Use a virtual network to secure inbound or outbound traffic for Azure API Management
APPLIES TO: Developer | Basic | Standard | Standard v2 | Premium
By default your API Management is accessed from the internet at a public endpoint, and acts as a gateway to public backends. API Management provides several options to secure access to your API Management instance and to backend APIs using an Azure virtual network. Available options depend on the service tier of your API Management instance.
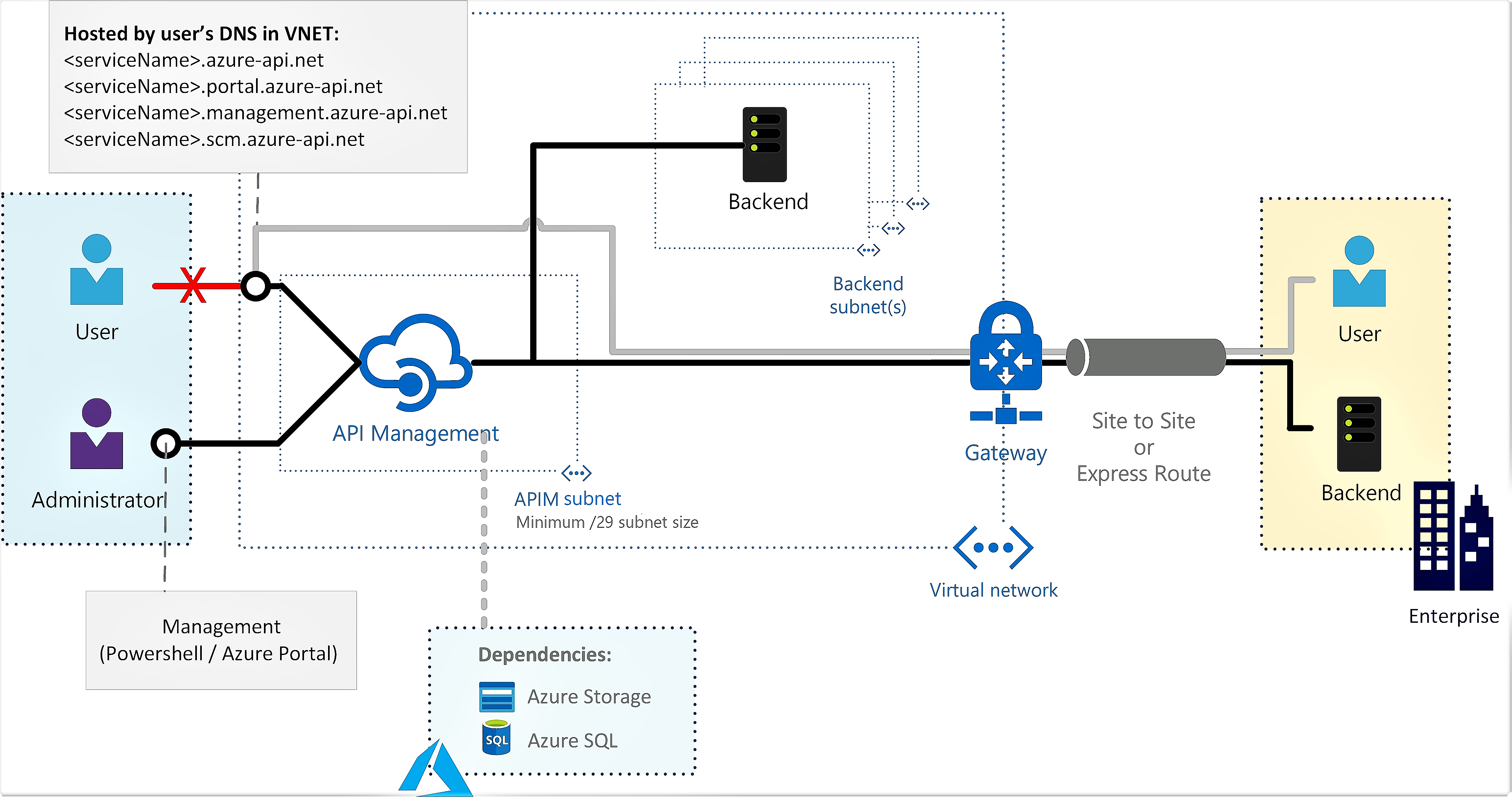
Injection of the API Management instance into a subnet in the virtual network, enabling the gateway to access resources in the network.
You can choose one of two injection modes: external or internal. They differ in whether inbound connectivity to the gateway and other API Management endpoints is allowed from the internet or only from within the virtual network.
Integration of your API Management instance with a subnet in a virtual network so that your API Management gateway can make outbound requests to API backends that are isolated in the network.
Enabling secure and private inbound connectivity to the API Management gateway using a private endpoint.
The following table compares virtual networking options. For more information, see later sections of this article and links to detailed guidance.
| Networking model | Supported tiers | Supported components | Supported traffic | Usage scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual network injection - external | Developer, Premium | Developer portal, gateway, management plane, and Git repository | Inbound and outbound traffic can be allowed to internet, peered virtual networks, Express Route, and S2S VPN connections. | External access to private and on-premises backends |
| Virtual network injection - internal | Developer, Premium | Developer portal, gateway, management plane, and Git repository | Inbound and outbound traffic can be allowed to peered virtual networks, Express Route, and S2S VPN connections. | Internal access to private and on-premises backends |
| Outbound integration | Standard v2 | Gateway only | Outbound request traffic can reach APIs hosted in a delegated subnet of a virtual network. | External access to private and on-premises backends |
| Inbound private endpoint | Developer, Basic, Standard, Premium | Gateway only (managed gateway supported, self-hosted gateway not supported) | Only inbound traffic can be allowed from internet, peered virtual networks, Express Route, and S2S VPN connections. | Secure client connection to API Management gateway |
Virtual network injection
With VNet injection, deploy ("inject") your API Management instance in a subnet in a non-internet-routable network to which you control access. In the virtual network, your API Management instance can securely access other networked Azure resources and also connect to on-premises networks using various VPN technologies. To learn more about Azure VNets, start with the information in the Azure Virtual Network Overview.
You can use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, Azure Resource Manager templates, or other tools for the configuration. You control inbound and outbound traffic into the subnet in which API Management is deployed by using network security groups.
For detailed deployment steps and network configuration, see:
- Deploy your API Management instance to a virtual network - external mode.
- Deploy your API Management instance to a virtual network - internal mode.
- Network resource requirements for API Management injection into a virtual network.
Access options
Using a virtual network, you can configure the developer portal, API gateway, and other API Management endpoints to be accessible either from the internet (external mode) or only within the VNet (internal mode).
External - The API Management endpoints are accessible from the public internet via an external load balancer. The gateway can access resources within the VNet.
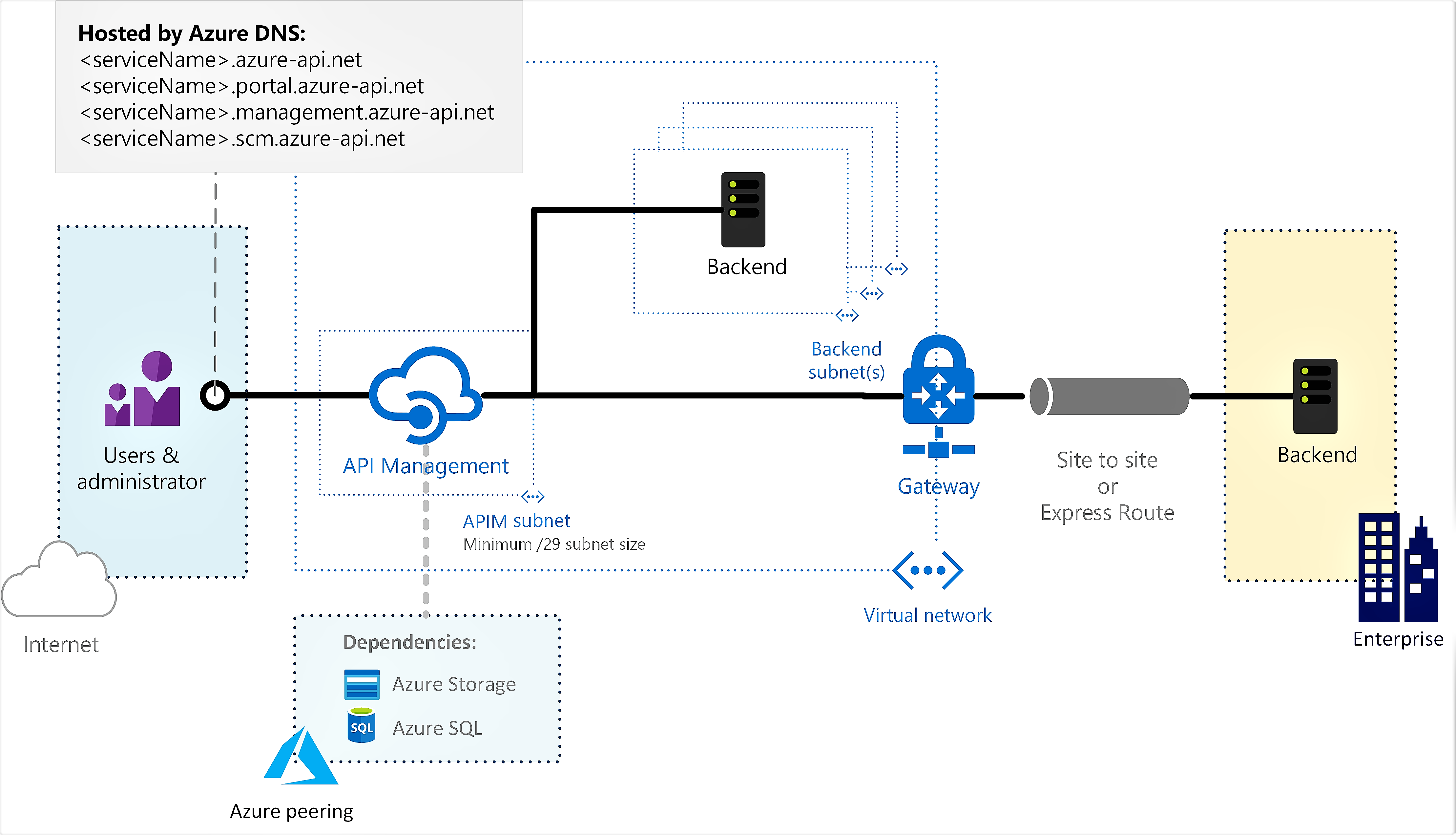
Use API Management in external mode to access backend services deployed in the virtual network.
Internal - The API Management endpoints are accessible only from within the VNet via an internal load balancer. The gateway can access resources within the VNet.
Use API Management in internal mode to:
- Make APIs hosted in your private datacenter securely accessible by third parties by using Azure VPN connections or Azure ExpressRoute.
- Enable hybrid cloud scenarios by exposing your cloud-based APIs and on-premises APIs through a common gateway.
- Manage your APIs hosted in multiple geographic locations, using a single gateway endpoint.
Outbound integration
The Standard v2 tier supports VNet integration to allow your API Management instance to reach API backends that are isolated in a single connected VNet. The API Management gateway, management plane, and developer portal remain publicly accessible from the internet.
Outbound integration enables the API Management instance to reach both public and network-isolated backend services.
For more information, see Integrate an Azure API Management instance with a private VNet for outbound connections.
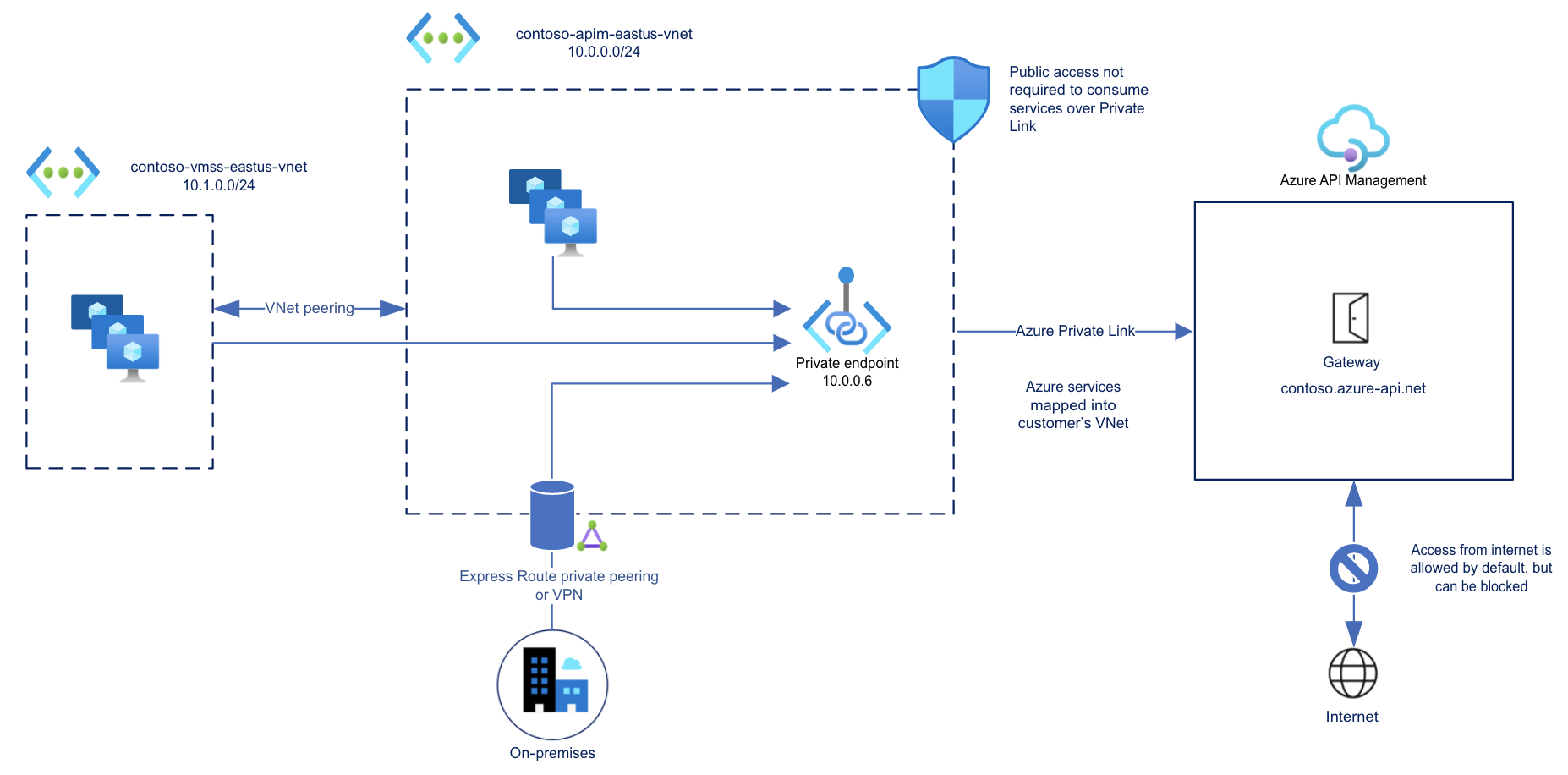
Inbound private endpoint
API Management supports private endpoints for secure inbound client connections to your API Management instance. Each secure connection uses a private IP address from your virtual network and Azure Private Link.
With a private endpoint and Private Link, you can:
Create multiple Private Link connections to an API Management instance.
Use the private endpoint to send inbound traffic on a secure connection.
Use policy to distinguish traffic that comes from the private endpoint.
Limit incoming traffic only to private endpoints, preventing data exfiltration.
Important
You can only configure a private endpoint connection for inbound traffic to the API Management instance. Currently, outbound traffic isn't supported.
You can use the external or internal virtual network model to establish outbound connectivity to private endpoints from your API Management instance.
To enable inbound private endpoints, the API Management instance can't be injected into an external or internal virtual network.
For more information, see Connect privately to API Management using an inbound private endpoint.
Advanced networking configurations
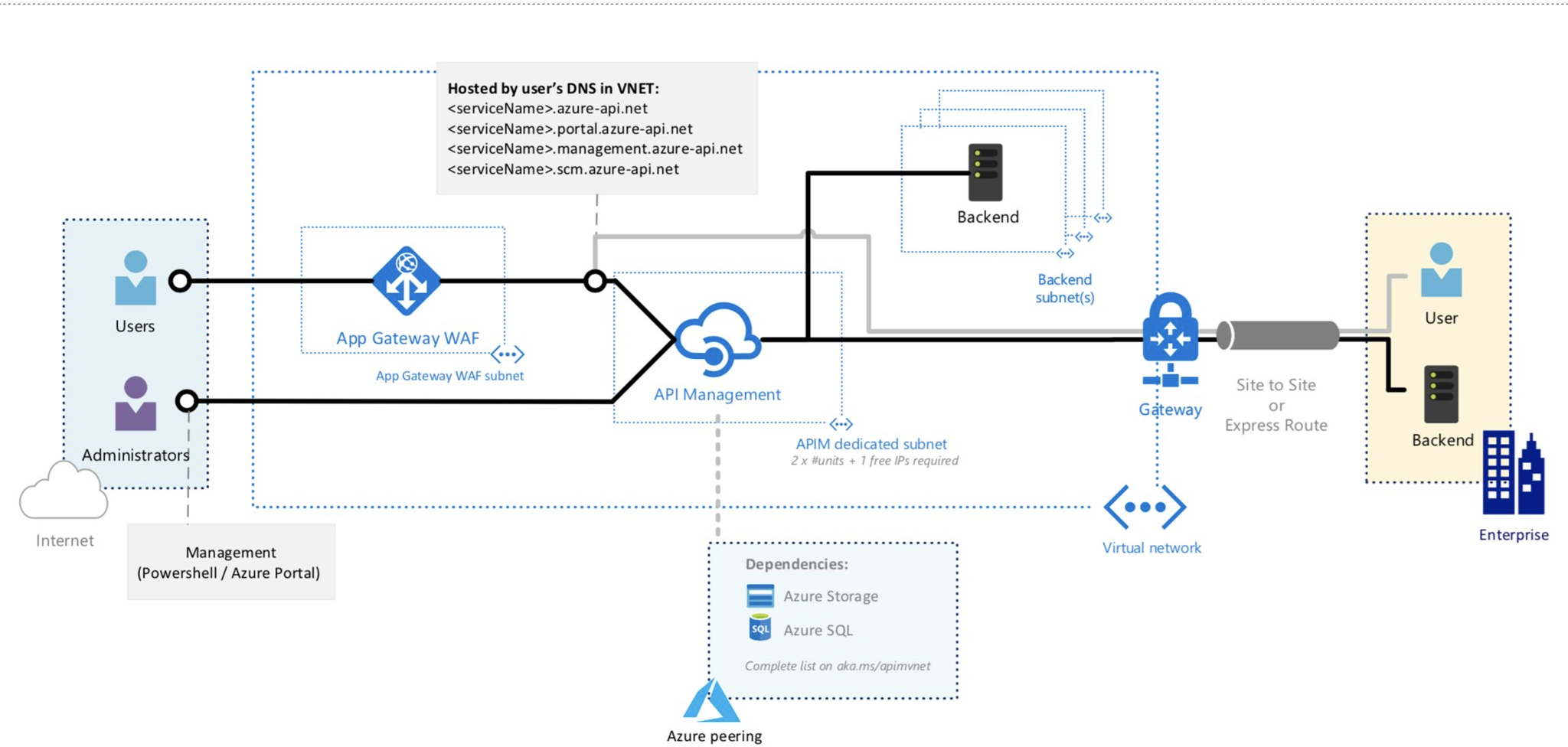
Secure API Management endpoints with a web application firewall
You may have scenarios where you need both secure external and internal access to your API Management instance, and flexibility to reach private and on-premises backends. For these scenarios, you may choose to manage external access to the endpoints of an API Management instance with a web application firewall (WAF).
One example is to deploy an API Management instance in an internal virtual network, and route public access to it using an internet-facing Azure Application Gateway:
For more information, see Deploy API Management in an internal virtual network with Application Gateway.
Next steps
Learn more about:
Virtual network configuration with API Management:
- Deploy your Azure API Management instance to a virtual network - external mode.
- Deploy your Azure API Management instance to a virtual network - internal mode.
- Connect privately to API Management using a private endpoint
- Integrate an Azure API Management instance with a private VNet for outbound connections
- Defend your Azure API Management instance against DDoS attacks
Related articles: