Getting started with Reliable Actors
This article walks through creating and debugging a simple Reliable Actor application in Visual Studio. For more information on Reliable Actors, see Introduction to Service Fabric Reliable Actors.
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure that you have the Service Fabric development environment, including Visual Studio, set up on your machine. For details, see how to set up the development environment.
Create a new project in Visual Studio
Launch Visual Studio 2019 or later as an administrator, and then create a new Service Fabric Application project:

In the next dialog box, choose Actor Service under .NET Core 2.0 and enter a name for the service.

The created project shows the following structure:
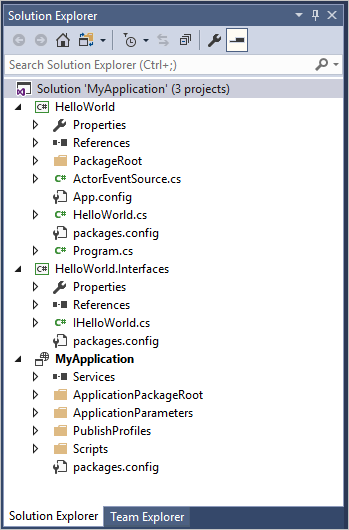
Examine the solution
The solution contains three projects:
The application project (MyApplication). This project packages all of the services together for deployment. It contains the ApplicationManifest.xml and PowerShell scripts for managing the application.
The interface project (HelloWorld.Interfaces). This project contains the interface definition for the actor. Actor interfaces can be defined in any project with any name. The interface defines the actor contract that is shared by the actor implementation and the clients calling the actor. Because client projects may depend on it, it typically makes sense to define it in an assembly that is separate from the actor implementation.
The actor service project (HelloWorld). This project defines the Service Fabric service that is going to host the actor. It contains the implementation of the actor, HelloWorld.cs. An actor implementation is a class that derives from the base type
Actorand implements the interfaces defined in the MyActor.Interfaces project. An actor class must also implement a constructor that accepts anActorServiceinstance and anActorIdand passes them to the baseActorclass.This project also contains Program.cs, which registers actor classes with the Service Fabric runtime using
ActorRuntime.RegisterActorAsync<T>(). TheHelloWorldclass is already registered. Any additional actor implementations added to the project must also be registered in theMain()method.
Customize the HelloWorld actor
The project template defines some methods in the IHelloWorld interface and implements them in the HelloWorld actor implementation. Replace those methods so the actor service returns a simple "Hello World" string.
In the HelloWorld.Interfaces project, in the IHelloWorld.cs file, replace the interface definition as follows:
public interface IHelloWorld : IActor
{
Task<string> GetHelloWorldAsync();
}
In the HelloWorld project, in HelloWorld.cs, replace the entire class definition as follows:
[StatePersistence(StatePersistence.Persisted)]
internal class HelloWorld : Actor, IHelloWorld
{
public HelloWorld(ActorService actorService, ActorId actorId)
: base(actorService, actorId)
{
}
public Task<string> GetHelloWorldAsync()
{
return Task.FromResult("Hello from my reliable actor!");
}
}
Press Ctrl-Shift-B to build the project and make sure everything compiles.
Add a client
Create a simple console application to call the actor service.
Right-click on the solution in Solution Explorer > Add > New Project....
Under the .NET Core project types, choose Console App (.NET Core). Name the project ActorClient.

Note
A console application is not the type of app you would typically use as a client in Service Fabric, but it makes a convenient example for debugging and testing using the local Service Fabric cluster.
The console application must be a 64-bit application to maintain compatibility with the interface project and other dependencies. In Solution Explorer, right-click the ActorClient project, and then click Properties. On the Build tab, set Platform target to x64.

The client project requires the reliable actors NuGet package. Click Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console. In the Package Manager Console, enter the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Actors -IncludePrerelease -ProjectName ActorClientThe NuGet package and all its dependencies are installed in the ActorClient project.
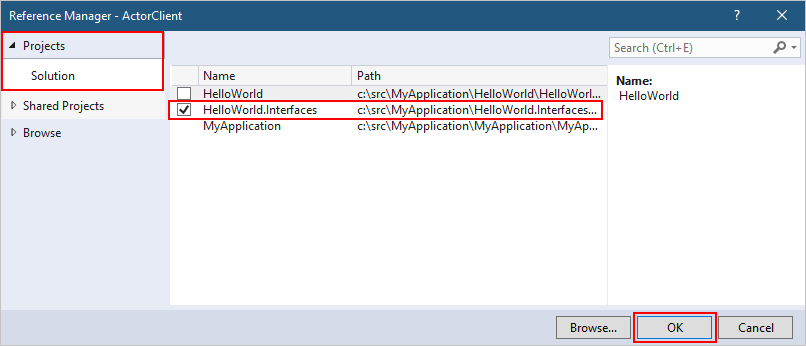
The client project also requires a reference to the interfaces project. In the ActorClient project, right-click Dependencies and then click Add Project Reference.... Select Projects > Solution (if not already selected), and then tick the checkbox next to HelloWorld.Interfaces. Click OK.
In the ActorClient project, replace the entire contents of Program.cs with the following code:
using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Actors; using Microsoft.ServiceFabric.Actors.Client; using HelloWorld.Interfaces; namespace ActorClient { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IHelloWorld actor = ActorProxy.Create<IHelloWorld>(ActorId.CreateRandom(), new Uri("fabric:/MyApplication/HelloWorldActorService")); Task<string> retval = actor.GetHelloWorldAsync(); Console.Write(retval.Result); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
Running and debugging
Press F5 to build, deploy, and run the application locally in the Service Fabric development cluster. During the deployment process, you can see the progress in the Output window.
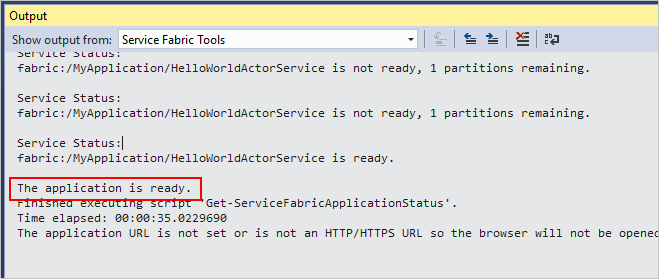
When the output contains the text, The application is ready, it's possible to test the service using the ActorClient application. In Solution Explorer, right-click on the ActorClient project, then click Debug > Start new instance. The command line application should display the output from the actor service.

Tip
The Service Fabric Actors runtime emits some events and performance counters related to actor methods. They are useful in diagnostics and performance monitoring.
Next steps
Learn more about how Reliable Actors use the Service Fabric platform.