Nota
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Pode tentar iniciar sessão ou alterar os diretórios.
O acesso a esta página requer autorização. Pode tentar alterar os diretórios.
This article describes some best practices for using Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). These best practices are derived from our experience with Azure RBAC and the experiences of customers like yourself.
Only grant the access users need
Com o RBAC do Azure, pode fazer a segregação de deveres na sua equipa e conceder aos utilizadores apenas a quantidade de acesso de que precisam para desempenhar as suas funções. Instead of giving everybody unrestricted permissions in your Azure subscription or resources, you can allow only certain actions at a particular scope.
When planning your access control strategy, it's a best practice to grant users the least privilege to get their work done. Evite atribuir funções mais amplas em escopos mais amplos, mesmo que inicialmente pareça mais conveniente fazê-lo. When creating custom roles, only include the permissions users need. Ao limitar funções e escopos, limita-se quais recursos estão em risco caso o principal de segurança seja comprometido.
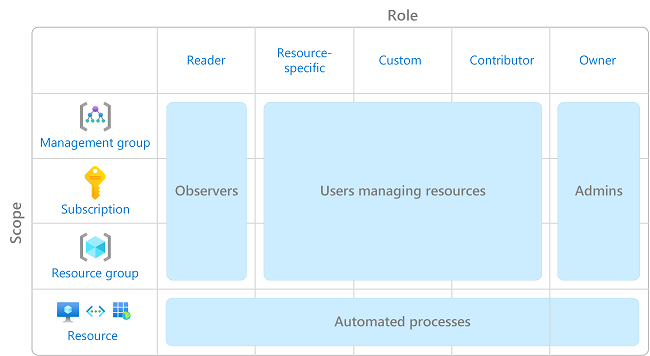
The following diagram shows a suggested pattern for using Azure RBAC.
For information about how to assign roles, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Limit the number of subscription owners
You should have a maximum of 3 subscription owners to reduce the potential for breach by a compromised owner. This recommendation can be monitored in Microsoft Defender for Cloud. For other identity and access recommendations in Defender for Cloud, see Security recommendations - a reference guide.
Limit privileged administrator role assignments
Some roles are identified as privileged administrator roles. Consider taking the following actions to improve your security posture:
- Remove unnecessary privileged role assignments.
- Avoid assigning a privileged administrator role when a job function role can be used instead.
- If you must assign a privileged administrator role, use a narrow scope, such as resource group or resource, instead of a broader scope, such as management group or subscription.
- If you are assigning a role with permission to create role assignments, consider adding a condition to constrain the role assignment. For more information, see Delegate Azure role assignment management to others with conditions.
For more information, see List or manage privileged administrator role assignments.
Use Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management
To protect privileged accounts from malicious cyber-attacks, you can use Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to lower the exposure time of privileges and increase your visibility into their use through reports and alerts. PIM helps protect privileged accounts by providing just-in-time privileged access to Microsoft Entra ID and Azure resources. Access can be time bound after which privileges are revoked automatically.
For more information, see What is Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management?.
Assign roles to groups, not users
Para tornar as atribuições de função mais gerenciáveis, evite atribuir funções diretamente aos usuários. Em vez disso, atribua funções a grupos. Assigning roles to groups instead of users also helps minimize the number of role assignments, which has a limit of role assignments per subscription.
Assign roles using the unique role ID instead of the role name
There are a couple of times when a role name might change, for example:
- You are using your own custom role and you decide to change the name.
- You are using a preview role that has (Preview) in the name. When the role is released, the role is renamed.
Mesmo que uma função seja renomeada, a ID da função não é alterada. Se você estiver usando scripts ou automação para criar suas atribuições de função, é uma prática recomendada usar o ID de função exclusivo em vez do nome da função. Portanto, se uma função for renomeada, é mais provável que seus scripts funcionem.
For more information, see Assign a role using the unique role ID and Azure PowerShell and Assign a role using the unique role ID and Azure CLI.
Avoid using a wildcard when creating custom roles
When creating custom roles, you can use the wildcard (*) character to define permissions. É recomendável especificar Actions e DataActions explicitamente em vez de usar o caractere curinga (*). The additional access and permissions granted through future Actions or DataActions might be unwanted behavior using the wildcard. Para obter mais informações, consulte Funções personalizadas do Azure.