หมายเหตุ
การเข้าถึงหน้านี้ต้องได้รับการอนุญาต คุณสามารถลอง ลงชื่อเข้าใช้หรือเปลี่ยนไดเรกทอรีได้
การเข้าถึงหน้านี้ต้องได้รับการอนุญาต คุณสามารถลองเปลี่ยนไดเรกทอรีได้
Learn how to use the unified experience in Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio. Helps you to assess your database requirements, get the right-sized SKU recommendations for Azure resources, and migrate your SQL Server database to Azure.
The Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio offers these key benefits:
A responsive UI for an end-to-end migration experience. The extension starts with a migration readiness assessment and SKU recommendation (preview) (based on performance data).
An enhanced assessment mechanism that can evaluate SQL Server instances. The extension identifies databases that are ready to migrate to Azure SQL targets.
Note
You can use the Azure SQL Migration extension to assess SQL Server databases running on Windows or Linux.
An SKU recommendation engine that collects performance data from the on-premises source SQL Server instance and then generates right-sized SKU recommendations based on your Azure SQL target.
A reliable Azure service powered by Azure Database Migration Service that orchestrates data movement activities to deliver a seamless migration experience.
You can run your migration online (for migrations that require minimal downtime) or offline (for migrations where downtime persists throughout the migration) depending on your business requirements.
You can configure a self-hosted integration runtime to use your own compute resources to access the source SQL Server instance backup files in your on-premises environment.
Provides a secure and improved user experience for migrating databases with transparent data encryption (TDE) enabled, and SQL/Windows logins, to Azure SQL.
For information about specific migration scenarios and Azure SQL targets, see the list of tutorials in the following table:
| Migration scenario | Migration mode |
|---|---|
| SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance | Online / Offline |
| SQL Server to SQL Server on an Azure virtual machine | Online / Offline |
| SQL Server to Azure SQL Database | Offline |
Important
If your target is Azure SQL Database, you can migrate database Schema and data both using Database Migration Service via Azure portal. Also, you can use tools like the SQL Server dacpac extension or the SQL Database Projects extension for Azure Data Studio to deploy the database schema before you begin the data migration.
The following video explains recent updates and features added to the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio:
Architecture of the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio
Azure Database Migration Service is a core component of the Azure SQL Migration extension architecture. Database Migration Service provides a reliable migration orchestrator to support database migrations to Azure SQL. You can create an instance of Database Migration Service or use an existing instance by using the Azure SQL Migration extension in Azure Data Studio.
Database Migration Service uses the Azure Data Factory self-hosted integration runtime to access and upload valid backup files from your on-premises network share or from your Azure storage account.
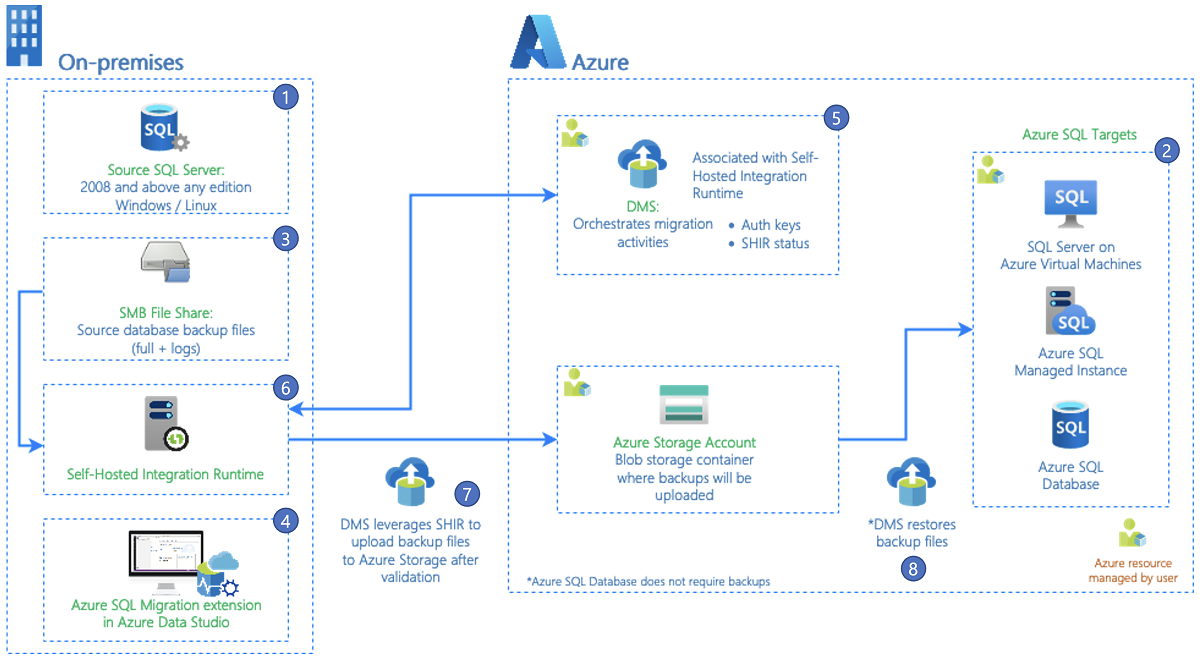
The workflow of the migration process is illustrated in the following diagram:
The following list describes each step in the workflow:
Source SQL Server: An on-premises instance of SQL Server that's in a private cloud or an instance of SQL Server on a virtual machine in a public cloud. SQL Server 2008 and later versions on Windows or Linux are supported.
Target Azure SQL: Supported Azure SQL targets are Azure SQL Managed Instance, SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (registered with the SQL infrastructure as a service extension in full management mode), and Azure SQL Database.
Network file share: A Server Message Block (SMB) network file share where backup files are stored for the databases to be migrated. Azure storage blob containers and Azure storage file share also are supported.
Azure Data Studio: Download and install the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio.
Azure Database Migration Service: An Azure service that orchestrates migration pipelines to do data movement activities from an on-premises environment to Azure. Database Migration Service is associated with the Azure Data Factory self-hosted integration runtime and provides the capability to register and monitor the self-hosted integration runtime.
Self-hosted integration runtime: Install a self-hosted integration runtime on a computer that can connect to the source SQL Server instance and to the location of the backup file. Database Migration Service provides the authentication keys and registers the self-hosted integration runtime.
Backup files upload to your Azure storage account: Database Migration Service uses a self-hosted integration runtime to upload valid backup files from the on-premises backup location to your Azure storage account. Data movement activities and pipelines are automatically created in the migration workflow to upload the backup files.
Restore backups on target Azure SQL: Database Migration Service restores backup files from your Azure storage account to the supported target Azure SQL instance.
Note
If your migration target is Azure SQL Database, you don't need backups for this migration. Database migration to Azure SQL Database is considered a logical migration that involves the database's precreation and data movement (performed by Database Migration Service).
The Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio doesn't take database backups, or neither initiate any database backups on your behalf. Instead, the service uses existing database backup files for the migration.
In online migration mode, Database Migration Service continuously uploads the backup source files to your Azure storage account and restores them to the target until you complete the final step of cutting over to the target.
In offline migration mode, Database Migration Service uploads the backup source files to Azure storage and restores them to the target without requiring a cutover.
Prerequisites
The following sections walk through the prerequisites for each supported Azure SQL target.
Install the Azure SQL Migration extension from Azure Data Studio Marketplace.
Have an Azure account that's assigned to one of the following built-in roles:
Important
An Azure account is required only when you configure the migration steps. An Azure account isn't required for the assessment or to view Azure recommendations in the migration wizard in Azure Data Studio.
Contributor for the target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance and for the storage account where you upload your database backup files from a Server Message Block (SMB) network share.
Reader role for the Azure resource groups that contain the target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance or your Azure Storage account.
Owner or Contributor role for the Azure subscription (required if you create a new Database Migration Service instance).
Using Managed Identity: Azure Database Migration Service supports the Managed identity for the Azure SQL Managed Instance migrations through the Azure portal only. Azure Database Migration Service uses this Managed identity to read the backups files from the storage blob container. To assign the permissions or role to the Managed identity, follow these steps:
Identify the target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance's associated managed identity.
Once you start the migration to Azure SQL Managed instance using Azure Database Migration service, when you select the target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance, its associated managed identity is shown. Otherwise, you can navigate to the Azure SQL Managed Instance pane, and select Security > Identity.
If the user assigned managed identity is added, the associated managed identity used is the same as the primary identity you selected.
If only the system assigned managed identity is enabled, the associated managed identity used is the same as Azure SQL Managed Instance.
In the Azure portal, go to Storage account (used for the migration for keeping backup files), and navigate to IAM roles > Assign role, and assign Storage Blob Data Reader to the associated managed identity.
For more information, see DMS - Support for Managed Identity for Azure SQL Managed Instance migration.
As an alternative to using one of these built-in roles, you can assign a custom role.
Note
When migrating to Azure SQL Managed Instance or Azure SQL Virtual Machine via Azure portal, make sure the signed in user has Storage Blob Data Reader access on the blob container that contains the backup files. This permission is needed to list folders and files in the blob container during migration setup via Azure portal only.
Create a target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Ensure that the logins that you use to connect the source SQL Server instance are members of the SYSADMIN server role or have CONTROL SERVER permission.
Provide an SMB network share, Azure storage account file share, or Azure storage account blob container that contains your full database backup files and subsequent transaction log backup files. Database Migration Service uses the backup location during database migration.
Important
- Always use a dedicated storage account for migration. Sharing it with other workloads can lead to conflicts and security risks.
- Once migration is done, either rotate the Storage Account Key to keep backups secure, or delete the storage account if it's no longer needed.
- The Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio doesn't take database backups, or neither initiate any database backups on your behalf. Instead, the service uses existing database backup files for the migration.
- If your database backup files are in an SMB network share, create an Azure storage account that Database Migration Service can use to upload database backup files to and to migrate databases. Make sure you create the Azure storage account in the same region where you create your instance of Database Migration Service.
- You can write each backup to either a separate backup file or to multiple backup files. Appending multiple backups such as full and transaction logs into a single backup media isn't supported.
- You can provide compressed backups to reduce the likelihood of experiencing potential issues associated with migrating large backups.
Ensure that the service account that's running the source SQL Server instance has read and write permissions on the SMB network share that contains database backup files.
If you're migrating a database that's protected by transparent data encryption (TDE), the certificate from the source SQL Server instance must be migrated to your target managed instance before you restore the database. For more information about migrating TDE-enabled databases, see Tutorial: Migrate TDE-enabled databases (preview) to Azure SQL in Azure Data Studio.
Tip
If your database contains sensitive data that's protected by Always Encrypted, the migration process automatically migrates your Always Encrypted keys to your target managed instance.
If your database backups are on a network file share, provide a computer on which you can install a self-hosted integration runtime to access and migrate database backups. The migration wizard gives you the download link and authentication keys to download and install your self-hosted integration runtime.
In preparation for the migration, ensure that the computer on which you install the self-hosted integration runtime has the following outbound firewall rules and domain names enabled:
Domain names Outbound port Description Public cloud: {datafactory}.{region}.datafactory.azure.net
or*.frontend.clouddatahub.net
Azure Government:{datafactory}.{region}.datafactory.azure.us
Microsoft Azure operated by 21Vianet:{datafactory}.{region}.datafactory.azure.cn443 Required by the self-hosted integration runtime to connect to Database Migration Service.
For a newly created data factory in a public cloud, locate the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) from your self-hosted integration runtime key, in the format{datafactory}.{region}.datafactory.azure.net.
For an existing data factory, if you don't see the FQDN in your self-hosted integration key, use*.frontend.clouddatahub.netinstead.download.microsoft.com443 Required by the self-hosted integration runtime for downloading the updates. If you have disabled auto-update, you can skip configuring this domain. *.core.windows.net443 Used by the self-hosted integration runtime that connects to the Azure storage account to upload database backups from your network share Tip
If your database backup files are already provided in an Azure storage account, a self-hosted integration runtime isn't required during the migration process.
If you use a self-hosted integration runtime, make sure that the computer on which the runtime is installed can connect to the source SQL Server instance and the network file share where backup files are located.
Enable outbound port 445 to allow access to the network file share. For more information, see Recommendations for using a self-hosted integration runtime.
If you use Database Migration Service for the first time, make sure that the Microsoft.DataMigration resource provider is registered in your subscription. You can complete the steps to register the resource provider.
Recommendations for using a self-hosted integration runtime for database migrations
Use a single self-hosted integration runtime for multiple source SQL Server databases.
Install only one instance of a self-hosted integration runtime on any single computer.
Associate only one self-hosted integration runtime with one instance of Database Migration Service.
The self-hosted integration runtime uses resources (memory and CPU) on the computer it's installed on. Install the self-hosted integration runtime on a computer that's separate from your source SQL Server instance. But the two computers should be in close proximity. Having the self-hosted integration runtime close to the data source reduces the time it takes for the self-hosted integration runtime to connect to the data source.
Use the self-hosted integration runtime only when you have your database backups in an on-premises SMB network share. A self-hosted integration runtime isn't required for database migrations if your source database backups are already in the storage blob container.
We recommend up to 10 concurrent database migrations per self-hosted integration runtime on a single computer. To increase the number of concurrent database migrations, scale out the self-hosted runtime to up to four nodes or create separate instances of the self-hosted integration runtime on different computers.
Configure the self-hosted integration runtime to auto-update and automatically apply any new features, bug fixes, and enhancements that are released. For more information, see Self-hosted integration runtime auto-update.
Monitor database migration progress in the Azure portal
The Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio orchestrates all migration tasks through the Database Migration Service selected in the migration wizard when migrating databases.
To monitor database migrations in the Azure portal:
In the Azure portal, search for your instance of Database Migration Service by using the resource name.
In the Database Migration Service instance overview, select Monitor migrations to view the details of your database migrations.
Known issues and limitations
Database Migration Service doesn't support overwriting existing databases in your target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance, Azure SQL Database, or SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines.
Database Migration Service doesn't support configuring high availability and disaster recovery on your target to match the source topology.
The following server objects aren't supported:
- SQL Server Agent jobs
- Credentials
- SQL Server Integration Services packages
- Server audit
For a complete list of metadata and server objects that you need to move, refer to the detailed information available in Manage Metadata When Making a Database Available on Another Server.
SQL Server 2008 and earlier as target versions aren't supported for migrations to SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines.
If you use SQL Server 2014 or SQL Server 2012, you must store your source database backup files in an Azure storage blob container instead of by using the network share option. Store the backup files as page blobs. Block blobs are supported only in SQL Server 2016 and later versions.
You can't use an existing self-hosted integration runtime that was created in Azure Data Factory for database migrations with Database Migration Service. Initially, create the self-hosted integration runtime by using the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio. You can reuse that self-hosted integration runtime in future database migrations.
Azure Data Studio currently supports both Microsoft Entra ID/Windows authentication and SQL logins for connecting to the source SQL Server instance. For the Azure SQL targets, only SQL logins are supported.
Pricing
Azure Database Migration Service is free to use. You can migrate multiple SQL Server databases by using Database Migration Service at no charge.
No data movement or data ingress costs are assessed when you migrate your databases from an on-premises environment to Azure. If the source database is moved from another region or from an Azure virtual machine, you might incur bandwidth charges depending on your bandwidth provider and routing scenario.
Use a virtual machine or an on-premises server to install Azure Data Studio.
A self-hosted integration runtime is required to access database backups from your on-premises network share.
Region availability
For the list of Azure regions that support database migrations by using the Azure SQL Migration extension for Azure Data Studio (powered by Azure Database Migration Service), see Azure products available by region.