How to create and manage an Azure AI Foundry hub
In Azure AI Foundry portal, hubs provide the environment for a team to collaborate and organize work, and help you as a team lead or IT admin centrally set up security settings and govern usage and spend. You can create and manage a hub from the Azure portal or from the Azure AI Foundry portal, and then your developers can create projects from the hub.
In this article, you learn how to create and manage a hub in Azure AI Foundry portal with the default settings so you can get started quickly. Do you need to customize security or the dependent resources of your hub? Then use Azure portal or template options.
Tip
If you're an individual developer and not an admin, dev lead, or part of a larger effort that requires a hub, you can create a project directly from the Azure AI Foundry portal without creating a hub first. For more information, see Create a project.
If you're an admin or dev lead and would like to create your Azure AI Foundry hub using a template, see the articles on using Bicep or Terraform.
Create a hub in Azure AI Foundry portal
To create a new hub, you need either the Owner or Contributor role on the resource group or on an existing hub. If you're unable to create a hub due to permissions, reach out to your administrator. If your organization is using Azure Policy, don't create the resource in Azure AI Foundry portal. Create the hub in the Azure portal instead.
Note
A hub in Azure AI Foundry portal is a one-stop shop where you manage everything your AI project needs, like security and resources, so you can develop and test faster. To learn more about how hubs can help you, see the Hubs and projects overview article.
To create a hub in Azure AI Foundry, follow these steps:
Go to Azure AI Foundry and sign in with your Azure account.
If you’re not already in a project, select one. It doesn't matter which one you select. If you have no projects, first create one by selecting + Create project at the top of the page.
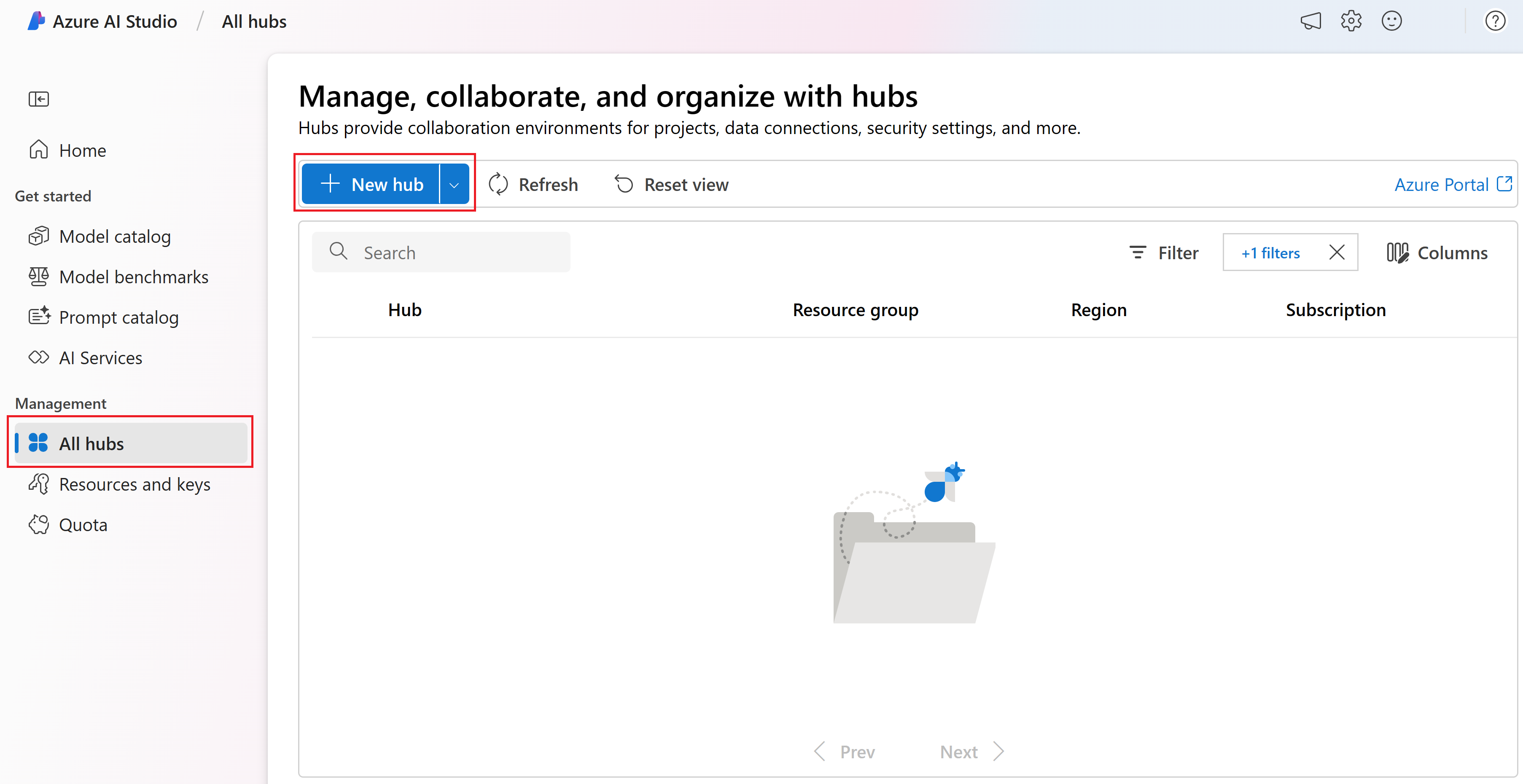
Select the Management center from the left menu.
Select All resources, the down arrow next to + New project and then select + New hub.
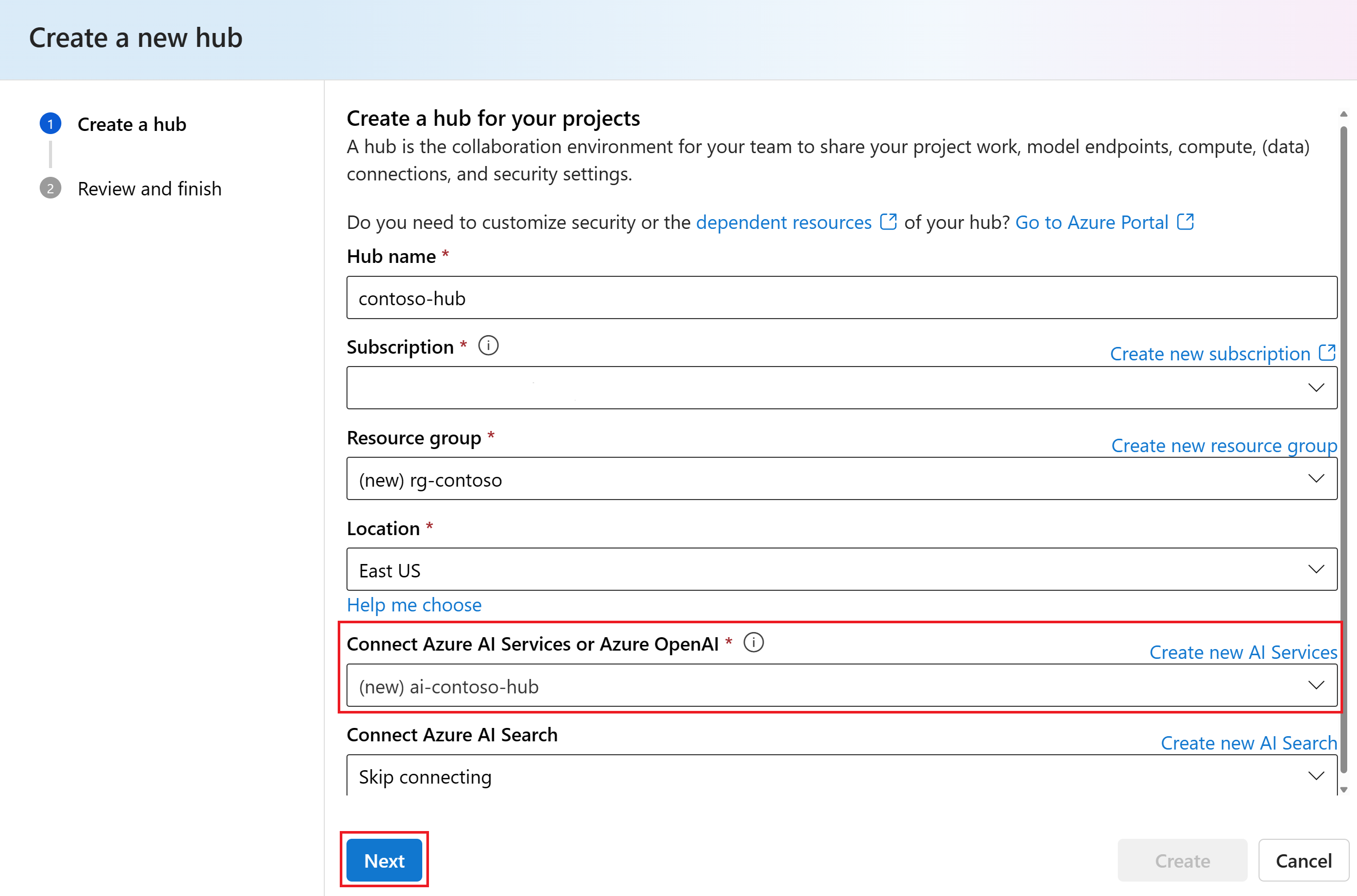
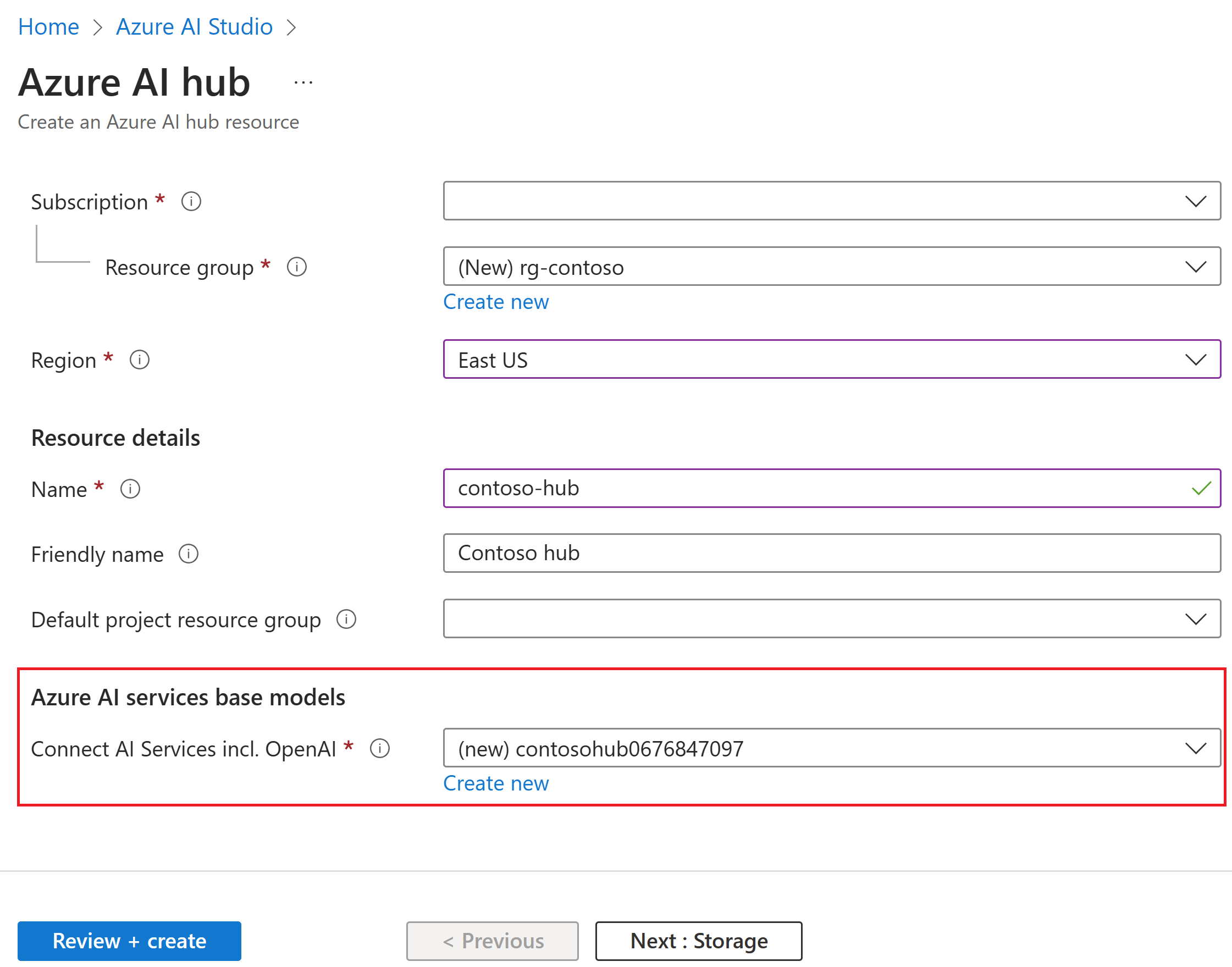
In the Create a new hub dialog, enter a name for your hub (such as contoso-hub) and modify the other fields as desired. By default, a new AI services connection is created for the hub.
Note
If you don't see (new) before the Resource group and Connect Azure AI Services entries then an existing resource is being used. For the purposes of this tutorial, create a separate entity via Create new resource group and Create new AI Services. This will allow you to prevent any unexpected charges by deleting the entities after the tutorial.
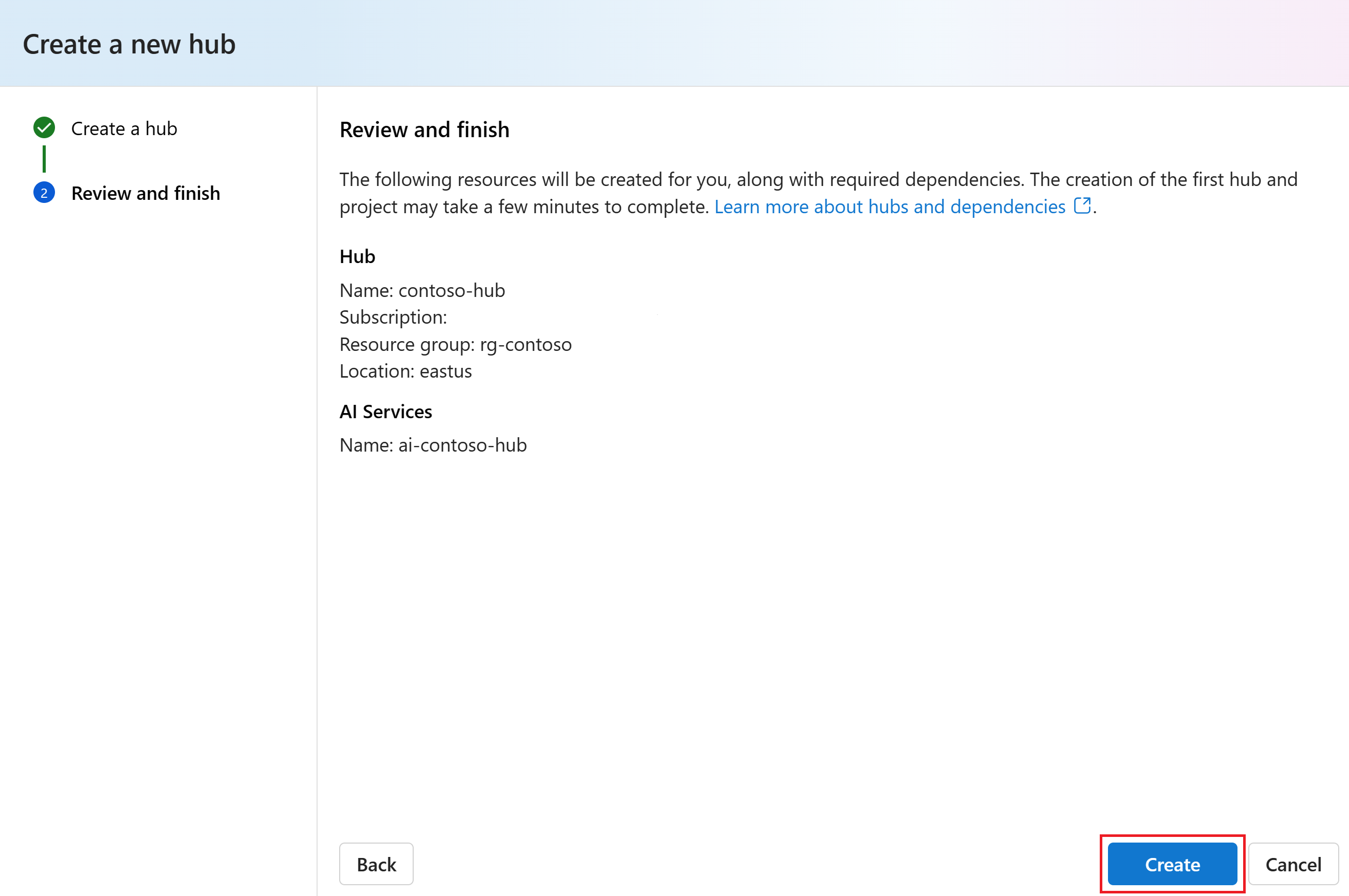
Select Next, review the information, and then select Create.
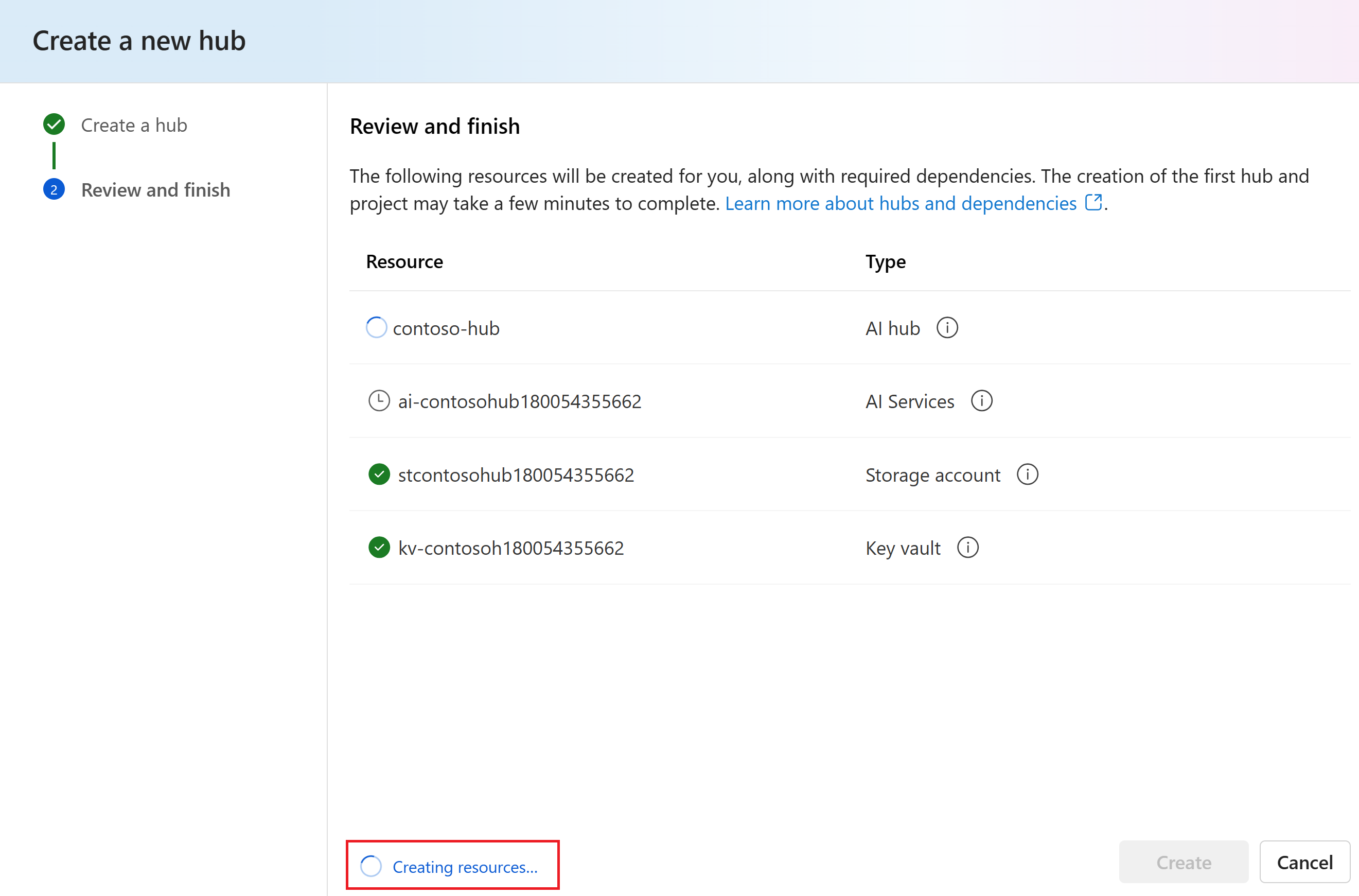
You can view the progress of the hub creation in the wizard.
Create a secure hub in the Azure portal
If your organization is using Azure Policy, set up a hub that meets your organization's requirements instead of using Azure AI Foundry for resource creation.
From the Azure portal, search for
Azure AI Foundryand create a new hub by selecting + New Azure AI hubEnter your hub name, subscription, resource group, and location details.
For Azure AI services base models, select an existing AI services resource or create a new one. Azure AI services include multiple API endpoints for Speech, Content Safety, and Azure OpenAI.
Select the Storage tab to specify storage account settings. For storing credentials, either provide your Azure Key Vault or use the Microsoft-managed credential store (preview).
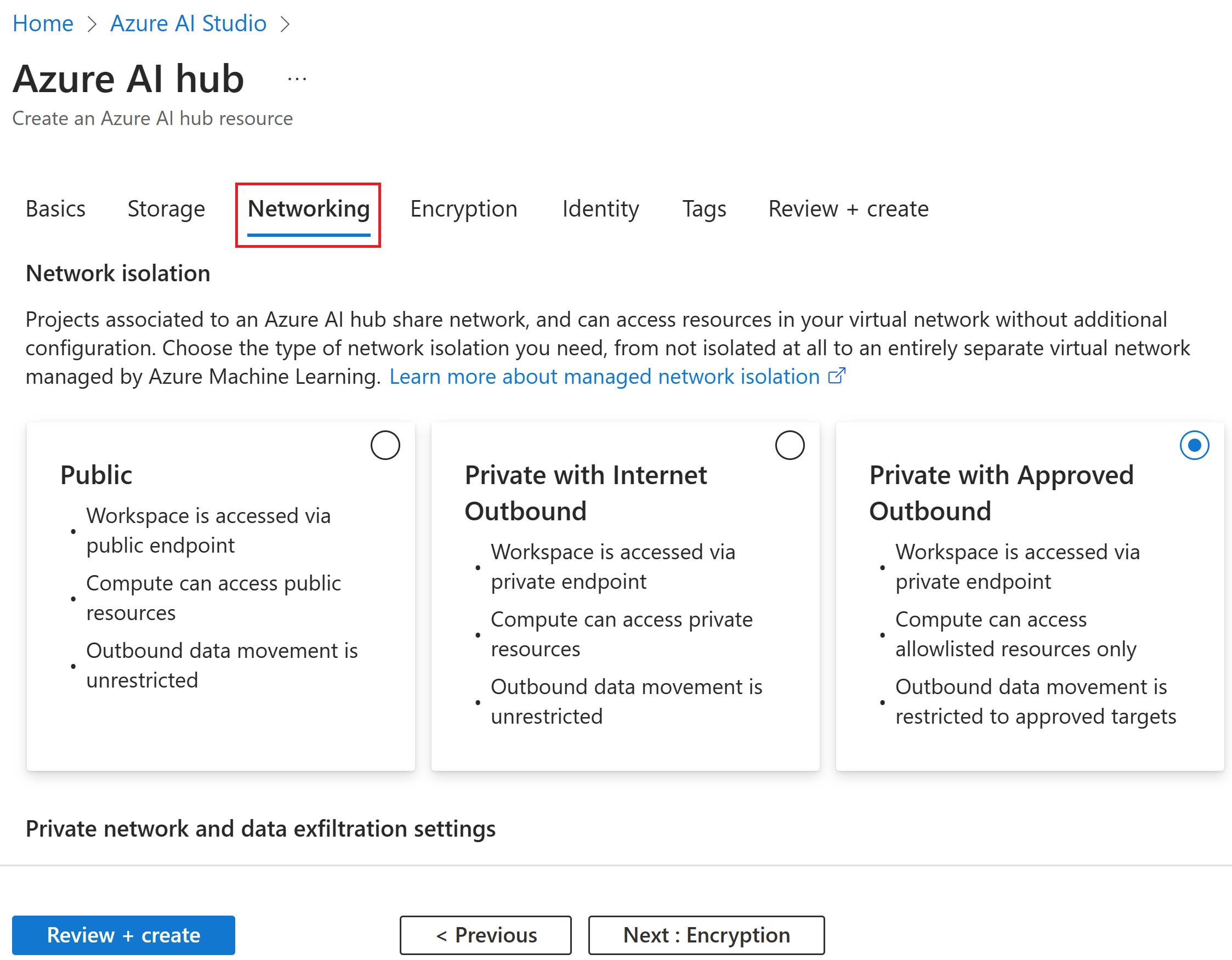
Select the Networking tab to set up Network isolation. Read more on network isolation. For a walkthrough of creating a secure hub, see Create a secure hub.
Select the Encryption tab to set up data encryption. By default, Microsoft-managed keys are used to encrypt data. You can select to Encrypt data using a customer-managed key.
Select the Identity tab. By default, System assigned identity is enabled, but you can switch to User assigned identity if existing storage, key vault, and container registry are selected in Storage. You can also select whether to use Credential-based or Identity-based access to the storage account.
Note
If you select User assigned identity, your identity needs to have the
Cognitive Services Contributorrole in order to successfully create a new hub.Select the Tags tab to add tags.
Select Review + create > Create.
Manage your hub from the Azure portal
Manage access control
You can add and remove users from the Azure AI Foundry portal management center. Both the hub and projects within the hub have a Users entry in the left-menu that allows you to add and remove users. When adding users, you can assign them built-in roles.
For custom role assignments, use Access control (IAM) within the Azure portal. Learn more about hub role-based access control.
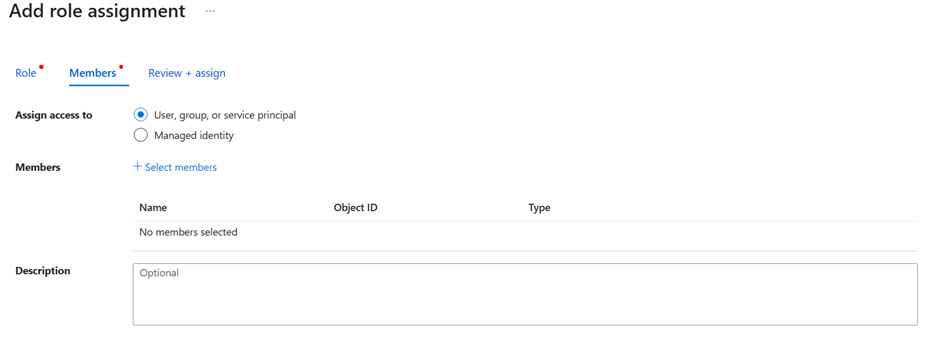
To add grant users permissions from the Azure portal:
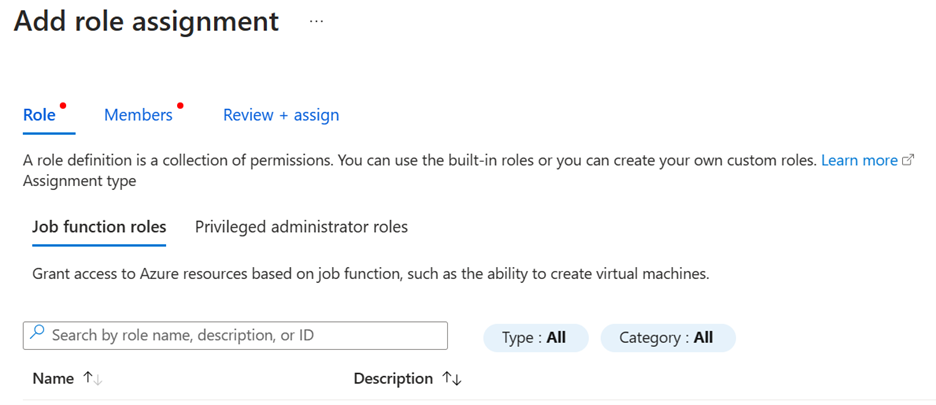
Select + Add to add users to your hub.
Select the Role you want to assign.
Select the Members you want to give the role to.
Review + assign. It can take up to an hour for permissions to be applied to users.
Networking
Hub networking settings can be set during resource creation or changed in the Networking tab in the Azure portal view. Creating a new hub invokes a Managed Virtual Network. This streamlines and automates your network isolation configuration with a built-in Managed Virtual Network. The Managed Virtual Network settings are applied to all projects created within a hub.
At hub creation, select between the networking isolation modes: Public, Private with Internet Outbound, and Private with Approved Outbound. To secure your resource, select either Private with Internet Outbound or Private with Approved Outbound for your networking needs. For the private isolation modes, a private endpoint should be created for inbound access. For more information on network isolation, see Managed virtual network isolation. To create a secure hub, see Create a secure hub.
At hub creation in the Azure portal, creation of associated Azure AI services, Storage account, Key vault (optional), Application insights (optional), and Container registry (optional) is given. These resources are found on the Resources tab during creation.
To connect to Azure AI services (Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Search, and Azure AI Content Safety) or storage accounts in Azure AI Foundry portal, create a private endpoint in your virtual network. Ensure the public network access (PNA) flag is disabled when creating the private endpoint connection. For more about Azure AI services connections, see Virtual networks for Azure AI Services. You can optionally bring your own Azure AI Search, but it requires a private endpoint connection from your virtual network.
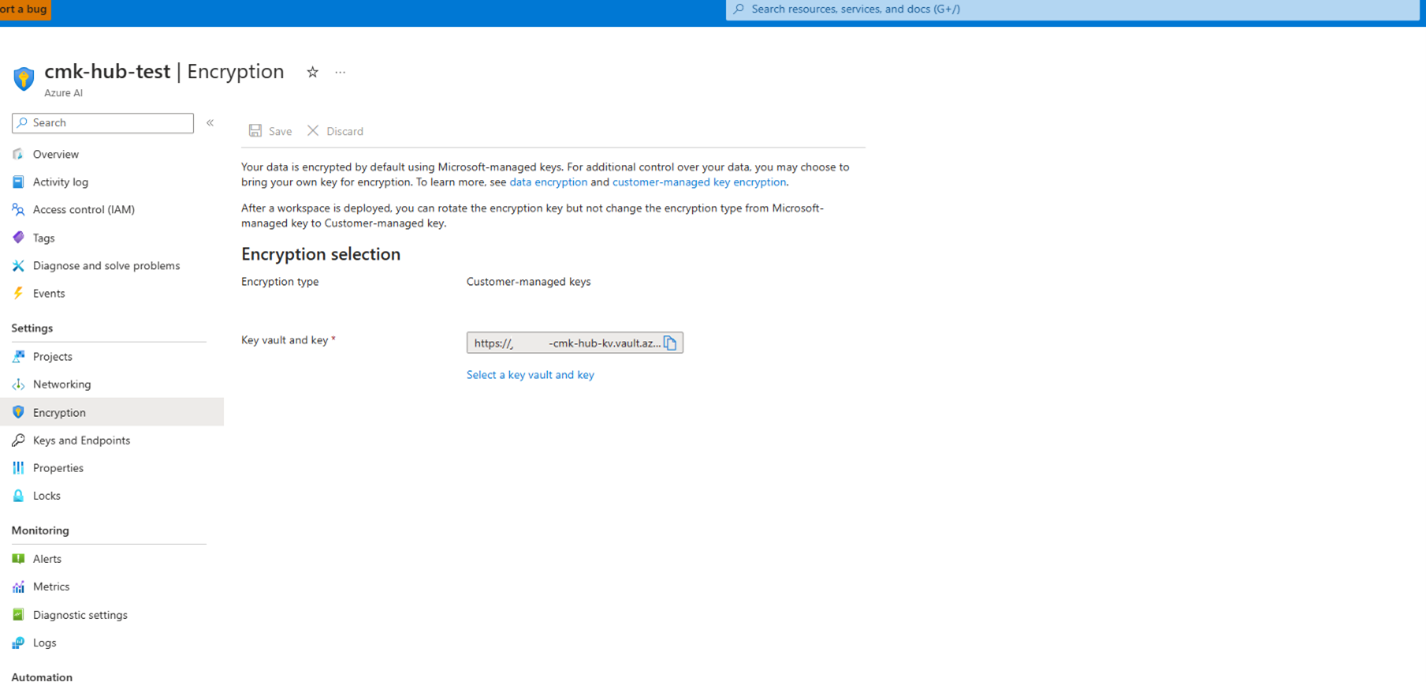
Encryption
Projects that use the same hub, share their encryption configuration. Encryption mode can be set only at the time of hub creation between Microsoft-managed keys and Customer-managed keys (CMK).
From the Azure portal view, navigate to the encryption tab, to find the encryption settings for your hub. For hubs that use CMK encryption mode, you can update the encryption key to a new key version. This update operation is constrained to keys and key versions within the same Key Vault instance as the original key.
Update Azure Application Insights and Azure Container Registry
To use custom environments for Prompt Flow, you're required to configure an Azure Container Registry for your hub. To use Azure Application Insights for Prompt Flow deployments, a configured Azure Application Insights resource is required for your hub. Updating the workspace-attached Azure Container Registry or Application Insights resources might break lineage of previous jobs, deployed inference endpoints, or your ability to rerun earlier jobs in the workspace. After association with an Azure AI Foundry hub, Azure Container Registry and Application Insights resources can't be disassociated (set to null).
You can use the Azure portal, Azure SDK/CLI options, or the infrastructure-as-code templates to update both Azure Application Insights and Azure Container Registry for the hub.
You can configure your hub for these resources during creation or update after creation.
To update Azure Application Insights from the Azure portal, navigate to the Properties for your hub in the Azure portal, then select Change Application Insights.
Choose how credentials are stored
Select scenarios in Azure AI Foundry portal store credentials on your behalf. For example, when you create a connection in Azure AI Foundry portal to access an Azure Storage account with stored account key, access Azure Container Registry with admin password, or when you create a compute instance with enabled SSH keys. No credentials are stored with connections when you choose Microsoft Entra ID identity-based authentication.
You can choose where credentials are stored:
Your Azure Key Vault: This requires you to manage your own Azure Key Vault instance and configure it per hub. It gives you more control over secret lifecycle, for example, to set expiry policies. You can also share stored secrets with other applications in Azure.
Microsoft-managed credential store (preview): In this variant Microsoft manages an Azure Key Vault instance on your behalf per hub. No resource management is needed on your side and the vault doesn't show in your Azure subscription. Secret data lifecycle follows the resource lifecycle of your hubs and projects. For example, when a project's storage connection is deleted, its stored secret is deleted as well.
After your hub is created, it isn't possible to switch between Your Azure Key Vault and using a Microsoft-managed credential store.
Delete an Azure AI Foundry hub
To delete a hub from Azure AI Foundry, select the hub and then select Delete hub from the Hub properties section of the page.
Note
You can also delete the hub from the Azure portal.
Deleting a hub deletes all associated projects. When a project is deleted, all nested endpoints for the project are also deleted. You can optionally delete connected resources; however, make sure that no other applications are using this connection. For example, another Azure AI Foundry deployment might be using it.