Contribute to the Help for Dynamics 365 Business Central
This article describes how to work with our GitHub repos and contribute to the Help for Business Central. You can also find guidance in the Docs Contributor Guide.
Get started with GitHub
To join Microsoft in the world of GitHub and Markdown, there are terminology and tools to get used to. The following list outlines the main steps, but you can find more content, tools, and ideas in the GitHub documentation and other forums.
We have two GitHub repos that you can contribute to:
MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs
This repo contains the Business Central business functionality content that is published here.MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-devitpro-pb
This repo contains the Business Central developer and IT Pro content that is published here.
In the following, we use the MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs repo as an example.
Fork the repo you want to contribute to.
You can't work directly in the Business Central repos in the MicrosoftDocs GitHub org. The first thing you need to do is create a fork of the MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs repo under your GitHub account. A fork is a copy of this repo that lets you work freely on the content without affecting the MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs repo.
Alternatively, you can clone the Microsoft repo. This is useful if you don't intend to customize Microsoft's content, for example. But in many cases, forking the repo is more preferable.
Learn more at Set up your GitHub account and Set up Git repository locally for documentation in the Docs Authoring Guide.
Tip
You aren't required to make your GitHub repos public. When you fork a public repo, you can specify whether the repo is public, private, or available only to specific GitHub accounts.
Install GitHub Desktop (optional) and clone your forked MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs repo.
GitHub Desktop makes is easy to work and collaborate with repos locally from your own desktop. Learn more at GitHub Desktop.
Get hold of your favorite Markdown editor, and start making changes.
The help content is stored in the business-central folder of the repo. Articles use a syntax for formatting text called MarkDig Flavored Markdown, which is CommonMark compliant. To learn more about working with Markdown, see Getting started with writing and formatting on GitHub.
If you want to work locally, you can edit using any text editor. Just save the file as an .md type. Here are two good tools that provide you with some nice features, including a preview of how the content renders in HTML:
-
Add the Docs Authoring Pack for Visual Studio Code, which gives you spell checker, Markdown validation, and many other productivity features
-
Atom has spell check and is good for managing many files
-
Internally at Microsoft, some authors use Visual Studio Code, others use Atom, and for light-weight work, we tend to just edit the content in the browser. You can find more guidance for how to get started with Markdown in the Docs Contributor Guide. This guide is published by the team that built the learn.microsoft.com site where the Business Central team publishes their docs.
For inspiration for how to build your own help website, go to Quick Start in the DocFx user assistance, or visit the Azure App Service documentation.
For tips and tricks about writing in markdown, go to the Authoring Guide.
Translate the content
You can use the Dynamics 365 Translation Service (DTS) to translate your content into other languages. The service is hosted in Lifecycle Services and currently supports translation of content in Word documents and HTML files. Learn more at Translate documentation files.
Contributing
A benefit of GitHub is the ability for you to contribute to the core content that the Microsoft team provides for Business Central. There's good advice and best practices published in the Microsoft Docs contributor guide. But this section provides information about how to apply that advice to the Business Central content.
For example, you might have a new article that you think would be beneficial, or you might have a correction to an existing article. If you would like to contribute to the Business Central content on the Microsoft Docs website, you create a pull request from your repo to the target repo. The Microsoft team then reviews the request and includes the changes as appropriate.
Get started
If you want to suggest a minor (or major) change to an existing article, follow these steps:
Find the published article, such as Using OData to Return or Obtain a JSON Document.
In the top right corner of the article, choose the Edit button.
Choosing the button takes you to the source file on GitHub. In this example, that's https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-devitpro/blob/main/dev-itpro/webservices/return-obtain-json-document.md.
Note
If you aren't signed in with a GitHub account, you'll be prompted to sign in or create a new account. You can't contribute to the Business Central content without a GitHub account.
In the top right corner of the Markdown file, choose the pencil icon. Depending on who you are, you're taken to a fork of Microsoft's repo, or you're able to work in a branch at Microsoft's repo.
Make the relevant changes (and remember to save them!).
Submit a pull request to the source repo.
You have something like this configuration in a browser:
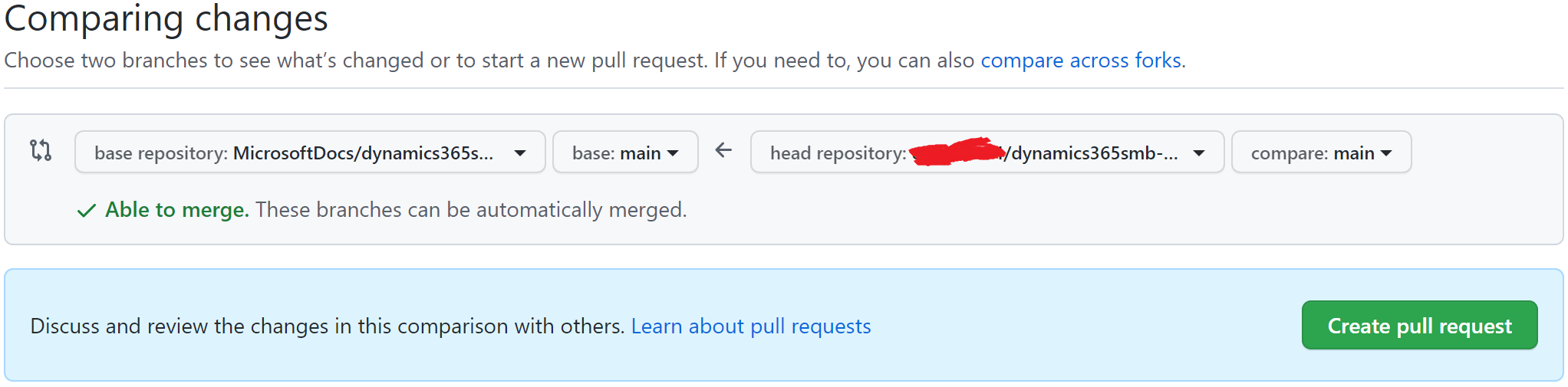
Learn more at Quick edits to existing documents.
If you come across errors or omissions in the developer reference content, you can submit a PR to add, for example, a code example, or a note. See more in the Autogenerated content in the developer and IT Pro content.
Get thorough
If you're going to contribute at a greater scale, for example as part of a community project that adds code examples to a bunch of technical walkthroughs, you'll probably prefer to work locally on your device, based on a clone of your fork. Go to Install content authoring tools in the Microsoft Docs Contributor Guide for recommended tools and processes. The Microsoft team typically follows that workflow.
To create a pull request to the MicrosoftDocs/dynamics365smb-docs repo by using GitHub Desktop, perform the following steps:
Commit the changes to your fork that you want to include in the pull request.
Choose Sync to push the changes up to your repo on GitHub.
When the sync is completed, choose Pull Request, make sure that the pull request points at the origin/main branch, and then choose Pull Request.
You'll have something like this configuration in a browser:

Tip
If you want to request brand new content, as opposed to contributing, we ask you to submit a request of type Documentation at https://aka.ms/bcideas.
Autogenerated content in the developer and IT Pro content
Some of the content in the developer and IT Pro help is autogenerated from the product code. This content reflects the source code at the time of the release. You can tell that the content is autogenerated when it contains a note like illustrated with the CommitBehavior option type in the CommitBehavior option type example. The autogenerated content has a (START>DO_NOT_EDIT) and a (IMPORTANT: END>DO_NOT_EDIT) section, which contains content that is overwritten when the autogeneration tooling is run. Any change needed to the content should be made in the source code, not in the Markdown file. If you come across an error in the autogenerated content, you can submit an issue on the GitHub repo instead.
But, if you want to add a note, a tip, a remark, or an example, you can do that in the Markdown file after the (IMPORTANT: END>DO_NOT_EDIT) section. This is illustrated in the Example of adding a note to autogenerated content.
CommitBehavior option type example
[//]: # (START>DO_NOT_EDIT)
[//]: # (IMPORTANT:Do not edit any of the content between here and the END>DO_NOT_EDIT.)
[//]: # (Any modifications should be made in the .xml files in the ModernDev repo.)
# CommitBehavior Option Type
> **Version**: _Available or changed with runtime version 6.0._
Specifies whether commit is allowed within the scope of the method.
## Members
| Member | Description |
|----------------|---------------|
|Ignore|Ignore commits within the scope of this method.|
|Error|Throw an error when a commit is attempted within the scope of this method.|
[//]: # (IMPORTANT: END>DO_NOT_EDIT)
Example of adding a note to autogenerated content
[//]: # (START>DO_NOT_EDIT)
[//]: # (IMPORTANT:Do not edit any of the content between here and the END>DO_NOT_EDIT.)
[//]: # (Any modifications should be made in the .xml files in the ModernDev repo.)
<auto-generated content>
[//]: # (IMPORTANT: END>DO_NOT_EDIT)
### Remarks
You must set the `CommitBehavior` property to `Ignore` if you want to use the `Commit` method within the scope of the method.
See also
Business Central User Assistance Model
Configuring the Help Experience
Authoring Guide
Docs Contributor Guide
Docs Authoring Pack for Visual Studio Code
Getting started with writing and formatting on GitHub
Visual Studio Code
Atom
DocFX
Blog post: Extending and customizing the Help
Blog post: Collaborate on content for Business Central
Commentaires
Prochainement : Tout au long de l'année 2024, nous supprimerons progressivement les GitHub Issues en tant que mécanisme de retour d'information pour le contenu et nous les remplacerons par un nouveau système de retour d'information. Pour plus d’informations, voir: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Soumettre et afficher des commentaires pour