BackgroundWorker Sınıf
Tanım
Önemli
Bazı bilgiler ürünün ön sürümüyle ilgilidir ve sürüm öncesinde önemli değişiklikler yapılmış olabilir. Burada verilen bilgilerle ilgili olarak Microsoft açık veya zımni hiçbir garanti vermez.
Ayrı bir iş parçacığında bir işlemi yürütür.
public ref class BackgroundWorker : IDisposablepublic ref class BackgroundWorker : System::ComponentModel::Componentpublic class BackgroundWorker : IDisposablepublic class BackgroundWorker : System.ComponentModel.Componenttype BackgroundWorker = class
interface IDisposabletype BackgroundWorker = class
inherit ComponentPublic Class BackgroundWorker
Implements IDisposablePublic Class BackgroundWorker
Inherits Component- Devralma
-
BackgroundWorker
- Devralma
- Uygulamalar
Örnekler
Aşağıdaki kod örneği, zaman alan bir işlemi zaman uyumsuz olarak yürütmek için sınıfının temellerini BackgroundWorker gösterir. Aşağıdaki çizimde çıktının bir örneği gösterilmektedir.
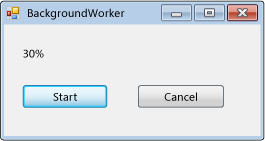
Bu kodu denemek için bir Windows Forms uygulaması oluşturun. adlı resultLabel bir Label denetim ekleyin ve ve cancelAsyncButtonadlı startAsyncButton iki Button denetim ekleyin. Her iki düğme için de olay işleyicileri oluşturun Click . Araç Kutusunun Bileşenler sekmesinden adlı backgroundWorker1bir BackgroundWorker bileşen ekleyin. için BackgroundWorker, ProgressChangedve RunWorkerCompleted olay işleyicileri oluşturunDoWork. Formun kodunda mevcut kodu aşağıdaki kodla değiştirin.
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace BackgroundWorkerSimple
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
}
private void startAsyncButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (backgroundWorker1.IsBusy != true)
{
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync();
}
}
private void cancelAsyncButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation == true)
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync();
}
}
// This event handler is where the time-consuming work is done.
private void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
BackgroundWorker worker = sender as BackgroundWorker;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (worker.CancellationPending == true)
{
e.Cancel = true;
break;
}
else
{
// Perform a time consuming operation and report progress.
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
worker.ReportProgress(i * 10);
}
}
}
// This event handler updates the progress.
private void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
resultLabel.Text = (e.ProgressPercentage.ToString() + "%");
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the background operation.
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Cancelled == true)
{
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled!";
}
else if (e.Error != null)
{
resultLabel.Text = "Error: " + e.Error.Message;
}
else
{
resultLabel.Text = "Done!";
}
}
}
}
Imports System.ComponentModel
Public Class Form1
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = True
backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True
End Sub
Private Sub startAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles startAsyncButton.Click
If backgroundWorker1.IsBusy <> True Then
' Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync()
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cancelAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles cancelAsyncButton.Click
If backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True Then
' Cancel the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync()
End If
End Sub
' This event handler is where the time-consuming work is done.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_DoWork(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.DoWork
Dim worker As BackgroundWorker = CType(sender, BackgroundWorker)
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 10
If (worker.CancellationPending = True) Then
e.Cancel = True
Exit For
Else
' Perform a time consuming operation and report progress.
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500)
worker.ReportProgress(i * 10)
End If
Next
End Sub
' This event handler updates the progress.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As ProgressChangedEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged
resultLabel.Text = (e.ProgressPercentage.ToString() + "%")
End Sub
' This event handler deals with the results of the background operation.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted
If e.Cancelled = True Then
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled!"
ElseIf e.Error IsNot Nothing Then
resultLabel.Text = "Error: " & e.Error.Message
Else
resultLabel.Text = "Done!"
End If
End Sub
End Class
Aşağıdaki kod örneği, zaman alan bir işlemi zaman uyumsuz olarak yürütmek için sınıfının kullanımını BackgroundWorker gösterir. Aşağıdaki çizimde çıktının bir örneği gösterilmektedir.
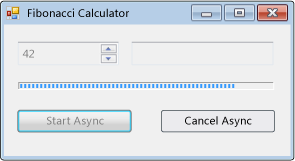
İşlem seçilen Fibonacci numarasını hesaplar, hesaplama devam ederken ilerleme durumunu bildirir ve bekleyen bir hesaplamanın iptal edilmesine izin verir.
#using <System.Drawing.dll>
#using <System.dll>
#using <System.Windows.Forms.dll>
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Collections;
using namespace System::ComponentModel;
using namespace System::Drawing;
using namespace System::Threading;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
public ref class FibonacciForm: public System::Windows::Forms::Form
{
private:
int numberToCompute;
int highestPercentageReached;
System::Windows::Forms::NumericUpDown^ numericUpDown1;
System::Windows::Forms::Button^ startAsyncButton;
System::Windows::Forms::Button^ cancelAsyncButton;
System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar^ progressBar1;
System::Windows::Forms::Label ^ resultLabel;
System::ComponentModel::BackgroundWorker^ backgroundWorker1;
public:
FibonacciForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
numberToCompute = highestPercentageReached = 0;
InitializeBackgoundWorker();
}
private:
// Set up the BackgroundWorker object by
// attaching event handlers.
void InitializeBackgoundWorker()
{
backgroundWorker1->DoWork += gcnew DoWorkEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_DoWork );
backgroundWorker1->RunWorkerCompleted += gcnew RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted );
backgroundWorker1->ProgressChanged += gcnew ProgressChangedEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged );
}
void startAsyncButton_Click( System::Object^ /*sender*/, System::EventArgs^ /*e*/ )
{
// Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel->Text = String::Empty;
// Disable the UpDown control until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this->numericUpDown1->Enabled = false;
// Disable the Start button until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this->startAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
// Enable the Cancel button while
// the asynchronous operation runs.
this->cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = true;
// Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = (int)numericUpDown1->Value;
// Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0;
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1->RunWorkerAsync( numberToCompute );
}
void cancelAsyncButton_Click( System::Object^ /*sender*/, System::EventArgs^ /*e*/ )
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
this->backgroundWorker1->CancelAsync();
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler is where the actual,
// potentially time-consuming work is done.
void backgroundWorker1_DoWork( Object^ sender, DoWorkEventArgs^ e )
{
// Get the BackgroundWorker that raised this event.
BackgroundWorker^ worker = dynamic_cast<BackgroundWorker^>(sender);
// Assign the result of the computation
// to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
// object. This is will be available to the
// RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e->Result = ComputeFibonacci( safe_cast<Int32>(e->Argument), worker, e );
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the
// background operation.
void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted( Object^ /*sender*/, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs^ e )
{
// First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
if ( e->Error != nullptr )
{
MessageBox::Show( e->Error->Message );
}
else
if ( e->Cancelled )
{
// Next, handle the case where the user cancelled
// the operation.
// Note that due to a race condition in
// the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
// flag may not have been set, even though
// CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel->Text = "Cancelled";
}
else
{
// Finally, handle the case where the operation
// succeeded.
resultLabel->Text = e->Result->ToString();
}
// Enable the UpDown control.
this->numericUpDown1->Enabled = true;
// Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton->Enabled = true;
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler updates the progress bar.
void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged( Object^ /*sender*/, ProgressChangedEventArgs^ e )
{
this->progressBar1->Value = e->ProgressPercentage;
}
// This is the method that does the actual work. For this
// example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
// reports progress as it does its work.
long ComputeFibonacci( int n, BackgroundWorker^ worker, DoWorkEventArgs ^ e )
{
// The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
// Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
if ( (n < 0) || (n > 91) )
{
throw gcnew ArgumentException( "value must be >= 0 and <= 91","n" );
}
long result = 0;
// Abort the operation if the user has cancelled.
// Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
// CancellationPending to true just after the
// last invocation of this method exits, so this
// code will not have the opportunity to set the
// DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
// that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
// not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
// event handler. This is a race condition.
if ( worker->CancellationPending )
{
e->Cancel = true;
}
else
{
if ( n < 2 )
{
result = 1;
}
else
{
result = ComputeFibonacci( n - 1, worker, e ) + ComputeFibonacci( n - 2, worker, e );
}
// Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
int percentComplete = (int)((float)n / (float)numberToCompute * 100);
if ( percentComplete > highestPercentageReached )
{
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete;
worker->ReportProgress( percentComplete );
}
}
return result;
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
this->numericUpDown1 = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::NumericUpDown;
this->startAsyncButton = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button;
this->cancelAsyncButton = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button;
this->resultLabel = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Label;
this->progressBar1 = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar;
this->backgroundWorker1 = gcnew System::ComponentModel::BackgroundWorker;
(dynamic_cast<System::ComponentModel::ISupportInitialize^>(this->numericUpDown1))->BeginInit();
this->SuspendLayout();
//
// numericUpDown1
//
this->numericUpDown1->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 16, 16 );
array<Int32>^temp0 = {91,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Maximum = System::Decimal( temp0 );
array<Int32>^temp1 = {1,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Minimum = System::Decimal( temp1 );
this->numericUpDown1->Name = "numericUpDown1";
this->numericUpDown1->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 80, 20 );
this->numericUpDown1->TabIndex = 0;
array<Int32>^temp2 = {1,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Value = System::Decimal( temp2 );
//
// startAsyncButton
//
this->startAsyncButton->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 16, 72 );
this->startAsyncButton->Name = "startAsyncButton";
this->startAsyncButton->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 120, 23 );
this->startAsyncButton->TabIndex = 1;
this->startAsyncButton->Text = "Start Async";
this->startAsyncButton->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::startAsyncButton_Click );
//
// cancelAsyncButton
//
this->cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
this->cancelAsyncButton->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 153, 72 );
this->cancelAsyncButton->Name = "cancelAsyncButton";
this->cancelAsyncButton->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 119, 23 );
this->cancelAsyncButton->TabIndex = 2;
this->cancelAsyncButton->Text = "Cancel Async";
this->cancelAsyncButton->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::cancelAsyncButton_Click );
//
// resultLabel
//
this->resultLabel->BorderStyle = System::Windows::Forms::BorderStyle::Fixed3D;
this->resultLabel->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 112, 16 );
this->resultLabel->Name = "resultLabel";
this->resultLabel->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 160, 23 );
this->resultLabel->TabIndex = 3;
this->resultLabel->Text = "(no result)";
this->resultLabel->TextAlign = System::Drawing::ContentAlignment::MiddleCenter;
//
// progressBar1
//
this->progressBar1->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 18, 48 );
this->progressBar1->Name = "progressBar1";
this->progressBar1->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 256, 8 );
this->progressBar1->Step = 2;
this->progressBar1->TabIndex = 4;
//
// backgroundWorker1
//
this->backgroundWorker1->WorkerReportsProgress = true;
this->backgroundWorker1->WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
//
// FibonacciForm
//
this->ClientSize = System::Drawing::Size( 292, 118 );
this->Controls->Add( this->progressBar1 );
this->Controls->Add( this->resultLabel );
this->Controls->Add( this->cancelAsyncButton );
this->Controls->Add( this->startAsyncButton );
this->Controls->Add( this->numericUpDown1 );
this->Name = "FibonacciForm";
this->Text = "Fibonacci Calculator";
(dynamic_cast<System::ComponentModel::ISupportInitialize^>(this->numericUpDown1))->EndInit();
this->ResumeLayout( false );
}
};
[STAThread]
int main()
{
Application::Run( gcnew FibonacciForm );
}
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace BackgroundWorkerExample
{
public class FibonacciForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private int numberToCompute = 0;
private int highestPercentageReached = 0;
private System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown numericUpDown1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button startAsyncButton;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button cancelAsyncButton;
private System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar progressBar1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label resultLabel;
private System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker backgroundWorker1;
public FibonacciForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeBackgroundWorker();
}
// Set up the BackgroundWorker object by
// attaching event handlers.
private void InitializeBackgroundWorker()
{
backgroundWorker1.DoWork +=
new DoWorkEventHandler(backgroundWorker1_DoWork);
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted +=
new RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler(
backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted);
backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged +=
new ProgressChangedEventHandler(
backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged);
}
private void startAsyncButton_Click(System.Object sender,
System.EventArgs e)
{
// Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel.Text = String.Empty;
// Disable the UpDown control until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this.numericUpDown1.Enabled = false;
// Disable the Start button until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this.startAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
// Enable the Cancel button while
// the asynchronous operation runs.
this.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = true;
// Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = (int)numericUpDown1.Value;
// Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0;
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(numberToCompute);
}
private void cancelAsyncButton_Click(System.Object sender,
System.EventArgs e)
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
this.backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync();
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler is where the actual,
// potentially time-consuming work is done.
private void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender,
DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
// Get the BackgroundWorker that raised this event.
BackgroundWorker worker = sender as BackgroundWorker;
// Assign the result of the computation
// to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
// object. This is will be available to the
// RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e.Result = ComputeFibonacci((int)e.Argument, worker, e);
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the
// background operation.
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(
object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
// First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
if (e.Error != null)
{
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.Message);
}
else if (e.Cancelled)
{
// Next, handle the case where the user canceled
// the operation.
// Note that due to a race condition in
// the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
// flag may not have been set, even though
// CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled";
}
else
{
// Finally, handle the case where the operation
// succeeded.
resultLabel.Text = e.Result.ToString();
}
// Enable the UpDown control.
this.numericUpDown1.Enabled = true;
// Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton.Enabled = true;
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler updates the progress bar.
private void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender,
ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
this.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage;
}
// This is the method that does the actual work. For this
// example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
// reports progress as it does its work.
long ComputeFibonacci(int n, BackgroundWorker worker, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
// The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
// Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
if ((n < 0) || (n > 91))
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n");
}
long result = 0;
// Abort the operation if the user has canceled.
// Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
// CancellationPending to true just after the
// last invocation of this method exits, so this
// code will not have the opportunity to set the
// DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
// that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
// not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
// event handler. This is a race condition.
if (worker.CancellationPending)
{
e.Cancel = true;
}
else
{
if (n < 2)
{
result = 1;
}
else
{
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1, worker, e) +
ComputeFibonacci(n - 2, worker, e);
}
// Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
int percentComplete =
(int)((float)n / (float)numberToCompute * 100);
if (percentComplete > highestPercentageReached)
{
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete;
worker.ReportProgress(percentComplete);
}
}
return result;
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.numericUpDown1 = new System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown();
this.startAsyncButton = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.cancelAsyncButton = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.resultLabel = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.progressBar1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar();
this.backgroundWorker1 = new System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.numericUpDown1)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// numericUpDown1
//
this.numericUpDown1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(16, 16);
this.numericUpDown1.Maximum = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
91,
0,
0,
0});
this.numericUpDown1.Minimum = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
1,
0,
0,
0});
this.numericUpDown1.Name = "numericUpDown1";
this.numericUpDown1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 20);
this.numericUpDown1.TabIndex = 0;
this.numericUpDown1.Value = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
1,
0,
0,
0});
//
// startAsyncButton
//
this.startAsyncButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(16, 72);
this.startAsyncButton.Name = "startAsyncButton";
this.startAsyncButton.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(120, 23);
this.startAsyncButton.TabIndex = 1;
this.startAsyncButton.Text = "Start Async";
this.startAsyncButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.startAsyncButton_Click);
//
// cancelAsyncButton
//
this.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
this.cancelAsyncButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(153, 72);
this.cancelAsyncButton.Name = "cancelAsyncButton";
this.cancelAsyncButton.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(119, 23);
this.cancelAsyncButton.TabIndex = 2;
this.cancelAsyncButton.Text = "Cancel Async";
this.cancelAsyncButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.cancelAsyncButton_Click);
//
// resultLabel
//
this.resultLabel.BorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle.Fixed3D;
this.resultLabel.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(112, 16);
this.resultLabel.Name = "resultLabel";
this.resultLabel.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(160, 23);
this.resultLabel.TabIndex = 3;
this.resultLabel.Text = "(no result)";
this.resultLabel.TextAlign = System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter;
//
// progressBar1
//
this.progressBar1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(18, 48);
this.progressBar1.Name = "progressBar1";
this.progressBar1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(256, 8);
this.progressBar1.Step = 2;
this.progressBar1.TabIndex = 4;
//
// backgroundWorker1
//
this.backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
this.backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
//
// FibonacciForm
//
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(292, 118);
this.Controls.Add(this.progressBar1);
this.Controls.Add(this.resultLabel);
this.Controls.Add(this.cancelAsyncButton);
this.Controls.Add(this.startAsyncButton);
this.Controls.Add(this.numericUpDown1);
this.Name = "FibonacciForm";
this.Text = "Fibonacci Calculator";
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.numericUpDown1)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FibonacciForm());
}
}
}
Imports System.Collections
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Public Class FibonacciForm
Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form
Private numberToCompute As Integer = 0
Private highestPercentageReached As Integer = 0
Private numericUpDown1 As System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
Private WithEvents startAsyncButton As System.Windows.Forms.Button
Private WithEvents cancelAsyncButton As System.Windows.Forms.Button
Private progressBar1 As System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
Private resultLabel As System.Windows.Forms.Label
Private WithEvents backgroundWorker1 As System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub startAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles startAsyncButton.Click
' Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel.Text = [String].Empty
' Disable the UpDown control until
' the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = False
' Disable the Start button until
' the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.startAsyncButton.Enabled = False
' Enable the Cancel button while
' the asynchronous operation runs.
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = True
' Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = CInt(numericUpDown1.Value)
' Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0
' Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(numberToCompute)
End Sub
Private Sub cancelAsyncButton_Click( _
ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles cancelAsyncButton.Click
' Cancel the asynchronous operation.
Me.backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync()
' Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
' This event handler is where the actual work is done.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_DoWork( _
ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.DoWork
' Get the BackgroundWorker object that raised this event.
Dim worker As BackgroundWorker = _
CType(sender, BackgroundWorker)
' Assign the result of the computation
' to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
' object. This is will be available to the
' RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e.Result = ComputeFibonacci(e.Argument, worker, e)
End Sub
' This event handler deals with the results of the
' background operation.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted
' First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
If (e.Error IsNot Nothing) Then
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.Message)
ElseIf e.Cancelled Then
' Next, handle the case where the user canceled the
' operation.
' Note that due to a race condition in
' the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
' flag may not have been set, even though
' CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled"
Else
' Finally, handle the case where the operation succeeded.
resultLabel.Text = e.Result.ToString()
End If
' Enable the UpDown control.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = True
' Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton.Enabled = True
' Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
' This event handler updates the progress bar.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ProgressChangedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged
Me.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage
End Sub
' This is the method that does the actual work. For this
' example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
' reports progress as it does its work.
Function ComputeFibonacci( _
ByVal n As Integer, _
ByVal worker As BackgroundWorker, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) As Long
' The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
' Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
If n < 0 OrElse n > 91 Then
Throw New ArgumentException( _
"value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n")
End If
Dim result As Long = 0
' Abort the operation if the user has canceled.
' Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
' CancellationPending to true just after the
' last invocation of this method exits, so this
' code will not have the opportunity to set the
' DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
' that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
' not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
' event handler. This is a race condition.
If worker.CancellationPending Then
e.Cancel = True
Else
If n < 2 Then
result = 1
Else
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1, worker, e) + _
ComputeFibonacci(n - 2, worker, e)
End If
' Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
Dim percentComplete As Integer = _
CSng(n) / CSng(numberToCompute) * 100
If percentComplete > highestPercentageReached Then
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete
worker.ReportProgress(percentComplete)
End If
End If
Return result
End Function
Private Sub InitializeComponent()
Me.numericUpDown1 = New System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
Me.startAsyncButton = New System.Windows.Forms.Button
Me.cancelAsyncButton = New System.Windows.Forms.Button
Me.resultLabel = New System.Windows.Forms.Label
Me.progressBar1 = New System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
Me.backgroundWorker1 = New System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
CType(Me.numericUpDown1, System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize).BeginInit()
Me.SuspendLayout()
'
'numericUpDown1
'
Me.numericUpDown1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(16, 16)
Me.numericUpDown1.Maximum = New Decimal(New Integer() {91, 0, 0, 0})
Me.numericUpDown1.Minimum = New Decimal(New Integer() {1, 0, 0, 0})
Me.numericUpDown1.Name = "numericUpDown1"
Me.numericUpDown1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(80, 20)
Me.numericUpDown1.TabIndex = 0
Me.numericUpDown1.Value = New Decimal(New Integer() {1, 0, 0, 0})
'
'startAsyncButton
'
Me.startAsyncButton.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(16, 72)
Me.startAsyncButton.Name = "startAsyncButton"
Me.startAsyncButton.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(120, 23)
Me.startAsyncButton.TabIndex = 1
Me.startAsyncButton.Text = "Start Async"
'
'cancelAsyncButton
'
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(153, 72)
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Name = "cancelAsyncButton"
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(119, 23)
Me.cancelAsyncButton.TabIndex = 2
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Text = "Cancel Async"
'
'resultLabel
'
Me.resultLabel.BorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle.Fixed3D
Me.resultLabel.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(112, 16)
Me.resultLabel.Name = "resultLabel"
Me.resultLabel.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(160, 23)
Me.resultLabel.TabIndex = 3
Me.resultLabel.Text = "(no result)"
Me.resultLabel.TextAlign = System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter
'
'progressBar1
'
Me.progressBar1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(18, 48)
Me.progressBar1.Name = "progressBar1"
Me.progressBar1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(256, 8)
Me.progressBar1.TabIndex = 4
'
'backgroundWorker1
'
Me.backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = True
Me.backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True
'
'FibonacciForm
'
Me.ClientSize = New System.Drawing.Size(292, 118)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.progressBar1)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.resultLabel)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.cancelAsyncButton)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.startAsyncButton)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.numericUpDown1)
Me.Name = "FibonacciForm"
Me.Text = "Fibonacci Calculator"
CType(Me.numericUpDown1, System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize).EndInit()
Me.ResumeLayout(False)
End Sub
<STAThread()> _
Shared Sub Main()
Application.Run(New FibonacciForm)
End Sub
End Class
Açıklamalar
BackgroundWorker sınıfı, ayrı, ayrılmış bir iş parçacığında bir işlem çalıştırmanıza olanak tanır. İndirmeler ve veritabanı işlemleri gibi zaman alan işlemler, kullanıcı arabiriminizin (UI) çalışırken yanıt vermeyi durdurmuş gibi görünmesine neden olabilir. Yanıt veren bir kullanıcı arabirimi istediğinizde ve bu tür işlemlerle ilişkili uzun gecikmelerle karşılaştığınızda, BackgroundWorker sınıfı kullanışlı bir çözüm sağlar.
Arka planda zaman alan bir işlem yürütmek için bir BackgroundWorker oluşturun ve işleminizin ilerleme durumunu bildiren olayları ve işleminiz tamamlandığında sinyal veren olayları dinleyin. Program aracılığıyla oluşturabilir BackgroundWorker veya Araç Kutusu'nunBileşenler sekmesinden formunuza sürükleyebilirsiniz. Windows Forms Designer oluşturursanızBackgroundWorker, Bileşen Tepsisinde görünür ve özellikleri Özellikler penceresi görüntülenir.
Arka plan işlemi ayarlamak için olaya bir olay işleyicisi DoWork ekleyin. Bu olay işleyicisinde zaman alan işleminizi çağırabilirsiniz. İşlemi başlatmak için çağrısında bulunur RunWorkerAsync. İlerleme güncelleştirmelerinin bildirimlerini almak için olayı işleyebilir ProgressChanged . İşlem tamamlandığında bildirim almak için olayı işleyebilirsiniz RunWorkerCompleted .
Not
Olay işleyicinizdeki DoWork kullanıcı arabirimi nesnelerini işlememeye dikkat etmelisiniz. Bunun yerine, ve RunWorkerCompleted olayları aracılığıyla kullanıcı arabirimiyle ProgressChanged iletişim kurun.
BackgroundWorker olaylar sınırlar arasında AppDomain sıralanmaz. Birden fazla AppDomainiçinde çok iş parçacıklı işlemler gerçekleştirmek için bir BackgroundWorker bileşen kullanmayın.
Arka plan işleminiz bir parametre gerektiriyorsa, parametresiyle çağrısında RunWorkerAsync bulunur. Olay işleyicisinin DoWork içinde parametresini özelliğinden DoWorkEventArgs.Argument ayıklayabilirsiniz.
hakkında BackgroundWorkerdaha fazla bilgi için bkz . Nasıl yapılır: Arka Planda İşlem Çalıştırma.
Oluşturucular
| BackgroundWorker() |
BackgroundWorker sınıfının yeni bir örneğini başlatır. |
Özellikler
| CancellationPending |
Uygulamanın bir arka plan işleminin iptalini isteyip istemediğinizi belirten bir değer alır. |
| CanRaiseEvents |
Bileşenin bir olay oluşturup oluşturamayacağını belirten bir değer alır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| Container |
öğesini IContainer içeren öğesini Componentalır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| DesignMode |
öğesinin şu anda tasarım modunda olup olmadığını Component gösteren bir değer alır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| Events |
Bu Componentöğesine eklenen olay işleyicilerinin listesini alır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| IsBusy |
öğesinin zaman uyumsuz bir işlem çalıştırıp çalıştırmadığını BackgroundWorker belirten bir değer alır. |
| Site |
öğesini alır veya ayarlar ISiteComponent. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| WorkerReportsProgress |
İlerleme durumu güncelleştirmelerini raporlayıp bildiremeyeceğini BackgroundWorker belirten bir değer alır veya ayarlar. |
| WorkerSupportsCancellation |
öğesinin zaman uyumsuz iptali BackgroundWorker destekleyip desteklemediğini belirten bir değer alır veya ayarlar. |
Yöntemler
| CancelAsync() |
Bekleyen bir arka plan işleminin iptalini istemektedir. |
| CreateObjRef(Type) |
Uzak bir nesneyle iletişim kurmak için kullanılan bir ara sunucu oluşturmak için gereken tüm ilgili bilgileri içeren bir nesne oluşturur. (Devralındığı yer: MarshalByRefObject) |
| Dispose() |
Uygulama tarafından tanımlanan, yönetilmeyen kaynakları serbest bırakma, salma veya sıfırlama ile ilişkili görevleri gerçekleştirir. |
| Dispose() |
Component tarafından kullanılan tüm kaynakları serbest bırakır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| Dispose(Boolean) |
Bu yöntem hiçbir şey yapmaz. |
| Dispose(Boolean) |
Component tarafından kullanılan yönetilmeyen kaynakları serbest bırakır ve yönetilen kaynakları isteğe bağlı olarak serbest bırakır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| Equals(Object) |
Belirtilen nesnenin geçerli nesneye eşit olup olmadığını belirler. (Devralındığı yer: Object) |
| GetHashCode() |
Varsayılan karma işlevi işlevi görür. (Devralındığı yer: Object) |
| GetLifetimeService() |
Geçersiz.
Bu örnek için yaşam süresi ilkesini denetleen geçerli yaşam süresi hizmet nesnesini alır. (Devralındığı yer: MarshalByRefObject) |
| GetService(Type) |
veya tarafından ComponentContainersağlanan bir hizmeti temsil eden bir nesnesi döndürür. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| GetType() |
Type Geçerli örneğini alır. (Devralındığı yer: Object) |
| InitializeLifetimeService() |
Geçersiz.
Bu örneğin yaşam süresi ilkesini denetlemek için bir yaşam süresi hizmet nesnesi alır. (Devralındığı yer: MarshalByRefObject) |
| MemberwiseClone() |
Geçerli Objectöğesinin sığ bir kopyasını oluşturur. (Devralındığı yer: Object) |
| MemberwiseClone(Boolean) |
Geçerli MarshalByRefObject nesnenin sığ bir kopyasını oluşturur. (Devralındığı yer: MarshalByRefObject) |
| OnDoWork(DoWorkEventArgs) |
Olayı tetikler DoWork . |
| OnProgressChanged(ProgressChangedEventArgs) |
Olayı tetikler ProgressChanged . |
| OnRunWorkerCompleted(RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) |
Olayı tetikler RunWorkerCompleted . |
| ReportProgress(Int32) |
Olayı tetikler ProgressChanged . |
| ReportProgress(Int32, Object) |
Olayı tetikler ProgressChanged . |
| RunWorkerAsync() |
Arka plan işleminin yürütülmesini başlatır. |
| RunWorkerAsync(Object) |
Arka plan işleminin yürütülmesini başlatır. |
| ToString() |
Geçerli nesneyi temsil eden dizeyi döndürür. (Devralındığı yer: Object) |
| ToString() |
Varsa, adını Componentiçeren bir String döndürür. Bu yöntem geçersiz kılınmamalıdır. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
Ekinlikler
| Disposed |
Bileşen yöntemine Dispose() yapılan bir çağrı tarafından atıldığında gerçekleşir. (Devralındığı yer: Component) |
| DoWork |
Çağrıldığında RunWorkerAsync() gerçekleşir. |
| ProgressChanged |
Çağrıldığında ReportProgress(Int32) gerçekleşir. |
| RunWorkerCompleted |
Arka plan işlemi tamamlandığında, iptal edildiğinde veya bir özel durum oluştuğunda gerçekleşir. |
