前のチュートリアルでは、完全な 88 キーピアノ キーボードのモデルを作成しました。 次に、XR 空間で再生できるようにします。
このチュートリアルでは、以下を実行する方法について説明します。
- ポインター イベントを使用して対話型ピアノ機能を追加する
- メッシュを別のサイズにスケーリングする
- XR でテレポートとマルチポインターのサポートを有効にする
開始する前に
シリーズの前のチュートリアルを完了し、コードへの追加を続行する準備ができていることを確認します。
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Piano in BabylonJS</title>
<script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script>
<script src="scene.js"></script>
<style>
body,#renderCanvas { width: 100%; height: 100%;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="renderCanvas"></canvas>
<script type="text/javascript">
const canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true);
createScene(engine).then(sceneToRender => {
engine.runRenderLoop(() => sceneToRender.render());
});
// Watch for browser/canvas resize events
window.addEventListener("resize", function () {
engine.resize();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
scene.js
const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) {
if (props.type === "white") {
/*
Props for building a white key should contain:
note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX
As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be
{type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}
*/
// Create bottom part
const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene);
// Create top part
const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene);
top.position.z = 4.75;
top.position.x += props.topPositionX;
// Merge bottom and top parts
// Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials)
const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false);
key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX;
key.name = props.note + props.register;
key.parent = parent;
return key;
}
else if (props.type === "black") {
/*
Props for building a black key should contain:
note, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX
As an example, the props for building the C#4 black key would be
{type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}
*/
// Create black color material
const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black");
blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0);
// Create black key
const key = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox(props.note + props.register, {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene);
key.position.z += 4.75;
key.position.y += 0.25;
key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX;
key.material = blackMat;
key.parent = parent;
return key;
}
}
const createScene = async function(engine) {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2;
const beta = Math.PI/50;
const radius = 220;
const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene);
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene);
light.intensity = 0.6;
const keyParams = [
{type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4},
{type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45},
{type: "white", note: "D", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -12},
{type: "black", note: "D#", wholePositionX: -10.6},
{type: "white", note: "E", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.45, wholePositionX: -9.6},
{type: "white", note: "F", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: -0.55, wholePositionX: -7.2},
{type: "black", note: "F#", wholePositionX: -6.35},
{type: "white", note: "G", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.2, wholePositionX: -4.8},
{type: "black", note: "G#", wholePositionX: -3.6},
{type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.2, wholePositionX: -2.4},
{type: "black", note: "A#", wholePositionX: -0.85},
{type: "white", note: "B", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0.55, wholePositionX: 0},
]
// Transform Node that acts as the parent of all piano keys
const keyboard = new BABYLON.TransformNode("keyboard");
// Register 1 through 7
var referencePositionX = -2.4*14;
for (let register = 1; register <= 7; register++) {
keyParams.forEach(key => {
buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: register, referencePositionX: referencePositionX}, key));
})
referencePositionX += 2.4*7;
}
// Register 0
buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.9, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.20, wholePositionX: -2.4, register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21});
keyParams.slice(10, 12).forEach(key => {
buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}, key));
})
// Register 8
buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 2.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -2.4*6, register: 8, referencePositionX: 84});
// Transform node that acts as the parent of all piano components
const piano = new BABYLON.TransformNode("piano");
keyboard.parent = piano;
// Import and scale piano frame
BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMesh("frame", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/mixed-reality/docs/mixed-reality-docs/mr-dev-docs/develop/javascript/tutorials/babylonjs-webxr-piano/files/", "pianoFrame.babylon", scene, function(meshes) {
const frame = meshes[0];
frame.parent = piano;
});
// Lift the piano keyboard
keyboard.position.y += 80;
const xrHelper = await scene.createDefaultXRExperienceAsync();
return scene;
}
ピアノ キーボードを再生可能にする
現在、作成したピアノ キーボードは、ユーザーの操作に応答しない静的モデルです。 このセクションでは、キーをプログラムして下に移動し、他のユーザーが押したときにサウンドを再生します。
Babylon.js は、対話できるさまざまな種類のイベント ( 監視可能なイベント) を提供します。 ここでは、マウス クリック、タッチ、XR コントローラー ボタンのクリックなど、ポインターを介してユーザーが操作を実行するキーをプログラムするため、
onPointerObservableを処理します。onPointerObservableに任意の動作を追加する方法の基本的な構造を次に示します。scene.onPointerObservable.add((pointerInfo) => { // do something });Babylon.js は さまざまな種類のポインター イベントを提供しますが、次の構造を使用して、
POINTERDOWNイベントとPOINTERUPイベントのみを使用してピアノ キーの動作をプログラムします。scene.onPointerObservable.add((pointerInfo) => { switch (pointerInfo.type) { case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERDOWN: // When the pointer is down on a piano key, // move the piano key downward (to show that it is pressed) // and play the sound of the note break; case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERUP: // When the pointer is released, // move the piano key upward to its original position // and stop the sound of the note of the key that is released break; } });まず、キーを押して離すときに、ピアノキーを下方向と上方向に動かしてみましょう。
ポインター ダウン イベントでは、クリックされているメッシュを検出し、それがピアノ キーであることを確認し、キーが押されたように見えるようにメッシュの y 座標を少量ずつ負に変更する必要があります。
ポインターアップ イベントの場合、キーを押したポインターがキーで解放されない可能性があるため、もう少し複雑になります。 たとえば、キー C4 を下にクリックし、マウスを E4 にドラッグし、クリックを離すとします。 この場合も、
pointerUpイベントが発生する場所 (E4) ではなく、押されたキー (C4) を解放する必要があります。次のコードが必要なものを達成する方法を見てみましょう。
const pointerToKey = new Map(); scene.onPointerObservable.add((pointerInfo) => { switch (pointerInfo.type) { case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERDOWN: if(pointerInfo.pickInfo.hit) { const pickedMesh = pointerInfo.pickInfo.pickedMesh; const pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId; if (pickedMesh.parent === keyboard) { pickedMesh.position.y -= 0.5; // play the sound of the note pointerToKey.set(pointerId, { mesh: pickedMesh }); } } break; case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERUP: const pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId; if (pointerToKey.has(pointerId)) { pointerToKey.get(pointerId).mesh.position.y += 0.5; // stop the sound of the note of the key that is released pointerToKey.delete(pointerId); } break; } });pointerIdはすべてのポインターに固有であり、複数のコントローラーがある場合やタッチ スクリーンを使用している場合にポインターを識別するのに役立ちます。 ここでは、pointerToKeyという名前のMapオブジェクトを初期化して、どのポインターがどのキーを押すかの関係を格納しました。これにより、解放の場所に関係なく、ポインターが解放されたときに解放するキーが認識されます。上記のコードとのやり取りは次のようになります。

次に、キーを押して離したときに、サウンドの再生と停止に取り組みましょう。 これを実現するために、 soundfont-player という名前の Javascript ライブラリを利用します。これにより、選択した楽器の MIDI サウンドを簡単に再生できます。
ライブラリの縮小されたコードをダウンロードし、 index.htmlと同じフォルダーに保存し、index.htmlの
<header>タグに含 めます 。<head> <title>Babylon Template</title> <script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script> <script src="scene.js"></script> <script src="soundfont-player.min.js"></script> <style> body,#renderCanvas { width: 100%; height: 100%;} </style> </head>ライブラリがインポートされたら、ライブラリを使用してインストゥルメントを初期化し、MIDIサウンドを再生/停止する方法を次に示します。
const pianoSound = await Soundfont.instrument(new AudioContext(), 'acoustic_grand_piano'); const C4 = piano.play("C4"); // Play note C4 C4.stop(); // Stop note C4次に、これをポインター イベントに組み込み、このセクションのコードを終了します。
const pointerToKey = new Map() const piano = await Soundfont.instrument(new AudioContext(), 'acoustic_grand_piano'); scene.onPointerObservable.add((pointerInfo) => { switch (pointerInfo.type) { case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERDOWN: if(pointerInfo.pickInfo.hit) { let pickedMesh = pointerInfo.pickInfo.pickedMesh; let pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId; if (keys.has(pickedMesh)) { pickedMesh.position.y -= 0.5; // Move the key downward pointerToKey.set(pointerId, { mesh: pickedMesh, note: pianoSound.play(pointerInfo.pickInfo.pickedMesh.name) // Play the sound of the note }); } } break; case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERUP: let pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId; if (pointerToKey.has(pointerId)) { pointerToKey.get(pointerId).mesh.position.y += 0.5; // Move the key upward pointerToKey.get(pointerId).note.stop(); // Stop the sound of the note pointerToKey.delete(pointerId); } break; } });各キーのメッシュに、それが表すノートを付けたので、メッシュの名前を
pianoSound.play()関数に渡すことで、再生するノートを簡単に指定できます。 また、キーが解放されたときに停止するサウンドを把握できるように、サウンドをpointerToKeyマップに格納することにも注意してください。
イマーシブ VR モードでピアノをスケーリングする
今では、インタラクティブな機能を追加すると、おそらくすでにマウス(またはタッチスクリーン)でピアノで演奏しています。 このセクションでは、イマーシブ VR 空間に移動します。
イマーシブ VR ヘッドセットでページを開くには、まずヘッドセットを開発者マシンに接続し、Windows Mixed Reality アプリで使用できるように設定されていることを確認する必要があります。 Windows Mixed Reality シミュレーターを使用している場合は、有効になっていることを確認します。
Web ページの右下にイマーシブ VR ボタンが表示されます。 それをクリックすると、接続先の XR デバイスにピアノが表示されます。

あなたが仮想空間に入ると、私たちが構築したピアノは非常に巨大であることに気付くかもしれません。 VR の世界では、その下部に立って、遠くのキーへのポインターを指すことによってのみ再生できます。
実際の生活の中で通常のスタンドアップピアノのようなサイズになるように、ピアノをスケールダウンしましょう。 そのためには、 空間内のポイントを基準にメッシュをスケーリングできるユーティリティ関数を使用する必要があります。 (
createScene()の外部) scene.js にこの関数を追加します。const scaleFromPivot = function(transformNode, pivotPoint, scale) { const _sx = scale / transformNode.scaling.x; const _sy = scale / transformNode.scaling.y; const _sz = scale / transformNode.scaling.z; transformNode.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(_sx, _sy, _sz); transformNode.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(pivotPoint.x + _sx * (transformNode.position.x - pivotPoint.x), pivotPoint.y + _sy * (transformNode.position.y - pivotPoint.y), pivotPoint.z + _sz * (transformNode.position.z - pivotPoint.z)); }この関数は、次の 3 つのパラメーターを受け取ります。
-
transformNode: スケーリングする
TransformNode -
pivotPoint: スケーリングが基準となるポイントを示す
Vector3オブジェクト - scale: スケール 係数
-
transformNode: スケーリングする
この関数を使用して、原点にピボット ポイントを設定して、ピアノ フレームとキーを 0.015 の係数でスケーリングします。
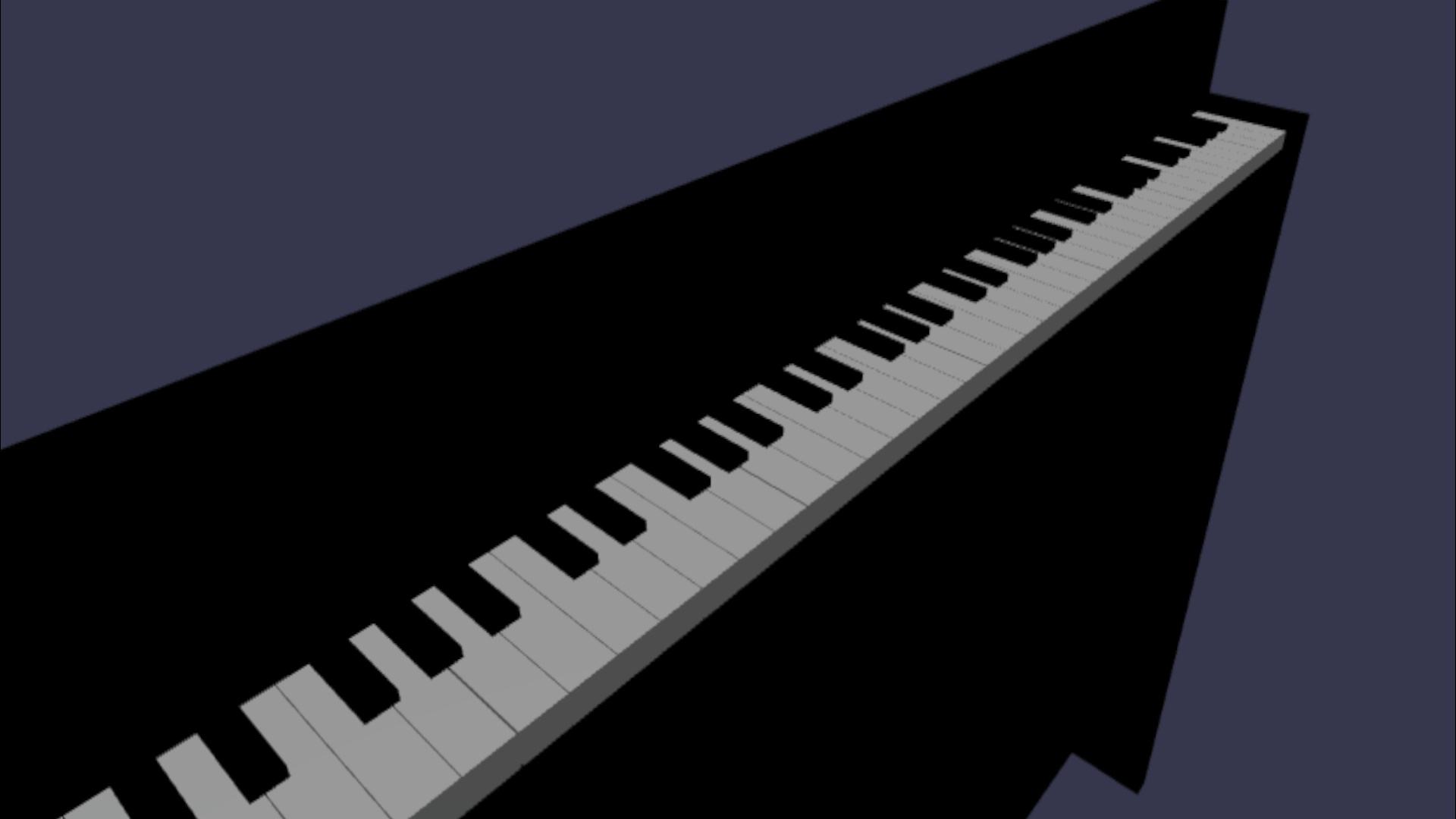
keyboard.position.y += 80;の後に配置して、関数呼び出しをcreateScene()関数に追加します。// Put this line at the beginning of createScene() const scale = 0.015;// Put this function call after keyboard.position.y += 80; // Scale the entire piano scaleFromPivot(piano, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0), scale);カメラの位置もスケールすることを忘れないでください。
const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2; const beta = Math.PI/50; const radius = 220*scale; // scale the radius const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0); const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene); camera.attachControl(canvas, true);VR空間に再び入ると、ピアノは通常のスタンドアップピアノの大きさになります。

WebXR 機能の有効化
VR 空間でピアノを適切なサイズにスケーリングしたので、いくつかのクールな WebXR 機能を有効にして、空間でのピアノ演奏の経験を向上させましょう。
イマーシブ VR コントローラーを使用してピアノを演奏している場合は、一度に 1 つのコントローラーしか使用できないことに気付いたかもしれません。 Babylon.js の WebXR 機能マネージャーを使用して、XR 空間でマルチポインターのサポートを有効にしましょう。
xrHelper初期化行の後に、次のコードをcreateScene()関数に追加します。const featuresManager = xrHelper.baseExperience.featuresManager; const pointerSelection = featuresManager.enableFeature(BABYLON.WebXRFeatureName.POINTER_SELECTION, "stable", { xrInput: xrHelper.input, enablePointerSelectionOnAllControllers: true });また、出発点によっては、ピアノの前に自分を配置するのが少し難しい場合があります。 イマーシブ VR 環境に慣れている場合は、 テレポーテーションについて既に知っている可能性があります。これは、それをポイントすることで、空間内の別の場所にすぐに移動できる機能です。
Babylon.js の テレポート機能を使用するには、まず、VR 空間で "オンに" できるグラウンド メッシュを用意する必要があります。
createScene()関数に次のコードを追加して、グラウンドを作成します。const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("ground", {width: 400, height: 400});テレポートのサポートには、 スナップ先の位置と呼ばれる非常に便利な機能も付属しています。 要するに、スナップ位置は、ユーザーが着陸する特定の位置です。
たとえば、ユーザーがポインターをピアノに近づけたときに、その場所に簡単にテレポートできるように、ピアノの前にスナップ先の位置を設定できます。
次のコードを追加してテレポート機能を有効にし、スナップ先を指定します。
const teleportation = featuresManager.enableFeature(BABYLON.WebXRFeatureName.TELEPORTATION, "stable", { xrInput: xrHelper.input, floorMeshes: [ground], snapPositions: [new BABYLON.Vector3(2.4*3.5*scale, 0, -10*scale)], });これで、ピアノの前にあるスナップツーポイントにテレポートすることで、ピアノの前に簡単に自分を配置でき、両方のコントローラーを使用して一度に2つのキーを再生できるはずです。


まとめ
おめでとうございます! Babylon.js ピアノ構築チュートリアルのシリーズを完了し、次の方法を学習しました。
- メッシュを作成、配置、マージして、ピアノ キーボードのモデルを構築する
- スタンドアップ ピアノ フレームの Babylon.js モデルをインポートする
- 各ピアノ キーにポインター操作を追加する
- ピボット ポイントに基づいてメッシュのサイズをスケーリングする
- テレポートやマルチポイントサポートなどの主要な WebXR 機能を有効にする
scene.jsとindex.html の最終的なコードを次に示します。
scene.js
const buildKey = function (scene, parent, props) {
if (props.type === "white") {
/*
Props for building a white key should contain:
note, topWidth, bottomWidth, topPositionX, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX
As an example, the props for building the middle C white key would be
{type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}
*/
// Create bottom part
const bottom = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyBottom", {width: props.bottomWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 4.5}, scene);
// Create top part
const top = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("whiteKeyTop", {width: props.topWidth, height: 1.5, depth: 5}, scene);
top.position.z = 4.75;
top.position.x += props.topPositionX;
// Merge bottom and top parts
// Parameters of BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes: (arrayOfMeshes, disposeSource, allow32BitsIndices, meshSubclass, subdivideWithSubMeshes, multiMultiMaterials)
const key = BABYLON.Mesh.MergeMeshes([bottom, top], true, false, null, false, false);
key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX;
key.name = props.note + props.register;
key.parent = parent;
return key;
}
else if (props.type === "black") {
/*
Props for building a black key should contain:
note, wholePositionX, register, referencePositionX
As an example, the props for building the C#4 black key would be
{type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45, register: 4, referencePositionX: 0}
*/
// Create black color material
const blackMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("black");
blackMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 0, 0);
// Create black key
const key = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox(props.note + props.register, {width: 1.4, height: 2, depth: 5}, scene);
key.position.z += 4.75;
key.position.y += 0.25;
key.position.x = props.referencePositionX + props.wholePositionX;
key.material = blackMat;
key.parent = parent;
return key;
}
}
const scaleFromPivot = function(transformNode, pivotPoint, scale) {
const _sx = scale / transformNode.scaling.x;
const _sy = scale / transformNode.scaling.y;
const _sz = scale / transformNode.scaling.z;
transformNode.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(_sx, _sy, _sz);
transformNode.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(pivotPoint.x + _sx * (transformNode.position.x - pivotPoint.x), pivotPoint.y + _sy * (transformNode.position.y - pivotPoint.y), pivotPoint.z + _sz * (transformNode.position.z - pivotPoint.z));
}
const createScene = async function(engine) {
const scale = 0.015;
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const alpha = 3*Math.PI/2;
const beta = Math.PI/50;
const radius = 220*scale;
const target = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("Camera", alpha, beta, radius, target, scene);
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 1, 0), scene);
light.intensity = 0.6;
const keyParams = [
{type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.45, wholePositionX: -14.4},
{type: "black", note: "C#", wholePositionX: -13.45},
{type: "white", note: "D", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -12},
{type: "black", note: "D#", wholePositionX: -10.6},
{type: "white", note: "E", topWidth: 1.4, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.45, wholePositionX: -9.6},
{type: "white", note: "F", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: -0.55, wholePositionX: -7.2},
{type: "black", note: "F#", wholePositionX: -6.35},
{type: "white", note: "G", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.2, wholePositionX: -4.8},
{type: "black", note: "G#", wholePositionX: -3.6},
{type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0.2, wholePositionX: -2.4},
{type: "black", note: "A#", wholePositionX: -0.85},
{type: "white", note: "B", topWidth: 1.3, bottomWidth: 2.4, topPositionX: 0.55, wholePositionX: 0},
]
// Transform Node that acts as the parent of all piano keys
const keyboard = new BABYLON.TransformNode("keyboard");
// Register 1 through 7
var referencePositionX = -2.4*14;
for (let register = 1; register <= 7; register++) {
keyParams.forEach(key => {
buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: register, referencePositionX: referencePositionX}, key));
})
referencePositionX += 2.4*7;
}
// Register 0
buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "A", topWidth: 1.9, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: -0.20, wholePositionX: -2.4, register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21});
keyParams.slice(10, 12).forEach(key => {
buildKey(scene, keyboard, Object.assign({register: 0, referencePositionX: -2.4*21}, key));
})
// Register 8
buildKey(scene, keyboard, {type: "white", note: "C", topWidth: 2.3, bottomWidth: 2.3, topPositionX: 0, wholePositionX: -2.4*6, register: 8, referencePositionX: 84});
// Transform node that acts as the parent of all piano components
const piano = new BABYLON.TransformNode("piano");
keyboard.parent = piano;
// Import and scale piano frame
BABYLON.SceneLoader.ImportMesh("frame", "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/mixed-reality/docs/mixed-reality-docs/mr-dev-docs/develop/javascript/tutorials/babylonjs-webxr-piano/files/", "pianoFrame.babylon", scene, function(meshes) {
const frame = meshes[0];
frame.parent = piano;
});
// Lift the piano keyboard
keyboard.position.y += 80;
// Scale the entire piano
scaleFromPivot(piano, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0), scale);
const pointerToKey = new Map()
const pianoSound = await Soundfont.instrument(new AudioContext(), 'acoustic_grand_piano');
scene.onPointerObservable.add((pointerInfo) => {
switch (pointerInfo.type) {
case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERDOWN:
// Only take action if the pointer is down on a mesh
if(pointerInfo.pickInfo.hit) {
let pickedMesh = pointerInfo.pickInfo.pickedMesh;
let pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId;
if (pickedMesh.parent === keyboard) {
pickedMesh.position.y -= 0.5; // Move the key downward
pointerToKey.set(pointerId, {
mesh: pickedMesh,
note: pianoSound.play(pointerInfo.pickInfo.pickedMesh.name) // Play the sound of the note
});
}
}
break;
case BABYLON.PointerEventTypes.POINTERUP:
let pointerId = pointerInfo.event.pointerId;
// Only take action if the released pointer was recorded in pointerToKey
if (pointerToKey.has(pointerId)) {
pointerToKey.get(pointerId).mesh.position.y += 0.5; // Move the key upward
pointerToKey.get(pointerId).note.stop(); // Stop the sound of the note
pointerToKey.delete(pointerId);
}
break;
}
});
const xrHelper = await scene.createDefaultXRExperienceAsync();
const featuresManager = xrHelper.baseExperience.featuresManager;
featuresManager.enableFeature(BABYLON.WebXRFeatureName.POINTER_SELECTION, "stable", {
xrInput: xrHelper.input,
enablePointerSelectionOnAllControllers: true
});
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("ground", {width: 400, height: 400});
featuresManager.enableFeature(BABYLON.WebXRFeatureName.TELEPORTATION, "stable", {
xrInput: xrHelper.input,
floorMeshes: [ground],
snapPositions: [new BABYLON.Vector3(2.4*3.5*scale, 0, -10*scale)],
});
return scene;
}
index.html
<html>
<head>
<title>Babylon Template</title>
<script src="https://cdn.babylonjs.com/babylon.js"></script>
<script src="scene.js"></script>
<script src="soundfont-player.min.js"></script>
<style>
body,#renderCanvas { width: 100%; height: 100%;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="renderCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas"); // Get the canvas element
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true); // Generate the BABYLON 3D engine
// Register a render loop to repeatedly render the scene
createScene(engine).then(sceneToRender => {
engine.runRenderLoop(() => sceneToRender.render());
});
// Watch for browser/canvas resize events
window.addEventListener("resize", function () {
engine.resize();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
次の手順
JavaScript 開発Mixed Reality詳細については、「JavaScript 開発の概要」を参照してください。