Discover static website hosting in Azure Storage
You can serve static content (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files) directly from a storage container named $web. Hosting your content in Azure Storage enables you to use serverless architectures that include Azure Functions and other Platform as a service (PaaS) services. Azure Storage static website hosting is a great option in cases where you don't require a web server to render content.
Static websites have some limitations. For example, If you want to configure headers, you have to use Azure Content Delivery Network (Azure CDN). There's no way to configure headers as part of the static website feature itself. Also, AuthN and AuthZ aren't supported. If these features are important for your scenario, consider using Azure Static Web Apps.
Enable static website hosting
Static website hosting is a feature that you have to enable on the storage account. When you configure your account for static website hosting, Azure Storage automatically creates a container named $web. The $web container contains the files for your static website.
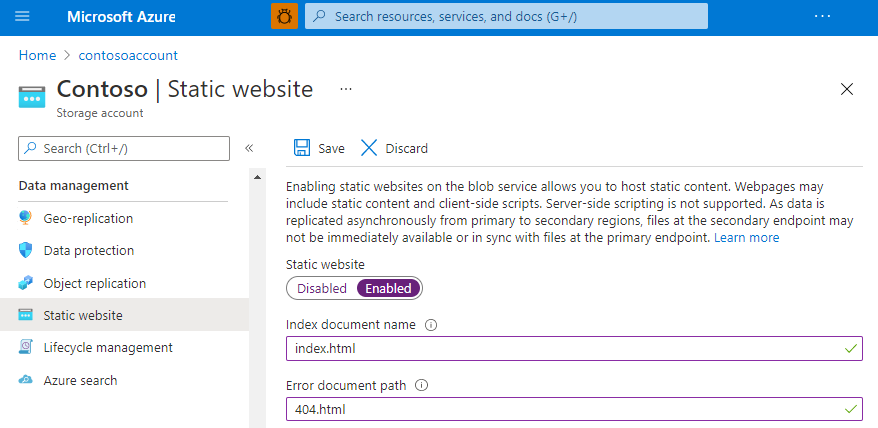
To enable static website hosting:
- Locate your storage account in the Azure portal and display the account overview
- Select Static website to display the configuration page
- Select Enabled to enable static website hosting for the account
- In the Index document name field, specify a default index page. For example, index.html.
- In the Error document path field, specify a default error page. For example, 404.html.
- Select Save.
Impact of setting the access level on the web container
You can modify the public access level of the $web container, but making this modification has no impact on the primary static website endpoint because these files are served through anonymous access requests. That means public (read-only) access to all files.
While the primary static website endpoint isn't affected, a change to the public access level does impact the primary blob service endpoint.
For example, if you change the public access level of the $web container from Private (no anonymous access) to Blob (anonymous read access for blobs only), then the level of public access to the primary static website endpoint https://contosoblobaccount.z22.web.core.windows.net/index.html doesn't change.
However, the public access to the primary blob service endpoint https://contosoblobaccount.blob.core.windows.net/$web/index.html does change from private to public. Now users can open that file by using either of these two endpoints.
Disabling public access on a storage account by using the public access setting of the storage account doesn't affect static websites that are hosted in that storage account. For more information, see Remediate anonymous public read access to blob data (Azure Resource Manager deployments).
Mapping a custom domain to a static website URL
You can make your static website available via a custom domain.
It's easier to enable HTTP access for your custom domain, because Azure Storage natively supports it. To enable HTTPS, you have to use Azure CDN because Azure Storage doesn't yet natively support HTTPS with custom domains. Visit Map a custom domain to an Azure Blob Storage endpoint for step-by-step guidance.