, the number of nodes in your AKS cluster is increased or decreased accordingly. The cluster autoscaler works with Kubernetes RBAC-enabled AKS clusters that run Kubernetes 1.10.x or higher.
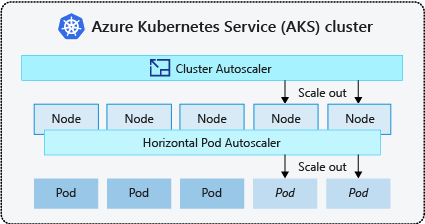
The cluster autoscaler is typically used alongside the horizontal pod autoscaler. When combined, the horizontal pod autoscaler increases or decreases the number of pods based on application demand, and the cluster autoscaler adjusts the number of nodes to run more pods.
Scale out events
If a node doesn't have sufficient compute resources to run a requested pod, that pod can't progress through the scheduling process. The pod can't start unless more compute resources are available within the node pool.
When the cluster autoscaler notices pods that can't be scheduled because of node pool resource constraints, the number of nodes within the node pool is increased to provide more compute resources. When those nodes are successfully deployed and available for use within the node pool, the pods are then scheduled to run on them.
If your application needs to scale rapidly, some pods may remain in a state waiting to be scheduled until the other nodes deployed by the cluster autoscaler can accept the scheduled pods. For applications that have high burst demands, you can scale with virtual nodes and Azure Container Instances.
Scale in events
The cluster autoscaler also monitors the pod scheduling status for nodes that haven't recently received new scheduling requests. This scenario indicates the node pool has more compute resources than required, and the number of nodes can be decreased. By default, nodes that pass a threshold for no longer being needed for 10 minutes is scheduled for deletion. When this situation occurs, pods are scheduled to run on other nodes within the node pool, and the cluster autoscaler decreases the number of nodes.
Your applications may experience some disruption as pods are scheduled on different nodes when the cluster autoscaler decreases the number of nodes. To minimize disruption, avoid applications that use a single pod instance.