Automating Windows as a Service
Bold lines are important. Blue lines are most important. (read with care) TL;DR; at the end - if you need it.
Hello together,
first of all I need to apologize again for the length of this blog post, but I personally think that the following topics need to stick together to be understood into depth and I don´t want to leave any chance for missunderstandings.
It took me some time (100h+) to create this article and it will take probably some time to read it.
But before you continue reading you should be aware of Windows as a Service and what really stands behind it.
(if not read Demystifying Windows as a Service – wake up! please and Update to the Windows as a Service Model)
I will start with a short intro and some theory - moving on to the procedural automation and to technical adoption in theory and finally to technical adoption with automation.
Disclaimer:
I´ve received so many negative feedback regarding WaaS after my previous extensive article and I have heard so many times that WaaS is so extremely complex and no one would ever be possible to adopt this in any way. First - nearly all of the topics, which I am speaking about, are mandatory know-how - either regarding to Project Management, ITIL, ALM, Security Management (updates) or obvious technical background. I am actually not explaining something new - I am only explaining how professional IT can and should be adopted. The answer is - professional.
I am also writing this as a private person, who thinks that DevOps is not only a buzzword. I see a huge need to show a theoretical approach for automating WaaS and also to show a technical Proof of Concept - otherwise it seems that no one will ever believe me.
By writing this article as a private person you might also recognize that I am doing this in my free time. (having not too much of it!)
Introduction
WaaS is not something "Microsoft-special" and nowadays there is this cruel necessity to keep up the pace and adopt the newest technologies just in time. With WaaS this is accomplished for the Operating System, where by speaking of the coming "new wonderful Features" we are mainly speaking about Security and Administration Features, which are increasing the Clients´ Security with hardening. Additionally we introduce new technologies like Windows Hello for Business with Companion Devices, Exploit Guard, Application Guard and later on also features using Artifical Intelligence on or with the OS like Advanced Threat Protection and even the Antivirus.
I see companies grumbling about this change, but this is just a kind of Digital Transformation. There is no time anymore to release new Operating Systems manually every 3 to 5 years.
I love to quote Jeffrey Snover: “If you want to fail in a transformative change just treat it as an incremental change.”
Video from PSConfEU 2017 - 13:10 ff. MUST see.
Theory
First of all I want to clarify our latest changes to make sure, that everyone is on the line. WaaS is an always recurring process in identical time frames as shown in the following picture:

One OS is supported 18 month. You will always have around 6 months between each OS release.
So you know when specific OS Versions are in Insider Preview, get released, become ready for broad deployment and when they run out of support. Always.
Michael Niehaus consolidated this vast information and complexity in its latest blog article.
It is probably the shortest article ever and he is right. This is the main information.
Everything else, that I am describing and explaining is just:
- how to do it professionally
- how to save time in the future
- and the most important one: how to do it structured!
Lets start by diving into a more detailed view:
The latest changes result into completely predictable time frames, which you should simply address in a recurring manner.
So - what has to be done for one specific OS Version?
Michael separated this into 3 phases (see here ), which makes it very simple to understand - and you should be aware of these 3 phases:

- Plan and Prepare. Leverage the Windows Insider Program to follow along with the development of new Windows 10 features (so that you can prepare to deploy those features), while at the same time validating compatibility and providing feedback on any issues or concerns.
- Targeted Deploy. Starting as soon as a new Semi-Annual Channel feature update is released, begin targeted pilot deployments to a targeted group of machines (we typically suggest around 10%) to validate app, device, and infrastructure compatibility.
- Broadly Deploy. Once you are satisfied with the results of the pilot deployments, begin broadly deploying throughout the organization. For some organizations, broad deployment can begin quickly; for others it can take longer. It is up to each organization to determine when to make that transition.
(see here)
As a result of this we will now dive deeper and take a detailed look for one specific OS Version - for example Windows 10 1803 - starting from Insider Preview up to its end of life and what has to be done in each time period.
Granular View for one Release:
[video width="800" height="1080" mp4="https://msdnshared.blob.core.windows.net/media/2017/08/WaaSArticle2.mp4"][/video]
The video ends up in this slide and demonstrates the transition from the specific acronyms and timestamps to fully understand the model and how all the time frames are actually working together:
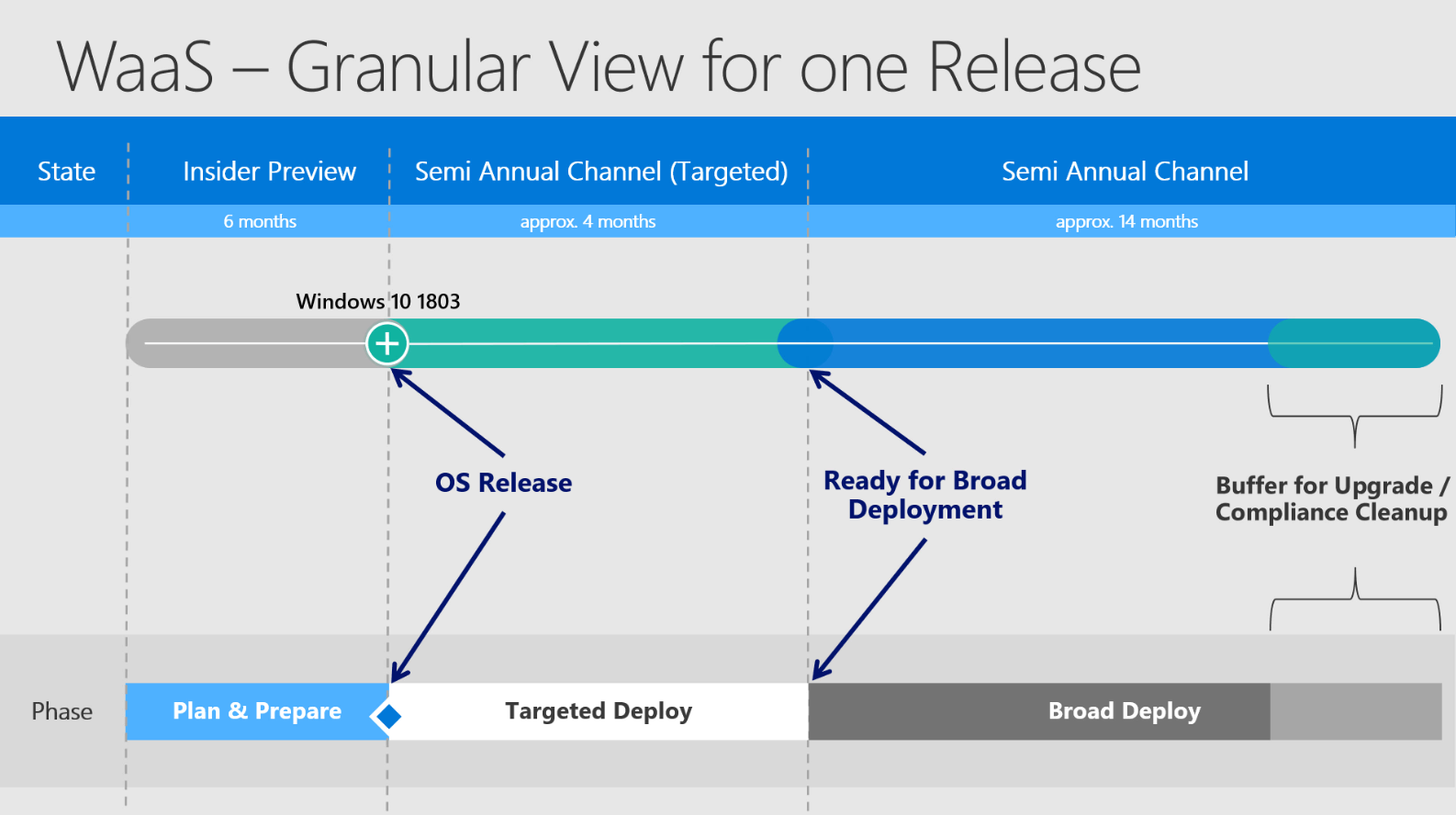
Starting from left to right you see the different states of the OS Version. Starting in Insider Preview and then becoming finally available in SACT - moving on to SAC and finally moving out of support.
The timestamp when a release finally becomes officially "Ready for Broad Deployment" may vary to different circumstances like feedback from Premier Support, feedback via Feedback Hub, feedback over Telemetry and also internal feedback. But as mentioned in my last article - it does not affect the general support time of 18 months.
Legend:

Also some more detailed words to the "Buffer for Upgrade":
Buffer for Upgrade = Compliance Cleanup = a defined time buffer, which is placed at the end of broad deploy to make sure having some time, if something does not work as desired and to target computers, which were not able to upgrade by any means. This ones need to be addressed specifically and therefore the naming "Compliance Cleanup" is used.
This was actually everything, what changed. Only names. Nothing less, nothing more. Now let´s continue and move from Theory into the Procedural Adoption.
Procedural Adoption

Speaking in times:
- around 6 months Insider Preview
- 18 months supportability
- consisting of approx. 4 months SACT
- and approx. 14 months SAC
- evaluate 10 months for broad deploy
- and 4 months for Compliance Cleanup and Buffer
This slide will show you what "User"-group (team/persons) has to accomplish which "Workflow" (tasks / processes) in which defined "State" (timeframe):
- State - predictable timeframe regarding the specific OS Version. Due to the fact of the OS releases in March and September every timeframe can be defined pretty exactly.
- User - a group of persons / a team / a outsourcer who has the lead for the defined tasks in this timeframe
- Phase - one of the 3 known phases to divide the OS deployment - for better explanation: Plan & Prepare, Targeted Deploy, Broad Deploy
- (scroll down) State 2 - Separation of the working tasks into Proactive Testing, Reactive Testing & Production and Upgrade
It describes what the approach should be at the shown timeframe. You start in Proactive Testing to set up the configuration and test LoB apps, but also moving in your internal first tests. In Reactive Testing you deploy your upgrade to dedicated machines (starting with small numbers) to find any incompatabilities, which were not identified without causing a high impact.
By defining small numbers and well chosen computers you predefine the possible impact and completely control your testing approach.Afterwards you move fluently into Production and at the end upgrading special or very sensitive machine. (VIP, industry computers, etc.) - Workflow - Defined work tasks that have to be accomplished in the current time frame.
You predefine the upcoming processes and because it is completely predictable you are able to set up a detailed recurring project plan! Let us go through each State in detail to discuss the Workflow and the specific "User"-group.
Plan & Prepare
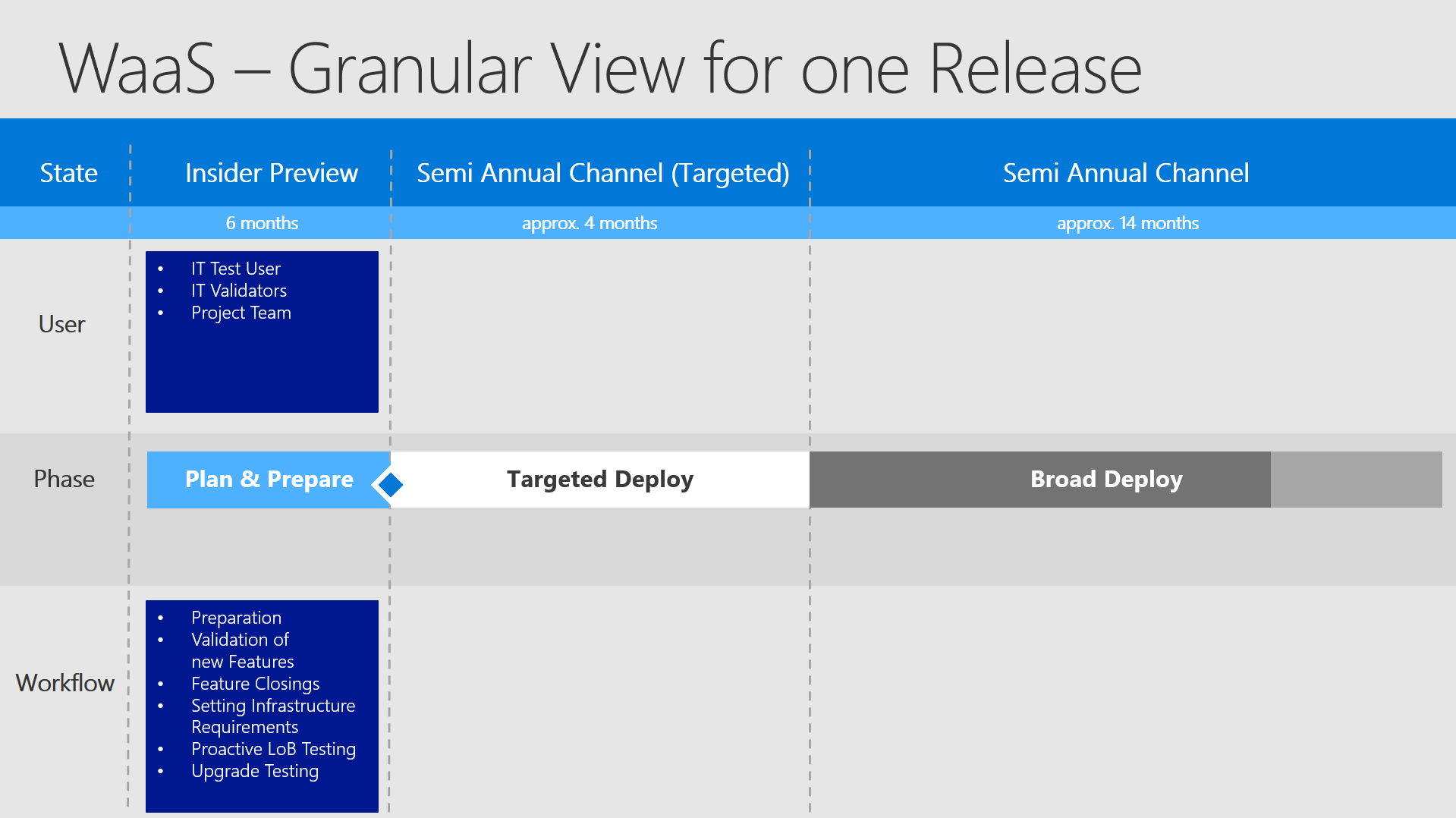
In this timeframe we now define our phases by our events - so we have the "Plan & Prepare" phase , where you start the first preparations for the upcoming OS version. The most important steps here are to test the most important LoB apps and to validate the new features. Regarding the new features you have to make the decision, if you want to use it and also to take a look at the prerequirements and including these tasks into your internal roadmap. Additionally you should also take a look at closing, deprecated or removed features, which might affect you. It is also a good idea to test the inplace upgrade itself - does the computer with a bunch of software installed on it still upgrade as intended? Are there any modifications made to the computer, which need to be addressed after the upgrade? For the first releases every customer is doing this process manually. Why? It was ever done this way and there was no need to change this. But now coming with updates every 6 months this won´t be possible anymore. So you should start building a procedural and technical workflow which addresses all recurring and automatable tasks completely.
Targeted Deploy

The "Targeted Deploy" is initialized by the official release and it is the most complicated phase and I will explain you why. The first things you need to achieve with the released version is to get everything ready for the broad deployment. This means that you have to create GPOs, enabling new features, making some modifications to configuration, CI or even other technologies and so on.
So you want to have some test/dev computers where the new release is just installed on as soon it is published. This should be done via Inplace Upgrades, because you passively just test, if the technical upgrade process itself works well and how the computer looks like after this upgrade. The project team (for probably new features) and the IT department can now set up the whole configuration and test on these dedicated machines. As you see - we have a defined collection of computers which should be upgraded automatically after this event (the release of the new OS Version). This task should take as less time as possible to push out the first testing rings.
Testing rings? You want to deploy the new OS as fast as possible to a small but very representative number of computers. The very first testing rings should include mostly IT-people which can handle small problems and give good feedback to - for example - missing GPOs or additional fixes which have to be made after the inplace upgrade. You want also to test applications in this phase - as you see in the picture I have mentioned the Application Holder and the App Test Users. While the configuration is evolving to its finish the first rings targetting the applications should start firing. And here it gets tricky - it´s not only about applications - there is much more that should be taken into consideration:
- Applications
- Organizational Units
- Network Segments
- Geographical Locations
Applications are pretty understandable. Who are the best testers? People who actually work with the software products. So you want to deploy as soon as possible the new OS version to people working with applications - BUT - you don´t want to have an huge impact. So you start with very small numbers trying to target ALL applications. It would be great if you upgrade a number of computers with all existing applications installed on it at least once.
Why Organizational Units? OUs are very similar to the transversal cut through all applications. There are some applications which only are used in specific teams, which at many customers are managed in specific OUs. Additionally to this you want also to test all different GPOs and don´t want to find some coincidences too late coming from specific settings and creating unusual errors.
Why Network Segments or Geographical Location? Actually you know the answer - you don´t want to find network-related errors too late for a whole building or even region. A great benefit by doing this - you create indirectly caching points in the whole field. For example - if you have 10 buildings and 100 machines in each building (depending on the technology for sure) the devices will reach out for the feature updates in the same building or even NAT. Therefore the best strategy would be to upgrade in the first place one computer for each building and then increasing this number step by step. Even if machines are offline - there will be pretty fast the situation that you have at least one caching point sitting in each building.
As you see - there are a lot of benefits for this approach - but how can you adopt this technically und fully automated? This is where the "tricky" begins.
The combination of all these transversal cuts split up into some rings will be the hardest part to accomplish in the automation of WaaS. Setting up the collections for the rings with well-chosen computers is hard - but manageable. And the good thing - if you have accomplished this task once you will never need to do it again, because it will be automated! We will take a more dedicated look at some possible solutions later on in the technical part.
Broad Deploy

As you can see in the following image the Broad Deploy area is divided into 3 parts. The first two parts are considered the typical "Broad Deploy" - pushing out the upgrade in a high number into the field. The second ring of this two though will mostly focus on some special machines which should not result in problems by any mean. So they will be deployed in the timeline rather late to have run through a vast amount of proactive and reactive testings before. And in the last region the computers become uncompliant.
Why?
In IT you should always calculate with time buffers. Therefore you should move your upgrading target date to around 4 months earlier, before the client itself gets out of support. So you would try to place all your upgrades between Insider Preview up to 2/3 of Broad Deploy (SAC). Then you can define a precise task for Compliance Cleanup, which is targetting all machines that did not upgrade / or could not being upgraded.
In the next picture (below) I added (by purpose) an additional "State" directly below the "Phase". The shown information is crucial to understand and adopt WaaS:
Understanding Reactive Testing

In WaaS you do "Proactive Testing" and you configure everything without making any mistakes and running through quality gates. (sure you do)
But - due to the fact of not having unlimited time like in Windows 7 - there will come a point in time, where you just suggest that everything will work.
This approach is called risk based approach, which is specifically targetting applications. (further information in previous WaaS Article)
The first question I always get is - WHAT? You want to possibly impact some of our machines in the field?
The answer is - Yes!
Who are the best testers? People who actually work with the applications!
What is the impact? You define the impact by defining the number of computers which are upgraded at the same time, in the same OU with the same applications.
What is the impact for the chosen users who will run into problems? They will call either Support desk or their Application Holder and then roll back --> 30 minutes to 60 minutes
What is the outcome? You will get very early dedicated and precise information, what is not working.
What is next? You have to prepare a workflow for this scenario. Depending on the application impacted - pausing further deployment and resolving the problem:
- internal validation
- validation by Application Holder
- Support Call at Manufacturer
- Contacting Premier Support from Microsoft
- Validating fallback or alternative options
After having fixed the issue you can just continue with your deployment.
Take a look later at "Target Deploy" in the topic "Technical Approach in Theory".
More information here.
Dividing into fixed Procedural Steps
As a result of this you should collect a list for who has to do what starting at a specific point in time and completing in a specific time frame with an end date and what should be the outcome.
This sentence is extremely important and therefore we will take all the necessary information out of it: 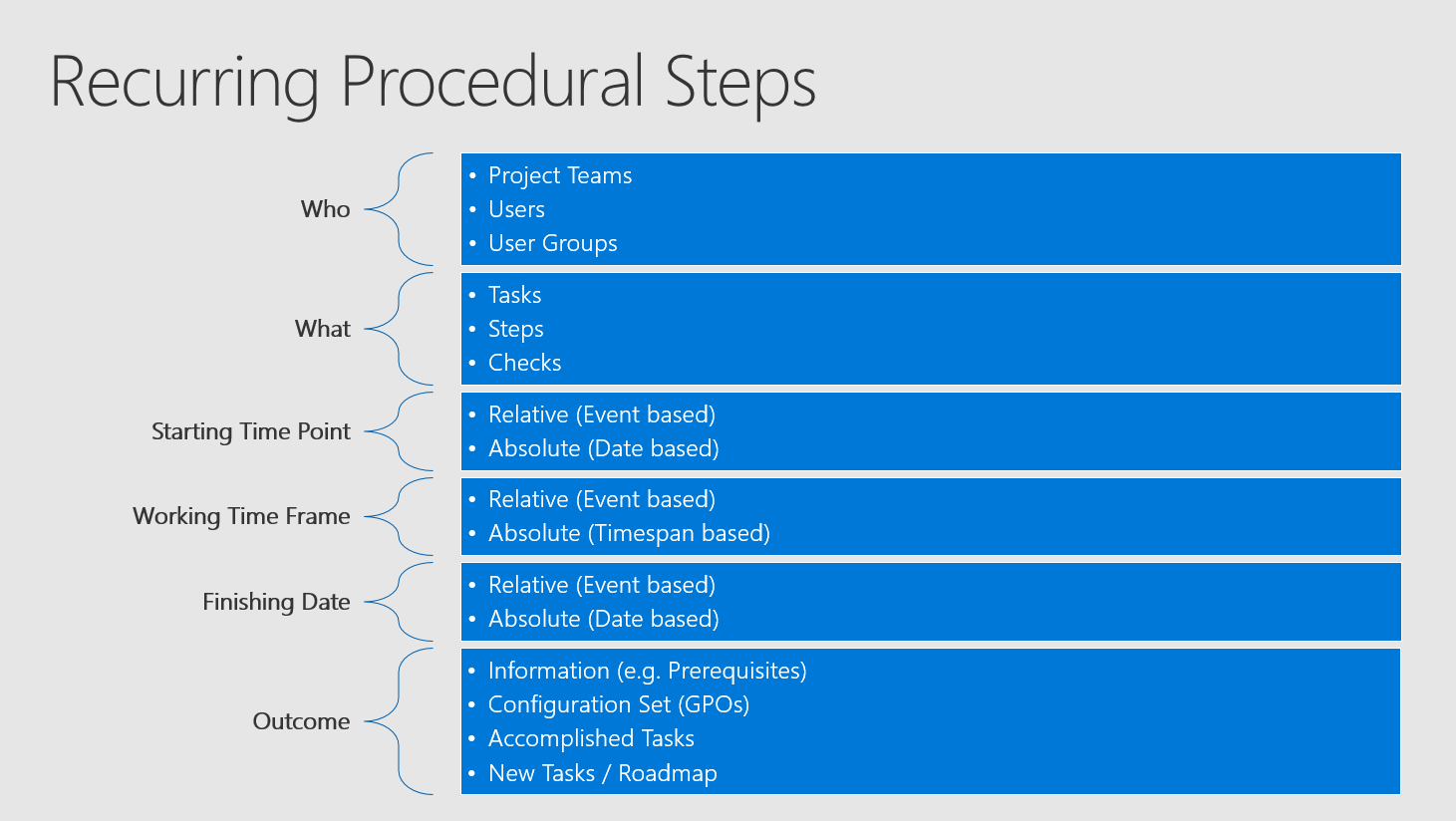
This is simple project management and setting up all the tasks should be easy work. The cool thing about this (every project manager should love this) - these tasks need only to be set up once. With every Feature Update normally only the settings of these tasks are optimized - sometimes there may be also some tasks added or removed, but - all in all the whole task list is a pretty solid setup (this has to be your target). And now you may see the first problem here:
You need to set it up with a decent amount of time and care.
Because of its impact you want to make absolutely sure, that the defined task list is complete and correctly "configured".
How?
Communication!
What else?
Project Management!
To retrieve a complete and well configured list of tasks you should set up meetings and firstly brainstorm from a technical, but also procedural and business-depending point of view. Just grab every idea from every team or person and write it down. Discuss about removing unnecessary or unappropriate tasks. Think also of consolidating or dividing tasks. Then you should define at least the values for who, what and the outcome for all tasks.Decide whether it makes sense to use Date-based or Event-based (prefer this one the most of the times) and then visualize all the tasks and put them into your timeline for ONE specific OS Version. In the end it is about fine-tuning.
The whole process can be seen in the next picture - depending on your company this process may take some time. (hopefully not months) 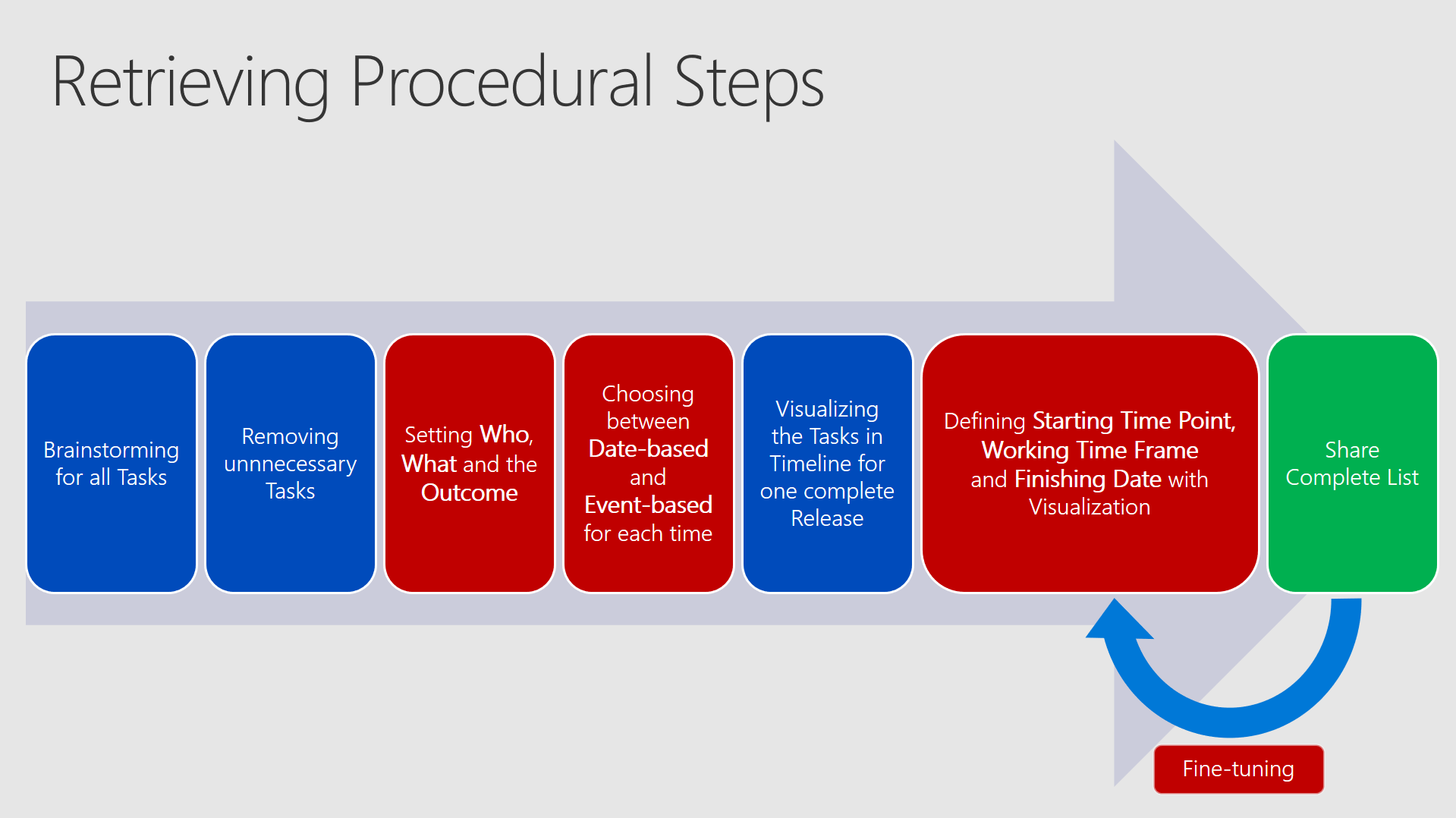
The blue boxes can be done with ease, but the red ones need to be really handled with care and should be well-considered.
Let us take a look at two demos of the mentioned tasks:


This is the same example for "Validating new Features" - the first one with absolute dates and the second one based on events. You need to decide by your own, which makes more sense, but we will see later on, that the distribution of each Windows 10 Feature Update (Upgrade) is implemented technically event-based.
Process Optimization
Some lines above I have spoken about the visualization of the tasks. A project manager normally should jump up and and shoot out, that he knows some techniques to accomplish this. We are now moving into some tasks of his job and therefore it may look complicated for some people. (it isn´t that complicated) Personally I would say, that there are two good approaches on this - depending to your company size:
Gantt Chart
The good thing about the Gantt Chart is, that nearly everyone has seen or worked with similar charts. It is straightforward und easy understandable - even for non project managers. But it has one devastating downside - if you want to manage and improve a lot of tasks with the Gantt Chart this will become unhandy and confusing. Therefore you should retrieve your amount of possible tasks and decide in one of the first steps, if the Gantt Chart is the technique you want to focus on.

Critical path method
The other possibility, which I have seen a couple of times is to work with the Critical Path Method or some similar methods. There is one downside here aswell - setting it up and staying up to date takes more time than with the Gantt Chart. But you can control even better your gaps and holds and optimize all the processes in a centralized way.
Due to its complexity you could even use both: Use process automation in the Critical Path Method by dedicated and trained project managers, but deliver simplified Gantt Charts - to the dedicated teams (with only partial outputs). By doing it that way you would have a complex (but effective) project management with the possibility to visualize it in a simplified way for all the teams and involved persons. 
Outcome
The outcome should be an optimized list of tasks which should be addressed for one dedicated release. I will just brainstorm to give you a brief overview, which tasks could be implemented:
- ADMX - Download & Install
- Manage GPOs
- Validating (new) Features
- Knowledge Management
- Internally
- Teams
- Users
- Validating Feature Closings
- Setting Infrastructure Requirement
- new projects
- Test Inplace Upgrade
- Upgrade itself
- Look & Feel afterwards
- Technical functionality afterwards
- LoB Testing
- Setting up OSD TS
- Download ISO/WIM
- Report evaluation
- Upgrades
- Versions
- ALM
- Feedback Management
- Retrieval
- Push
- Pilot Deployment
- Outcome
- Targeted Deployment
- Outcome
- Broad Deployment
- SLA
- Compliance Cleanup
- Change Management
- Security evaluation
- Evaluation with Legal (Telemetry etc.)
- Evaluation with workers council (new features / changes)
- Upgrading depending technologies (Configuration Manager, O365 etc.)
- Remediation Task
- Application Incompatibility Workflow
- more
Technical Approach in Theory
After knowing about the 3 phases we will now divide all the phases into smaller chunks.
This is what we (Microsoft) call rings - targeting a defined collection to be applied to a specific timestamp which is relative to one of the events "Insider Preview", "SACT" and "SAC". What does this look like?
[video width="800" height="1080" mp4="https://msdnshared.blob.core.windows.net/media/2017/08/WaaSArticle2_Rings.mp4"][/video]
The video showed how the timeline is split into these rings and ended up in this slide (beware count of rings only for demo purposes):
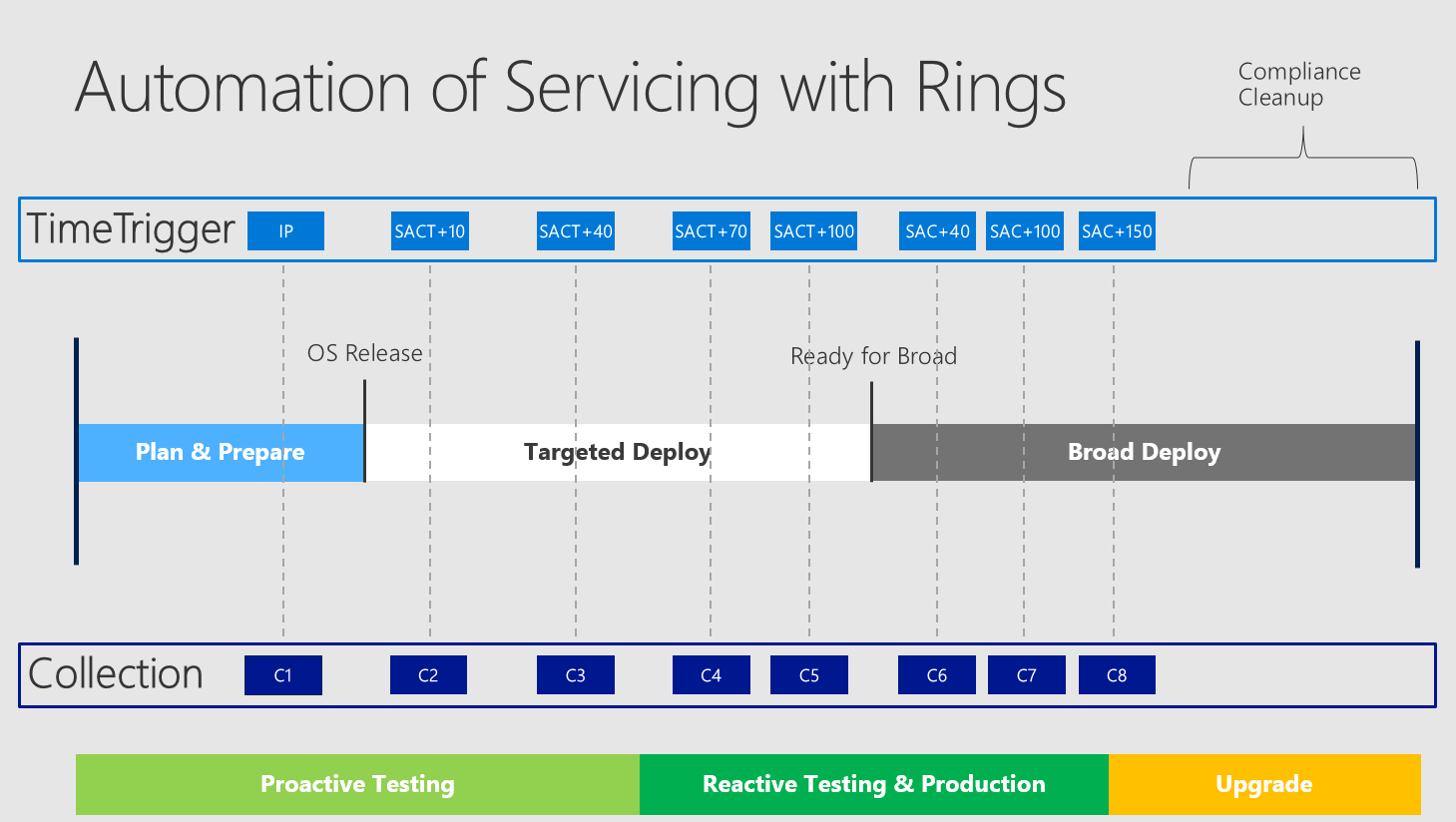
So you divide your complete timeline for one OS version into rings ("TimeTrigger" with specific "Collections"). These specific collections are used for the automatic upgrade and do have different purposes.
Centrally-Controlled vs. User-Controlled Upgrade
The date which is event-based could be the starting point of the deployment or a forced and fixed upgrading date.
I usually recommend that we (administrators) define the time frame where the upgrades are available (1-4 weeks - afterwards forced) and the user defines the point in time, when he initializes the upgrade.
Depending to your environment either the one or the other or even both methods could make sense and should be used. This is something that you have to discuss.
If the user initializes the upgrades he definitely needs to be aware of, what that means for him and his machine. (1h upgrade time)
Okay - let us take now a closer look to the collection numbers. What are the right numbers for collections? To discuss this question let us take a look at the 3 areas in detail:
Plan & Prepare / Insider
As you have read above, the main target here is to evaluate new or possible deprecated / removed Features and probably aswell some or all LoB Apps.
How many collections do you need in the space of the Insider Preview / Plan & Prepare?
I would say - not much. One might come into consideration - for example with a virtualized machine, which can easily be rolled back to defined checkpoints and easily by repaired by recreating it. This one could also be greatly shared along different teams to connecting remotely to it. But using also some dedicated machines should be discussed. (2nd devices, dedicated testing machines, etc.) You would configure Insider Preview - Fast Ring on these machines.
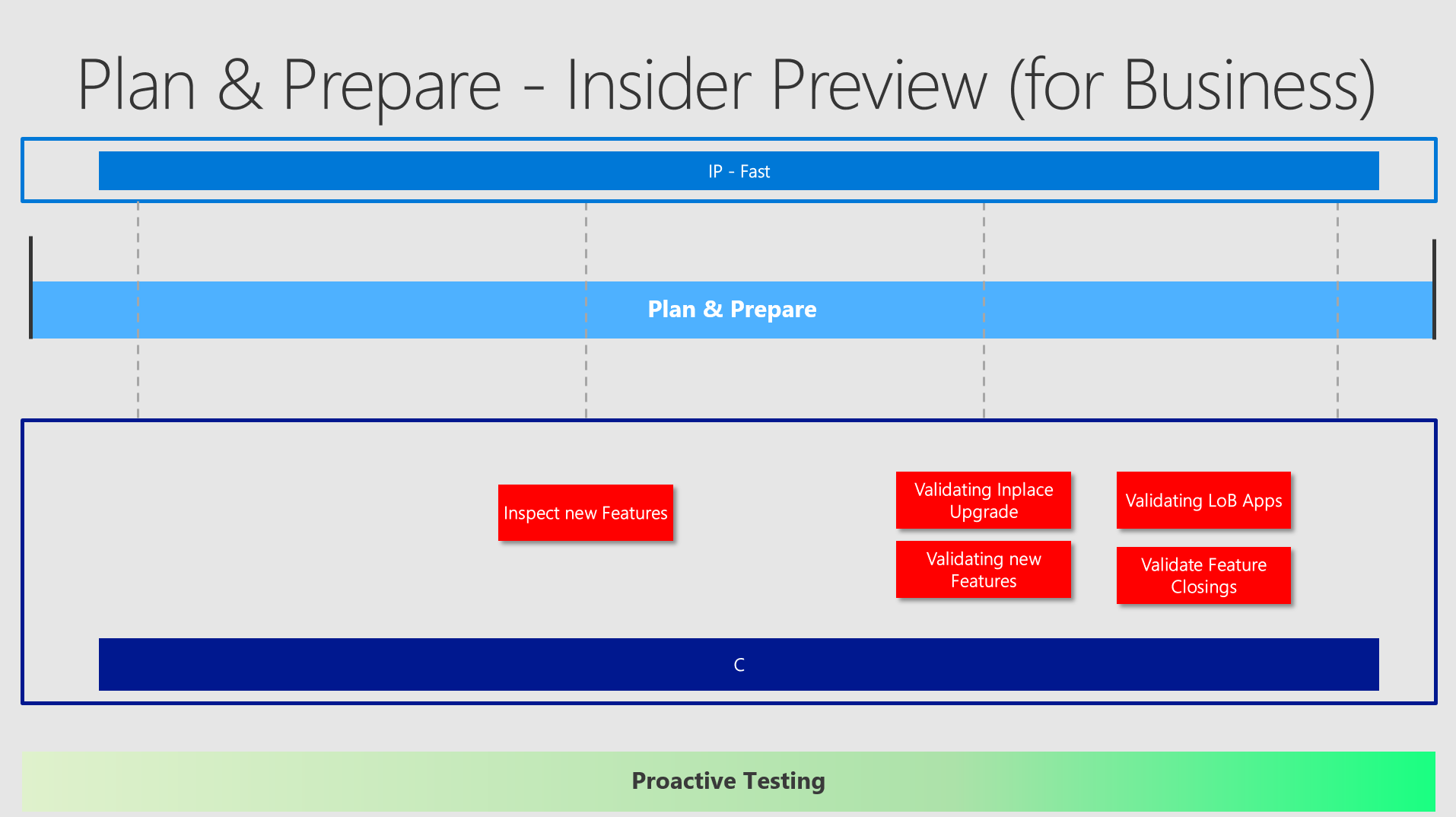
Additionally you could add two more rings and having the following three:
- Insider Preview - Fast
- Insider Preview - Slow
- Preview Release
Targeted Deploy / Semi Annual Channel (Targeted)
Okay - now it gets more complicated. What are the first aims in the Targeted Deploy? Definitely to set up the client configuration and to get everything ready for broad deployment:
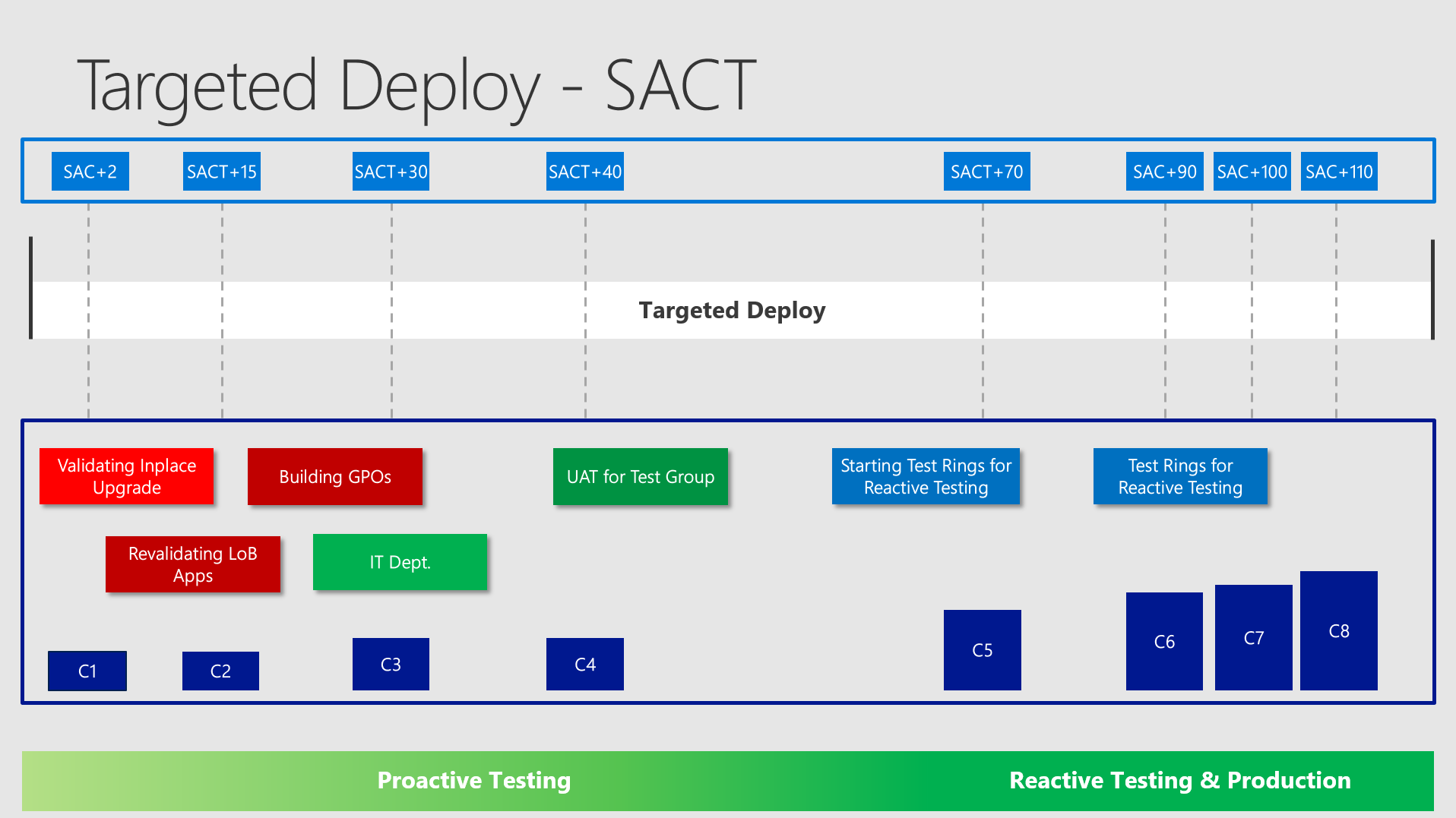
You would probably set up machines for the GPO team and Application Testers on VMs or dedicated machines and so on. You should take a look at your complete task list and decide whether you need a specific collection for some tasks and define the earliest time of usage.
Targeted Deploy - Reactive Testing
This part is for sure some of the biggest challenges. As you have read you should target a transversal cut of:
- Applications
- Organizational Units
- Network Segments
- Geographical Locations
and divide them into representative collections. For this you will need many information and some script / tools to assist you in doing this. I will discuss some of the ideas in the Technical Approach later in this article.
Testing Rings
In targeted deploy you want to get as soon as possible ready to push out your testing rings. In the example I am starting the "UserAcceptanceTest" (UAT) 40 days after release and the "Testing Rings" after 70 days. The earlier you can address this - the better!
A good advice here is to upgrade around 10% of all the devices in your environment in Targeted Deploy to be ready for broad deployment. You don´t want to find any suprises in Broad Deployment - therefore you provoke them as soon as possible. (By experience these suprises are easily handleable as long you detect them very early and in small number counts!)
Broad Deploy / Semi Annual Channel
In this phase you push out the higher numbers - depending on how many rings you want to define here and how many clients you have in total, you could easily have numbers above 10k for one collection.
In the middle you see the group of sensitive machines and VIPs. There may be this kind of machines which should possibly never fail / or you want to reduce the chance for this to a very maximum.

In the end you have the Compliance Cleanup where you want to make sure to address the computers, which had problems and did not upgrade properly. A good idea would be to set up collections finding all the computers which are sitting on the old version and then pushing out another upgrade. The last instance would be to reinstall them - surely with the newer OS Version on it.
Defining the numbers of total rings
We can easily ignore the Insider Preview / Plan & Prepare Phase for this, because more than 3 rings in this phase wouldn´t make sense at all. But speaking of the rings placed in SACT and SAC this decision could easily get harder. I want to show and discuss the following numbers:

For Insider Preview you could set up 1-3 and letting the machines always upgrade for themselves as configured. (Fast / Slow / Release Preview)
For Targeted Deploy I would always say the absolute minimum is 3. You will need one at the very beginning, but you want also to start reactive testing at the end of the time span.
For Broad Deployment you should evaluate the number of clients in your environment, aswell the number of locations and possibly also the number of OUs or the specialization of your teams. The more complex your environment is - the more rings you should just use to control the impact.
And how many do you exactly need? It depends.
I would say a pretty solid approach is the illustrated 1 - 8 - 12 - 2 approach.
If your company has more than 50k Clients I would definitely recommend starting to increase the numbers. After hitting 100k you should evaluate the maximal recommendation count. I hope that you also did understand till here, that these collections don´t need to be created nor filled manually.
Technical Approach
Okay - as we have read now all the theoretical approaches, we should move on and trying to adopt it technically. This part is actually the most simple one, after you have determined all the processes and also planned for a specific number for all the rings. To give you an overview we should take a look at the possibilities and evaluate them:
- Windows Update for Business
- WSUS standalone
- System Center Configuration Manager + WSUS
- Upgrade-Tasksequence
- Servicing Plans
- Third-party Deployment Tool
More information here.
Windows Update for Business
WUfB is the client-side Windows Update Agent which is configured via GPOs. As for know these GPOs look like this (SAC and SACT will show up in 1709):
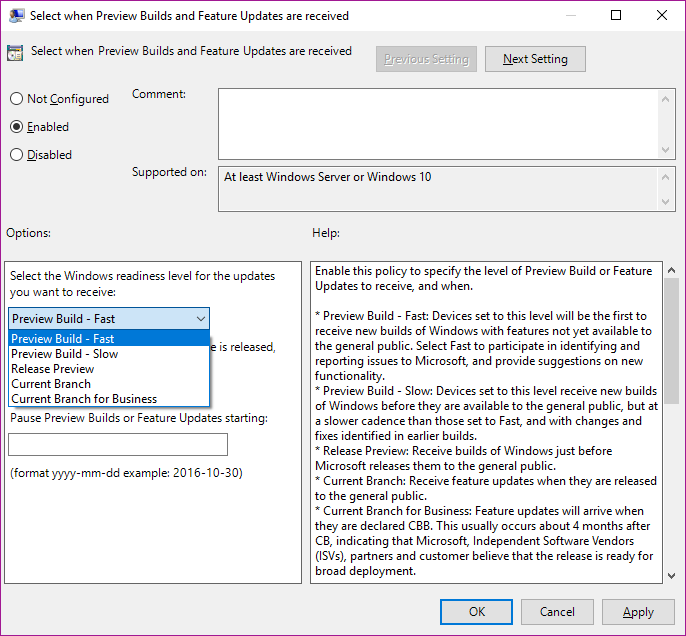
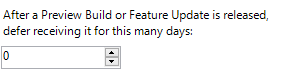
More information here.
As you see you can choose between the different "States" of the OS and postpone it by days, which was decribed in the previous topic "rings". The main management would be done with GPOs or even AD groups to set up the rings.
This technology should be considered for devices, which are mainly attached to the Internet. You should also configure some kind of caching technology - for WUfB this would be Delivery Optimization:
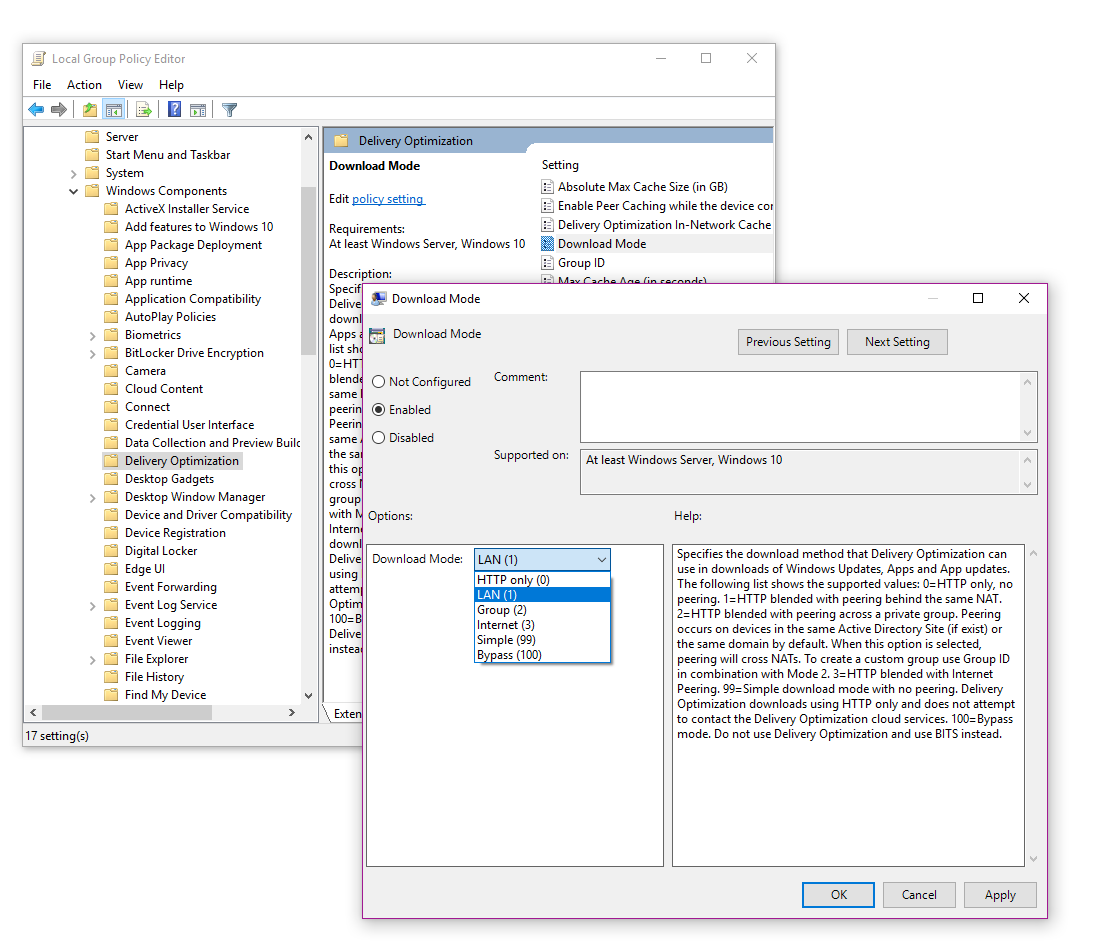
A good way of controlling which computers share with each other is configured as "LAN" and also by "Group". By "Group" can be configured to your specific environment - you would then also define the specific groups via GPO:
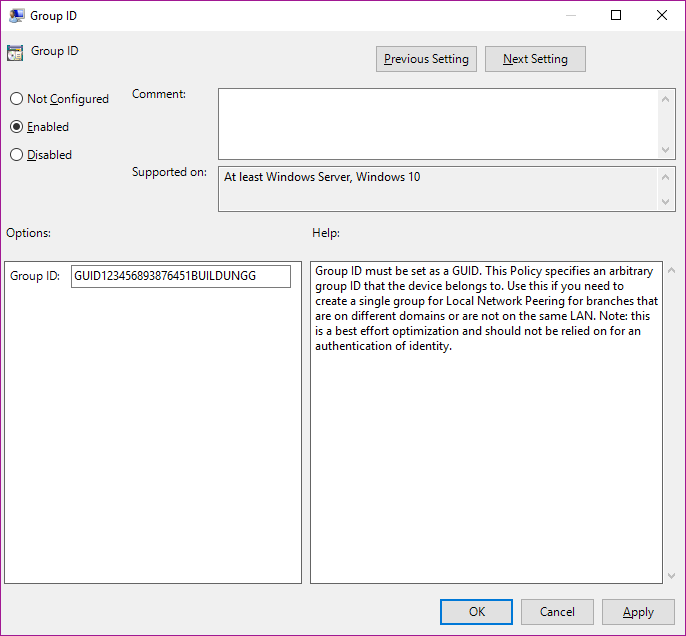
More information here.
The good thing about WUfB is that the Windows Update Agent gathers by default with UUP only the delta ESD material for Upgrades. (read here)
WSUS standalone
There are not many companies which are using WSUS standalone, though it is also possible to apply the ring-model to this:

We have improved our official docs - take a look here for a real good description, how it can be configured.
System Center Configuration Manager + WSUS
In this area we have actually two possible ways for adoption:
- Upgrade-Tasksequence
- Servicing Plans
The main difference between these two is that in the Tasksequence a complete WIM is used, where in Servicing Plans you are sending out the Feature Updates consisting of an delta ESD. We are technically speaking from a difference of 3,6GB vs approx. 2GB. As you have read this you may think, that Servicing Plans is the way to go. It is, but unfortunately it seems that no customer has even tested Servicing Plans and the cause is pretty understandable. The Upgrade-TS is a known and very approved way how to create and work with deployments in SCCM. All admins know how it works and how to set it up. Additional to this - lazy - argument you can also include easily and many steps before and after the upgrade. In the past this may be often been necessary. e.g. till Windows 10 1703 all apps were reinstalled to the computer and there have been some issues with Language Packs and some of the Personalization Settings.
We are working on these issues and targetting an upgrade without the necessity for too many post-upgrade tasks. As for know my personal recommendation is this:
- Implement the Upgrade-TS with all necessary steps
- communicate necessary steps / cleanup tasks / neccesities for repairs to TAMs / PFEs
- Build up the structure for Servicing Plans aside
- Define the rings
- Define the collections and what computers are in there
- Train yourself and get the understanding how it is working
- Understand the Reporting
As you have read you may have catched that I personally think Servicing Plans will replace Upgrade TS pretty fast in the future. Let us take a closer look and you will see some more arguments for Servicing Plans.
Upgrade-Tasksequence
The Upgrade-TS gives you control to define a complete workflow before and after the upgrading process.
This unfortunately allows to do steps, which are normaly not intended to be done in Upgrade.
Examples for don´ts:
- Upgrading applications before OS Upgrade (Application Lifecycle Management! Update the package in your environment before moving to next OS version)
- Upgrading all your software ( you should have a working Application Lifecycle Management in Place continuously updating your applications!)
- Reinstalling all your software - just in case (What ? no. Find the errors why upgraded packages / applications stop working after an upgrade and fix them correctly in the package itself)
- [...]
There might be some scenarios where additional steps are necessary and therefore Upgrade-Tasksequences are the better choice.
Example for do´s:
- Moving from BIOS to UEFI --> MBR2GPT
- Moving from 3rd-party disk encryption to Bitlocker
- Multi-Language environments with unsolvable issues (till now)
- LTSB feature updates. With the LTSB servicing branch, feature updates are never provided to the Windows clients themselves. Instead, feature updates must be installed like a traditional in-place upgrade.
- [...]
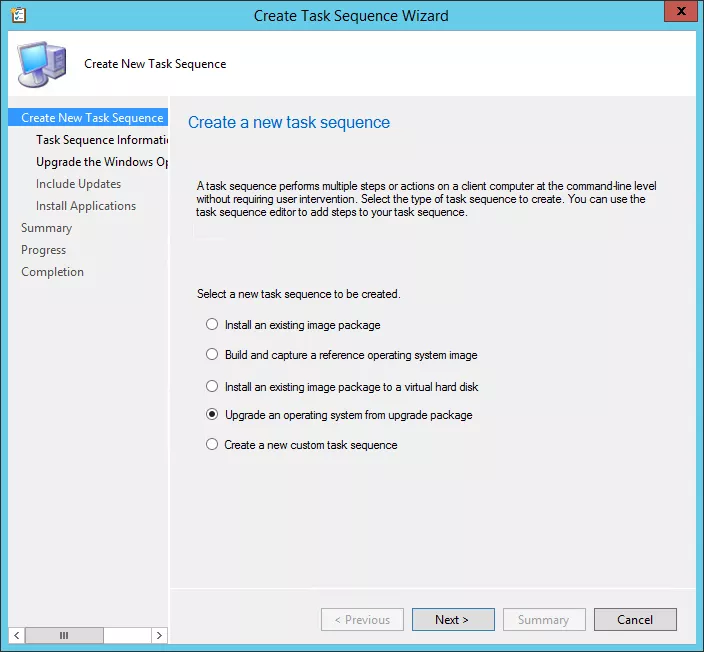
The problem with this technology is the requirement to prepare all collections in the first steps for all the rings and the necessity to fire each ring manually or by script. This needs a huge workload as overhead to automate WaaS as described. I don´t say it is not possible - it actually is, but I doubt that this kind of time investment is necessary for the adoption of all rings.
Therefore I recommend only using Upgrade-Tasksequence for manual deployment and not as complete solution for the rings.
More information here.
Servicing Plans
This whole article is actually targetting Servicing Plans. Let us take a look at the Servicing Dashboard: (old namings visible - I will replace with newer and better pic asap)
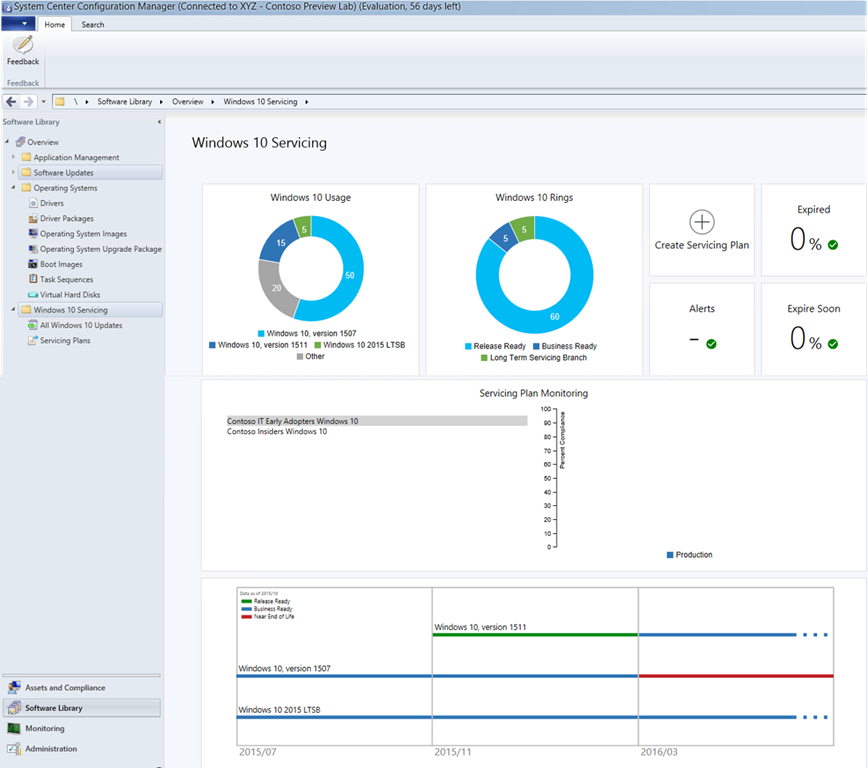
I recommend reading the great blog article from Niall C. Brady, Enterprise Client Management MVP - it is a perfect guide for how Servicing Plans are manually created.
So you would set up the rings with automatic deployment rules to trigger at the specific events, which you configured. This is actually the exact thing we need to have.
The good thing about this - you just need to configure it once - it will reapply for every coming OS Version. (main difference to Upgrade TS)
You should also take a look at the PowerShell CmdLets: New-CMWindowsServicingPlan, Get-CMWindowsServicingPlan, New-CMCollection, New-CMSoftwareUpdateDeploymentPackage, Get-CMSoftwareUpdateDeploymentPackage,
Get-CMWindowsUpdate, Save-CMSoftwareUpdate, Start-CMContentDistribution

For automating the creation with PowerShell you could easily create the collections, the deployments and the ServicingPlans via Script:
Take a look here or here from Kaido Järvemets.
I am currently working to set up some clever script to allow the creation of the collections, the plans and the more complicated queries for the collections used. (next topic)
Also in comparison to the Upgrade-TS there IS also the possibility to initialize post-upgrade tasks. Take a look here.
And more information here and here.
Third-party Deployment Tool
It depends to your third-party deployment tool, if it is capable to deploy and control Feature Updates in an automated manner AND with using Delta ESD material. If it does - good. If not - I would always recommend to use some of the described technologies. WUfB or WSUS standalone should come here into consideration and be discussed.
Filling Collections with representative Devices for Reactive Testing
This part is for sure some of the biggest challenges. As you have read you should target a transversal cut of:
- Applications
- Organizational Units
- Network Segments
- Geographical Locations
and divide them into representative collections. For this you will need many information and some script / tools to assist you in doing this.
Setting up well-chosen collections is the point where all this model could shine or either collapse. Unfortunately to its importance it is also - I would say - the most challenging part of this all.
Let us take a look at the different targets:
Applications
You want to reactively test all applications to not running into any suprises in the broad deployment, where you deploy your upgrade to larger collections. So you are provoking on purpose possible problems to find them as soon as possible to have enough time to react. The idea is pretty easy. The problem - do you have a complete list of all your applications and can you define good testing machines?
As mentioned in my last extensive article you should work in collaboration with the Application Holders. One approach can be to allow them to define test users. Another approach would be to let the user define his collection by himself. I will get into this later in "What I am working on"
Organizational Units
This is easy possible with a PowerShell Script running through all OUs and picking a by algorithm defined number of devices and moving them into the first collections. You want to do this to have the additional safety to not miss some applications out and also to validate some coincidences with GPOs.
Network Segments
This is about bandwith and about clever caching. By configuring - for example - the Windows Update Delivery Optimization for NAT and upgrading a small number of computers in each location, you will have caching points in place without the necessity to reevaluate this all the time. This information could be retrieved via Script from SCCM.
Geographical Locations
With this marker you just want to make sure not to find any special locations with dedicated networking problems. It should be included in OUs and Network Segment, but you should just make sure that you did not miss any location out in your tests. May be there is some naming convention in the device names which allows you to identify the locations - or it is managed via OUs.
What I am working on
I am working on two possible approaches
- PowerShell Script / Module / Tool with UI to create the rings manually, semi-manually (changing) and automatically - the idea is to define all the rings till "Targeted Deploy" C6-7 (semi-)manually and the rest automatically by just dividing the left devices into chunks and spreading them with an algorithm into all the collections
- Tool to allow the User himself from a client to move him into specific collections
Let me know your ideas and feedback - are there any other ideas to be discussed?
Exception Handler
What do you do, when you encounter some problems / application incompatibilities? As described in my last article you should have up some workflows for these situations. Working with Servicing Plans (and all other technologies) you can always pause the current deployment and just continue it, when you have fixed the cause.
Further Improvement
After reaching this kind of automation there will be still space to improve:
Knowledge and Information Management
- Update of central information stores (OneNote / SharePoint / Teams) and pushing out email to IT Teams / End Users automatically at a specific event
- Preparing the layout of emails
- Setting up Meetings automatically
- Setting up Webinars automatically
Reporting / Alerting
- Automatic control of reports
- Sending emails on defined SLAs automatically
- Sending out reports automaticaly
Automatic creation of Compliance Cleanup Collections
- Automatically inform the impacted users of the state - warning and advising them
- After defined alerts automatically create cleanup collections for forced upgrades or reinstallations
- Send out automatically reports of its success
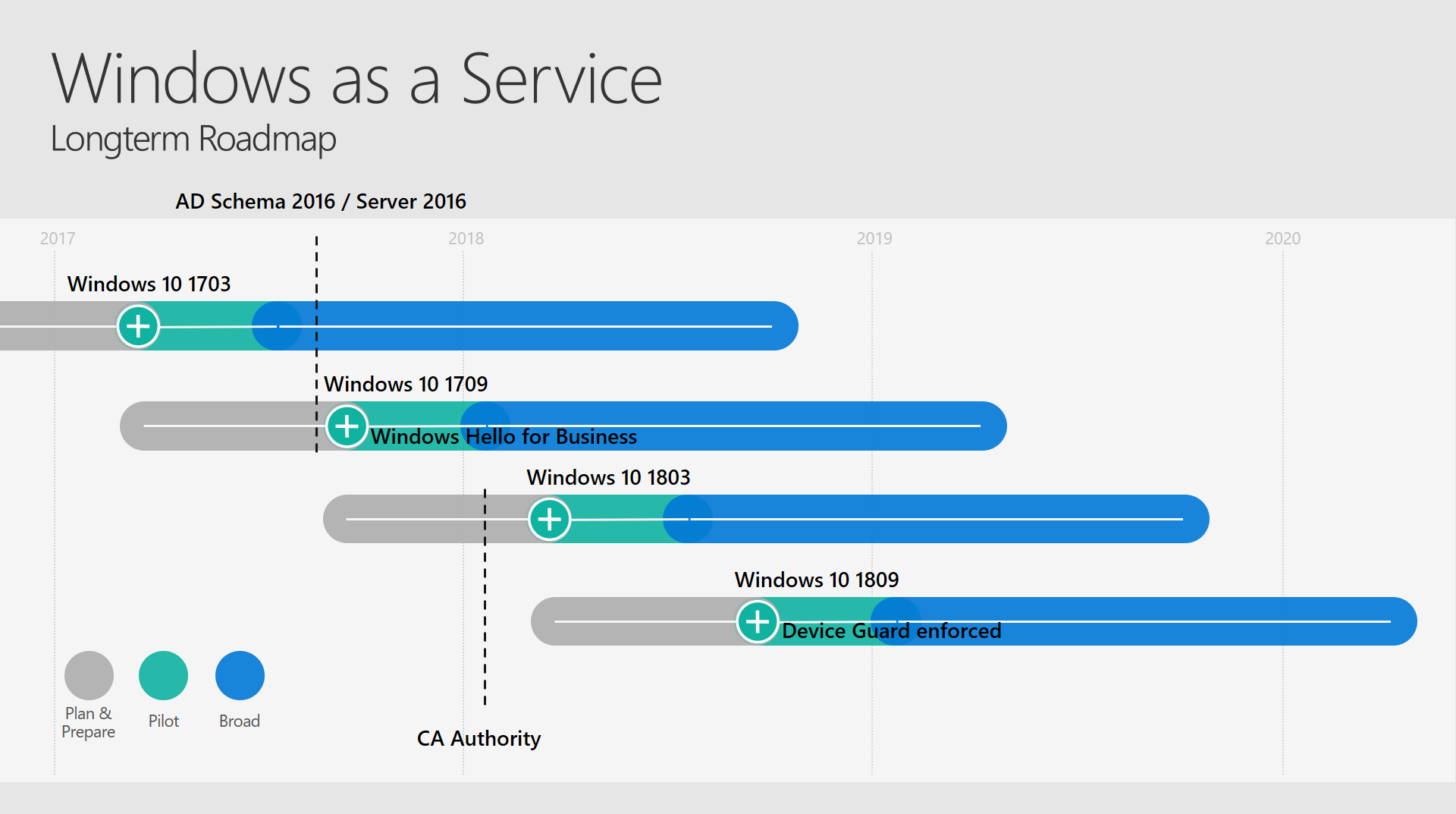
Longterm Roadmap
- Plan longterm adoption of technologies
- Define target versions for specific OS releases
- Create more automation around this
- Information and Knowledge Management
- Setting up defined Meetings automatically
- Automatic Involvement of Finance Team
Summary
If you have come this far I am very proud of you. (Yeee... too long - I know)
What are the main points?
You want to have the information at the earliest point in time where you could get it.
You want to mix proactive and reactive testing depending your company. (more proactive or more reactive)
Workflow:
- Set up processes and work with project management techniques
- Understand and define rings
- Define a method for upgrades: fixed date (centrally-controlled) vs time frame (user-controlled upgrade)
- Implement the rings technically
- Keep automating additional recurring steps - like:
- Knowledge and information management
- Reporting / Alerting
- Automatic creation of Compliance Cleanup Collections
- [...]
- Address Feedback to us
TL;DR;
Automating the Windows as a Service Model is possible and I actually recommend doing this for EVERY enterprise customer. You will need some time in the preparation phase and setting up the whole process, but in the end you will save a huge upcoming and recurring workload.
By defining well chosen computers into your rings you predefine the possible impact and completely control your testing approach. The best toolset for this task is probably SCCM with Servicing Plans, but it is also possible with WSUS standalone or Windows Update for Business (or even a third-party solution) - you have just to implement the automation steps.
The target must be to set up an technically automated environment where every team and user (who may need this information) at every time know, on which phases is currently being worked and what follows.
It needs to become a always recurring adoption cycle where manual tasks should consecutively being replaced by automation / scripts / automatic processes.
The outcome will be to integrate Feature Updates mostly in the operative work. If you ignore this recommendation you might end up struggling a lot.
Thank you all and I hope it was somehow helpful and you could take some points for your environment out of this huge article.
All the best,
David das Neves
Premier Field Engineer, EMEA, Germany
Windows Client, PowerShell, Security
Comments
- Anonymous
August 12, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
August 17, 2017
Would definitely be interested in seeing more about this "Compatibility Workshop", as application testing is (rightly or wrongly) a big concern for our adopters...The only information I can find about it is on MPN Canada's blog: https://blogs.partner.microsoft.com/mpn-canada/windows-10-app-compatibility-guide/Is that the same thing? i.e. Only achieved through a Fast Track engagement?- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
No it´s a different one - I will specify some important points regarding Compat (and the WS) after my vacation in a dedicated article. :)
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
Those of us without TAMs or PFEs should do rely on what to help us through various Windows 10 issues? {and if you recommend calling Microsoft support I challenge every Microsoft employee to call your own non premier support department and see how well the experience is}.- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
Hi Susan, I would say that there are different ways to reach out for help even without TAMs and PFEs. The Microsoft Answers forums and the Microsoft Technet Forums are very often helpful - in addition you should always use Feedback Hub and the User Voice for dedicated technologies to communicate your ideas and problems. Also most of the PFEs are very helpful in any case, if you reach out to them directly. (but not too often)All the best,David- Anonymous
August 18, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
August 19, 2017
What is a small business that don´t have the technical knowledge for IT and still uses it? When you´re that small you normally buy operational service and they should have the knowledge. Stability is nowadays insecure - we learned it with WannaCry and NotPetya.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
No offense, but the fact that you needed a blog post this long to fully explain how to properly do the update process speaks volumes.- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
The comment has been removed
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
Very informative and brief work ! As always you will always find lazy and inefficient sys admins not doing their job well and blame Microsoft for everything. The entire job of admins is to facilitate the pace of technology and smooth implementation to your environment.- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
Hello,I have just gave you my feedbacks that a lot vendors software are not ready to follow the WAAS lifecycle.I hope all this will change in the near future.I'm very interreting by new features in Windows 10. In my opinion, enterprise adoption of Windows 10 is easier if MS improve the system upgrade (reduce the size of a build and the time to install it) and MS extend the end of life of CBB build 2 or 3 years.Thanks
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
Hello,I don't know where your telemetry come from (some more information would be welcome) but there are many firms worldwide which use WSUS\Group Policy servicing model and many where the "Allow Telemetry" policy is set to "0 (Security)".- Anonymous
August 13, 2017
Hello cas77,not every customer is configuring the GPO to Security - some customers are staying at 1 / Basic, because they want to use Upgrade Readiness which is a very valuable and free service. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/deployment/upgrade/upgrade-readiness-get-startedhttps://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/configuration/basic-level-windows-diagnostic-events-and-fieldsSome of our customers are also working together with us in so called TAP programs and additionally to this there are millions of Windows Insiders which are sending more data like Windows Error Reporting: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/dashboard/windows-error-reporting-getting-started All the best,David
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 14, 2017
Like this emphasis on ongoing process, which is what IT teams successfully adopting WaaS tell me they do. Suggestion: having gone through a lengthy discussion with confused IT admins on Twitter, make it clearer that 'targeted' isn't a different version or an official release in the way that CB->CBB was; targeted is just when you decide that this Windows version is sufficiently tested for your broad deployment - something Microsoft expects to take about 4 months.- Anonymous
August 14, 2017
The comment has been removed
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 14, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
August 15, 2017
Merci.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 14, 2017
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
August 15, 2017
Very good blog post. I've appreciated that WaaS is not a tech issue but a PM objective. Congrats. - Anonymous
August 15, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
August 16, 2017
Thank you John for your very comprehensive comment. 1) Not all sites have the available bandwidth required to distribute such a large update. Even 2GB is too much (500 MB would be ideal).These feature Updates are coming only twice per year. You should definitely think of adding distribution point or some type of caching technology to assis you regarding this problem: Windows Update Delivery Optimization, Branch Cache, Peer Cache, additional DPs2) Delivery Optimization is a hindrance. We learned that “LAN” mode does not work for us because our Internet presence is funneled through a regional data center. Also, we have too many sites to micromanage DO using Group ID GUIDs. We need DO to allow for a “subnet” download mode. But for some reason, Microsoft refuses to provide such functionality.Branch Cache or Peer Cache an idea?3) Upgrades take too long to install. 1 hour of downtime during business hours is unacceptable. Does Microsoft want us to ask each individual user what time is a good time to install this 1 hour update? Their response is usually ‘never.’ Hopefully most users have experienced this on their home PC by now so they will know what to expect. Most users have laptops and take their laptops home and shut them down overnight. Training users to change their habits is more difficult than managing WaaS in an enterprise environment.Need to be timed wisely - end of day / lunch / via WoL 4) The 1703 upgrade breaks our (GPO) customized Win10 start menu. We have already contacted Microsoft about this – Microsoft classifies this as a bug with no further guidance.How deployed? GPO or PowerShell? partially lockdown?5) As TwittApic stated, we need to update our SEP client as well. This can be done, but not in a timely enough fashion.This is Application Lifecycle Management - this is something you have to discuss and actually to achieve - there should always be the possibility to stay up to date. Sorry for the unfulfilling recommendation here, but I don´t see another proper way ad hoc.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
"The target must be to set up an technically automated environment where every team and user at every time know, on which phases is currently being worked and what follows."Surely I must be misunderstanding; are you suggesting that my 1700 employees should know what Windows build they're on and in which phase of OS deployment? They want a computer that enables them to do their work, and that's it. And the rest of the IT department? Busy coding, supporting our users, apps, etc. To ask everyone to always be aware seems a little presumptuous.- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
Depending on the company - in an IT or tech company it could make sense. (like we are with a lot of IT professionals.)But the statement should be more - the current state should be completely transparent for the people who may need this information. (Support Desks, Client Team, Infrastructure Teams etc.) Another approach would be the complete contrast and to just upgrade the machines without delivering more information as needed. (Upgrades take 1 hour - plan it at the end of the day) Thank you for the hint for the probable missunderstandings.David- Anonymous
August 22, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
September 01, 2017
Hi Chris,je - AppCompat is a topic for itself. I was actually planning further blog articles, if there is a demand for this. Java itself may be a project of its own - meaning the following steps:- Gathering information (there is a tool proved by oracle to assist here - just no remembering the name) - Apps, Java versions, java versions installed on computers- Cleaning up old java versions in the field- leveraging all apps to use a single provided Java version, which is continuously updated (or at least reducing the number of exceptional apps to a minimum)and so on.. We are spreading the information and working with many companies together, but we cannot force manfucturers to keep up to date. Especially in the SPS area you will still today find today systems explicitly working on Win XP. It is necessary that customers reach out to their OEMs / hardware and software manufacturers.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 17, 2017
Honestly, you should delete this and start over.If you have to have to color code important points, include a summary section, AND a TL/DR section in your excessively long blog post, you've completely failed in making your point in a concise manner. It's no excuse to say this covers technical subjects so you have to do it this way. No one in their right mind would show this post to their management and expect them to make any sense out of it.If Microsoft could decide on a consistent way to develop and promote Windows 10 then none of this would even be necessary. The uncertainty of how many Win10 feature updates would be released in a year, then changed to a twice a year schedule. Then changed to align with Office 365. Changing the name from Current Branch to the nonsensical word salad Semi Annual Channel Pilot and Broad. The changes to Insider Preview update release channels. - Anonymous
August 18, 2017
Hi David,Very interesting article and especially on Service Plan. I use SCCM TS because Service plan don't offer me actually the possiblity to easylly manage multi-language ... To be honest, if I could stop the longue process to create TS Upgrade and use Service plan, it could be nice.Do you have more information on Multi-language with Service Plan ? or what Rss Feed I should look to see any evolution.Last thing and bad thing. Our upgrade is completely managed by SCCM and even if I don't release the last version of Windows 10 (Creator) to users, I already saw some computers with this version on the network. ... I really don't know how to prevent this sort of upgrade uncontrolled by us (and find nowhere what sort of settings we could implement)Philippe- Anonymous
August 18, 2017
I had mistakenly configured Defer Upgrades GPO which enables "dual scan" so a few clients managed to get 1703 from Microsoft Update. Maybe check you dont have any of the Windows Updates for Business configured?- Anonymous
August 19, 2017
Good point.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 19, 2017
Hi Phillippe,we are taking a look at all these multi-language problems into depth. Hope to "fix" them in the future (by handling them much easier).I will provide additional information regarding Servicing Plans as soon I get them.Sean could have just found your issue with dual scan. Either you update with SCCM or WUfB - if you additionally configure WUfB GPOs though it will enable the WUfB technology. Validate all your GPOs - especially the upgraded machines. David
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 18, 2017
Nice one, David. Cheers. Bookmark worthy!Enjoy your break :) - Anonymous
August 18, 2017
It really sounds like you are expecting all organizations to have the staffing availability to perform the necessary testing for their organization in a timely matter.What you don't seem to understand is that IT budgets in some areas are dropping, or virtually non-existent.We have less than 50 staff supporting over 3000 users, covering a whole state, 2 large datacenters, 3 smaller virtual environments running datacenter equipment, and well over 500 servers. We have additional staff, again limited (under 50), supporting all the internal applications (several dozen), which may be homegrown by our org or designed and built by 3rd party contracts.Now we have to add bi-annual testing and deployment of OS upgrades.To add to the application testing of OS upgrades, we also have to test the upgrade processes.Along with testing the upgrade processes, we also have to test/check that the upgrade doesn't reinstall garbage applications that are absolutely unwanted in an Enterprise environment (especially running Enterprise edition!) I'm looking at you, Candy Crush, Solitaire pack, Xbox garbage applications. Why are these included in Enterprise to begin with?!Then, to add even more, we have to attempt to find differences in GPOs between build updates and correct those.Add/update/modify/whatever options are deprecated/changed/moved/whatever. It's not like that data is documented very well; or, at least, it is not exactly easy to find documentation on changes/additions/removals/deprecation/etc.Oh, then add to that, what other changes are needed with the feature update?Oh, you have to revamp your start layout again.What else changes?Now we have to spend hours researching all the changes that get documented by other IT professionals because the documentation on all those changes tends to be limited, not put out in a timely fashion, and/or not centrally documented by Microsoft for their customers to easily find.- Anonymous
August 19, 2017
Hi Jeremy,this is actually the point. I see organizations / enterprise customers very often waisting a lot of time. Yes there are some tasks which need to be addressed, but today this is done manually one by one with additonal meetings to speak and discuss about topics over and over again to finally define who has to do what. I have seen companies having only about 20 IT people for more than 10k users. It is all about structure and automation. And no - there is no necessity to proactively test everything. You could also go for mostly reactive testing and pushing out the feature updates as soon you have your GPOs ready - sending it out to small numbers of computers and increasing these numbers continuously. You would probably save a lot of resources doing it like this - BUT it was never worked in IT like this before and as this is a complete transition from a 3-year release model to an agile model the adoption needs to come in a form of a transition. Sure - there are manual steps, but these can be just collected and set up to a workflow. GPOs e.g. - you should just set up a diff between your current GPOs for a version and the newer one (technical diff set up within a script in seconds) and focus on these changes. Between 1607 and 1703 the number of GPOs which needed to be taken a look at was around 120. Most of them were dedicated to new features or just adding new functionality like the "Sync Favorites between IE and Edge" or "Block all consumer Microsoft Account user authentication". These all tasks, we are speaking about, can be accomplished within days if addressed correctly and in parallel. (as I have done so) Afterwards you should just start pushing out your new OS version with the GPOs and features - and for the uncomfortable situation that there are more GPOs to be changed or some issues become visible you have plenty of time to do so.I will now get into your points - and this is actually all good feedback which can be consolidated into this: app reinstallations and modifications to user or feature settings should not occur with an upgrade. I agree here - They did literally did and they all getting identified and solved:To demonstrate you that we are on on this - for example:"reinstall garbage applications that are absolutely unwanted in an Enterprise environment"Fixed in and after 1703. Unprovisioned applications won´t come back. GPO "Turn off the Microsoft Consumer Experience" addresses your mentioned apps."Now we have to spend hours researching all the changes that get documented by other IT professionals because the documentation on all those changes tends to be limited, not put out in a timely fashion, and/or not centrally documented by Microsoft for their customers to easily find."I will forward this point internally, but as I have seen and I am very proud of - our documentation has become great, technically well explained and is continuously held up to date. The new "docs" are raising in great steps and I look forward to see more to come.As for the current moment I recommend to take a look at next two websites:http://aka.ms/win10branchservicing (Covers the significant changes across each feature update (build))http://changewindows.org/ (not officially from MSFT but detailed, easy to understand with detailed release notes)Thanks for your feedback! :)David
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 22, 2017
what is Microsoft doing to prepare a security baseline that is available for SAC testing. Ideally, we would want a security baseline in place for SACT testing. At this time we use the previous channels baseline. I see that MS has published a drafty 1703 baseline, however an update to the Security compliance toolkit has not been made. version 1.0 still includes a baseline for 1507, 1511, 1607. The other source for a final security baseline SCM is EOL, so what is the delivery strategy for a Security baseline. 7/11/2-17 is the SAC date for version 1703, yet I do not see a final version of the security baseline published. This to me is troublesome as 1709 SACT is around the corner. How can we maintain the recommended model if the tools are not yet ready.- Anonymous
September 01, 2017
Hi Christian,we have just currently published the official baseline of 1703, which has only slight differences to the draft:https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/secguide/2017/08/30/security-baseline-for-windows-10-creators-update-v1703-final/You can ask Aaron directly what the upcoming plans are. AFAIK there is some work done to evolve the newer toolset, but unfortunately I am not into this.Thank you
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 22, 2017
what is Microsoft doing to prepare a security baseline that is available for SAC testing. Ideally, we would want a security baseline in place for SACT testing. At this time we use the previous channels baseline. I see that MS has published a drafty 1703 baseline, however an update to the Security compliance toolkit has not been made. version 1.0 still includes a baseline for 1507, 1511, 1607. The other source for a final security baseline SCM is EOL, so what is the delivery strategy for a Security baseline. 7/11/2-17 is the SAC date for version 1703, yet I do not see a final version of the security baseline published. This to me is troublesome as 1709 SACT is around the corner. How can we maintain the recommended model if the tools are not yet ready. - Anonymous
August 22, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
September 01, 2017
Thanks for the comment. It is important to provide this feedback from a customer-side to Microsoft and more directly to the product groups and program managers. Till now I did not have a customer of mine, which did have unsolvable problems (crucial blockers as you mentioned), which could not be solved or mitigated somehow. They just need to be communicated via the feedback channels:- Enterprise customers via PFE, TAMs, Windows Insider for Business, UserVoice- Consumers and other customers via Feedback Hub, UserVoice, OEMs, Microsoft Technet and Answers Forum and so onI hope this helps - you can also write me directly to trying to help you directly.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
August 24, 2017
Hallo! Thanks for the very interesting blog post. One thing I am not able to understand:In your example with the timeline of the 1803 (or whatever) release: At the end of the 18 month you deploy the build to the last machines with problems - you call it "buffer".Now - after 18 month of deployment - you are ready with the upgrade. However, the support ends 18 month after release. If you are ready with the latest machines the support ends.What do I misunderstand? How do you manage this? Thanks!- Anonymous
September 01, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
September 11, 2017
Thanks for your answer. OK, this is how I understand WaaS-Timeframe:- On release date of 1703 (March). - Start with SACT for 1703 the next 4 month - Start testing with insider preview 1709 for the next 6 month- 4 month after the release of 1703 (July same year): - Start with SAC of 1703, the broadly rollout of 1703- 6 month after the release of 1703 (September same year): - 1709 is released - Start with SACT for 1709 for the next 4 month - Start testing with insider preview 1803 for the next 6 month- 10 month after the release of 1703 (January next year): - Stop deployment of 1703 <<< IMHO here stops your 18 month timeframe for one Windows 10 version from administrators point of view - Start with SAC for 1709, the broadly rollout of 1703 - Start with upgrade of the machines to 1709- 12 month after the release of 1703 (March next year): - 1803 is released - Start with SACT for 1803 for the next 4 month - Start testing with insider preview 1809 for the next 6 month- 16 month after the release of 1703 (July next year): - Stop deployment of 1709 - Start with SAC for 1803, the broadly rollout of 1803 - Start with upgrade of the machines to 1803 - Now it's time to solve the problems with upgrade from 1703 because the support of 1703 ends in 2 month - 18 month after the release of 1703 (September next year): << At this point your timeframe for 1703 is reached - all machines should be upgraded because support ends for 1703 - 1809 is released - Start with SACT for 1809 for the next 4 month - Start testing with insider preview 1903 for the next 6 month- 22 month after the release of 1703: - Stop deployment of 1803 - Start with SAC for 1809, the broadly rollout of 1809 - Start with upgrade of the machines to 1809 - Now it's time to solve the problems with upgrade from 1803 because the support of 1803 ends in 2 month - 24 month after the release of 1703 (two years now): - all machines should be upgraded because support ends for 1803 - 1903 is released - Start with SACT for 1903 for the next 4 month - Start testing with insider preview 1909 for the next 6 month- ... and the story continues ...IMHO this time frame should be used in every documentation because it includes all milestones in WaaS from administrators point of view.Do not focus on 18 month. The focus should be 10 month including SACT and SAC. 4 month SACT and 6 month effective SAC because after 6 month of SAC you start to deploy the next version.The last 8 month of the timeframe are only for upgrade to the current version inluding troubleshooting.- Anonymous
September 11, 2017
Once more: 1703 was released in March and the support is 18 month from release. However, 1709 is not release in September because it's released in October. No 18 month left.- Anonymous
September 12, 2017
The 18 months is all in all a very theoretical number - even if you start to push out the newest version as soon as possible till the end - you need to cut some time off at the beginning and at the end. I like your 10 month approach much more and it makes it much more transparent. In my previous blog article I visually showed that skipping one OS version seems to be theoretically possible, but in practice it may lead into timing problems and it brings more problems than it really solves. One of the problems is - you need to plan everything manually than practicing a always recurring workflow.Some recommendations from my side - what are the most important steps?- target to have max. 2 versions in field in parallel- push out every update as soon as possible and target to do this in a 6 month-cycle- set up your ring structure for your company and visualize it- Inform the peopleThat´s it.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
September 12, 2017
Hi Dietmar,this looks pretty solid. Some timeframes are discussable or I would say - dependent to your company, but yes. This would be a good way to handle WaaS. One thing I just want to clarify - in SAC you start your Broad Deployment, but actually you should try to push out the first increasing rings in SACT. A good value is to target approx. 10% till end of SACT for that release.Next steps would be to visualize this - adopt it technically and prepare everything. Inform the relevant teams and get everyone involved.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
September 10, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
September 11, 2017
I received the feedbadk that many customers were somehow struggling in this area and that Microsoft shares information at too many places or nowhere. My intention was to consolidate WaaS in one blog article.Therefore, I have just written down simply the facts how WaaS can be adopted with a reduction of manual and recurring tasks and trying to automate it. There is a huge difference between the explanation of WaaS (2 releases per year - try to push out the releases as soon as possible) up to an Automated Adoption of WaaS for an Enterprise Environment (Clients 10k - xxxk)As working in an Enterprise Environment - this cannot be simplified in 100 words. You need to prepare for all the upcoming workload and not once for years as like in the past.And this guide was intended for Enterprise Customers and not small and midsized companies. To accomplish this processes must be modified and adopted technically. I even did not touch the migration from Windows 7/8 to Windows 10 and AppCompat in WaaS by any mean. Seeing customers getting intimidated by this explanation shows even more the gap.And - as I can see - nearly every Enterprise Customer is moving their strategy somehow into this direction and I got also a lot of positive feedback. People wanted to have a simple solution for this complexity. Most of them are getting frustrated that they have to change their mind completely.But - as an IT-pro I am always flexible to learn something new. It would be great to get in touch to discuss these topics in detail.All the best,David
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
September 12, 2017
Hello mr. David das Never.I think I have to already start calling you SIR or SER, maybe a King.Thank you so much, this is awesome.Best Regards, Joonas Pakkanenjj.pakkanen@gmail.com - Anonymous
September 20, 2017
The comment has been removed- Anonymous
September 20, 2017
Hi David,thank you very much for your comment and the feedback! I really understand your point - this was actually my motivation when writing these blog articles around WaaS. Many customers are ignoring WaaS completely and that´s why they will find themselves into trouble at some point in the future or even just right now. Windows 10 with WaaS needs to be very well prepared to adopt it - and adopting it means to run through a complete transformation - and tranformations have never been easy. I am currently working on these topics to set up official and proof-read content and I hopefully motivated some customers to take some of the mentioned points into consideration, because WaaS cannot be handled as a side-topic. I was actually just the PFE, who recognized the really important need for such a guideline and blogged it. Actually this is just a part of the whole story - AppCompat and transforming into Modern IT is still missing with a bunch of even more information - and I will hopefully find some time to add some more blog articles to the present ones. David
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
March 27, 2018
The comment has been removed




