Azure Data Studio extensibility
Important
Azure Data Studio is retiring on February 28, 2026. We recommend that you use Visual Studio Code. For more information about migrating to Visual Studio Code, visit What's happening to Azure Data Studio?
Azure Data Studio has several extensibility mechanisms to customize the user experience and make those customizations available to the entire user community. The core Azure Data Studio platform is built upon Visual Studio Code, so most of the Visual Studio Code extensibility APIs are available. Additionally, we've provided other extensibility points for data management-specific activities.
Some of the key extensibility points are:
- Visual Studio Code extensibility APIs
- Azure Data Studio extension authoring tools
- Manage Dashboard tab panel contributions
- Insights with Action experience
- Azure Data Studio extensibility APIs
- Custom Data Provider APIs
Visual Studio Code extensibility APIs
Because the core Azure Data Studio platform is built upon Visual Studio Code, details about the Visual Studio Code extensibility APIs are found in the Extension Authoring and Extension API documentation on the Visual Studio Code website.
Note
Azure Data Studio releases align with a recent VS Code version. However, the included VS Code engine might not be the current VS Code release. For example, in November 2020, the VS Code engine in Azure Data Studio was 1.48, and the current VS Code version is 1.51. The error message "Unable to install extension '<name>' as it isn't compatible with VS Code <version>" when installing an extension is caused by an extension that has a later VS Code engine version defined in the package manifest (package.json). You can verify the VS Code engine version in your Azure Data Studio through the Help menu under About.
Manage Dashboard tab panel contributions
For details, see Contribution Points and Context Variables.
Azure Data Studio extensibility APIs
For details, see Extensibility APIs.
Contribution points
This section covers the various contribution points defined in the package.json extension manifest.
The IntelliSense is supported inside azuredatastudio.
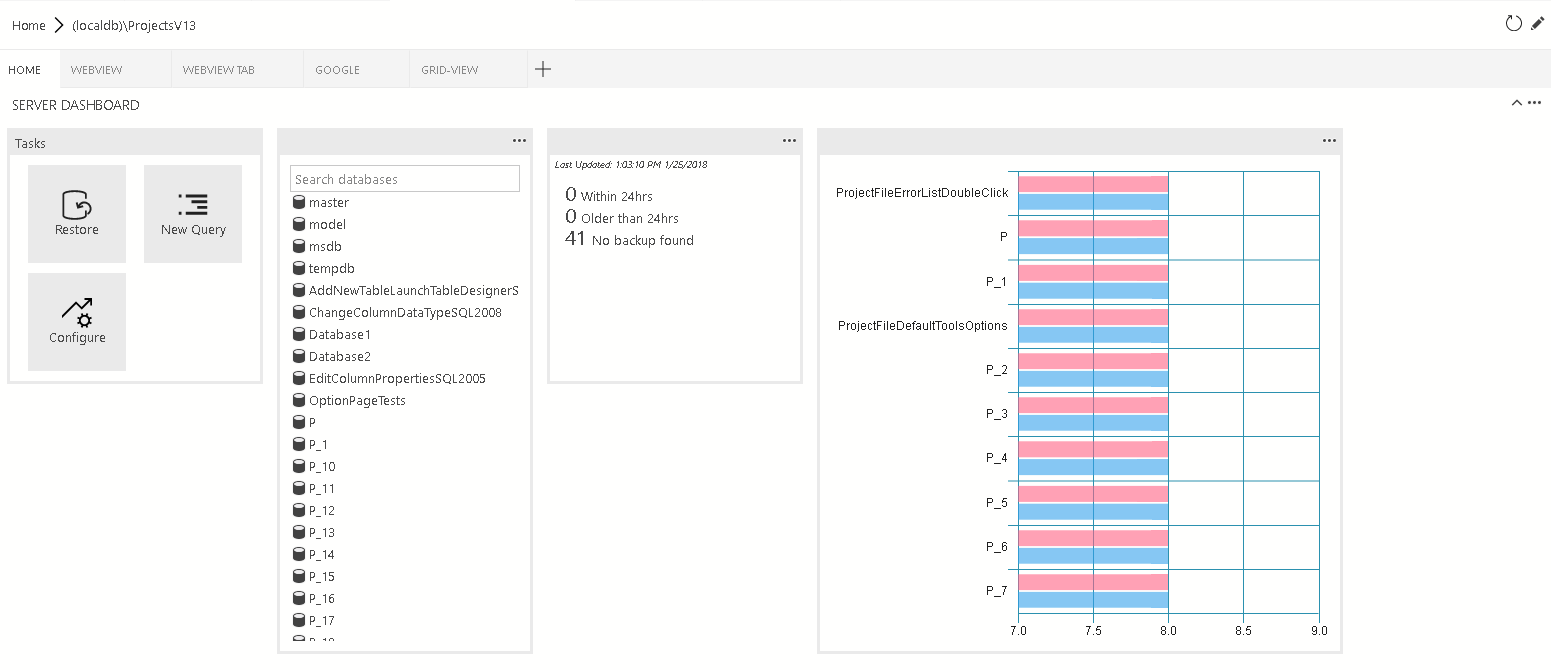
Dashboard contribution points
Contribute a tab, container, and/or insight widget to the dashboard.
dashboard.tabs
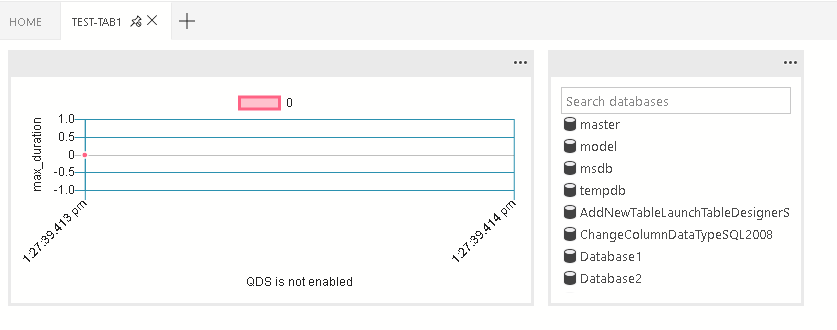
Dashboard.tabs creates the tab sections inside the dashboard page. It expects an object or an array of objects.
"dashboard.tabs": [
{
"id": "test-tab1",
"title": "Test 1",
"description": "The test 1 displays a list of widgets.",
"when": "connectionProvider == 'MSSQL' && !mssql:iscloud",
"alwaysShow": true,
"container": {
...
}
}
]
dashboard.containers
Instead of specifying the dashboard container inline (inside the dashboard tab), you can register containers using dashboard.containers. It accepts an object or an array of objects.
"dashboard.containers": [
{
"id": "innerTab1",
"widgets-container": [
{
"widget": {
"query-data-store-db-insight": {}
}
},
{
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
}
}
]
},
{
"id": "innerTab2",
"webview-container": {}
},
{
"id": "innerTab3",
"grid-container": [
{
"name": "widget 1",
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
},
"row": 0,
"col": 0
},
{
"name": "widget 2",
"widget": {
"tasks-widget": {
"backup",
"restore",
"configureDashboard",
"newQuery"
}
},
"row": 0,
"col": 1
},
{
"name": "Webview 1",
"webview": {
"id": "google"
},
"row": 1,
"col": 0,
"colspan": 2
},
{
"name": "widget 3",
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
},
To refer to registered container, specify the ID of the container.
"dashboard.tabs": [
{
"id": "test-tab1",
"title": "Test 1",
"description": "The test 1 displays a list of widgets.",
"when": "connectionProvider == 'MSSQL' && !mssql:iscloud",
"alwaysShow": true,
"container": {
"id": "innerTab1"
}
}
]
dashboard.insights
You can register insights using dashboard.insights. This is similar to Tutorial: Build a custom insight widget. It accepts an object or an array of objects.
"dashboard.insights": {
"id": "my-widget",
"type": {
"count": {
"dataDirection": "vertical",
"dataType": "number",
"legendPosition": "none",
"labelFirstColumn": false,
"columnsAsLabels": false
}
},
"queryFile": "{your file folder}/activeSession.sql"
}
Dashboard container types
There are currently four supported container types:
widgets-container
The list of widgets that will be displayed in the container is a flow layout that accepts this list.
"container": {
"widgets-container": [
{
"widget": {
"query-data-store-db-insight": {}
}
},
{
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
}
}
]
}
webview-container
The webview is displayed in the entire container. It expects webview ID to be the same is tab ID.
"container": {
"webview-container": {}
}
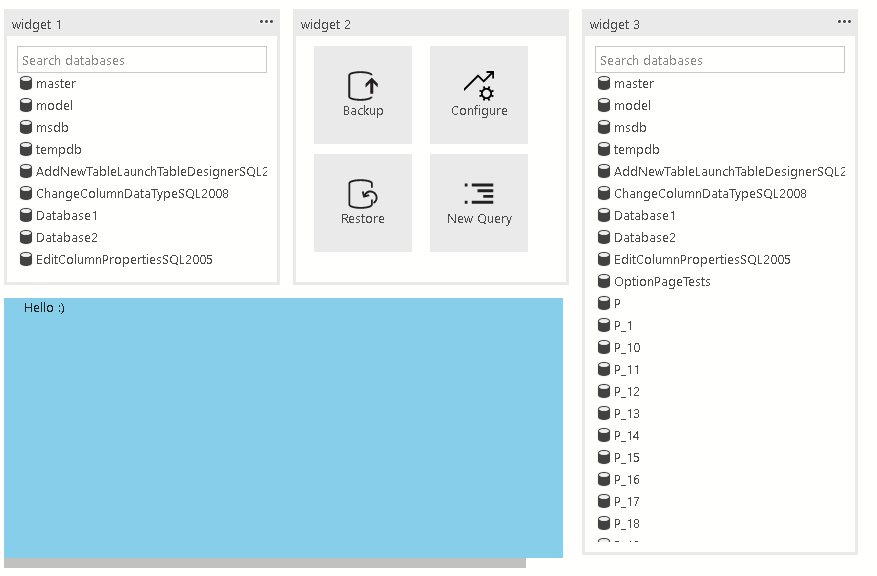
grid-container
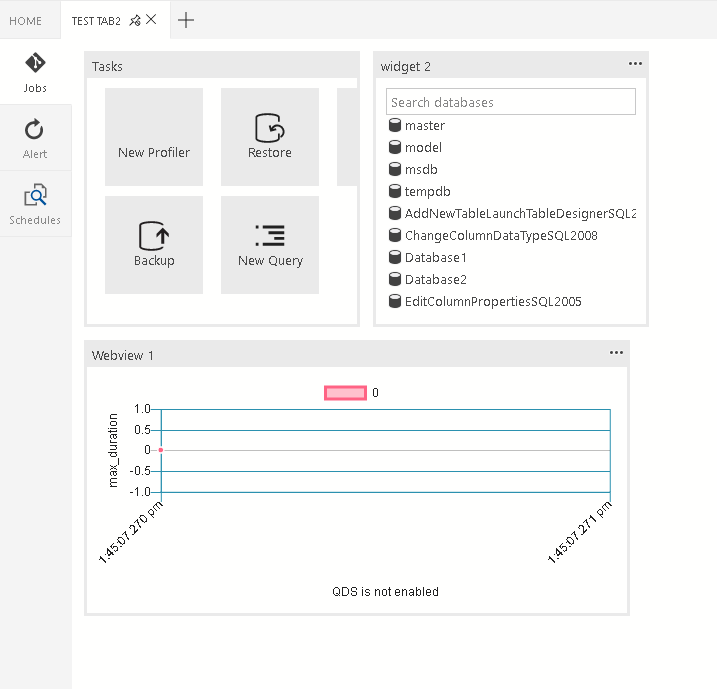
The list of widgets or webviews that are displayed in the grid layout. The grid layout is a 2x2 grid layout that accepts this list.
"container": {
"grid-container": [
{
"name": "widget 1",
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
},
"row": 0,
"col": 0
},
{
"name": "widget 2",
"widget": {
"tasks-widget": {
"backup",
"restore",
"configureDashboard",
"newQuery"
}
},
"row": 0,
"col": 1
},
{
"name": "Webview 1",
"webview": {
"id": "google"
},
"row": 1,
"col": 0,
"colspan": 2
},
{
"name": "widget 3",
"widget": {
"explorer-widget": {}
},
"row": 0,
"col": 3,
"rowspan": 2
}
]
}
nav-section
The navigation section is displayed in the container. It expects an array of objects.
"container": {
"nav-section": [
{
"id": "innerTab1",
"title": "inner-tab1",
"icon": {
"light": "./icons/tab1Icon.svg",
"dark": "./icons/tab1Icon_dark.svg"
},
"container": {
...
}
},
{
"id": "innerTab2",
"title": "inner-tab2",
"icon": {
"light": "./icons/tab2Icon.svg",
"dark": "./icons/tab2Icon_dark.svg"
},
"container": {
...
}
}
]
}
Context variables
For general information about context in Visual Studio Code and later Azure Data Studio, see Extensibility.
In Azure Data Studio, we have specific context around database connections available for extensions.
Dashboard
In the dashboard, we provide the following context variables:
| Context Variable | Description |
|---|---|
connectionProvider |
A string of the identifier for the provider of the current connection. Ex. connectionProvider == 'MSSQL'. |
serverName |
A string of the server name of the current connection. Ex. serverName == 'localhost'. |
databaseName |
A string of the database name of the current connection. Ex. databaseName == 'master'. |
connection |
The full connection profile object for the current connection (IConnectionProfile) |
dashboardContext |
A string of the context of the page the dashboard is currently on. Either 'database' or 'server'. Ex. dashboardContext == 'database' |