Troubleshoot Teams
When users experience calling problems, an organization's Teams administrator must quickly diagnose and fix the problems. Troubleshooting problems within Microsoft Teams may include a wide array of possible areas that must be investigated. Issues can be examined in the log files and various tools.
Resources from Microsoft
Common problems are documented in the Teams Troubleshooting section of the Microsoft Teams documentation. If there's a problem, refer to this documentation for details of symptoms, causes, and how it can be resolved.
For initial troubleshooting steps, see Troubleshoot for end users.
For common Teams issues, see Information about Teams known issues.
Self-help diagnostics in Microsoft 365 admin center.
Use Help from Teams client to report a problem.
Check client connectivity
If you're experiencing connectivity issues with the Teams client, the most likely causes are firewall or proxy settings. Verify the necessary URLs, IP addresses, and ports are opened in the organization's firewall or proxy server. The following services require specific URLs and ports to be opened in the firewall:
- Authentication
- Microsoft Teams Client Connectivity
- Collaboration
- Media
- Shared Services
- Third-party Integration
- Skype for Business Interoperability
- Skype for Business Client Interoperability
Additional reading. For more information on the URLs and IPs required for Microsoft Teams, see Office 365 URLs and IP address ranges.
For more information on Microsoft Teams networking requirements, see Prepare your organization's network for Microsoft Teams.
Self-help diagnostics
Self-help diagnostics won't make changes to your tenant. They provide insight into known issues and the instructions that you’ll need to fix the issues quickly.
Teams-specific diagnostic scenarios that cover top support topics and the most common tasks for which administrators request configuration help, are available in Support section of Microsoft 365 admin center
Sign into Microsoft 365 admin center. In the navigation pane, select Show all > Support > New service request.
Describe the issue briefly. As you type search terms, a type-ahead query assists you to find the topics that you’re searching for. The system determines whether a diagnostic scenario matches your issue. Select the closest scenario that matches the issue.
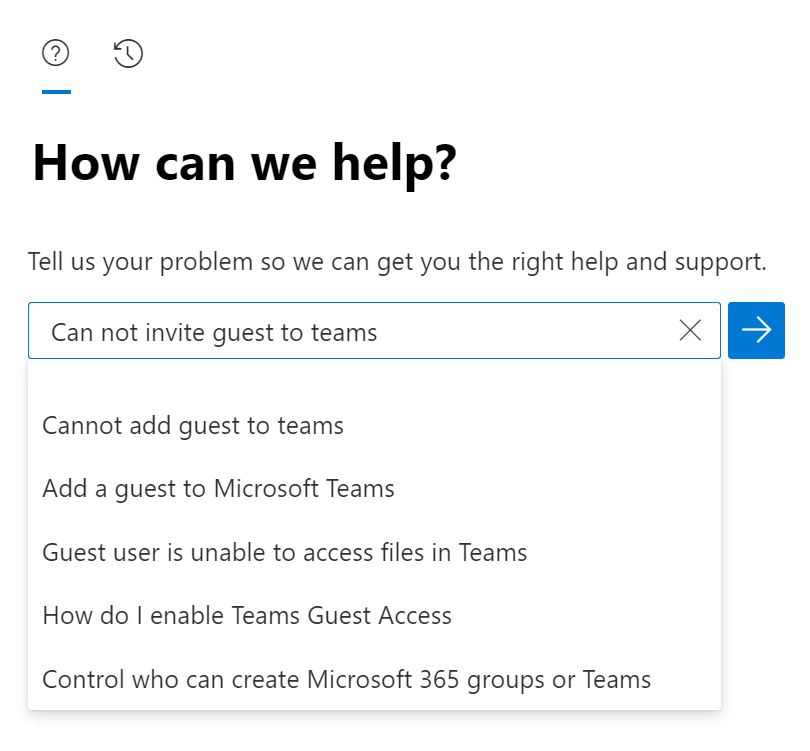
Select Run Tests to find the best way to solve the issue.
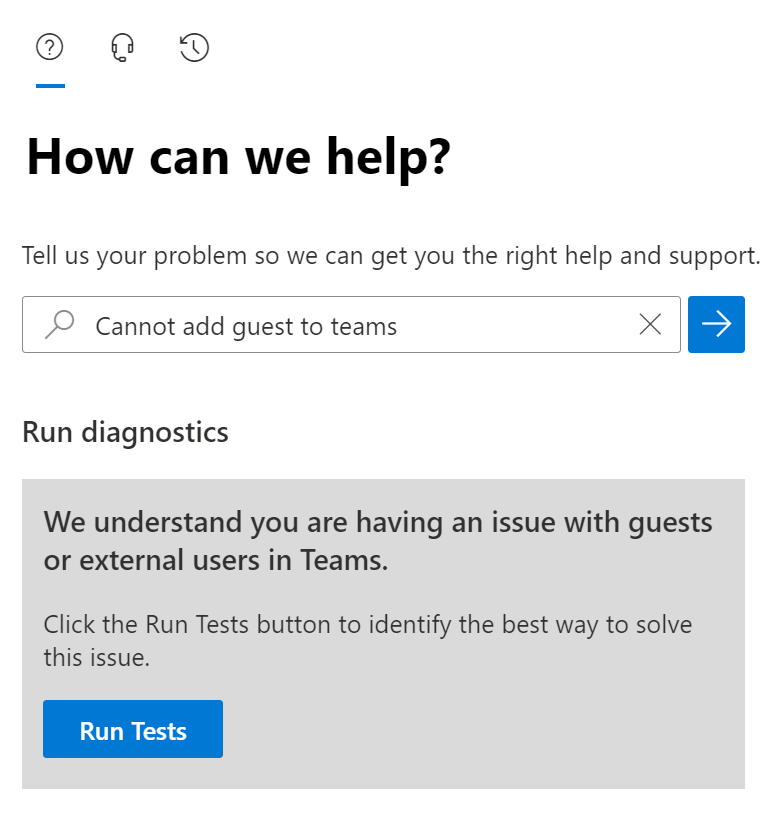
After the diagnostic checks finish and the configuration issue is found, the system provides the steps to resolve the issue.
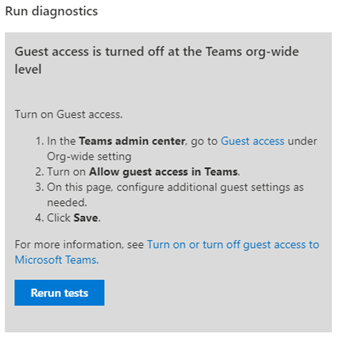
Note
If a diagnostic detects an issue, and you've implemented a fix based on the results, consider rerunning the diagnostic to ensure the issue is completely resolved.
For more details on the diagnostics that are currently available, with brief scenario descriptions, see Scenario descriptions and shortcut commands
Monitor usage and feedback
It's important to know how users are using Teams and what their experience is with Teams, using the reports available in Teams admin center
Teams reports in the Microsoft Teams admin center to get insights into how Teams is used in your organization.
Customer feedback and problems reported using Teams client
Tools for monitoring and troubleshooting
The following tools are designed to help organizations monitor and troubleshoot call quality in Microsoft Teams:
Log files: Log files are created automatically and provide information to help troubleshoot specific issues.
Call Analytics: Call analytics provide detailed information about the devices, networks, and connectivity related to specific calls and meetings for each user in Teams. Teams administrators and helpdesk agents use this information to troubleshoot call quality and connection problems in a specific call.
Call Quality Dashboard: Call Quality Dashboard (CQD) provides a network-wide view of call quality across an organization. Call Quality Dashboard (CQD) is designed to help Microsoft Teams administrators, Skype for Business administrators, and network engineers optimize a network.
Direct Routing Health Dashboard: Health Dashboard for Direct Routing monitors the connection between a Session Border Controller (SBC) and the Direct Routing interface.
Teams Room considerations
Device selection for Microsoft Teams Room
Evaluate which Microsoft Teams Rooms solution is the most suitable for each room based on the future capabilities you want for the room. Decide which AV peripheral devices are the best fit, depending on room size and layout.
For guidance for the type of system and peripheral devices by room type and size, see Teams Rooms devices by space and select your room size.
Based on the vendor you prefer, use the information provided in the requirements article to define your Microsoft Teams Rooms and supported peripheral device configuration per room type, and use this as a template for your deployment.
Tip
Some room types might not be applicable for your deployment.
| Decision points |
|
| Next steps |
|
Sample Microsoft Teams Rooms deployment template for your organization
| Room type/size | Number of people | Microsoft Teams Rooms system | Peripheral devices | Display(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus 10' by 9' | 2–4 | |||
| Small 16' by 16' | 4–6 | |||
| Medium 18' by 20' | 6–12 | |||
| Large 15' by 32' | 12–16 |
Tip
Now is a great time to start gathering information about the Microsoft Teams Rooms solution you've chosen.
Wireless network considerations
We strongly recommend that you connect your Teams Rooms devices to a wired network for greater stability and performance, ensuring a seamless meeting experience. If using a wired connection is not available, you may opt to use a wireless connection.
Important
Wireless networks can be prone to network interference leading to quality degradation. We strongly recommend that you follow your wireless equipment provider's best practices when configuring a wireless connection to improve video and audio quality.
Here are some examples of wireless network configuration best practices recommended by various manufacturers:
- Deploy wireless equipment, such as access points and routers that can handle and distribute the bandwidth load across all connected devices in the network.
- As much as possible, use access points and routers from a single manufacturer to avoid further congesting the radio-spectrum.
- Ensure wireless equipment is installed in a way that reduces or eliminates interference from objects and other equipment.
- Ensure the wireless network shows strong signal strength (Wi-Fi signal showing full bars is preferred) on Teams Rooms and other device screens.
- Default to prioritizing 5 GHz coverage for devices to optimize for higher bandwidth.
- Enable band steering to ensure that 5 GHz is always given more priority when sharing the same network name (SSID) as 2.4 GHz.
- Keep wireless channel utilization below 50%.
- Keep access point and router firmware up to date with the latest firmware versions and hot fixes.
- Verify that Teams Rooms devices and at least one access point see each other with a signal strength of -60 dBm or better. A dBm value closer to zero is preferred. Follow your equipment manufacturer's recommendations.
- Implement QoS whenever possible to allow monitoring and resolution of issues in real time.
For additional best practices specific to your wireless network hardware, check your manufacturer's documentation.
You can also troubleshoot wireless network issues using the wireless network report built into Windows 10. For more information, see Analyze the wireless network report - Microsoft Support.
For more information see Deploy Microsoft Teams Rooms on Android and Microsoft Teams Rooms (Windows)