Nuta
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zalogować się lub zmienić katalogi.
Dostęp do tej strony wymaga autoryzacji. Możesz spróbować zmienić katalogi.
W tym przykładzie pokazano, jak używać interfejsów IXMLHTTPRequest2 i IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback wraz z zadaniami do wysyłania żądań HTTP GET i POST do usługi internetowej w aplikacji platformy platforma uniwersalna systemu Windows (UWP). Połączenie interfejsu IXMLHTTPRequest2 z zadaniami pozwala pisać kod, który komponuje się z innymi zadaniami. Na przykład zadanie pobierania można umieścić w łańcuchu zadań. Zadanie pobierania może być również inicjowane w odpowiedzi na anulowanie pracy.
Napiwek
Możesz również użyć zestawu SDK REST języka C++ do wykonywania żądań HTTP z aplikacji platformy UWP przy użyciu aplikacji języka C++ lub aplikacji klasycznej C++. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Zestaw SDK REST języka C++ (Nazwa kodu "Dokumentacja").
Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat zadań, zobacz Równoległość zadań. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat używania zadań w aplikacji platformy UWP, zobacz Programowanie asynchroniczne w języku C++ i Tworzenie operacji asynchronicznych w języku C++ dla aplikacji platformy UWP.
W tym dokumencie najpierw pokazano, jak utworzyć klasę HttpRequest i jej klasy pomocnicze. Następnie pokazano, jak używać tej klasy z aplikacji platformy UWP, która używa języka C++ i XAML.
Aby zapoznać się z przykładem, który używa IXMLHTTPRequest2 zadań, ale nie używa zadań, zobacz Szybki start: nawiązywanie połączenia przy użyciu żądania HTTP XML (IXMLHTTPRequest2).
Napiwek
IXMLHTTPRequest2 i IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback to interfejsy, które zalecamy do użycia w aplikacji platformy UWP. Niniejszy przykład można również przystosować do aplikacji klasycznej.
Wymagania wstępne
Obsługa platformy UWP jest opcjonalna w programie Visual Studio 2017 lub nowszym. Aby go zainstalować, otwórz Instalator programu Visual Studio z menu Start systemu Windows i wybierz używaną wersję programu Visual Studio. Kliknij przycisk Modyfikuj i upewnij się, że kafelek Programowanie platformy UWP jest zaznaczony. W obszarze Składniki opcjonalne upewnij się, że jest zaznaczone pole wyboru Narzędzia platformy UWP języka C++. Użyj wersji 141 dla programu Visual Studio 2017 lub v142 dla programu Visual Studio 2019.
Definiowanie klas HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback i HttpRequestStringCallback
Gdy interfejs IXMLHTTPRequest2 jest używany do tworzenia żądań sieci Web wysyłanych przez protokół HTTP, następuje zaimplementowanie interfejsu IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback w celu odbierania odpowiedzi z serwera i reagowania na inne zdarzenia. W tym przykładzie jest definiowana klasa HttpRequest służąca do tworzenia żądań sieci Web oraz klasy HttpRequestBuffersCallback i HttpRequestStringCallback służące do przetwarzania odpowiedzi. Klasy HttpRequestBuffersCallback i HttpRequestStringCallback wspierają klasę HttpRequest. Użytkownik w kodzie aplikacji pracuje tylko na klasie HttpRequest.
Metody GetAsync i PostAsync klasy HttpRequest umożliwiają inicjowanie operacji HTTP odpowiednio GET i POST. Metody te za pomocą klasy HttpRequestStringCallback odczytują odpowiedź serwera jako ciąg tekstowy. Metody SendAsync i ReadAsync umożliwiają strumieniowe przesyłanie dużej ilości treści we fragmentach. Te metody zwracają współbieżność::task reprezentującą operację. Metody GetAsync i PostAsync generują task<std::wstring> wartość, gdzie wstring część reprezentuje odpowiedź serwera. Metody SendAsync i ReadAsync generują wartości task<void>. Zadania kończą się z chwilą zakończenia operacji wysyłania i odczytu.
IXMLHTTPRequest2 Ponieważ interfejsy działają asynchronicznie, w tym przykładzie użyto współbieżności::task_completion_event do utworzenia zadania, które zostanie ukończone po zakończeniu operacji wywołania zwrotnego lub anulowaniu operacji pobierania. Klasa HttpRequest tworzy na podstawie tego zadania kontynuację opartą na zadaniach, aby wygenerować ostateczny rezultat. Klasa HttpRequest wykorzystuje kontynuację opartą na zadaniach do zapewnienia, że kolejne zadania będą wykonywane nawet w przypadku błędu lub anulowania poprzednich zadań. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat kontynuacji opartych na zadaniach, zobacz Równoległość zadań
Aby zapewnić obsługę anulowania, klasy HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback i HttpRequestStringCallback używają tokenów anulowania. Klasy HttpRequestBuffersCallback i HttpRequestStringCallback używają metody concurrency::cancellation_token::register_callback , aby włączyć zdarzenie ukończenia zadania w odpowiedzi na anulowanie. To zwrotne wywołanie anulowania przerywa operację pobierania. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat anulowania, zobacz Anulowanie.
Aby zdefiniować klasę HttpRequest
W menu głównym wybierz pozycję Plik>>
Użyj szablonu Pustej aplikacji języka C++ (uniwersalnego systemu Windows), aby utworzyć pusty projekt aplikacji XAML. W tym przykładzie nazwa projektu
UsingIXMLHTTPRequest2.Dodaj do projektu plik nagłówkowy o nazwie HttpRequest.h oraz plik źródłowy o nazwie HttpRequest.cpp.
W pliku pch.h dodaj następujący kod:
#include <ppltasks.h> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <wrl.h> #include <msxml6.h>W pliku HttpRequest.h dodaj następujący kod:
#pragma once #include "pch.h" inline void CheckHResult(HRESULT hResult) { if (hResult == E_ABORT) { concurrency::cancel_current_task(); } else if (FAILED(hResult)) { throw Platform::Exception::CreateException(hResult); } } namespace Web { namespace Details { // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when partial buffers are needed from the response. // When only the complete response is needed, use HttpRequestStringCallback instead. class HttpRequestBuffersCallback : public Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClass< Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassFlags<Microsoft::WRL::ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, Microsoft::WRL::FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestBuffersCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, concurrency::cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct), responseReceived(false), dataHResult(S_OK), statusCode(200) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } dataEvent = concurrency::task_completion_event<void>(); } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* stream) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { // Store a reference on the stream so it can be accessed by the task. dataStream = stream; // The work must be done as fast as possible, and must not block this thread, // for example, waiting on another event object. Here we simply set an event // that can be processed by another thread. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2* xhr, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { responseReceived = true; return OnDataAvailable(xhr, responseStream); } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataHResult = hrError; dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. concurrency::task<void> CreateDataTask(); HRESULT GetError() const { return dataHResult; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } bool IsResponseReceived() const { return responseReceived; } // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize); private: ~HttpRequestBuffersCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. concurrency::cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when data is available or error is triggered. concurrency::task_completion_event<void> dataEvent; concurrency::critical_section dataEventLock; // We cannot store the error obtained from IXHR2 in the dataEvent since any value there is first-writer-wins, // whereas we want a subsequent error to override an initial success. HRESULT dataHResult; // Referenced pointer to the data stream. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<ISequentialStream> dataStream; // HTTP status code and reason returned by the server. int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received. bool responseReceived; }; }; // Utility class for performing asynchronous HTTP requests. // This class only supports one outstanding request at a time. class HttpRequest { public: HttpRequest(); int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool IsResponseComplete() const { return responseComplete; } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> GetAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, const std::wstring& str, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). concurrency::task<void> SendAsync( const std::wstring& httpMethod, Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. concurrency::task<void> ReadAsync( Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead); static void CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream); private: // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> DownloadAsync( PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamBytesToSend); // Referenced pointer to the callback, if using SendAsync/ReadAsync. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback> buffersCallback; int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool responseComplete; }; };W pliku HttpRequest.cpp dodaj następujący kod:
#include "pch.h" #include "HttpRequest.h" #include <robuffer.h> #include <shcore.h> using namespace concurrency; using namespace Microsoft::WRL; using namespace Platform; using namespace std; using namespace Web; using namespace Windows::Foundation; using namespace Windows::Storage::Streams; // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when only the complete response is needed. // When processing chunks of response data as they are received, use HttpRequestBuffersCallback instead. class HttpRequestStringCallback : public RuntimeClass<RuntimeClassFlags<ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestStringCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream*) { return S_OK; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { wstring wstr; HRESULT hr = ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(responseStream, wstr); // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hr), move(wstr))); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Simulate the functionality of DataReader.ReadString(). // This is needed because DataReader requires IRandomAccessStream and this // code has an ISequentialStream that does not have a conversion to IRandomAccessStream like IStream does. HRESULT ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(ISequentialStream* readStream, wstring& str) { // Convert the response to Unicode wstring. HRESULT hr; // Holds the response as a Unicode string. wstringstream ss; while (true) { ULONG cb; char buffer[4096]; // Read the response as a UTF-8 string. Since UTF-8 characters are 1-4 bytes long, // we need to make sure we only read an integral number of characters. So we'll // start with 4093 bytes. hr = readStream->Read(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 3, &cb); if (FAILED(hr) || (cb == 0)) { break; // Error or no more data to process, exit loop. } if (cb == sizeof(buffer) - 3) { ULONG subsequentBytesRead; unsigned int i, cl; // Find the first byte of the last UTF-8 character in the buffer. for (i = cb - 1; (i >= 0) && ((buffer[i] & 0xC0) == 0x80); i--); // Calculate the number of subsequent bytes in the UTF-8 character. if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0x80) { cl = 1; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xE0) { cl = 2; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xF0) { cl = 3; } else { cl = 4; } // Read any remaining bytes. if (cb < i + cl) { hr = readStream->Read(buffer + cb, i + cl - cb, &subsequentBytesRead); if (FAILED(hr)) { break; // Error, exit loop. } cb += subsequentBytesRead; } } // First determine the size required to store the Unicode string. int const sizeRequired = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, nullptr, 0); if (sizeRequired == 0) { // Invalid UTF-8. hr = HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError()); break; } unique_ptr<char16[]> wstr(new(std::nothrow) char16[sizeRequired + 1]); if (wstr.get() == nullptr) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; break; } // Convert the string from UTF-8 to UTF-16LE. This can never fail, since // the previous call above succeeded. MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, wstr.get(), sizeRequired); wstr[sizeRequired] = L'\0'; // Terminate the string. ss << wstr.get(); // Write the string to the stream. } str = SUCCEEDED(hr) ? ss.str() : wstring(); return (SUCCEEDED(hr)) ? S_OK : hr; // Don't return S_FALSE. } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hrError), wstring())); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Retrieves the completion event for the HTTP operation. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> const& GetCompletionEvent() const { return completionEvent; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } wstring GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } private: ~HttpRequestStringCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when the // download operation completes. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> completionEvent; int statusCode; wstring reasonPhrase; }; // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize) { // Lock the data event while doing the read, to ensure that any bytes we don't read will // result in the correct event getting triggered. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); ULONG bytesRead; CheckHResult(dataStream.Get()->Read(outputBuffer, outputBufferSize, &bytesRead)); if (bytesRead < outputBufferSize) { // We need to reset the data event, which we can only do by creating a new one. dataEvent = task_completion_event<void>(); } return bytesRead; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. task<void> Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::CreateDataTask() { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); return create_task(dataEvent, cancellationToken); } HttpRequest::HttpRequest() : responseComplete(true), statusCode(200) { } // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::DownloadAsync(PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. auto stringCallback = Make<HttpRequestStringCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(stringCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); auto completionTask = create_task(stringCallback->GetCompletionEvent()); // Create a request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod, uri, stringCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); if (postStream != nullptr && contentType != nullptr) { CheckHResult(xhr->SetRequestHeader(L"Content-Type", contentType)); } // Send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Send(postStream, postStreamSizeToSend)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return completionTask.then([this, stringCallback](tuple<HRESULT, wstring> resultTuple) { // If the GET operation failed, throw an Exception. CheckHResult(std::get<0>(resultTuple)); statusCode = stringCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = stringCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); return std::get<1>(resultTuple); }); } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::GetAsync(Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"GET", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, nullptr, nullptr, 0); } void HttpRequest::CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream) { auto randomAccessStream = ref new Windows::Storage::Streams::InMemoryRandomAccessStream(); CheckHResult(CreateStreamOverRandomAccessStream(randomAccessStream, IID_PPV_ARGS(stream))); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, const wstring& body, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { int length = 0; ComPtr<IStream> postStream; CreateMemoryStream(&postStream); if (body.length() > 0) { // Get the required buffer size. int size = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size nullptr, // Output buffer 0, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((size != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); std::unique_ptr<char[]> tempData(new char[size]); length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size tempData.get(), // Output buffer size, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((length != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); CheckHResult(postStream->Write(tempData.get(), length, nullptr)); } return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, L"text/plain;charset=utf-8", postStream.Get(), length); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, contentType, postStream, postStreamSizeToSend); } // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). task<void> HttpRequest::SendAsync(const wstring& httpMethod, Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. buffersCallback = Make<Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(buffersCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback> xhrCallback; CheckHResult(buffersCallback.As(&xhrCallback)); // Open and send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod.c_str(), uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), xhrCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); responseComplete = false; CheckHResult(xhr->Send(nullptr, 0)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // Since buffersCallback holds a reference on the callback, the lifetime of the callback will exceed // the operation and ensure that cancellation works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); statusCode = buffersCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = buffersCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); }); } // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. task<void> HttpRequest::ReadAsync(Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead) { if (offsetInBuffer + requestedBytesToRead > readBuffer->Capacity) { throw ref new InvalidArgumentException(); } // Return a task that completes when a read completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this, readBuffer, offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); // Get a pointer to the location to copy data into. ComPtr<IBufferByteAccess> bufferByteAccess; CheckHResult(reinterpret_cast<IUnknown*>(readBuffer)->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&bufferByteAccess))); byte* outputBuffer; // Returned internal pointer, do not free this value. CheckHResult(bufferByteAccess->Buffer(&outputBuffer)); // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. readBuffer->Length = buffersCallback->ReadData(outputBuffer + offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead); if (buffersCallback->IsResponseReceived() && (readBuffer->Length < requestedBytesToRead)) { responseComplete = true; } }); }
Korzystanie z klasy HttpRequest w aplikacji platformy UWP
W tej sekcji pokazano, jak używać HttpRequest klasy w aplikacji platformy UWP. Aplikacja zawiera pole wprowadzania danych definiujące zasób adresu URL, polecenia przycisków wykonujące operacje GET i POST oraz polecenie przycisku, które anuluje bieżącą operację.
Aby użyć klasy HttpRequest
W pliku MainPage.xaml zdefiniuj element StackPanel w następujący sposób.
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="440" Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <TextBox x:Name="InputTextBox" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="http://www.fourthcoffee.com/"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button x:Name="GetButton" Content="Get" Background="Green" Click="GetButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="PostButton" Content="Post" Background="Blue" Click="PostButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="CancelButton" Content="Cancel" Background="Red" IsEnabled="False" Click="CancelButton_Click"/> <ProgressRing x:Name="ResponseProgressRing" /> </StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="ResponseTextBlock" TextWrapping="Wrap"/> </StackPanel>W pliku MainPage.xaml.h dodaj następującą dyrektywę
#include:#include "HttpRequest.h"W pliku MainPage.xaml.h dodaj następujące zmienne składowe
privatedo klasyMainPage:// Produces HTTP requets. Web::HttpRequest m_httpRequest; // Enables us to cancel the active HTTP request. concurrency::cancellation_token_source m_cancelHttpRequestSource;W pliku MainPage.xaml.h zadeklaruj metodę
privateProcessHttpRequest:// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void ProcessHttpRequest(concurrency::task<std::wstring> httpRequest);W pliku MainPage.xaml.cpp dodaj następujące instrukcje
using:using namespace concurrency; using namespace std; using namespace Web;W pliku MainPage.xaml.cpp zaimplementuj metody
GetButton_Click,PostButton_ClickiCancelButton_ClickklasyMainPage.void MainPage::GetButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the GET request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.GetAsync(uri, token)); } void MainPage::PostButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the POST request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); wstring postData(L"This is sample POST data."); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.PostAsync(uri, postData, token)); } void MainPage::CancelButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Disable the Cancel button. // It will be re-enabled during the next web request. CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Initiate cancellation. m_cancelHttpRequestSource.cancel(); }Napiwek
Jeśli aplikacja nie wymaga obsługi anulowania, przekaż współbieżność ::cancellation_token::none do
HttpRequest::GetAsyncmetod iHttpRequest::PostAsync.W pliku MainPage.xaml.cpp zaimplementuj metodę
MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest.// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest(task<wstring> httpRequest) { // Enable only the Cancel button. GetButton->IsEnabled = false; PostButton->IsEnabled = false; CancelButton->IsEnabled = true; // Clear the previous response and start the progress ring. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ""; ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = true; // Create a continuation that shows the results on the UI. // The UI must be updated on the ASTA thread. // Therefore, schedule the continuation to run on the current context. httpRequest.then([this](task<wstring> previousTask) { try { // // Show the result on the UI. wstring response = previousTask.get(); if (m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() == 200) { // The request succeeded. Show the response. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(response.c_str()); } else { // The request failed. Show the status code and reason. wstringstream ss; ss << L"The server returned " << m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() << L" (" << m_httpRequest.GetReasonPhrase() << L')'; ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(ss.str().c_str()); } } catch (const task_canceled&) { // Indicate that the operation was canceled. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation was canceled"; } catch (Exception^ e) { // Indicate that the operation failed. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation failed"; // TODO: Handle the error further. (void)e; } // Enable the Get and Post buttons. GetButton->IsEnabled = true; PostButton->IsEnabled = true; CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Stop the progress ring. ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = false; }, task_continuation_context::use_current()); }We właściwościach projektu w obszarze Konsolidator, Dane wejściowe określ
shcore.libimsxml6.lib.
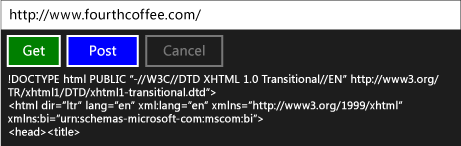
Oto działająca aplikacja:
Następne kroki
Środowisko uruchomieniowe współbieżności — wskazówki
Zobacz też
Równoległość zadań
Anulowanie w PPL
Programowanie asynchroniczne w języku C++
Tworzenie operacji asynchronicznych w języku C++ dla aplikacji platformy uniwersalnej systemu Windows
Szybki start: nawiązywanie połączenia przy użyciu żądania HTTP XML (IXMLHTTPRequest2)klasa zadań (środowisko uruchomieniowe współbieżności)
task_completion_event, klasa