Create and manage custom detections rules
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender XDR
Custom detection rules are rules you can design and tweak using advanced hunting queries. These rules let you proactively monitor various events and system states, including suspected breach activity and misconfigured endpoints. You can set them to run at regular intervals, generating alerts and taking response actions whenever there are matches.
Required permissions for managing custom detections
Important
Microsoft recommends that you use roles with the fewest permissions. This helps improve security for your organization. Global Administrator is a highly privileged role that should be limited to emergency scenarios when you can't use an existing role.
To manage custom detections, you need to be assigned one of these roles:
Security settings (manage) - Users with this Microsoft Defender XDR permission can manage security settings in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Security Administrator - Users with this Microsoft Entra role can manage security settings in the Microsoft Defender portal and other portals and services.
Security Operator - Users with this Microsoft Entra role can manage alerts and have global read-only access to security-related features, including all information in the Microsoft Defender portal. This role is sufficient for managing custom detections only if role-based access control (RBAC) is turned off in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. If you have RBAC configured, you also need the *Manage Security Settings permission for Defender for Endpoint.
You can manage custom detections that apply to data from specific Microsoft Defender XDR solutions if you have the right permissions for them. For example, if you only have manage permissions for Microsoft Defender for Office 365, you can create custom detections using Email* tables but not Identity* tables.
Likewise, since the IdentityLogonEvents table holds authentication activity information from both Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps and Defender for Identity, you need to have manage permissions for both services to manage custom detections querying the said table.
Note
To manage custom detections, Security Operators must have the Manage Security Settings permission in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint if RBAC is turned on.
To manage required permissions, a Global Administrator can:
Assign the Security Administrator or Security Operator role in Microsoft 365 admin center under Roles > Security Administrator.
Check RBAC settings for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint in Microsoft Defender XDR under Settings > Permissions > Roles. Select the corresponding role to assign the manage security settings permission.
Note
A user also needs to have the appropriate permissions for the devices in the device scope of a custom detection rule that they are creating or editing before they can proceed. A user can't edit a custom detection rule that is scoped to run on all devices, if the same user does not have permissions for all devices.
Create a custom detection rule
1. Prepare the query
In the Microsoft Defender portal, go to Advanced hunting and select an existing query or create a new query. When using a new query, run the query to identify errors and understand possible results.
Important
To prevent the service from returning too many alerts, each rule is limited to generating only 100 alerts whenever it runs. Before creating a rule, tweak your query to avoid alerting for normal, day-to-day activity.
Required columns in the query results
To create a custom detection rule, the query must return the following columns:
Timestamp- Used to set the timestamp for generated alerts- A column or combination of columns that uniquely identify the event in Defender XDR tables:
- For Microsoft Defender for Endpoint tables, the
Timestamp,DeviceId, andReportIdcolumns must appear in the same event - For Alert* tables,
Timestampmust appear in the event - For Observation* tables,
TimestampandObservationIdmust appear in the same event - For all others,
TimestampandReportIdmust appear in the same event
- For Microsoft Defender for Endpoint tables, the
- One of the following columns that contain a strong identifier for an impacted asset:
DeviceIdDeviceNameRemoteDeviceNameRecipientEmailAddressSenderFromAddress(envelope sender or Return-Path address)SenderMailFromAddress(sender address displayed by email client)RecipientObjectIdAccountObjectIdAccountSidAccountUpnInitiatingProcessAccountSidInitiatingProcessAccountUpnInitiatingProcessAccountObjectId
Note
Support for additional entities will be added as new tables are added to the advanced hunting schema.
Simple queries, such as those that don't use the project or summarize operator to customize or aggregate results, typically return these common columns.
There are various ways to ensure more complex queries return these columns. For example, if you prefer to aggregate and count by entity under a column such as DeviceId, you can still return Timestamp and ReportId by getting it from the most recent event involving each unique DeviceId.
Important
Avoid filtering custom detections using the Timestamp column. The data used for custom detections is pre-filtered based on the detection frequency.
The sample query below counts the number of unique devices (DeviceId) with antivirus detections and uses this count to find only the devices with more than five detections. To return the latest Timestamp and the corresponding ReportId, it uses the summarize operator with the arg_max function.
DeviceEvents
| where ingestion_time() > ago(1d)
| where ActionType == "AntivirusDetection"
| summarize (Timestamp, ReportId)=arg_max(Timestamp, ReportId), count() by DeviceId
| where count_ > 5
Tip
For better query performance, set a time filter that matches your intended run frequency for the rule. Since the least frequent run is every 24 hours, filtering for the past day will cover all new data.
2. Create new rule and provide alert details
With the query in the query editor, select Create detection rule and specify the following alert details:
- Detection name - Name of the detection rule; should be unique
- Frequency -Interval for running the query and taking action. See more guidance in the rule frequency section
- Alert title - Title displayed with alerts triggered by the rule; should be unique.
- Severity - Potential risk of the component or activity identified by the rule.
- Category - Threat component or activity identified by the rule.
- MITRE ATT&CK techniques - One or more attack techniques identified by the rule as documented in the MITRE ATT&CK framework. This section is hidden for certain alert categories, including malware, ransomware, suspicious activity, and unwanted software.
- Description - More information about the component or activity identified by the rule.
- Recommended actions - Additional actions that responders might take in response to an alert.
Rule frequency
When you save a new rule, it runs and checks for matches from the past 30 days of data. The rule then runs again at fixed intervals, applying a lookback period based on the frequency you choose:
- Every 24 hours - Runs every 24 hours, checking data from the past 30 days.
- Every 12 hours - Runs every 12 hours, checking data from the past 48 hours.
- Every 3 hours - Runs every 3 hours, checking data from the past 12 hours.
- Every hour - Runs hourly, checking data from the past 4 hours.
- Continuous (NRT) - Runs continuously, checking data from events as they're collected and processed in near real-time (NRT), see Continuous (NRT) frequency.
Tip
Match the time filters in your query with the lookback period. Results outside of the lookback period are ignored.
When you edit a rule, it will run with the applied changes in the next run time scheduled according to the frequency you set. The rule frequency is based on the event timestamp and not the ingestion time.
Continuous (NRT) frequency
Setting a custom detection to run in Continuous (NRT) frequency allows you to increase your organization's ability to identify threats faster. Using the Continuous (NRT) frequency has minimal to no impact to your resource usage and should thus be considered for any qualified custom detection rule in your organization.
From the custom detection rules page, you can migrate custom detections rules that fit the Continuous (NRT) frequency with a single button, Migrate now:
Selecting Migrate now gives you a list of all compatible rules according to their KQL query. You can choose to migrate all or selected rules only according to your preferences:
Once you click Save, the selected rules' frequency gets updated to Continuous (NRT) frequency.
Queries you can run continuously
You can run a query continuously as long as:
- The query references one table only.
- The query uses an operator from the list of supported KQL operators. Supported KQL features
- The query doesn't use joins, unions, or the
externaldataoperator. - The query doesn't include any comments line/information.
Tables that support Continuous (NRT) frequency
Near real-time detections are supported for the following tables:
AlertEvidenceCloudAppEventsDeviceEventsDeviceFileCertificateInfoDeviceFileEventsDeviceImageLoadEventsDeviceLogonEventsDeviceNetworkEventsDeviceNetworkInfoDeviceInfoDeviceProcessEventsDeviceRegistryEventsEmailAttachmentInfoEmailEvents(exceptLatestDeliveryLocationandLatestDeliveryActioncolumns)EmailPostDeliveryEventsEmailUrlInfoIdentityDirectoryEventsIdentityLogonEventsIdentityQueryEventsUrlClickEvents
Note
Only columns that are generally available can support Continuous (NRT) frequency.
3. Choose the impacted entities
Identify the columns in your query results where you expect to find the main affected or impacted entity. For example, a query might return sender (SenderFromAddress or SenderMailFromAddress) and recipient (RecipientEmailAddress) addresses. Identifying which of these columns represent the main impacted entity helps the service aggregate relevant alerts, correlate incidents, and target response actions.
You can select only one column for each entity type (mailbox, user, or device). Columns that aren't returned by your query can't be selected.
4. Specify actions
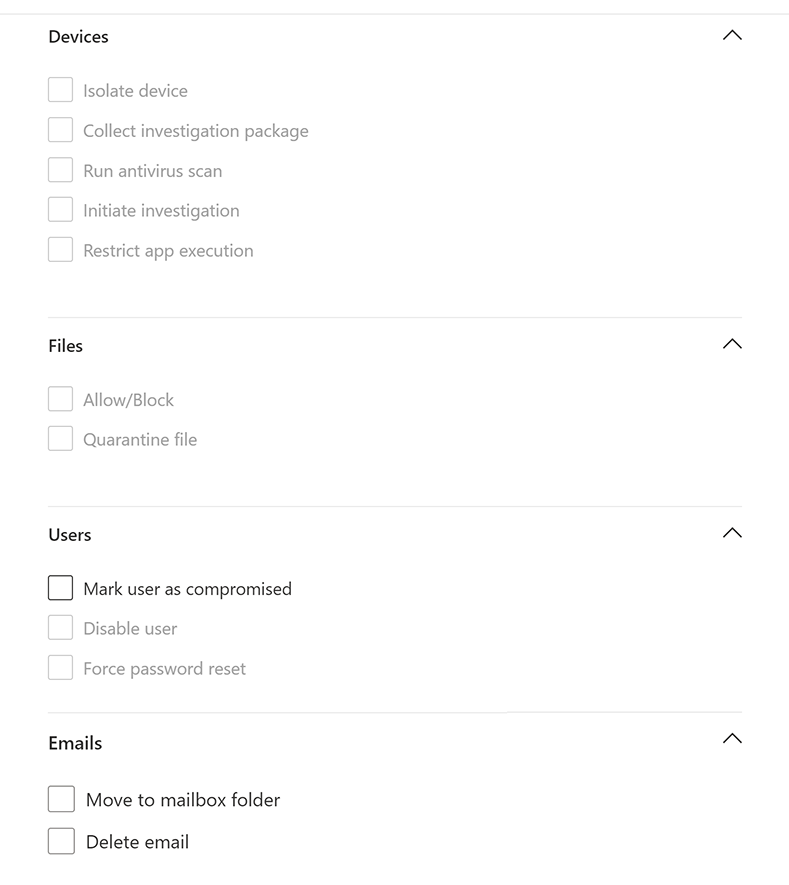
Your custom detection rule can automatically take actions on devices, files, users, or emails that are returned by the query.
Actions on devices
These actions are applied to devices in the DeviceId column of the query results:
- Isolate device - Uses Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to apply full network isolation, preventing the device from connecting to any application or service. Learn more about Microsoft Defender for Endpoint machine isolation.
- Collect investigation package - Collects device information in a ZIP file. Learn more about the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint investigation package.
- Run antivirus scan - Performs a full Microsoft Defender Antivirus scan on the device.
- Initiate investigation - Initiates an automated investigation on the device.
- Restrict app execution - Sets restrictions on device to allow only files that are signed with a Microsoft-issued certificate to run. Learn more about app restrictions with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Actions on files
When selected, the Allow/Block action can be applied to the file. Blocking files are only allowed if you have Remediate permissions for files and if the query results have identified a file ID, such as an SHA1. Once a file is blocked, other instances of the same file in all devices are also blocked. You can control which device group the blocking is applied to, but not specific devices.
When selected, the Quarantine file action can be applied to files in the
SHA1,InitiatingProcessSHA1,SHA256, orInitiatingProcessSHA256column of the query results. This action deletes the file from its current location and places a copy in quarantine.
Actions on users
When selected, the Mark user as compromised action is taken on users in the
AccountObjectId,InitiatingProcessAccountObjectId, orRecipientObjectIdcolumn of the query results. This action sets the users risk level to "high" in Microsoft Entra ID, triggering corresponding identity protection policies.Select Disable user to temporarily prevent a user from logging in.
Select Force password reset to prompt the user to change their password on the next sign in session.
Both the
Disable userandForce password resetoptions require the user SID, which are in the columnsAccountSid,InitiatingProcessAccountSid,RequestAccountSid, andOnPremSid.
For more details on user actions, read Remediation actions in Microsoft Defender for Identity.
Actions on emails
If the custom detection yields email messages, you can select Move to mailbox folder to move the email to a selected folder (any of Junk, Inbox, or Deleted items folders). Specifically, you can move email results from quarantined items (for instance, in the case of false positives) by selecting the Inbox option.
Alternatively, you can select Delete email and then choose to either move the emails to Deleted Items (Soft delete) or delete the selected emails permanently (Hard delete).
The columns NetworkMessageId and RecipientEmailAddress must be present in the output results of the query to apply actions to email messages.
5. Set the rule scope
Set the scope to specify which devices are covered by the rule. The scope influences rules that check devices and doesn't affect rules that check only mailboxes and user accounts or identities.
When setting the scope, you can select:
- All devices
- Specific device groups
Only data from devices in the scope will be queried. Also, actions are taken only on those devices.
Note
Users are able to create or edit a custom detection rule only if they have the corresponding permissions for the devices included in the scope of the rule. For instance, admins can only create or edit rules that are scoped to all device groups if they have permissions for all device groups.
6. Review and turn on the rule
After reviewing the rule, select Create to save it. The custom detection rule immediately runs. It runs again based on configured frequency to check for matches, generate alerts, and take response actions.
Important
Custom detections should be regularly reviewed for efficiency and effectiveness. To make sure you are creating detections that trigger true alerts, take time to review your existing custom detections by following the steps in Manage existing custom detection rules.
You maintain control over the broadness or specificity of your custom detections so any false alerts generated by custom detections might indicate a need to modify certain parameters of the rules.
Manage existing custom detection rules
You can view the list of existing custom detection rules, check their previous runs, and review the alerts that were triggered. You can also run a rule on demand and modify it.
Tip
Alerts raised by custom detections are available over alerts and incident APIs. For more information, see Supported Microsoft Defender XDR APIs.
View existing rules
To view all existing custom detection rules, navigate to Hunting > Custom detection rules. The page lists all the rules with the following run information:
- Last run - When a rule was last run to check for query matches and generate alerts
- Last run status - Whether a rule ran successfully
- Next run - The next scheduled run
- Status - Whether a rule has been turned on or off
View rule details, modify rule, and run rule
To view comprehensive information about a custom detection rule, go to Hunting > Custom detection rules and then select the name of rule. You can then view general information about the rule, including information, its run status, and scope. The page also provides the list of triggered alerts and actions.
You can also take the following actions on the rule from this page:
- Run - Run the rule immediately. This also resets the interval for the next run.
- Edit - Modify the rule without changing the query.
- Modify query - Edit the query in advanced hunting.
- Turn on / Turn off - Enable the rule or stop it from running.
- Delete - Turn off the rule and remove it.
View and manage triggered alerts
In the rule details screen (Hunting > Custom detections > [Rule name]), go to Triggered alerts, which lists the alerts generated by matches to the rule. Select an alert to view detailed information about it and take the following actions:
- Manage the alert by setting its status and classification (true or false alert)
- Link the alert to an incident
- Run the query that triggered the alert on advanced hunting
Review actions
In the rule details screen (Hunting > Custom detections > [Rule name]), go to Triggered actions, which lists the actions taken based on matches to the rule.
Tip
To quickly view information and take action on an item in a table, use the selection column [✓] at the left of the table.
Note
Some columns in this article might not be available in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Turn on Microsoft Defender XDR to hunt for threats using more data sources. You can move your advanced hunting workflows from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to Microsoft Defender XDR by following the steps in Migrate advanced hunting queries from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
See also
- Custom detections overview
- Advanced hunting overview
- Learn the advanced hunting query language
- Migrate advanced hunting queries from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Graph security API for custom detections
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender XDR Tech Community.