Tutorial: How to access SQL Managed Instance from Data Factory Managed VNET using Private Endpoint
Pomembno
SQL Managed Instance now has native support for private endpoints. Instead of implementing the solution in this document, we recommend creating a private endpoint directly to the SQL Managed Instance resource as described in Managed private endpoints.
This tutorial provides steps for using the Azure portal to setup Private Link Service and access SQL Managed Instance from Managed VNET using Private Endpoint.
Opomba
When using this solution to connect to Azure SQL Database Managed Instance, "Redirect" connection policy is not supported, you need to switch to "Proxy" mode.
- Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- Virtual Network. If you don’t have a Virtual Network, create one following Create Virtual Network.
- Virtual network to on-premises network. Create a connection between virtual network and on-premises network either using ExpressRoute or VPN.
- Data Factory with Managed VNET enabled. If you don’t have a Data Factory or Managed VNET is not enabled, create one following Create Data Factory with Managed VNET.
Use the portal to create subnets in your virtual network.
| Subnet | Description |
|---|---|
| be-subnet | subnet for backend servers |
| fe-subnet | subnet for standard internal load balancer |
| pls-subnet | subnet for Private Link Service |
Use the portal to create a standard internal load balancer.
In the search bar at the top of the portal, search for and select Load Balancers in the Services section of the search pane.
On the Load balancing services page, Select Create to create a new load balancer.
On the Basics tab of the Create load balancer page, enter, or select the following details:
Setting Value Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select your resource group. Name Enter myLoadBalancer. Region Select East US. SKU Select Standard. Type Select Internal. On the Frontend IP configuration tab of the Create load balancer page, select Add a frontend IP configuration, and then enter, or select the following details on the Add frontend IP address configuration pane:
Setting Value Frontend IP name Enter a name for your frontend IP Virtual network Select your virtual network. Subnet Select fe-subnet created in the previous step. IP address assignment Select Dynamic. Availability zone Select Zone-redundant. Accept the defaults for the remaining settings, and then select Review + create.
In the Review + create tab, select Create.
A backend address pool contains the IP addresses of the virtual (NICs) connected to the load balancer.
Create the backend address pool myBackendPool to include virtual machines for load-balancing internet traffic.
- Select All services in the left-hand menu, select All resources, and then select myLoadBalancer from the resources list.
- Under Settings, select Backend pools, then select Add.
- On the Add a backend pool page, for name, type myBackendPool, as the name for your backend pool, and then select Add.
The load balancer monitors the status of your app with a health probe.
The health probe adds or removes VMs from the load balancer based on their response to health checks.
Create a health probe named myHealthProbe to monitor the health of the VMs.
Select All services in the left-hand menu, select All resources, and then select myLoadBalancer from the resources list.
Under Settings, select Health probes, then select Add.
Setting Value Name Enter myHealthProbe. Protocol Select TCP. Port Enter 22. Interval Enter 15 for number of Interval in seconds between probe attempts. Unhealthy threshold Select 2 for number of Unhealthy threshold or consecutive probe failures that must occur before a VM is considered unhealthy. Leave the rest the defaults and select OK.
A load balancer rule is used to define how traffic is distributed to the VMs. You define the frontend IP configuration for the incoming traffic and the backend IP pool to receive the traffic. The source and destination port are defined in the rule.
In this section, you'll create a load balancer rule:
Select All services in the left-hand menu, select All resources, and then select myLoadBalancer from the resources list.
Under Settings, select Load-balancing rules, then select Add.
Use these values to configure the load-balancing rule:
Setting Value Name Enter myRule. IP Version Select IPv4. Frontend IP address Select LoadBalancerFrontEnd. Protocol Select TCP. Port Enter 1433. Backend port Enter 1433. Backend pool Select myBackendPool. Health probe Select myHealthProbe. Idle timeout (minutes) Move the slider to 15 minutes. TCP reset Select Disabled. Leave the rest of the defaults and then select OK.
In this section, you'll create a Private Link service behind a standard load balancer.
On the upper-left part of the page in the Azure portal, select Create a resource.
Search for Private Link in the Search the Marketplace box.
Select Create.
In Overview under Private Link Center, select the blue Create private link service button.
In the Basics tab under Create private link service, enter, or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource Group Select your resource group. Instance details Name Enter myPrivateLinkService. Region Select East US. Select the Outbound settings tab or select Next: Outbound settings at the bottom of the page.
In the Outbound settings tab, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Load balancer Select myLoadBalancer. Load balancer frontend IP address Select LoadBalancerFrontEnd. Source NAT subnet Select pls-subnet. Enable TCP proxy V2 Leave the default of No. Private IP address settings Leave the default settings. Select the Access security tab or select Next: Access security at the bottom of the page.
Leave the default of Role-based access control only in the Access security tab.
Select the Tags tab or select Next: Tags at the bottom of the page.
Select the Review + create tab or select Next: Review + create at the bottom of the page.
Select Create in the Review + create tab.
On the upper-left side of the portal, select Create a resource > Compute > Virtual machine.
In Create a virtual machine, type or select the values in the Basics tab:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your Azure subscription. Resource Group Select your resource group. Instance details Virtual machine name Enter myVM1. Region Select East US. Availability Options Select Availability zones. Availability zone Select 1. Image Select Ubuntu Server 18.04LTS - Gen1. Azure Spot instance Select No. Size Choose VM size or take default setting. Administrator account Username Enter a username. SSH public key source Generate new key pair. Key pair name mySSHKey. Inbound port rules Public inbound ports None. Select the Networking tab, or select Next: Disks, then Next: Networking.
In the Networking tab, select or enter:
Setting Value Network interface Virtual network Select your virtual network. Subnet be-subnet. Public IP Select None. NIC network security group Select None. Load balancing Place this virtual machine behind an existing load balancing solution? Select Yes. Load balancing settings Load balancing options Select Azure load balancing. Select a load balancer Select myLoadBalancer. Select a backend pool Select myBackendPool. Select Review + create.
Review the settings, and then select Create.
You can repeat step 1 to 6 to have more than 1 backend server VM for HA.
Login and copy script ip_fwd.sh to your backend server VMs.
Opomba
This script will only temporarily set IP forwarding. To make this setting permanent, please ensure that the line "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" is uncommented in the file /etc/sysctl.conf
Run the script on with the following options:
sudo ./ip_fwd.sh -i eth0 -f 1433 -a <FQDN/IP> -b 1433
<FQDN/IP> is the host of your SQL Managed Instance.Run below command and check the iptables in your backend server VMs. You can see one record in your iptables with your target IP.
sudo iptables -t nat -v -L PREROUTING -n --line-number
Opomba
Note: If you have more than one SQL MI or other data sources, you need to define multiple load balancer rules and IP table records with different ports. Otherwise, there will be some conflict. For example,
Port in load balancer rule Backend port in load balance rule Command run in backend server VM SQL MI 1 1433 1433 sudo ./ip_fwd.sh -i eth0 -f 1433 -a <FQDN/IP> -b 1433 SQL MI 2 1434 1434 sudo ./ip_fwd.sh -i eth0 -f 1434 -a <FQDN/IP> -b 1433 Opomba
Run the script again every time you restart the VMs behind the load balancer.
Select All services in the left-hand menu, select All resources, and then select your data factory from the resources list.
Select Author & Monitor to launch the Data Factory UI in a separate tab.
Go to the Manage tab and then go to the Managed private endpoints section.
Select + New under Managed private endpoints.
Select the Private Link Service tile from the list and select Continue.
Enter the name of private endpoint and select myPrivateLinkService in private link service list.
Add FQDN of your target SQL Managed Instance.

Create private endpoint.
Go to the Manage tab and then go to the Managed private endpoints section.
Select + New under Linked Service.
Select the Azure SQL Database Managed Instance tile from the list and select Continue.

Enable Interactive Authoring.
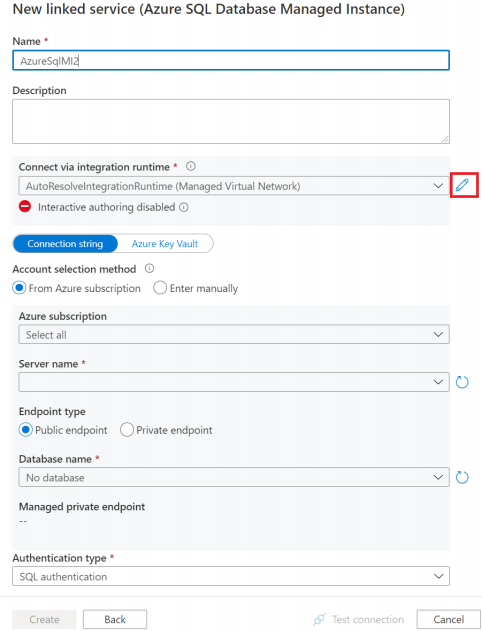
Input the Host of your SQL Managed Instance, user name and password.
Opomba
Please input SQL Managed Instance host manually. Otherwise it’s not full qualified domain name in the selection list.
Then click Test connection.

Advance to the following tutorial to learn about accessing on premises SQL Server from Data Factory Managed VNET using Private Endpoint:

