About Kanban boards
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
A Kanban board in Azure DevOps is a visual tool used to manage work items and track progress in a project. It provides a clear overview of tasks, their status, and their flow through different stages. Teams can use Kanban boards to visualize work, limit work in progress, and optimize their workflow. Each work item is represented as a card on the board, and columns represent different stages, such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." As work progresses, cards move across columns, allowing teams to monitor and improve their efficiency. Kanban boards are commonly used in agile methodologies and are essential for effective project management.
Both Kanban boards and Taskboards support visualizing the flow of work and monitoring metrics to optimize that flow. Kanban boards track requirements are sprint-independent, and provide a cumulative flow chart for monitoring progress. Each sprint is associated with a Taskboard that supports tracking tasks defined for the sprint. You can monitor progress through capacity charts and the sprint burndown chart. For more information, see Update and monitor your Taskboard.
Note
Kanban is a Japanese word that literally translates to "signboard." In this article, we focus on Kanban boards, but moving forward, we refer the them as "boards."
Product and portfolio boards
Each product and portfolio backlog corresponds to a board. These boards are associated with teams and display work items based on the selected area and iteration paths. For more information, see Define and configure iterations.
To enhance consistent delivery of high-quality software, Kanban emphasizes two key practices. First, visualize the flow of work by mapping your team's workflow stages and configuring the board appropriately. Second, constrain work in progress, by setting work-in-progress (WIP) limits. With these practices in place, you can track progress and monitor metrics to reduce lead or cycle time. Get started by exploring how to use your board.

Kanban concepts and terms
The following table outlines terms and tools commonly used for tracking work with Kanban boards and Kanban methods.
| Concept or term | Description |
|---|---|
| Blocker | An issue that prevents work from progressing. You can highlight work that is blocked by using tags and changing the card color. For more information, see Customize cards, Define style rules to highlight cards. |
| Bottleneck | A constraint in the system that limits the flow of work. Identifying bottlenecks makes it easier to reduce their effect and provides a mechanism for controlling work flowing through the process. For more information, see Manage columns, Identify bottlenecks. |
| Card reordering | Card reordering lets you change the priority order and forces cards to maintain the backlog priority when you drag and drop them on the board. For more information, see Reorder cards. |
| Cumulative flow diagram (CFD) | The in-context CFD report shows the count of items in each column for the past 30 weeks or less. From this chart, you can gain an idea of the amount of work in progress and lead time. Work in progress counts unfinished requirements. For more information, see Cumulative flow, lead time, and cycle time guidance. |
| Cycle time | Cycle time is the time calculated for a work item from first entering an In Progress category state to entering a Completed state category. For more information, see Cumulative flow, lead time, and cycle time guidance. You can gain valuable metrics and visualize the cycle time for a team and a configurable time period by adding the Cycle Time widget to the dashboard. |
| Definition of done | Criteria that a team specifies for each stage of work to share and standardize on what makes up work being done at that stage. |
| Kanban board | An interactive, electronic sign board that supports visualization of the flow of work from concept to completion and lean methods. Azure DevOps provides a board for each product and portfolio backlog. For more information, see Board basics and Board features and epics and Track work in swimlanes. |
| Columns | A column maps to a stage of work. The default columns map to the workflow states of the work item types that appear on the board. You configure the columns to map workflow states of your team. For more information, see Map the flow. |
| Lead time | Lead time is the time calculated for a work item from first entering a Proposed category state to entering a Completed state category. For more information, see Cumulative flow, lead time, and cycle time guidance. You can gain valuable metrics and visualize the lead time for a team and a configurable time period by adding the Lead Time widget to the dashboard. |
| Product backlog | An interactive list of work items that corresponds to a team's project plan or roadmap for what the team plans to deliver. The product backlog supports prioritizing work, forecasting work by sprints, and quickly linking work to portfolio backlog items. You can define your backlog items and then manage their status using the board. Each team can customize its product backlog. For more information, see Create your backlog. |
| Product backlog item | A type of work item that defines the applications, requirements, and elements that teams plan to create. Product owners typically define and stack rank product backlog items, which are defined with the Scrum process. For more information, see Scrum process work item types and workflow. |
| Portfolio backlog | An interactive list of work items, similar to the product backlog that supports organizing or grouping work under features epics, or scenarios. Portfolio backlogs work similarly to product backlogs in that you can prioritize work and view the tree hierarchy of work. For more information, see Define features and epics. |
| Swimlanes | A swimlane is a configurable row on a board, used to support different service class levels of work. For more information, see Speed up work with swimlanes. |
| Split columns | The Split columns feature lets your team implement a pull mechanism within the workflow process. Without split columns, teams push work forward, to signal that they completed their stage of work. However, pushing it to the next stage doesn't necessarily mean that a team member immediately starts work on that item. With split columns, your team knows exactly how many items sit idle, waiting for work to begin. For more information, see Manage columns. |
| Task checklists | A task is a type of work item used to track work required to complete a user story or product backlog item. You can add tasks from your board that appear as a checklist of work to be done. As you complete a task, you can update its status by checking the checkbox for the task. For more information, see Add tasks or child items as checklists. |
| Task switching | Task switching, also referred to as context switching or multitasking, is when a team member shifts their attention among different tasks. Limiting task switching can allow a person to work more efficiently by minimizing the amount of time required to redirect cognitive function to a new activity. |
| User story | A type of work item that defines the applications, requirements, and elements that teams plan to create. Product owners typically define and stack rank user stories. User story is defined with the Agile process. For more information, see Agile process work item types and workflow. |
| Work in progress (WIP) | Work that is started but isn't done or completed. |
| WIP limit | A WIP limit is a constraint that a team applies to one or more workflow stages to help prevent potential bottlenecks that hinder the continuous flow of work in the system. For more information, see Work in Progress limits. |
| Workflow states | Workflow states are defined for each work item type to support tracking the status of a work item, from its creation to its completion. These states define the workflow process: actions, steps, or stages that a piece of work goes through from inception to completion. The State and Reason fields differ depending on the work item type and process selected for the project. For more information, see Customize the workflow. |
| Workflow state categories | State categories determine how the board treats each workflow state. The state categories used by the backlogs are Proposed, In Progress, Resolved, and Completed. For more information, see Workflow states and state categories. |
For more information, see the following articles:
Use board controls
You can quickly switch from the backlog view to the board view using the Backlog and Board links. Use the following icons to enable other user interface features.
| Control | Function |
|---|---|
| Backlog | Switch to backlog view |
| Board | Switch to board view |
| Filter by keywords, tags, or fields | |
| Customize the board and configure team settings: Cards | Card reordering | Columns | Swimlanes | CFD chart | Backlogs | Working with bugs |
|
| Enter or exit full screen mode |
Open keyboard shortcuts
Enter ? to open the board keyboard shortcuts. The following image isn't a comprehensive representation.

For more information, see Keyboard shortcuts for Azure DevOps and Team Explorer.
Configure & customize your board
Your board is highly configurable to support your team's workflow. Each team can configure each board with the following tasks:
Configure boards
Configure card displays
Along with these team configurations, you can customize your project by adding or modifying work item types, the workflow, and add customized portfolio backlogs and boards.
Can you define a board configuration that multiple teams can subscribe to?
Answer: No. Each team controls their own team settings and board configurations.
Update work item status
Once you configure your board, you can add work items directly to the board. Update the status of work by dragging a card to another column on the board. You can even change the order of items as you move a card to a new column. For more information, see Workflow states and state categories.

Display leaf node work items
You can create a hierarchy of backlog items, tasks, and bugs. We don't recommend that you create same-category hierarchies. In other words, don't create parent-child links among work items of the same type, such as story-story, bug-bug, or task-task.
The last node in a same-category hierarchy might only appear on boards, sprint backlogs, and Taskboards. For example, if you link items within a same-category hierarchy that is four levels deep, only the items at the fourth level appear on the board, sprint backlog, and taskboard.
Rather than nest requirements, bugs, and tasks, we recommend that you maintain a flat list. Create parent-child links one level deep between items that belong to a different category. For more information, see Troubleshoot reordering and nesting issues.
Reorder and reparent work items
All backlogs and boards support drag-and-drop to reorder and reparent work items. Updates made to one team's backlogs and boards are reflected in other team backlogs and boards that share the same area path. You might need to refresh the page to view the changes.
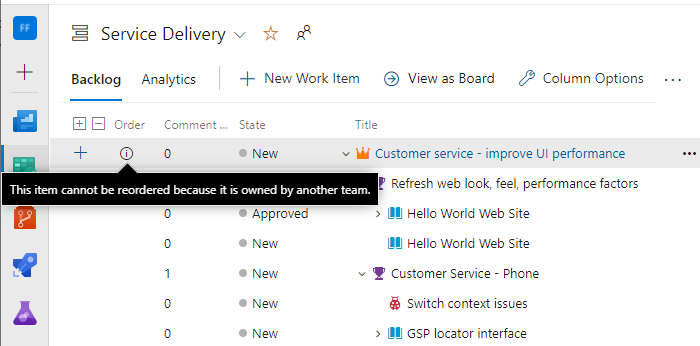
You can only use drag-and-drop to reorder or reparent work items assigned to area paths selected for your team. When the Parents view option is enabled, work items might appear on your backlog that your team doesn't own. Anything that appears with the ![]() information icon can't be reordered nor reparented as another team owns it.
information icon can't be reordered nor reparented as another team owns it.
Update columns
Each team can customize the board columns and swimlanes. The values that get assigned to board fields might differ from what you expect when another team updates the work item from a different board.
Even if the management team and the feature teams configure their board columns with identical workflow mapping, one team's board items aren't reflected on another team's board. Only when the work item moves to a column that maps to a workflow state does the card column reflect the same on all boards.
For more information, see Manage columns.
Provide permissions and access
As a member added to the Contributors group of a project, you can use most features provided under Boards or Work. Users with Basic access have full access to all features. Users with Stakeholder access are limited to certain features.
For more information, see Set permissions and access for work tracking and Stakeholder access quick reference. To add users to a project, see Add users to a project or team.
Customize your project and board inheritance
If you require more than three board levels, you can add additional ones. For more information, see Customize your backlogs or boards for a process.
You can also add or modify the fields defined for a work item type (WIT), add a custom WIT, or modify the workflow. For more information, see Customize an inheritance process.