Burst to Azure Container Instances
To rapidly scale your AKS cluster, you can integrate with Azure Container Instances (ACI). Kubernetes has built-in components to scale the replica and node count. However, if your application needs to rapidly scale, the horizontal pod autoscaler may schedule more pods than the existing compute resources in the node pool can handle. The cluster autoscaler would deploy more nodes in the node pool, but it may take a few minutes for those nodes to successfully provision and allow the Kubernetes scheduler to run pods.
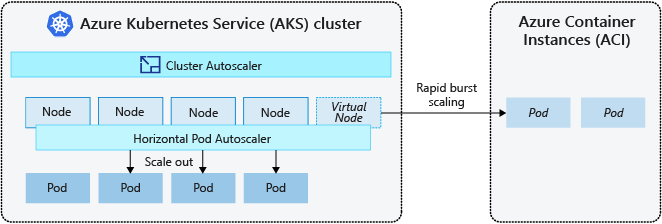
ACI lets you quickly deploy container instances without added infrastructure overhead. When you connect with AKS, ACI becomes a secured, logical extension of your AKS cluster. The virtual nodes component, which is based on virtual Kubelet, is installed in your AKS cluster that presents ACI as a virtual Kubernetes node. Kubernetes can then schedule pods that run as ACI instances through virtual nodes, not as pods on VM nodes directly in your AKS cluster.
Your application requires no modifications to use virtual nodes. Your deployments can scale across AKS and ACI and with no delay as the cluster autoscaler deploys new nodes in your AKS cluster.
Virtual nodes are deployed to another subnet in the same virtual network as your AKS cluster. This virtual network configuration secures the traffic between ACI and AKS. Like an AKS cluster, an ACI instance is a secure, logical compute resource isolated from other users.