Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
In modern business intelligence (BI) projects, understanding the flow of data from the data source to its destination can be a challenge. The challenge is even bigger if you build advanced analytical projects that span multiple data sources, items, and dependencies.
Questions like "What happens if I change this data?" or "Why isn't this report up to date?" can be hard to answer. Such questions might require a team of experts or deep investigation to understand. The Microsoft Fabric lineage view helps you answer these questions.
Lineage and machine learning
There are several reasons why lineage is important in your machine learning workflow:
- Reproducibility: Knowing the lineage of a model makes it easier to reproduce the model and its results. If someone else wants to replicate the model, they can follow the same steps that you used to create it, and use the same data and parameters.
- Transparency: Understanding the lineage of a model helps to increase its transparency. Stakeholders, such as regulators or users, can understand how the model was created, and how it works. This factor can be important for ensuring fairness, accountability, and ethical considerations.
- Debugging: If a model doesn't perform as expected, knowing its lineage can help to identify the source of the problem. By examining the training data, parameters, and decisions that were made during the training process, users might be able to identify issues that affect the model's performance.
- Improvement: Knowing the lineage of a model can also help to improve it. By understanding how the model was created and trained, users might be able to make changes to the training data, parameters, or process that can improve the model's accuracy or other performance metrics.
Data science item types
Microsoft Fabric integrates machine learning models and experiments into a unified platform. As part of this approach, users can browse the relationship between Fabric Data Science items and other Fabric items.
Machine learning models
In Fabric, users can create and manage machine learning models. A machine learning model item represents a versioned list of models, which allows users to browse the various iterations of the model.
In the lineage view, users can browse the relationship between a machine learning model and other Fabric items to answer the following questions:
- What is the relationship between machine learning models and experiments in my workspace?
- Which machine learning models exist in my workspace?
- How can I trace back the lineage to see which Lakehouse items were related to this model?
Machine learning experiments
A machine learning experiment is the primary unit of organization and control for all related machine learning runs.
In the lineage view, users can browse the relationship between a machine learning experiment and other Fabric items to answer the following questions:
- What is the relationship between machine learning experiments and code items in my workspace? For example, what's the relationship between notebooks and Spark Job Definitions?
- Which machine learning experiments exist in my workspace?
- How can I trace back the lineage to see which Lakehouse items were related to this experiment?
Explore lineage view
Every Fabric workspace has a built-in lineage view. To access this view, you must have at least the Contributor role within the workspace. To learn more about permissions in Fabric, see Data science roles and permissions.
To access the lineage view:
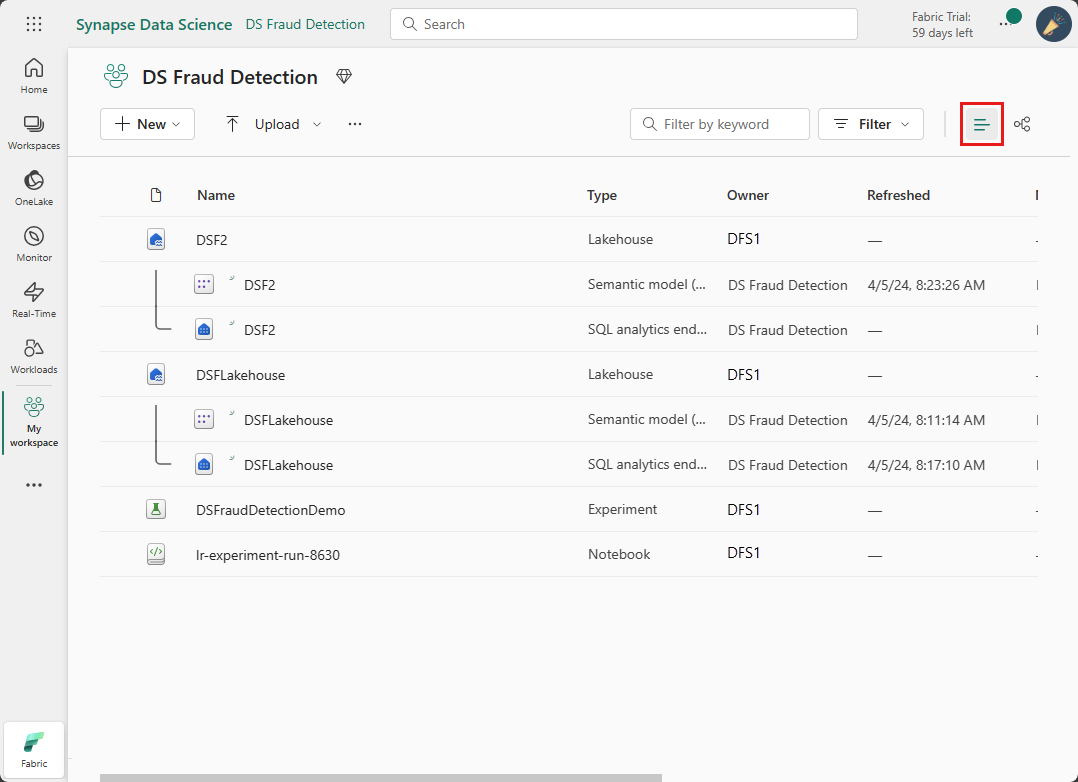
Select your Fabric workspace and then navigate to the workspace list.
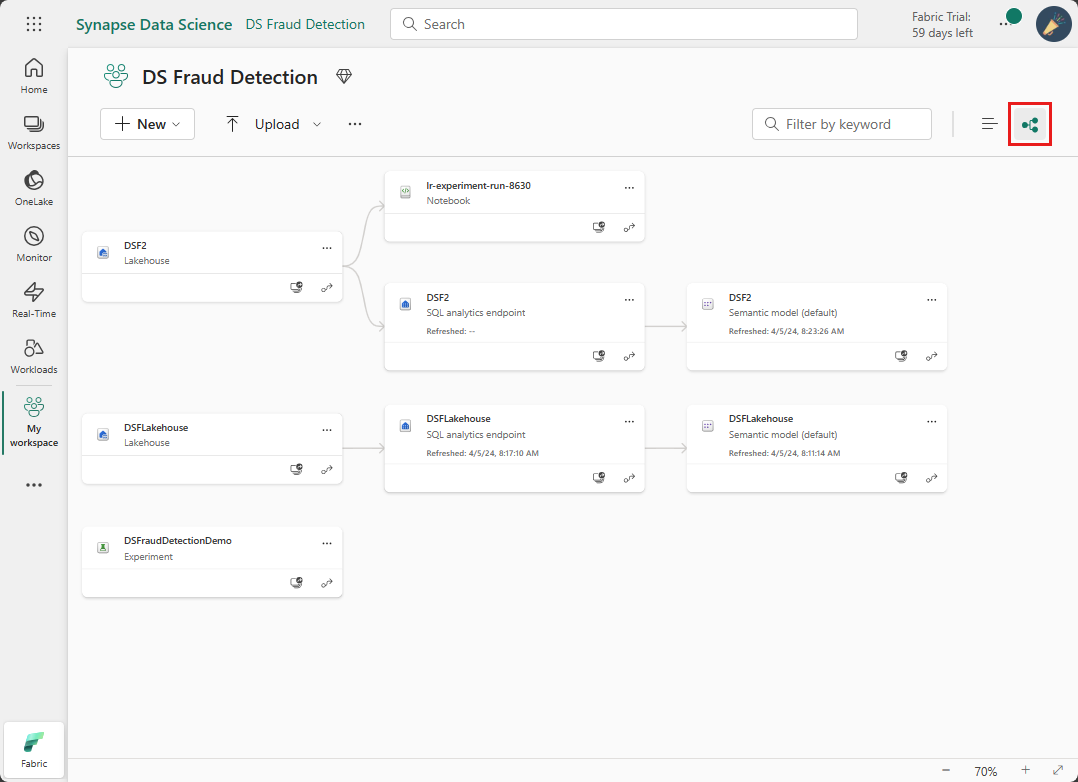
Switch from the workspace List view to the Workspace Lineage view.
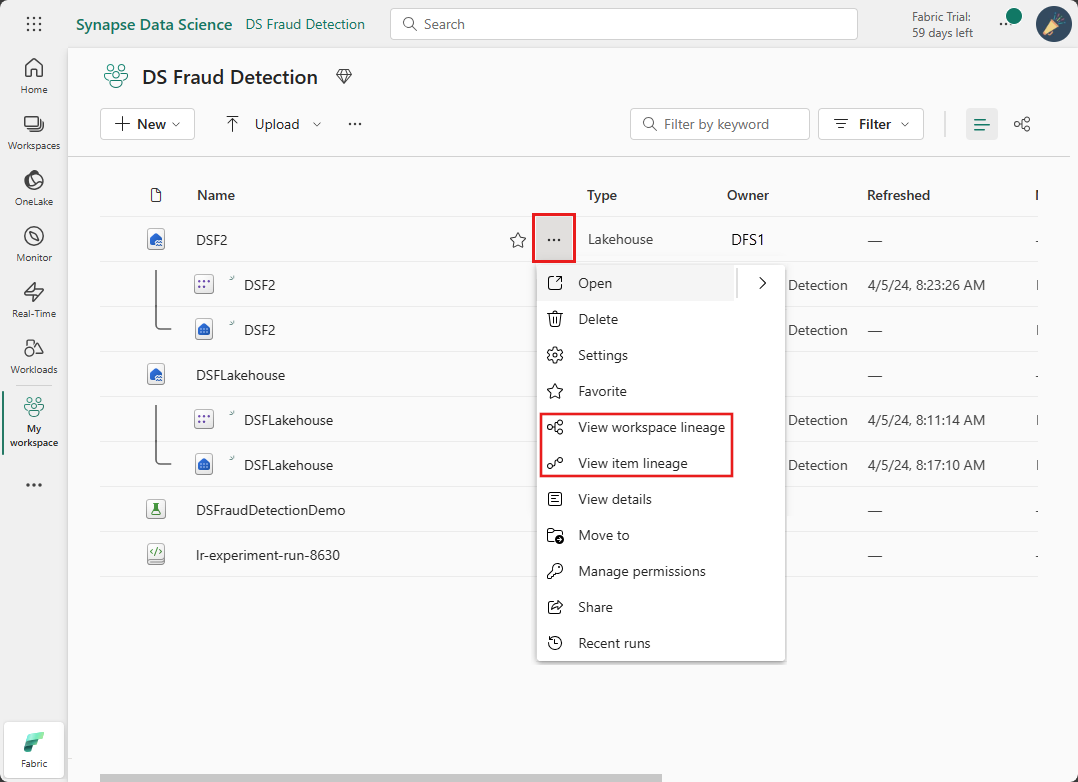
You can also navigate to Lineage view for a specific item by opening the context menu and selecting to view the workspace or item lineage.
Related content
- Learn about machine learning models: Machine learning models
- Learn about machine learning experiments: Machine learning experiments