Use personal access tokens
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
A Personal Access Token (PAT) serves as an alternative password for authenticating into Azure DevOps. This PAT identifies you and determines your accessibility and scope of access. Therefore, treat PATs with the same level of caution as passwords.
When you use Microsoft tools, your Microsoft account (MSA) or Microsoft Entra ID is a recognized and supported method. If you use non-Microsoft tools that don't support Microsoft or Microsoft Entra accounts, or if you prefer not to share your primary credentials with these tools, PATs are a suitable alternative.
This article guides you through creating, using, modifying, and revoking PATs for Azure DevOps.
You can manage PATs using the following methods:
- User interface (UI): Through user settings, as detailed in this article
- PAT Lifecycle Management API
To establish PATs for non-Microsoft tools, you can use Git credential managers or generate them manually. We recommend reviewing our authentication guidance to choose the appropriate authentication mechanism. PATs provide a straightforward alternative for smaller projects that don't require an extensive solution. Without a credential manager, users input their credentials each time.
Prerequisites
- Permissions:
- Have permission to access and modify your user settings where PATs are managed.
- Check permissions: To check your permissions, do either of the following processes in Azure DevOps:
- Go to your profile and select User settings > Personal access tokens. If you can see and manage your PATs here, you have the necessary permissions.
- Go to your project and select Project settings > Permissions. Find your user account in the list and check the permissions assigned to you. Look for permissions related to managing tokens or user settings.
- Check permissions: To check your permissions, do either of the following processes in Azure DevOps:
- If your organization has policies in place, an Azure DevOps Administrator might need to grant you specific permissions or add you to an allowlist to create and manage PATs.
- Depending on the tasks you want to perform with the PAT, you might need additional permissions. For example:
- Build: Read & execute
- Code: Read, write, & manage
- Environment: Read & manage
- Project and team: Read, write, & manage
- Variable groups: Read & create
- Have permission to access and modify your user settings where PATs are managed.
- Access levels: Have at least Basic access.
- Security best practices: Familiarize yourself with security best practices for managing PATs, such as using them only when necessary and regularly rotating them.
Create a PAT
Sign in to your organization (
https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization}).From your home page, open user settings
 and select Personal access tokens.
and select Personal access tokens.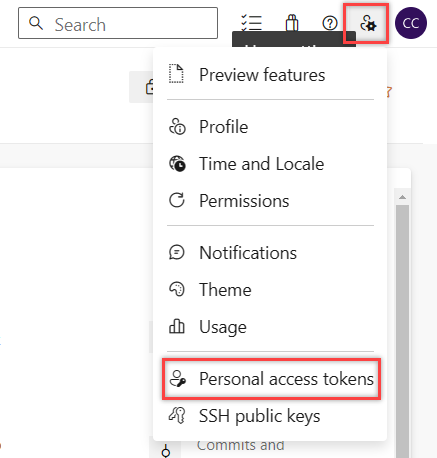
Select + New Token.
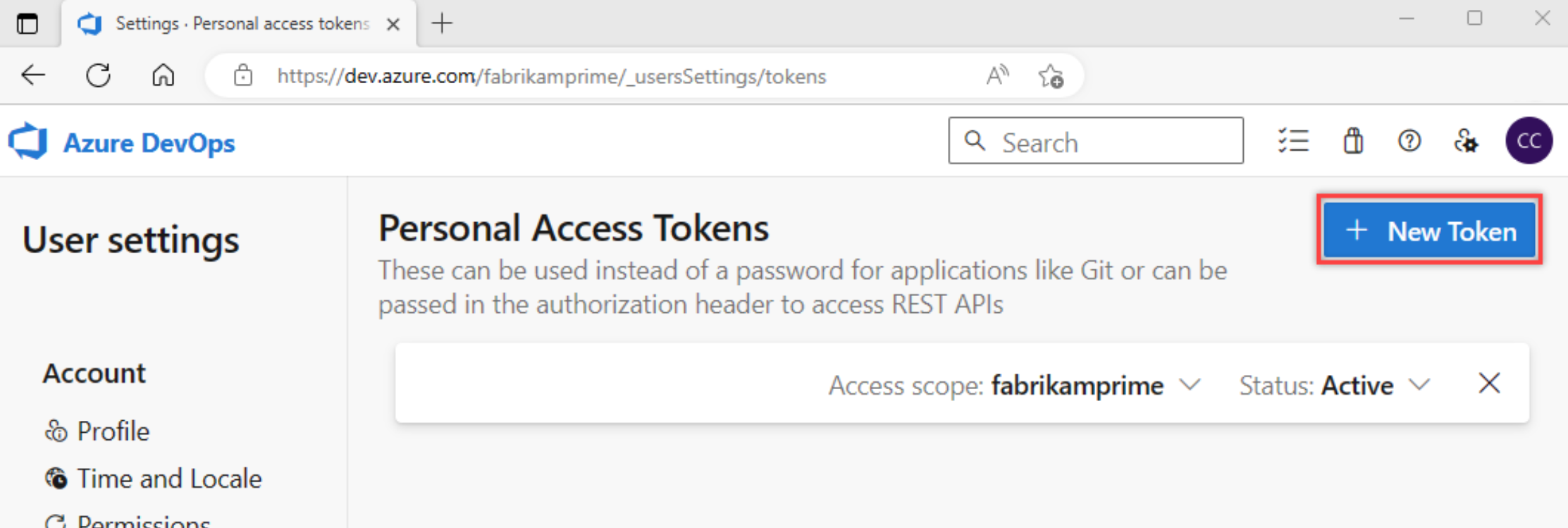
Name your token, select the organization where you want to use the token, and then set your token to automatically expire after a set number of days.
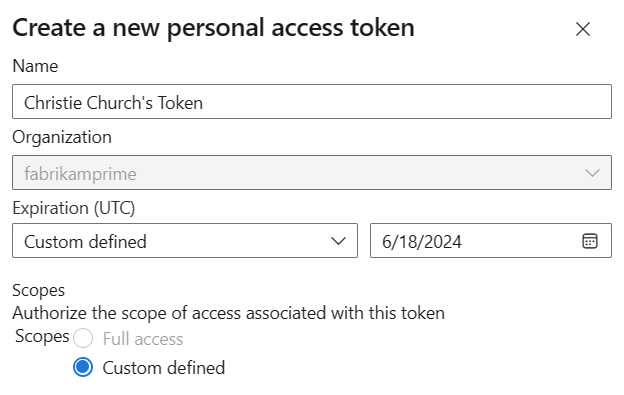
Select the scopes for this token to authorize for your specific tasks.
For example, to create a token for a build and release agent to authenticate to Azure DevOps, set the token's scope to Agent Pools (Read & manage). To read audit log events and manage or delete streams, select Read Audit Log, and then select Create.

Note
You might be restricted from creating full-scoped PATs. If so, your Azure DevOps Administrator in Microsoft Entra ID has enabled a policy that limits you to a specific custom-defined set of scopes. For more information, see Manage PATs with policies/Restrict creation of full-scoped PATs. For a custom-defined PAT, the required scope for accessing the Component Governance API,
vso.governance, isn't selectable in the UI.When you're done, copy the token and store it in a secure location. For your security, it doesn't display again.

Use your PAT anywhere your user credentials are required for authentication in Azure DevOps.
Important
- Treat a PAT with the same caution as your password and keep it confidential.
- Sign in with your new PAT within 90 days for organizations backed by Microsoft Entra ID; otherwise, the PAT becomes inactive. For more information, see User sign-in frequency for Conditional Access.
Notifications
During the lifespan of a PAT, users receive two notifications: the first at the time of creation and the second seven days before its expiration.
After you create a PAT, you receive a notification similar to the following example. This notification serves as confirmation that your PAT was successfully added to your organization.

The following image shows an example of the seven-day notification before your PAT expires.
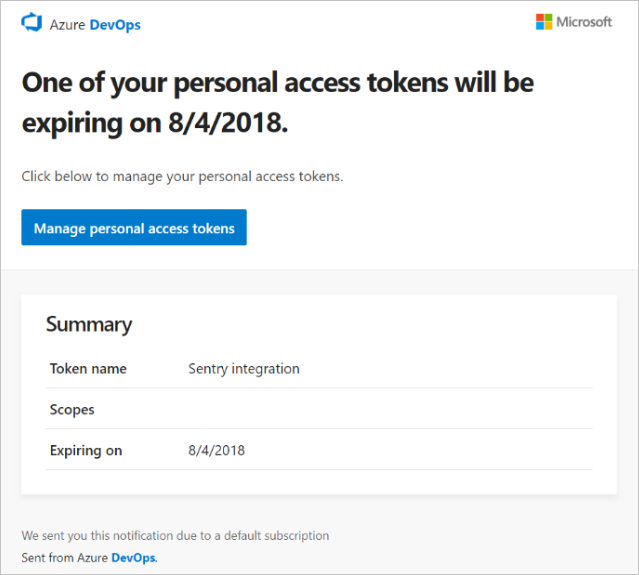
For more information, see Configure an SMTP server and customize email for alerts and feedback requests.
Unexpected notification
If you get an unexpected PAT notification, it might mean that an administrator or tool created a PAT for you. Here are some examples.
- A token named "git:
https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization}on YourMachine" gets created when you connect to an Azure DevOps Git repo via git.exe. - A token named "Service Hooks: : Azure App Service: : Deploy web app" gets created when you or an administrator sets up an Azure App Service web app deployment.
- A token named "WebAppLoadTestCDIntToken" gets created when web load testing is set up as part of a pipeline by you or an administrator.
- A token named "Microsoft Teams Integration" gets created when a Microsoft Teams Integration Messaging Extension is set up.
Warning
- Revoke the PAT if you suspect it exists in error. Follow the steps to revoke the PAT and change your password.
- Check with your administrator if you are a Microsoft Entra user to see if your organization was accessed by an unknown source or location.
- Review the FAQ on accidental PAT check-ins to public GitHub repositories.
Use a PAT
Your PAT serves as your digital identity, much like a password.
Git
Git interactions require a username, which can be anything except an empty string. To use a PAT with HTTP basic authentication, Base64-encode your $MyPat as shown in the following code block.
In PowerShell, enter the following code.
$MyPat = 'yourPat'
$headerValue = "Authorization: Basic " + [Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes(":" + $MyPat))
$env:GIT_AUTH_HEADER = $headerValue
git --config-env=http.extraheader=GIT_AUTH_HEADER clone https://dev.azure.com/yourOrgName/yourProjectName/_git/yourRepoName
Use credential managers to avoid entering your credentials every time and keep your token more secure:
- Use Git Credential Manager.
- Install Git for Windows.
Existing repositories
Remove existing origin: If you previously added the origin using a username, remove it by running the following command:
git remote remove originAuthenticate with a PAT: If you encounter issues with standard authentication, run the following command to authenticate via the command line:
git remote add origin https://dev.azure.com/<PAT>@<company_machineName>:/<project-name>/_git/<repo_name>git push -u origin --allThe
path to git repo = /_git/dorefers to the URL path structure used in Azure DevOps for Git repositories. The/_git/segment indicates that you're accessing a Git repository, and you should replacedowith the actual name of your repository. For example, if your repository is namedmy-repo, the path would be '/_git/my-repo'.Clone repository: If you're using Git and need to authenticate, run the following command:
git clone https://{organization}@dev.azure.com/{organization}/_git/{repository}Replace
{organization}with your Azure DevOps organization name and{repository}with the name of your repository.
Use a PAT in your code
You can use a PAT in your code to authenticate API requests and automate workflows. To do so, include the PAT in the authorization header of your HTTP requests.
To provide the PAT through an HTTP header, first convert it to a Base64 string. The following example shows how to convert to Base64 using C#.
Authorization: Basic BASE64_USERNAME_PAT_STRING
The resulting string can then be provided as an HTTP header in the following format.
The following sample uses the HttpClient class in C#.
public static async void GetBuilds()
{
try
{
var personalaccesstoken = "PATFROMWEB";
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(
new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic",
Convert.ToBase64String(
System.Text.ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(
string.Format("{0}:{1}", "", personalaccesstoken))));
using (HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync(
"https://dev.azure.com/{organization}/{project}/_apis/build/builds?api-version=5.0").Result)
{
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine(responseBody);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
}
Tip
When you're using variables, add a $ at the beginning of the string, like in the following example.
public static async void GetBuilds()
{
try
{
var personalaccesstoken = "PATFROMWEB";
using (HttpClient client = new HttpClient())
{
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(
new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue("application/json"));
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic",
Convert.ToBase64String(
System.Text.ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(
string.Format("{0}:{1}", "", personalaccesstoken))));
using (HttpResponseMessage response = client.GetAsync(
$"https://dev.azure.com/{organization}/{project}/_apis/build/builds?api-version=5.0").Result)
{
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine(responseBody);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
}
When your code is working, it's a good time to switch from basic auth to OAuth.
For more information and examples of how to use PATs, see the following articles:
- Set up Git credential managers
- Access REST APIs
- Use NuGet on a Mac
- Authenticate reporting clients
- Get started with Azure DevOps CLI
Modify a PAT
Do the following steps to:
- Regenerate a PAT to create a new token, which invalidates the previous one.
- Extend a PAT to increase its validity period.
- Alter the scope of a PAT to change its permissions.
From your home page, open your user settings, and then select Profile.

Under Security, select Personal access tokens. Select the token you want to modify, and then Edit.

Edit the token name, token expiration, or the scope of access associated with the token, and then select Save.

Revoke a PAT
You can revoke a PAT at any time for these and other reasons:
- Revoke a PAT if you suspect it is compromised.
- Revoke a PAT when it's no longer needed.
- Revoke a PAT to enforce security policies or compliance requirements.
From your home page, open your user settings, and then select Profile.

Under Security, select Personal access tokens. Select the token for which you want to revoke access, and then select Revoke.

Select Revoke in the confirmation dialog.

For more information, see Revoke user PATs for admins.
Changes to format
As of July 2024, we significantly changed the format of PATs issued by Azure DevOps. These changes provide more security benefits and improve secret detection tooling available through our partner offerings, like GitHub Advanced Security for Azure DevOps. This new PAT format follows the recommended format across all Microsoft products. The inclusion of more identifiable bits improves the false positive detection rate of these secret detection tools and enables us to mitigate detected leaks faster.
Key changes:
- Increased token length: The new tokens are now 84 characters long, with 52 characters being randomized data. This increased length improves overall entropy, making the tokens more resistant to potential brute force attacks.
- Fixed signature: Tokens issued by our service include a fixed
AZDOsignature at positions 76-80.
Action required:
- Regenerate existing PATs: We strongly recommend regenerating all PATs currently in use to take advantage of these security enhancements.
- Integrator support: Integrators should update their systems to accommodate both the new and existing token lengths.
Important
Both formats remain valid for the foreseeable future, but we actively encourage customers to transition to the new 84-character format. As adoption of the new format increases, we consider retiring the older 52-character format and all tokens issued in that style.
Related articles
- Learn about security, authentication, and authorization
- Review default permissions and access for Azure DevOps
- Revoke user PATs (for admins)
- Manage service principals and managed identities in Azure DevOps
FAQs
Q: Why can't I edit or regenerate a PAT scoped to a single organization?
A: Ensure you're signed into the organization where your PAT is scoped. You can view all of your PATs while signed into any organization in the same Microsoft Entra ID, but you can only edit organization-scoped tokens when you're signed into the organization to which they're scoped.
Q: What happens to a PAT if a user account is disabled?
A: When a user is removed from Azure DevOps, the PAT invalidates within 1 hour. If your organization is connected to Microsoft Entra ID, the PAT also invalidates in Microsoft Entra ID, as it belongs to the user. We recommend rotating the PAT to another user or service account to keep services running.
Q: Is there a way to renew a PAT via REST API?
A: Yes, there's a way to renew, manage, and create PATs using our PAT Lifecycle Management APIs. For more information, see Manage PATs using REST API and FAQs.
Q: Can I use basic auth with all Azure DevOps REST APIs?
A: No. You can use basic auth with most Azure DevOps REST APIs, but organizations and profiles only support OAuth. For more information, see Manage PATs using REST API.
Q: What happens if I accidentally check my PAT into a public repository on GitHub?
A: Azure DevOps scans for PATs checked into public repositories on GitHub. When we find a leaked token, we immediately send a detailed email notification to the token owner and log an event in your Azure DevOps organization's audit log. Unless you disabled the Automatically revoke leaked personal access tokens policy, we immediately revoke the leaked PAT. We encourage affected users to mitigate the issue by revoking the leaked token and replacing it with a new token.
For more information, see Revoke leaked PATs automatically.
Q: Can I use a personal access token as an ApiKey to publish NuGet packages to an Azure Artifacts feed using the dotnet/nuget.exe command line?
A: No. Azure Artifacts doesn't support passing a personal access token as an ApiKey. When using a local development environment, we recommended installing the Azure Artifacts Credential Provider to authenticate with Azure Artifacts. For more information, see the following examples: dotnet, NuGet.exe. If you want to publish your packages using Azure Pipelines, use the NuGet Authenticate task to authenticate with your feed example.
Q: Why did my PAT stop working?
A: PAT authentication requires you to regularly sign into Azure DevOps using the full authentication flow. Signing in once every 30 days is sufficient for many users, but you might need to sign in more frequently depending on your Microsoft Entra configuration. If your PAT stops working, first try signing into your organization and complete the full authentication prompt. If your PAT still doesn't work, check if it expired.
Q: How do I create access keys that aren't tied to a specific person for deployment purposes?
A: In Azure DevOps, you can create access keys that aren't tied to a specific person by using Service Principals or Manage Identities. For more information, see Manage service connections, Use Azure Key Vault secrets in Azure Pipelines.