Copy and transform data from Hive using Azure Data Factory
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the Copy Activity in an Azure Data Factory or Synapse Analytics pipeline to copy data from Hive. It builds on the copy activity overview article that presents a general overview of copy activity.
Supported capabilities
This Hive connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/-) | ① ② |
| Mapping data flow (source/-) | ① |
| Lookup activity | ① ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources/sinks by the copy activity, see the Supported data stores table.
The service provides a built-in driver to enable connectivity, therefore you don't need to manually install any driver using this connector.
The connector supports the Windows versions in this article.
Prerequisites
If your data store is located inside an on-premises network, an Azure virtual network, or Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, you need to configure a self-hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
If your data store is a managed cloud data service, you can use the Azure Integration Runtime. If the access is restricted to IPs that are approved in the firewall rules, you can add Azure Integration Runtime IPs to the allow list.
You can also use the managed virtual network integration runtime feature in Azure Data Factory to access the on-premises network without installing and configuring a self-hosted integration runtime.
For more information about the network security mechanisms and options supported by Data Factory, see Data access strategies.
Getting started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to Hive using UI
Use the following steps to create a linked service to Hive in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
Search for Hive and select the Hive connector.

Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
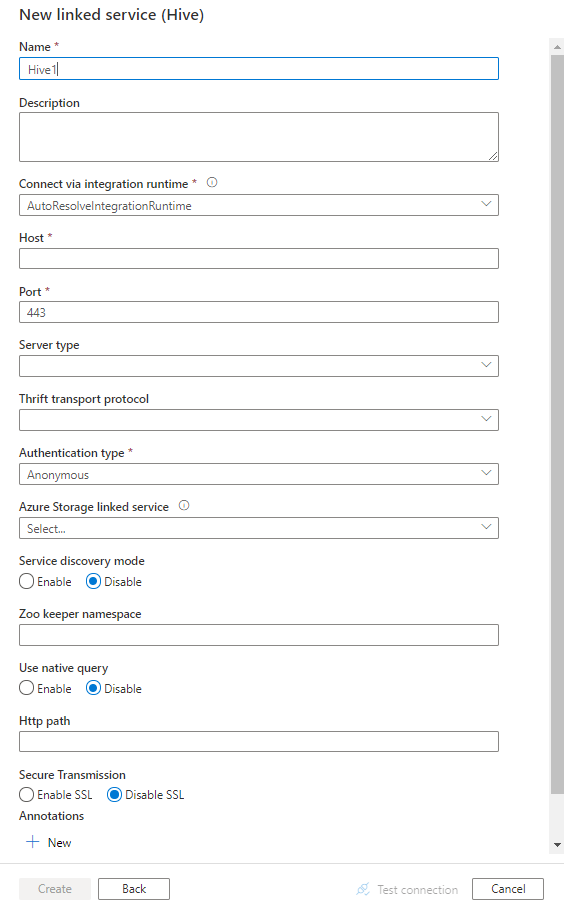
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define Data Factory entities specific to Hive connector.
Linked service properties
The following properties are supported for Hive linked service:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to: Hive | Yes |
| host | IP address or host name of the Hive server, separated by ';' for multiple hosts (only when serviceDiscoveryMode is enabled). | Yes |
| port | The TCP port that the Hive server uses to listen for client connections. If you connect to Azure HDInsight, specify port as 443. | Yes |
| serverType | The type of Hive server. Allowed values are: HiveServer1, HiveServer2, HiveThriftServer |
No |
| thriftTransportProtocol | The transport protocol to use in the Thrift layer. Allowed values are: Binary, SASL, HTTP |
No |
| authenticationType | The authentication method used to access the Hive server. Allowed values are: Anonymous, Username, UsernameAndPassword, WindowsAzureHDInsightService. Kerberos authentication is not supported now. |
Yes |
| serviceDiscoveryMode | true to indicate using the ZooKeeper service, false not. | No |
| zooKeeperNameSpace | The namespace on ZooKeeper under which Hive Server 2 nodes are added. | No |
| useNativeQuery | Specifies whether the driver uses native HiveQL queries, or converts them into an equivalent form in HiveQL. | No |
| username | The user name that you use to access Hive Server. | No |
| password | The password corresponding to the user. Mark this field as a SecureString to store it securely, or reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | No |
| httpPath | The partial URL corresponding to the Hive server. | No |
| enableSsl | Specifies whether the connections to the server are encrypted using TLS. The default value is false. | No |
| trustedCertPath | The full path of the .pem file containing trusted CA certificates for verifying the server when connecting over TLS. This property can only be set when using TLS on self-hosted IR. The default value is the cacerts.pem file installed with the IR. | No |
| useSystemTrustStore | Specifies whether to use a CA certificate from the system trust store or from a specified PEM file. The default value is false. | No |
| allowHostNameCNMismatch | Specifies whether to require a CA-issued TLS/SSL certificate name to match the host name of the server when connecting over TLS. The default value is false. | No |
| allowSelfSignedServerCert | Specifies whether to allow self-signed certificates from the server. The default value is false. | No |
| connectVia | The Integration Runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, it uses the default Azure Integration Runtime. | No |
| storageReference | A reference to the linked service of the storage account used for staging data in mapping data flow. This is required only when using the Hive linked service in mapping data flow | No |
Example:
{
"name": "HiveLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Hive",
"typeProperties": {
"host" : "<cluster>.azurehdinsight.net",
"port" : "<port>",
"authenticationType" : "WindowsAzureHDInsightService",
"username" : "<username>",
"password": {
"type": "SecureString",
"value": "<password>"
}
}
}
}
Dataset properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see the datasets article. This section provides a list of properties supported by Hive dataset.
To copy data from Hive, set the type property of the dataset to HiveObject. The following properties are supported:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to: HiveObject | Yes |
| schema | Name of the schema. | No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
| table | Name of the table. | No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
| tableName | Name of the table including schema part. This property is supported for backward compatibility. For new workload, use schema and table. |
No (if "query" in activity source is specified) |
Example
{
"name": "HiveDataset",
"properties": {
"type": "HiveObject",
"typeProperties": {},
"schema": [],
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Hive linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
Copy activity properties
For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see the Pipelines article. This section provides a list of properties supported by Hive source.
HiveSource as source
To copy data from Hive, set the source type in the copy activity to HiveSource. The following properties are supported in the copy activity source section:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to: HiveSource | Yes |
| query | Use the custom SQL query to read data. For example: "SELECT * FROM MyTable". |
No (if "tableName" in dataset is specified) |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromHive",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Hive input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "HiveSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM MyTable"
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Mapping data flow properties
The hive connector is supported as an inline dataset source in mapping data flows. Read using a query or directly from a Hive table in HDInsight. Hive data gets staged in a storage account as parquet files before getting transformed as part of a data flow.
Source properties
The below table lists the properties supported by a hive source. You can edit these properties in the Source options tab.
| Name | Description | Required | Allowed values | Data flow script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Store | Store must be hive |
yes | hive |
store |
| Format | Whether you are reading from a table or query | yes | table or query |
format |
| Schema name | If reading from a table, the schema of the source table | yes, if format is table |
String | schemaName |
| Table name | If reading from a table, the table name | yes, if format is table |
String | tableName |
| Query | If format is query, the source query on the Hive linked service |
yes, if format is query |
String | query |
| Staged | Hive table will always be staged. | yes | true |
staged |
| Storage Container | Storage container used to stage data before reading from Hive or writing to Hive. The hive cluster must have access to this container. | yes | String | storageContainer |
| Staging database | The schema/database where the user account specified in the linked service has access to. It is used to create external tables during staging and dropped afterwards | no | true or false |
stagingDatabaseName |
| Pre SQL Scripts | SQL code to run on the Hive table before reading the data | no | String | preSQLs |
Source example
Below is an example of a Hive source configuration:

These settings translate into the following data flow script:
source(
allowSchemaDrift: true,
validateSchema: false,
ignoreNoFilesFound: false,
format: 'table',
store: 'hive',
schemaName: 'default',
tableName: 'hivesampletable',
staged: true,
storageContainer: 'khive',
storageFolderPath: '',
stagingDatabaseName: 'default') ~> hivesource
Known limitations
- Complex types such as arrays, maps, structs, and unions are not supported for read.
- Hive connector only supports Hive tables in Azure HDInsight of version 4.0 or greater (Apache Hive 3.1.0)
- By default, Hive driver provides "tableName.columnName" in sink. If you do not wish to see the table name in the column name, then there are two ways to fix this. a. Check the setting "hive.resultset.use.unique.column.names" in Hive server side and set it to false. b. Use column mapping to rename the column name.
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Related content
For a list of data stores supported as sources and sinks by the copy activity, see supported data stores.