Nota:
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar iniciar sesión o cambiar directorios.
El acceso a esta página requiere autorización. Puede intentar cambiar los directorios.
En esta sección final se explica cómo crear una aplicación para UWP sencilla con una GUI para transmitir la cámara web y detectar objetos mediante la evaluación de nuestro modelo YOLO con Windows ML.
Creación de una aplicación para UWP en Visual Studio
- Abra Visual Studio y seleccione
Create a new project.Buscar UWP y seleccioneBlank App (Universal Windows).
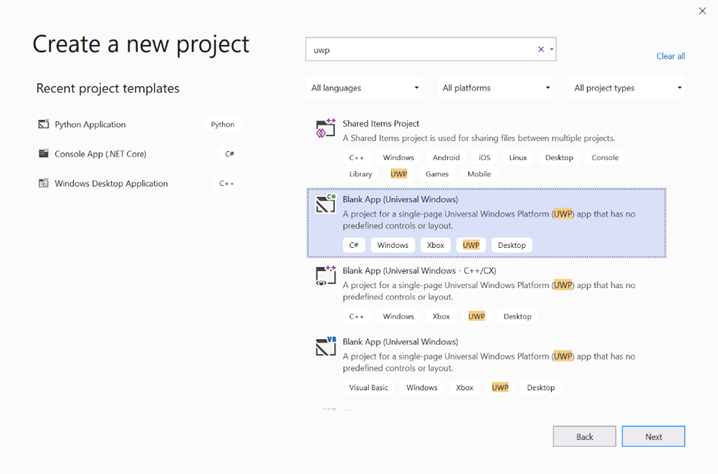
- En la página siguiente, configure los valores del proyecto proporcionando al proyecto un nombre y una ubicación. A continuación, seleccione un destino y una versión mínima del sistema operativo de la aplicación. Para usar las API de Windows ML, debe usar X o puede elegir el paquete NuGet para admitir hasta X. Si decide usar el paquete NuGet, siga estas instrucciones [vínculo].
Llamada a las API de Windows ML para evaluar el modelo
Paso 1: Use el generador de código de Machine Learning para generar clases contenedoras para las API de Windows ML.
Paso 2: Modificar el código generado en el archivo .cs generado. El archivo final tiene este aspecto:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Windows.Media;
using Windows.Storage;
using Windows.Storage.Streams;
using Windows.AI.MachineLearning;
namespace yolodemo
{
public sealed class YoloInput
{
public TensorFloat input_100; // shape(-1,3,416,416)
}
public sealed class YoloOutput
{
public TensorFloat concat_1600; // shape(-1,-1,-1)
}
public sealed class YoloModel
{
private LearningModel model;
private LearningModelSession session;
private LearningModelBinding binding;
public static async Task<YoloModel> CreateFromStreamAsync(IRandomAccessStreamReference stream)
{
YoloModel learningModel = new YoloModel();
learningModel.model = await LearningModel.LoadFromStreamAsync(stream);
learningModel.session = new LearningModelSession(learningModel.model);
learningModel.binding = new LearningModelBinding(learningModel.session);
return learningModel;
}
public async Task<YoloOutput> EvaluateAsync(YoloInput input)
{
binding.Bind("input_1:0", input.input_100);
var result = await session.EvaluateAsync(binding, "0");
var output = new YoloOutput();
output.concat_1600 = result.Outputs["concat_16:0"] as TensorFloat;
return output;
}
}
}
Evalúe cada fotograma de vídeo para detectar objetos y dibujar cajas delimitadoras.
- Agregue las siguientes bibliotecas a mainPage.xaml.cs.
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Windows.Devices.Enumeration;
using Windows.Media;
using Windows.Media.Capture;
using Windows.Storage;
using Windows.UI;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media.Imaging;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Shapes;
using Windows.AI.MachineLearning;
- Agregue las siguientes variables en
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page.
private MediaCapture _media_capture;
private LearningModel _model;
private LearningModelSession _session;
private LearningModelBinding _binding;
private readonly SolidColorBrush _fill_brush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Transparent);
private readonly SolidColorBrush _line_brush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.DarkGreen);
private readonly double _line_thickness = 2.0;
private readonly string[] _labels =
{
"<list of labels>"
};
- Cree una estructura para dar formato a los resultados de detección.
internal struct DetectionResult
{
public string label;
public List<float> bbox;
public double prob;
}
- Cree un objeto Comparer que compare dos objetos de tipo Box. Esta clase se usará para dibujar cuadros de límite alrededor de los objetos detectados.
class Comparer : IComparer<DetectionResult>
{
public int Compare(DetectionResult x, DetectionResult y)
{
return y.prob.CompareTo(x.prob);
}
}
- Agregue el siguiente método para inicializar la secuencia de cámara web del dispositivo y empezar a procesar cada fotograma para detectar objetos.
private async Task InitCameraAsync()
{
if (_media_capture == null || _media_capture.CameraStreamState == Windows.Media.Devices.CameraStreamState.Shutdown || _media_capture.CameraStreamState == Windows.Media.Devices.CameraStreamState.NotStreaming)
{
if (_media_capture != null)
{
_media_capture.Dispose();
}
MediaCaptureInitializationSettings settings = new MediaCaptureInitializationSettings();
var cameras = await DeviceInformation.FindAllAsync(DeviceClass.VideoCapture);
var camera = cameras.FirstOrDefault();
settings.VideoDeviceId = camera.Id;
_media_capture = new MediaCapture();
await _media_capture.InitializeAsync(settings);
WebCam.Source = _media_capture;
}
if (_media_capture.CameraStreamState == Windows.Media.Devices.CameraStreamState.NotStreaming)
{
await _media_capture.StartPreviewAsync();
WebCam.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
}
ProcessFrame();
}
- Agregue el siguiente método para procesar cada fotograma. Este método llama a EvaluateFrame y DrawBoxes, que implementaremos en un paso posterior.
private async Task ProcessFrame()
{
var frame = new VideoFrame(Windows.Graphics.Imaging.BitmapPixelFormat.Bgra8, (int)WebCam.Width, (int)WebCam.Height);
await _media_capture.GetPreviewFrameAsync(frame);
var results = await EvaluateFrame(frame);
await DrawBoxes(results.ToArray(), frame);
ProcessFrame();
}
- Crear un nuevo flotante de Sigmoid
private float Sigmoid(float val)
{
var x = (float)Math.Exp(val);
return x / (1.0f + x);
}
- Cree un umbral para detectar objetos correctamente.
private float ComputeIOU(DetectionResult DRa, DetectionResult DRb)
{
float ay1 = DRa.bbox[0];
float ax1 = DRa.bbox[1];
float ay2 = DRa.bbox[2];
float ax2 = DRa.bbox[3];
float by1 = DRb.bbox[0];
float bx1 = DRb.bbox[1];
float by2 = DRb.bbox[2];
float bx2 = DRb.bbox[3];
Debug.Assert(ay1 < ay2);
Debug.Assert(ax1 < ax2);
Debug.Assert(by1 < by2);
Debug.Assert(bx1 < bx2);
// determine the coordinates of the intersection rectangle
float x_left = Math.Max(ax1, bx1);
float y_top = Math.Max(ay1, by1);
float x_right = Math.Min(ax2, bx2);
float y_bottom = Math.Min(ay2, by2);
if (x_right < x_left || y_bottom < y_top)
return 0;
float intersection_area = (x_right - x_left) * (y_bottom - y_top);
float bb1_area = (ax2 - ax1) * (ay2 - ay1);
float bb2_area = (bx2 - bx1) * (by2 - by1);
float iou = intersection_area / (bb1_area + bb2_area - intersection_area);
Debug.Assert(iou >= 0 && iou <= 1);
return iou;
}
- Implemente la lista siguiente para realizar un seguimiento de los objetos actuales detectados en el marco.
private List<DetectionResult> NMS(IReadOnlyList<DetectionResult> detections,
float IOU_threshold = 0.45f,
float score_threshold=0.3f)
{
List<DetectionResult> final_detections = new List<DetectionResult>();
for (int i = 0; i < detections.Count; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < final_detections.Count; j++)
{
if (ComputeIOU(final_detections[j], detections[i]) > IOU_threshold)
{
break;
}
}
if (j==final_detections.Count)
{
final_detections.Add(detections[i]);
}
}
return final_detections;
}
- Implemente el método siguiente.
private List<DetectionResult> ParseResult(float[] results)
{
int c_values = 84;
int c_boxes = results.Length / c_values;
float confidence_threshold = 0.5f;
List<DetectionResult> detections = new List<DetectionResult>();
this.OverlayCanvas.Children.Clear();
for (int i_box = 0; i_box < c_boxes; i_box++)
{
float max_prob = 0.0f;
int label_index = -1;
for (int j_confidence = 4; j_confidence < c_values; j_confidence++)
{
int index = i_box * c_values + j_confidence;
if (results[index] > max_prob)
{
max_prob = results[index];
label_index = j_confidence - 4;
}
}
if (max_prob > confidence_threshold)
{
List<float> bbox = new List<float>();
bbox.Add(results[i_box * c_values + 0]);
bbox.Add(results[i_box * c_values + 1]);
bbox.Add(results[i_box * c_values + 2]);
bbox.Add(results[i_box * c_values + 3]);
detections.Add(new DetectionResult()
{
label = _labels[label_index],
bbox = bbox,
prob = max_prob
});
}
}
return detections;
}
- Agregue el método siguiente para dibujar los cuadros alrededor de los objetos detectados en el marco.
private async Task DrawBoxes(float[] results, VideoFrame frame)
{
List<DetectionResult> detections = ParseResult(results);
Comparer cp = new Comparer();
detections.Sort(cp);
IReadOnlyList<DetectionResult> final_detetions = NMS(detections);
for (int i=0; i < final_detetions.Count; ++i)
{
int top = (int)(final_detetions[i].bbox[0] * WebCam.Height);
int left = (int)(final_detetions[i].bbox[1] * WebCam.Width);
int bottom = (int)(final_detetions[i].bbox[2] * WebCam.Height);
int right = (int)(final_detetions[i].bbox[3] * WebCam.Width);
var brush = new ImageBrush();
var bitmap_source = new SoftwareBitmapSource();
await bitmap_source.SetBitmapAsync(frame.SoftwareBitmap);
brush.ImageSource = bitmap_source;
// brush.Stretch = Stretch.Fill;
this.OverlayCanvas.Background = brush;
var r = new Rectangle();
r.Tag = i;
r.Width = right - left;
r.Height = bottom - top;
r.Fill = this._fill_brush;
r.Stroke = this._line_brush;
r.StrokeThickness = this._line_thickness;
r.Margin = new Thickness(left, top, 0, 0);
this.OverlayCanvas.Children.Add(r);
// Default configuration for border
// Render text label
var border = new Border();
var backgroundColorBrush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.Black);
var foregroundColorBrush = new SolidColorBrush(Colors.SpringGreen);
var textBlock = new TextBlock();
textBlock.Foreground = foregroundColorBrush;
textBlock.FontSize = 18;
textBlock.Text = final_detetions[i].label;
// Hide
textBlock.Visibility = Visibility.Collapsed;
border.Background = backgroundColorBrush;
border.Child = textBlock;
Canvas.SetLeft(border, final_detetions[i].bbox[1] * 416 + 2);
Canvas.SetTop(border, final_detetions[i].bbox[0] * 416 + 2);
textBlock.Visibility = Visibility.Visible;
// Add to canvas
this.OverlayCanvas.Children.Add(border);
}
}
- Ahora que hemos controlado la infraestructura necesaria, es el momento de incorporar la propia evaluación. Este método evalúa el modelo con respecto al marco actual para detectar objetos.
private async Task<List<float>> EvaluateFrame(VideoFrame frame)
{
_binding.Clear();
_binding.Bind("input_1:0", frame);
var results = await _session.EvaluateAsync(_binding, "");
Debug.Print("output done\n");
TensorFloat result = results.Outputs["Identity:0"] as TensorFloat;
var shape = result.Shape;
var data = result.GetAsVectorView();
return data.ToList<float>();
}
- Nuestra aplicación debe empezar de alguna manera. Agregue un método que comience la transmisión de webcam y la evaluación del modelo cuando el usuario presione el
Gobotón.
private void button_go_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
InitModelAsync();
InitCameraAsync();
}
- Agregue un método para llamar a las API de Windows ML para evaluar el modelo. En primer lugar, el modelo se carga desde el almacenamiento y, a continuación, se crea una sesión y se enlaza a la memoria.
private async Task InitModelAsync()
{
var model_file = await StorageFile.GetFileFromApplicationUriAsync(new Uri("ms-appx:///Assets//Yolo.onnx"));
_model = await LearningModel.LoadFromStorageFileAsync(model_file);
var device = new LearningModelDevice(LearningModelDeviceKind.Cpu);
_session = new LearningModelSession(_model, device);
_binding = new LearningModelBinding(_session);
}
Inicio de la aplicación
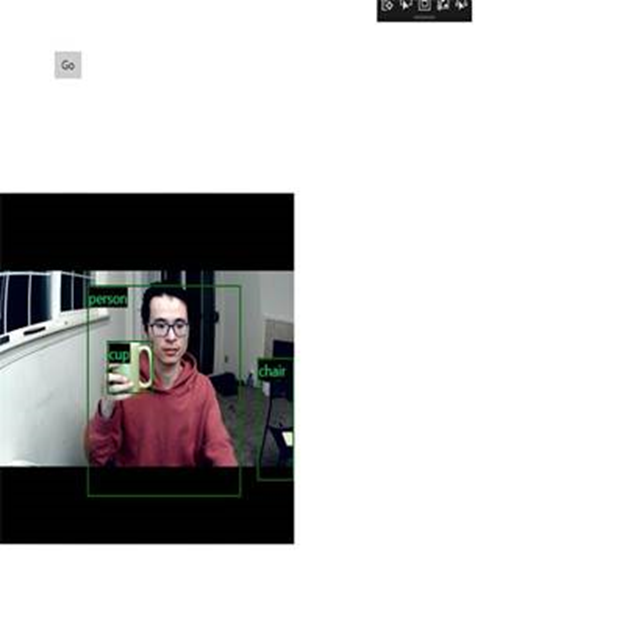
Ahora ha creado correctamente una aplicación de detección de objetos en tiempo real. Seleccione el Run botón de la barra superior de Visual Studio para iniciar la aplicación. La aplicación debe tener este aspecto.
Recursos adicionales
Para obtener más información sobre los temas mencionados en este tutorial, visite los siguientes recursos:
- Herramientas de Windows ML: obtenga más información sobre herramientas como el panel de Windows ML, WinMLRunner y el generador de código mglen Windows ML.
- Modelo ONNX: obtenga más información sobre el formato ONNX.
- Rendimiento y memoria de Windows ML: obtenga más información sobre cómo administrar el rendimiento de las aplicaciones con Windows ML.
- Referencia de la API de Windows Machine Learning: obtenga más información sobre tres áreas de las API de Windows ML.