Estimate RU/s using the Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner - Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
Note
If you're planning a data migration to Azure Cosmos DB and all that you know is the number of vcores and servers in your existing sharded and replicated database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs.
Configuring your Azure Cosmos DB databases and containers with the right amount of provisioned throughput, or Request Units (RU/s), for your workload is essential to optimizing cost and performance. This article describes how to use the Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner to estimate the required RU/s and cost of your workload when using Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. If you're using Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB, see Estimate RU/s - Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB.
Capacity planner modes
Basic
Provides a quick, high-level RU/s and cost estimate. This mode assumes the default Azure Cosmos DB settings for indexing policy, consistency, and other parameters.
Use basic mode for a quick, high-level estimate when you're evaluating a potential workload to run on Azure Cosmos DB. To learn more, see how to estimate cost with basic mode.
Advanced
Provides a more detailed RU/s and cost estimate, with the ability to tune more settings: indexing policy, consistency level, and other parameters that affect the cost and throughput.
Use advanced mode when you're estimating RU/s for a new project or want a more detailed estimate. To learn more, see how to estimate cost with advanced mode.
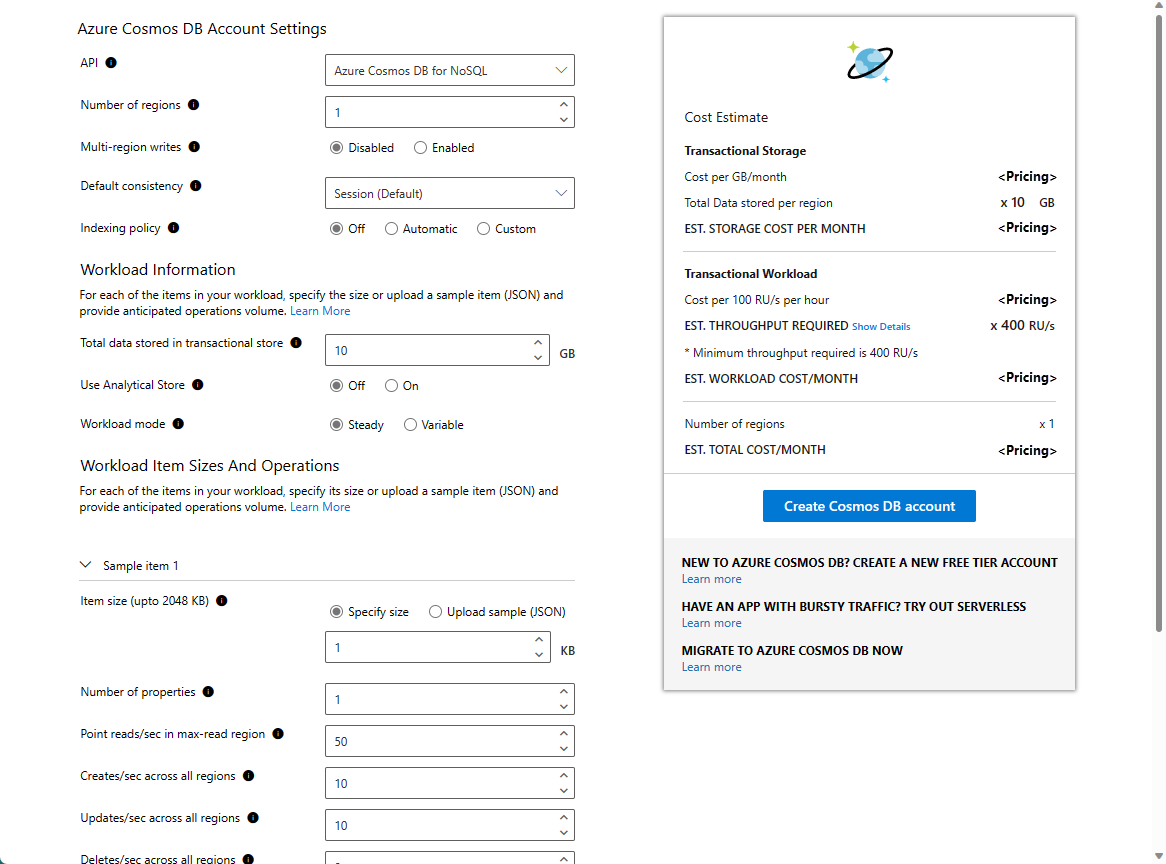
Estimate provisioned throughput and cost using basic mode
To get a quick estimate for your workload using the basic mode, open the capacity planner. Enter the following parameters based on your workload:
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| API | Choose Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. |
| Number of regions | Azure Cosmos DB is available in all Azure regions. Select the number of regions required for your workload. You can associate any number of regions with your Azure Cosmos DB account. For more information, see Distribute your data globally with Azure Cosmos DB. |
| Multi-region writes | If you enable multi-region writes, your application can read and write to any Azure region. If you disable multi-region writes, your application can write data to a single region. Enable multi-region writes if you expect to have an active-active workload that requires low latency writes in different regions. For example, an IOT workload that writes data to the database at high volumes in different regions. Multi-region writes guarantees 99.999% read and write availability. Multi-region writes require more throughput when compared to the single write regions. For more information, see Optimize multi-region cost in Azure Cosmos DB. |
| Total data stored in transactional store | Total estimated data stored, in GB, in the transactional store in a single region. |
| Use Analytical Store | Choose On if you want to use analytical store. Enter the Total data stored in analytical store, which represents the estimated data stored, in GB, in the analytical store in a single region. |
| Item size | The estimated size of the data item, for example, document. |
| Point reads/sec in max-read region | Number of point read operations expected per second per region. Point reads are the key/value lookup on a single item ID and a partition key. For more information about point reads, see Reading data: point reads and queries. |
| Creates/sec across all regions | Number of create operations expected per second per region. |
| Updates/sec across all regions | Number of update operations expected per second per region. When you choose automatic indexing, the estimated RU/s for the update operation is calculated as one property being changed per an update. |
| Deletes/sec across all regions | Number of delete operations expected per second per region. |
| Queries/sec across all regions | Number of queries expected per second per region. The average RU charge to run a query is estimated at 10 RUs. |
After you fill in the required details, select Calculate. The Cost Estimate table shows the total cost for storage and provisioned throughput. You can expand the Show Details link to get the breakdown of the throughput required for different CRUD and query requests. Each time you change the value of any field, select Calculate to recalculate the estimated cost.
Estimate provisioned throughput and cost using advanced mode
Advanced mode allows you to provide more settings that affect the RU/s estimate. To use this option, go to the capacity planner and sign in with an account you use for Azure. The Sign In option is available at the right-hand corner.
After you sign in, you can see more fields compared to the fields in basic mode. Enter the other parameters based on your workload.
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| API | Azure Cosmos DB is a multi-model and multi-API service. Choose Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. |
| Number of regions | Azure Cosmos DB is available in all Azure regions. Select the number of regions required for your workload. You can associate any number of regions with your Azure Cosmos DB account. For more information, see Distribute your data globally with Azure Cosmos DB. |
| Multi-region writes | If you enable multi-region writes, your application can read and write to any Azure region. If you disable multi-region writes, your application can write data to a single region. Enable multi-region writes if you expect to have an active-active workload that requires low latency writes in different regions. For example, an IOT workload that writes data to the database at high volumes in different regions. Multi-region writes guarantees 99.999% read and write availability. Multi-region writes require more throughput when compared to the single write regions. For more information, see Optimize multi-region cost in Azure Cosmos DB. |
| Default consistency | Azure Cosmos DB supports five consistency levels to allow you to balance the consistency, availability, and latency tradeoffs. For more information, see consistency levels. By default, Azure Cosmos DB uses Session consistency, which guarantees the ability to read your own writes in a session. Choosing Strong or Bounded staleness requires double the required RU/s for reads, when compared to Session, Consistent prefix, and Eventual consistency. Strong consistency with multi-region writes isn't supported and automatically defaults to single-region writes with strong consistency. |
| Indexing policy | By default, Azure Cosmos DB indexes all properties in all items for flexible and efficient queries. This approach maps to the Automatic indexing policy. If you choose Off, none of the properties are indexed. This approach results in the lowest RU charge for writes. Select Off if you expect to only do point reads (key value lookups) and writes, and no queries. If you choose Automatic, Azure Cosmos DB automatically indexes all the items as they're written. The Custom indexing policy allows you to include or exclude specific properties from the index for lower write throughput and storage. For more information, see Indexing in Azure Cosmos DB and Indexing policy examples. |
| Total data stored in transactional store | Total estimated data stored, in GB, in the transactional store in a single region. |
| Use Analytical Store | Choose On if you want to use analytical store. Enter the Total data stored in analytical store, which represents the estimated data stored, in GB, in the analytical store in a single region. |
| Workload mode | Select Steady if your workload volume is constant. Select Variable if your workload volume changes over time, for example, during a specific day or a month. The Percentage of time at peak setting is available if you choose the Variable workload option. |
| Percentage of time at peak | Available only with Variable workload option. Percentage of time in a month where your workload requires peak (highest) throughput. For example, if you have a workload that has high activity during 9 AM – 6 PM weekday business hours, then the percentage of time at peak is: (9 hours per weekday at peak * 5 days per week at peak) / (24 hours per day at peak * 7 days in a week) = 45 / 168 = ~27%. With peak and off-peak intervals, you can optimize your cost by programmatically scaling your provisioned throughput up and down accordingly. |
| Item size | The size of the data item, for example, document. You can add estimates for multiple sample items. You can also Upload sample (JSON) document for a more accurate estimate. If your workload has multiple types of items with different JSON content in the same container, you can upload multiple JSON documents and get the estimate. Select Add new item to add multiple sample JSON documents. |
| Number of properties | The average number of properties per an item. |
| Point reads/sec | Number of point read operations expected per second per region. Point reads are the key/value lookup on a single item ID and a partition key. Point read operations are different from query read operations. For more information about point reads, see Reading data: point reads and queries. If your workload mode is Variable, you can provide the expected number of point read operations at peak and off peak. |
| Creates/sec | Number of create operations expected per second per region. |
| Updates/sec | Number of update operations expected per second per region. |
| Deletes/sec | Number of delete operations expected per second per region. |
| Queries/sec | Number of queries expected per second per region. For an accurate estimate, either use the average cost of queries or enter the RU/s your queries use from query stats in Azure portal. |
| Average RU/s charge per query | By default, the average cost of queries/sec per region is estimated at 10 RU/s. You can increase or decrease it based on the RU/s charges based on your estimated query charge. |
The prices shown in the Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner are estimates based on the public pricing rates for throughput and storage. All prices are shown in US dollars. To see all rates by region, see Azure Cosmos DB pricing page.