Manage Search indexing
Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
You can manage your search extension and indexing status, which include the following actions:
Prerequisites
- Install and configure Search.
- Be assigned to the Project Collection Administrator (PCA) role for the organization to manage Search and indexing.
Manage indexing
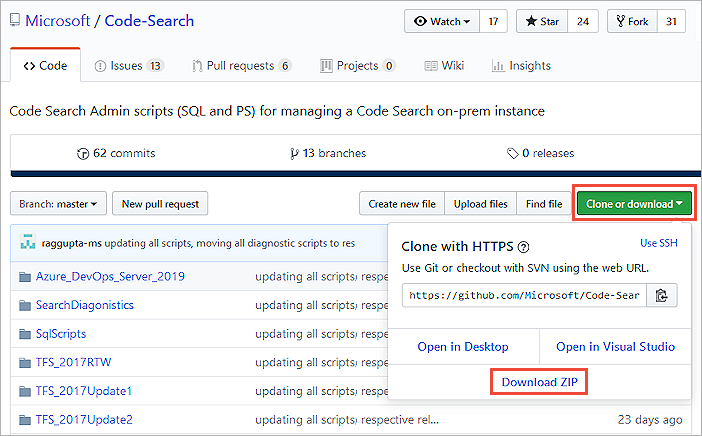
Search gets managed by running PowerShell and SQL scripts. All of these scripts are available to download from the Code-Search GitHub repository. You can download all scripts into a local folder on the server. This server runs the database for Azure DevOps Server using the Download ZIP option.
The PowerShell scripts require the SQL script files, so ensure the SqlScripts folder and its contents are present, along with the PowerShell scripts.
Note
When you execute scripts, ensure that you run the appropriate script for your version:
Check indexing status
To check the indexing status after Search is configured, or after the extension is installed for a collection, do the following steps.
Execute the
ExtensionInstallIndexingStatus.ps1script with administrative privileges and enter the following information:- The SQL server instance name where the Azure DevOps Server configuration database is located.
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server collection database.
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server configuration database.
- The name of the collection.
- The number of previous days to check indexing status.
Review the following outputs:
- Collection indexing was triggered successfully: Indicates that indexing is in progress.
- Repositories Indexing Completed: Lists repositories whose indexing completed and is searchable.
- Status of repositories currently indexing: Lists the names of all the repositories that are still being indexed and are partially searchable. It takes some time for indexing to complete.
Execute the
RecentIndexingActivity.ps1script at intervals for indexing progress. This script takes the same parameters as theExtensionInstallIndexingStatus.ps1script:- Repositories completed fresh indexing: Shows number of repositories for which indexing completed within the specified time interval.
- Count of repositories with fresh indexing in progress: Shows the number of repositories for which indexing isn't complete. These repositories are still being indexed and are partially searchable.
- Repositories completed continuous indexing: Shows the number of commits processed in the specified time interval. The number might not exactly match the total number of pushes to the repository because merges are committed as they're indexed.
- Count of repositories with continuous indexing in progress: Shows the number of repositories for which the commits are still being processed. These repositories show incomplete results until indexing is completed.
- Count of indexing job failures: Shows the number of indexing jobs that failed. Repositories associated with these indexing jobs could potentially show incomplete results until later indexing jobs for the same repositories patched the failed indexing.
Execute the
CheckIndexingStatus.ps1script with administrative privileges and enter the following information:- The SQL server instance name where the TFS configuration database is located.
- The name of the TFS collection database.
- The name of the TFS configuration database.
- The name of the collection.
- The number of previous days to check indexing status.
Review the following outputs:
- Collection indexing was triggered successfully: Indicates that indexing is in progress.
- Repositories Indexing Completed: Lists repositories whose indexing completed and is searchable.
- Repositories in File Discovery Phase: Repositories where files are yet to be discovered. These files are indexed after this stage.
- Repositories Indexing In Progress: Repositories that are partially indexed and should be searchable, even if the results are only partial. It might take some time for indexing to complete.
Monitor progress:
- Execute the
CheckIndexingStatus.ps1script at intervals for indexing progress. - If indexing isn’t working or if the number of pending files doesn't change for some time, execute the
TriggerCollectionIndexing.ps1script with administrative permission.
- Execute the
If you encounter any issues, get support on the Developer Community.
Pause indexing
To pause all indexing, execute: PauseSearchIndexing.ps1, which is useful if you see spikes in CPU utilization after configuring Search. You're prompted to enter the following information.
- The SQL server instance name where the Azure DevOps Server configuration database is
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server configuration database
Resume indexing
If you paused indexing, execute: ResumeIndexing.ps1 to start again. You're prompted to enter the following information.
- The SQL server instance name where the Azure DevOps Server configuration database is
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server configuration database
Reindex a repository or collection
To reindex a Git or TFVC repository, execute the appropriate
version of the script, Re-IndexingRepository.ps1, for your Azure DevOps Server version.
You're prompted to enter the following information.
- The SQL server instance name where the Azure DevOps Server configuration database is
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server collection database
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server configuration database
- The type of reindexing to execute, either
Git\_RepositoryorTFVC\_Repository - The name of the collection
- The name of the repository to reindex
To reindex a collection, execute the script: TriggerCollectionIndexing.ps1.
You're prompted to enter the following information.
- The SQL server instance name where the Azure DevOps Server configuration database is
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server collection database
- The name of the Azure DevOps Server configuration database
- The name of the collection
- The entities to reindex, either
All,Code,WorkItem, orWiki
Search limitations
If you do a disaster recovery (DR) operation and move your server back to an earlier snapshot of your SQL database, reindex all your collections.