Notitie
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen u aan te melden of de directory te wijzigen.
Voor toegang tot deze pagina is autorisatie vereist. U kunt proberen de mappen te wijzigen.
Copilot uses on-behalf-of authentication to access security-related data through active Microsoft plugins. Specific Security Copilot roles must be assigned in order for a group or individual to access the Security Copilot platform. After you're authenticated to the platform, your Microsoft Entra and Azure Role Based Access Control (RBAC) determines what plugins are available in prompts. Your Security Copilot role controls what other activities you have access to on the platform, such as configuring settings, assigning permissions, and performing tasks.
Security Copilot RBAC roles are not Microsoft Entra roles. Security Copilot roles are defined and managed within Copilot and only grant access to Security Copilot features.
Microsoft Entra RBAC grants access across the Microsoft portfolio of products including services that contain security data. These roles are managed through the Microsoft Entra admin center. For more information, see Assign Microsoft Entra roles to users.
Azure RBAC controls access to Azure resources like Security Capacity Units (SCU) in a resource group, or Microsoft Sentinel enabled workspaces. For more information, see Assign Azure roles.
Access Security Copilot platform
After Security Copilot is onboarded for your organization, configure Security Copilot RBAC to determine users' access to the Security Copilot platform. Then layer your security coverage with conditional access policies. For more information about securing access to the Security Copilot platform beyond RBAC, see Protect AI with Conditional Access policy.
Security Copilot roles
Security Copilot introduces two roles that function like access groups but aren't Microsoft Entra ID roles. Instead, they only control access to the capabilities of the Security Copilot platform and provide no access by themselves to security data.
- Security Copilot owner
- Security Copilot contributor
Note
To prevent accidental removal of owners, Security Copilot enforces retention of two owners at all times. These two owners cannot be removed.
Microsoft Entra and Microsoft Purview roles
The following Microsoft Entra and Microsoft Purview roles automatically inherit Copilot owner access, ensuring Security Copilot always has at least two owners.
Microsoft Entra roles:
- Billing Administrator
- Entra Compliance Administrator
- Global Administrator
- Intune Administrator
- Security Administrator
For more information on continuity in Microsoft Entra, see Manage emergency access accounts.
Microsoft Purview roles:
- Purview Compliance Administrator
- Purview Data Governance Administrator
- Purview Organization Management
As part of the Security Copilot inclusion in the Microsoft 365 E5 license, the Compliance pack is automatically added.
Recommended Security Copilot owner roles
You can update the set of Security Copilot at any time. The list of recommended roles includes Microsoft Entra ID roles and some service specific roles, like Microsoft Purview roles and Microsoft Defender roles.
Note
Only the selected owner roles will inherit the owner role on that workspace. For more information on the supported roles see, Microsoft Entra or Microsoft Purview role.
If a Microsoft plugin requires a different role to access its security data, you need to ensure that the appropriate service role is assigned as well. For example, the bundle works well for an analyst assigned the Compliance Administrator role. This role is one of the Microsoft Purview recommended roles and gives them access to Microsoft Purview plugin data. That same analyst needs additional role assignments to access security data like Microsoft Sentinel though. For more examples, see access the capabilities of Microsoft plugins.
Recommended Security Copilot contributor roles
Provision access to Security Copilot with the Recommended Microsoft Security roles group, which uses a balanced approach to security and administrative efficiency. Users who already have security permission through Microsoft Entra roles are given contributor access to the Security Copilot platform with this bundle. If the Everyone group is assigned, you must remove it before you add the recommended security roles.
| Role assignment | Advantage | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| Recommended Microsoft Security roles (Default) | Quick, secure way to give users in your organization who already have access to security data the access they need to the platform. More roles, users and groups can still be added. | The group is all or nothing. If there's a role in the recommended group you don't want to have access, the entire group must be removed. |
| Everyone | This group was initially given contributor access by default to simplify provisioning. | If a user in the everyone group doesn't have access to any security data, the experience in Security Copilot is confusing. |
| Custom | Complete control over users and groups with access to the platform. | Requires more administrative complexity. |
Note
The assignment of the recommended Microsoft security roles to Copilot is the default for new Security Copilot instances. Existing customers who have the everyone group assigned may continue to use the assignment. If the everyone group is removed though, it can't be assigned again. Security Copilot only supports assigning permissions to Role-assignable groups. For more information about these groups, see Creating role-assignable groups in Entra ID.
Access the capabilities of Microsoft plugins
Security Copilot doesn't go beyond the access you have, aligning with Microsoft's Security and privacy RAI principle. Each Microsoft plugin has its own role requirements that remain in effect to access the plugin's service and its data. Verify that you have the proper roles and licenses assigned to use the capabilities of the Microsoft plugins that are activated.
Consider these examples:
Copilot contributor
As an analyst, you're assigned the Copilot contributor role for access to the Copilot platform and the ability to create sessions. This assignment by itself doesn't give you access to your organization's security data. Following the least privilege model, you don't have any sensitive Microsoft Entra roles like Security Administrator. In order to use Copilot to access security data like the Microsoft Sentinel plugin, you still need an appropriate Azure RBAC role like Microsoft Sentinel Reader. This role gives you access to incidents in your Microsoft Sentinel workspace from Copilot. For your Copilot session to access the devices, policies, and postures available through the Intune plugin, you need an Intune role like the Endpoint Security Manager. The same pattern is true for access to Microsoft Defender XDR data through your Copilot session or the embedded Security Copilot experiences.
For more information on service specific RBAC, see the following articles:
Microsoft Entra security group
Although the Security Administrator role inherits access to Copilot and certain plugin capabilities, this role includes
 permissions. Don't assign users this role purely for Copilot access. Instead, create a security group and add that group to the appropriate Copilot role (Owner or Contributor).
permissions. Don't assign users this role purely for Copilot access. Instead, create a security group and add that group to the appropriate Copilot role (Owner or Contributor).For more information, see Best practices for Microsoft Entra roles.
Recommended Microsoft Security roles
An analyst with access to Microsoft's unified security operations platform has a custom Defender XDR role assigned that gives them access to multiple workloads in the Defender portal. If the custom role security operations include Security Copilot, then the Recommende Microsoft Security roles gives them access to the Security Copilot platform as well as Copilot in Microsoft Defender, simplifying security management.

Access embedded experiences
In addition to the Copilot contributor role, verify the requirements for each Security Copilot embedded experience to understand what extra roles and licenses are required.
For more information, see Security Copilot experiences.
Assign roles
The following table illustrates the default access granted to starting roles.
Note
Some organizations may still have the Everyone group assigned to Copilot contributor access. Consider replacing this broad access with Recommended Microsoft Security roles group.
| Capability | Copilot owner | Copilot contributor |
|---|---|---|
| Create sessions | Yes | Yes |
| Manage personal custom plugins | Yes | Default No |
| Allow contributors to manage personal custom plugins | Yes | No |
| Allow contributors to publish custom plugins for the tenant | Yes | No |
| Change availability of preinstalled plugins for the tenant | Yes | No |
| Upload files | Yes | Default Yes |
| Manage upload file usage | Yes | No |
| Run promptbooks | Yes | Yes |
| Manage personal promptbooks | Yes | Yes |
| Share promptbooks with tenant | Yes | Yes |
| Update data sharing and feedback options | Yes | No |
| Capacity management | Yes* | No |
| View usage dashboard | Yes | No |
| Select language | Yes | Yes |
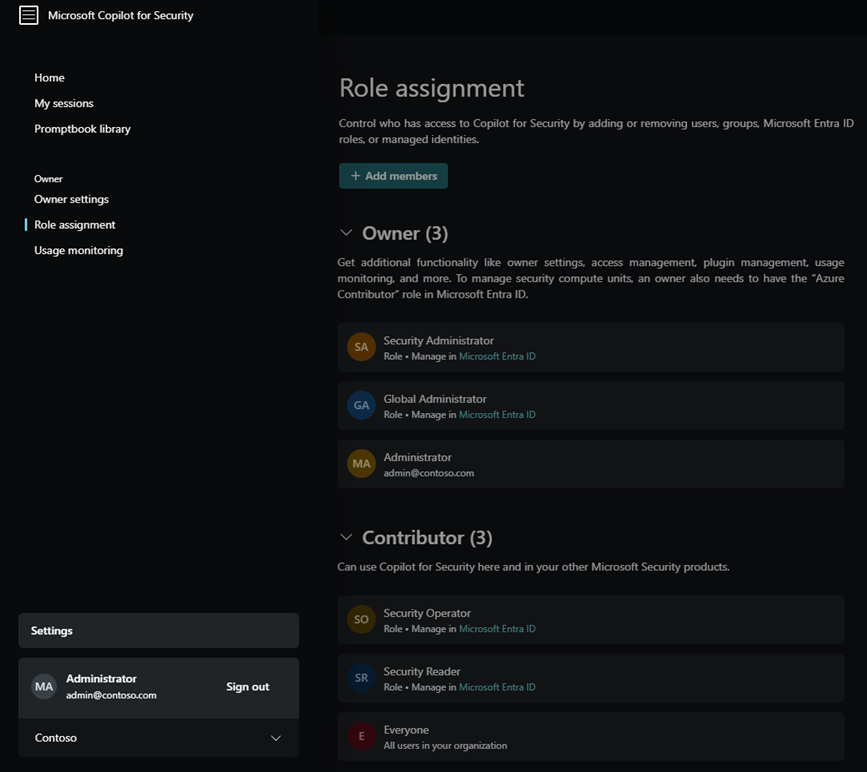
Assign Security Copilot access
Assign Copilot roles within Security Copilot settings.
- Select the
 home menu.
home menu. - Select Role assignment > Add members.
- Start typing the name of the person or group in the Add members dialog box.
- Select the person or group.
- Select the Security Copilot role to assign (Copilot owner or Copilot contributor).
- Select Add.
Tip
We recommend using security groups to assign Security Copilot roles instead of individual users. This reduces administrative complexity.
The Everyone group is removable from Contributor access. Consider adding the recommended roles after you remove the everyone group.
Microsoft Entra role membership is only manageable from the Microsoft Entra admin center. For more information, see Manage Microsoft Entra user roles.
Shared sessions
Copilot contributor role is the only requirement for sharing a session link or viewing it from that tenant.
When you share a session link, consider these access implications:
- Security Copilot needs to access a plugin's service and data to generate a response, but that same access isn't evaluated when viewing the shared session. For example, if you have access to devices and policies in Intune, and the Intune plugin is utilized to generate a response that you share, the recipient of the shared session link doesn't need Intune access to view the full results of the session.
- A shared session contains all the prompts and responses included in the session, whether it was shared after the first prompt or the last.
- Only the user that creates a session controls which Copilot users can access that session. If you receive a link for a shared session from the session creator, you have access. If you forward that link to someone else, it doesn't grant them access.
- Shared sessions are read-only.
- Sessions can only be shared with users in the same tenant that have access to Copilot.
- Some regions don't support session sharing via email.
SouthAfricaNorthUAENorth
For more information on shared sessions, see Navigating Security Copilot.
Multitenant
If your organization has multiple tenants or you leverage a managed service provider partner (MSSP), Security Copilot can accommodate authentication across them to access security data where Security Copilot is provisioned. The tenant that is provisioned for Security Copilot doesn’t need to be the tenant your security analysts logs in from. We currently support the authentication models below through different access approaches.
Azure B2B & Guest Accounts are able to leverage “Tenant Switching” which is natively built into the Security Copilot standalone portal. For more information, see Navigating Security Copilot tenant switching.
Granular Delegated Admin Privileges (GDAP) through the Partner Center. For more information, see Grant MSSPs access to Microsoft Security Copilot.
Azure Lighthouse through the Azure Portal. For more information, see Grant MSSPs access to Microsoft Security Copilot.
Tenant-switching is available through the Security Copilot standalone portal but only supports B2B collaboration accounts or guest account. For more information, see Navigating Security Copilot tenant switching.
Cross tenant sign-in example
Contoso recently merged with Fabrikam. Both tenants have security analysts, but only Contoso purchased and provisioned Security Copilot. Angus MacGregor, an analyst from Fabrikam wants to use their Fabrikam credential to use Security Copilot. Here are the steps to accomplish this access:
Ensure Angus MacGregor's Fabrikam account has an external member account in the Contoso tenant.
Assign the external member account the necessary roles to access Security Copilot and the desired Microsoft plugins.
Sign in to the Security Copilot portal with the Fabrikam account.
Switch tenants to Contoso.
For more information, see Grant MSSP access.
Manage promptbooks
Promptbook creation is available to all roles, including the ability to publish a custom promptbook for the tenant. Choose whether to publish a promptbook for yourself or the tenant at the time of creation.
For more information, see Build your own promptbook.
Preinstalled plugin authentication
Preinstalled plugins, like Microsoft Sentinel and Azure AI Search, require more setup. The plugin provider determines the type of authentication. Any plugin with the gear  or Set up button is configured per user. Whether a preinstalled plugin is restricted, all users who have access to the plugin configure that plugin's setup for themselves.
or Set up button is configured per user. Whether a preinstalled plugin is restricted, all users who have access to the plugin configure that plugin's setup for themselves.
Note
Website plugins use anonymous authentication to access content.
For more information, see Manage preinstalled plugins.