Manage Microsoft Entra roles in Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
This article describes how you can create a Microsoft Entra ID enabled database roles within an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
Note
This guide assumes you already enabled Microsoft Entra authentication on your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. See How to Configure Microsoft Entra authentication
If you like to learn about how to create and manage Azure subscription users and their privileges, you can visit the Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) article or review how to customize roles.
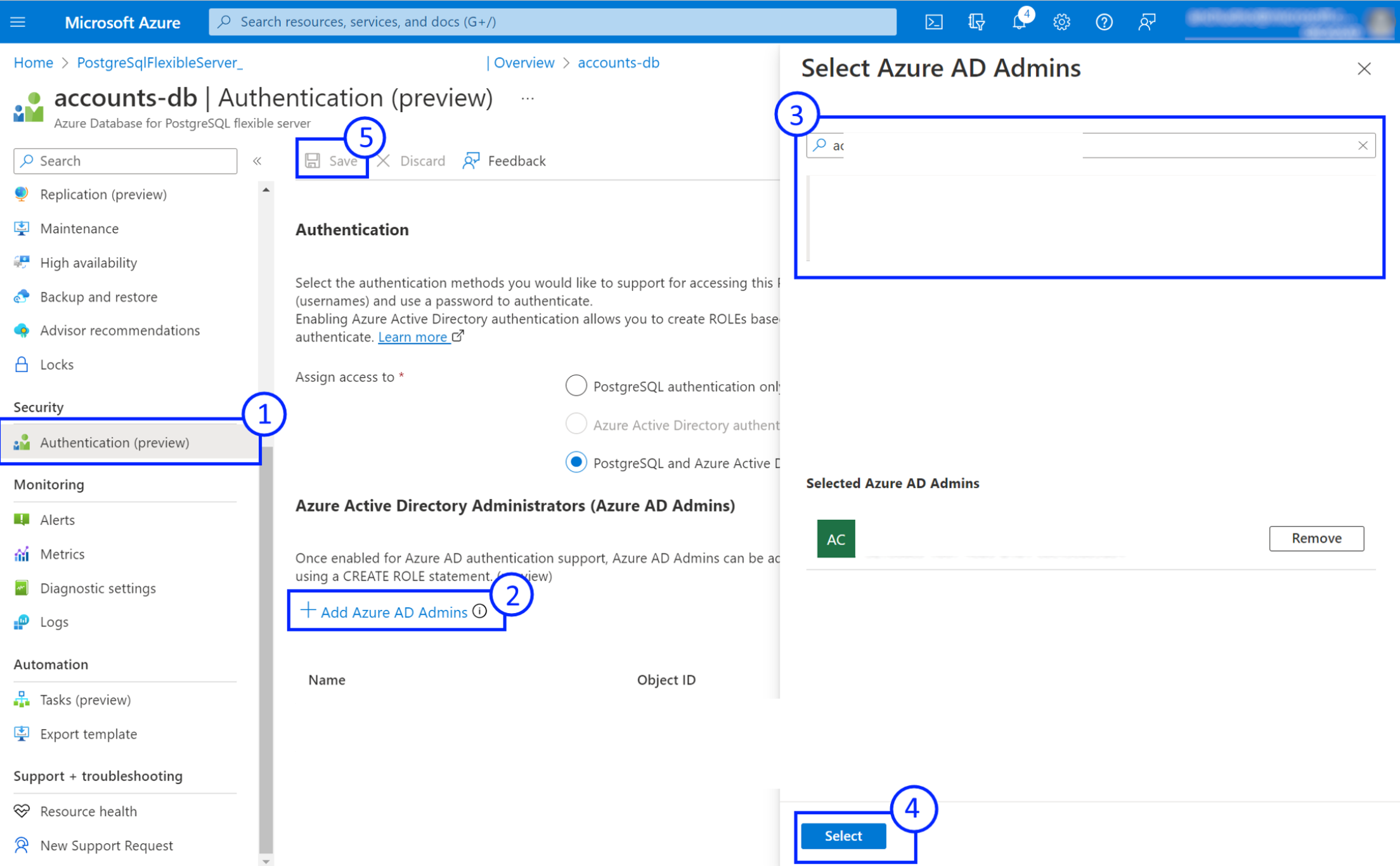
Create or delete Microsoft Entra administrators using Azure portal or Azure Resource Manager (ARM) API
- Open the Authentication page for your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance in the Azure portal.
- To add an administrator - select Add Microsoft Entra Admin and select a user, group, application, or a managed identity from the current Microsoft Entra tenant.
- To remove an administrator - select Delete icon for the one to remove.
- Select Save and wait for provisioning operation to completed.
Note
Support for Microsoft Entra Administrators management via Azure SDK, az cli and Azure PowerShell is coming soon.
Manage Microsoft Entra roles using SQL
Once the first Microsoft Entra administrator is created from the Azure portal or API, you can use the administrator role to manage Microsoft Entra roles in your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
We recommend getting familiar with Microsoft identity platform for best use of Microsoft Entra integration with Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Principal types
Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server internally stores mapping between PostgreSQL database roles and unique identifiers of AzureAD objects. Each PostgreSQL database role can be mapped to one of the following Microsoft Entra object types:
- User - Including Tenant local and guest users.
- Service Principal. Including Applications and Managed identities
- Group When a PostgreSQL role is linked to a Microsoft Entra group, any user or service principal member of this group can connect to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance with the group role.
List Microsoft Entra roles using SQL
pg_catalog.pgaadauth_list_principals(isAdminValue boolean)
Arguments
isAdminValue
boolean when true returns Admin users. When falsereturns all Microsoft Entra users, including Microsoft Entra admins and non-admins.
Return type
TABLE(rolname name, principalType text, objectId text, tenantId text, isMfa integer, isAdmin integer) a table with the following schema:
rolnamethe name of the role in PostgreSQL.principalTypethe type of principal in Microsoft Entra ID. It can beuser,group, orservice.objectIdthe identifier of the object in Microsoft Entra ID for this principal.tenantIdthe identifier of the tenant hosting this principal in Microsoft Entra ID.isMfareturns a value of1if the user/role has MFA enforced.isAdminreturns a value of1if the user/role is an administrator in PostgreSQL.
Create a user/role using Microsoft Entra principal name
pg_catalog.pgaadauth_create_principal(roleName text, isAdmin boolean, isMfa boolean)
Arguments
roleName
text name of the role to be created. This must match the name of the Microsoft Entra principal.
- For users use User Principal Name from Profile. For guest users, include the full name in their home domain with #EXT# tag.
- For groups and service principals use display name. The name must be unique in the tenant.
isAdmin
boolean when true it creates a PostgreSQL admin user (member of azure_pg_admin role and with CREATEROLE and CREATEDB permissions). When false it creates a regular PostgreSQL user.
isMfa
boolean when true it enforces multifactor authentication for this PostgreSQL user.
Important
The isMfa flag tests the mfa claim in the Microsoft Entra ID token, but it doesn't impact the token acquisition flow. For example, if the tenant of the principal is not configured for multifactor authentication, it will prevent the use of the feature. And if the tenant requires multifactor authentication for all tokens, it will make this flag useless.
Return type
text single value that consists of a string "Created role for roleName", where roleName is the argument passed for the roleName parameter.
Drop a role using Microsoft Entra principal name
Remember that any Microsoft Entra role that is created in PostgreSQL must be dropped using a Microsoft Entra Admin. If you use a regular PostgreSQL admin to drop an Entra role then it will result in an error.
DROP ROLE rolename;
Create a role using Microsoft Entra object identifier
pg_catalog.pgaadauth_create_principal_with_oid(roleName text, objectId text, objectType text, isAdmin boolean, isMfa boolean)
Arguments
roleName
text name of the role to be created.
objectId
text unique object identifier of the Microsoft Entra object.
- For users, groups, and managed identities, the objectId can be found by searching for the object name in Microsoft Entra ID page in Azure portal. See this guide as example
- For groups and service principals use display name. The name must be unique in the tenant.
- For applications, the objectId of the corresponding Service Principal must be used. In Azure portal the required objectId can be found on Enterprise Applications page in Azure portal.
objectType
text the type of Microsoft Entra object to link to this role. It can be user, group, or service.
isAdmin
boolean when true it creates a PostgreSQL admin user (member of azure_pg_admin role and with CREATEROLE and CREATEDB permissions). When false it creates a regular PostgreSQL user.
isMfa
boolean when true it enforces multifactor authentication for this PostgreSQL user.
Important
The isMfa flag tests the mfa claim in the Microsoft Entra ID token, but it doesn't impact the token acquisition flow. For example, if the tenant of the principal is not configured for multifactor authentication, it will prevent the use of the feature. And if the tenant requires multifactor authentication for all tokens, it will make this flag useless.
Return type
text single value that consists of a string "Created role for roleName", where roleName is the argument passed for the roleName parameter.
Enable Microsoft Entra authentication for an existing PostgreSQL role using SQL
Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server uses security labels associated with database roles to store their corresponding Microsoft Entra ID mapping.
You can use the following SQL to assign the required security label to map it to a Microsoft Entra object:
SECURITY LABEL for "pgaadauth" on role "<roleName>" is 'aadauth,oid=<objectId>,type=<objectType>,admin';
Arguments
roleName
text name of an existing PostgreSQL role to which Microsoft Entra authentication needs to be enabled.
objectId
text unique object identifier of the Microsoft Entra object.
objectType
text it can be set to user, group, or service (for applications or managed identities connecting under their own service credentials).
admin
text it can be present or absent. Users/roles for which this part is present in their security label, can manage other Microsoft Entra ID roles.
Next steps
- Review the overall concepts for Microsoft Entra authentication with Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server