你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
借助 HTTP 触发器,可以使用 HTTP 请求调用函数。 可以使用 HTTP 触发器生成无服务器 API 和响应 Webhook。
HTTP 触发函数的默认返回值如下:
-
HTTP 204 No Content,在 Functions 2.x 及更高版本中为空主体 -
HTTP 200 OK,在 Functions 1.x 中为空主体
若要修改 HTTP 响应,请配置输出绑定。
提示
如果计划使用 HTTP 或 WebHook 绑定,请制定计划来避免因实例化 HttpClient 不当导致的端口耗尽现象。 有关详细信息,请参阅如何在 Azure Functions 中管理连接。
重要
本文使用选项卡来支持多个版本的 Node.js 编程模型。 v4 模型已正式发布,旨在为 JavaScript 和 TypeScript 开发人员提供更为灵活和直观的体验。 有关 v4 模型工作原理的更多详细信息,请参阅 Azure Functions Node.js 开发人员指南。 要详细了解 v3 和 v4 之间的差异,请参阅迁移指南。
Azure Functions 支持两种 Python 编程模型。 定义绑定的方式取决于选择的编程模型。
使用 Python v2 编程模型,可以直接在 Python 函数代码中使用修饰器定义绑定。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Python 开发人员指南。
本文同时支持两个编程模型。
示例
可使用以下 C# 模式之一来创建 C# 函数:
-
独立辅助角色模型:编译的 C# 函数,该函数在独立于运行时的工作进程中运行。 需要独立工作进程才能支持在 LTS 和非 LTS 版 .NET 和 .NET Framework 上运行的 C# 函数。 独立工作进程函数的扩展使用
Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Extensions.*命名空间。 -
进程内模型:编译的 C# 函数,该函数在与 Functions 运行时相同的进程中运行。 在此模型的变体中,可以使用 C# 脚本运行 Functions,该脚本主要用于 C# 门户编辑。 进程内函数的扩展使用
Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs.Extensions.*命名空间。
重要
对进程内模型的支持将于 2026 年 11 月 10 日结束。 为获得完全支持,强烈建议将应用迁移到独立工作模型。
本文中的代码默认使用 .NET Core 语法,该语法在 Functions 2.x 版及更高版本中使用。 有关 1.x 语法的信息,请参阅 1.x functions 模板。
以下例子展示了一个 HTTP 触发器,它使用 .NET Isolated 中的 ASP.NET Core 集成返回了“hello, world”响应作为 IActionResult:
[Function("HttpFunction")]
public IActionResult Run(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Anonymous, "get")] HttpRequest req)
{
return new OkObjectResult($"Welcome to Azure Functions, {req.Query["name"]}!");
}
下面的示例演示了一个 HTTP 触发器,该触发器将“hello world”响应作为 HttpResponseData 对象返回:
[Function(nameof(HttpFunction))]
public static HttpResponseData Run([HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Anonymous, "get", "post", Route = null)] HttpRequestData req,
FunctionContext executionContext)
{
var logger = executionContext.GetLogger(nameof(HttpFunction));
logger.LogInformation("message logged");
var response = req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK);
response.Headers.Add("Content-Type", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
response.WriteString("Welcome to .NET isolated worker !!");
return response;
}
本部分包含以下示例:
下面的示例演示 HTTP 触发器绑定。
从查询字符串中读取参数
以下示例从查询字符串中读取名为 id 的参数,然后使用该参数构建返回到客户端的 JSON 文档(内容类型为 application/json)。
@FunctionName("TriggerStringGet")
public HttpResponseMessage run(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req",
methods = {HttpMethod.GET},
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS)
HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
final ExecutionContext context) {
// Item list
context.getLogger().info("GET parameters are: " + request.getQueryParameters());
// Get named parameter
String id = request.getQueryParameters().getOrDefault("id", "");
// Convert and display
if (id.isEmpty()) {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Document not found.")
.build();
}
else {
// return JSON from to the client
// Generate document
final String name = "fake_name";
final String jsonDocument = "{\"id\":\"" + id + "\", " +
"\"description\": \"" + name + "\"}";
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(jsonDocument)
.build();
}
}
从 POST 请求中读取正文
以下示例将 POST 请求的正文读取为 String,然后使用该正文构建返回到客户端的 JSON 文档(内容类型为 application/json)。
@FunctionName("TriggerStringPost")
public HttpResponseMessage run(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req",
methods = {HttpMethod.POST},
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS)
HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
final ExecutionContext context) {
// Item list
context.getLogger().info("Request body is: " + request.getBody().orElse(""));
// Check request body
if (!request.getBody().isPresent()) {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Document not found.")
.build();
}
else {
// return JSON from to the client
// Generate document
final String body = request.getBody().get();
final String jsonDocument = "{\"id\":\"123456\", " +
"\"description\": \"" + body + "\"}";
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(jsonDocument)
.build();
}
}
从路由中读取参数
此示例读取名为 id 的必选参数,并从路由路径中读取可选参数 name,然后使用这两个参数构建返回到客户端的 JSON 文档(内容类型为 application/json)。
@FunctionName("TriggerStringRoute")
public HttpResponseMessage run(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req",
methods = {HttpMethod.GET},
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS,
route = "trigger/{id}/{name=EMPTY}") // name is optional and defaults to EMPTY
HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
@BindingName("id") String id,
@BindingName("name") String name,
final ExecutionContext context) {
// Item list
context.getLogger().info("Route parameters are: " + id);
// Convert and display
if (id == null) {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Document not found.")
.build();
}
else {
// return JSON from to the client
// Generate document
final String jsonDocument = "{\"id\":\"" + id + "\", " +
"\"description\": \"" + name + "\"}";
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(jsonDocument)
.build();
}
}
从 POST 请求中读取 POJO 正文
下面是此示例中引用的 ToDoItem 类的代码:
public class ToDoItem {
private String id;
private String description;
public ToDoItem(String id, String description) {
this.id = id;
this.description = description;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ToDoItem={id=" + id + ",description=" + description + "}";
}
}
此示例读取 POST 请求的正文。 该请求正文会自动反序列化为 ToDoItem 对象,然后以内容类型 application/json 返回到客户端。 当 ToDoItem 参数分配给 body 类的 HttpMessageResponse.Builder 属性时,它会由 Functions 运行时序列化。
@FunctionName("TriggerPojoPost")
public HttpResponseMessage run(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req",
methods = {HttpMethod.POST},
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS)
HttpRequestMessage<Optional<ToDoItem>> request,
final ExecutionContext context) {
// Item list
context.getLogger().info("Request body is: " + request.getBody().orElse(null));
// Check request body
if (!request.getBody().isPresent()) {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Document not found.")
.build();
}
else {
// return JSON from to the client
// Generate document
final ToDoItem body = request.getBody().get();
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(body)
.build();
}
}
以下示例显示了 HTTP 触发的 TypeScript 函数。 该函数在查询字符串或 name正文中查找参数。
import { app, HttpRequest, HttpResponseInit, InvocationContext } from '@azure/functions';
export async function httpTrigger1(request: HttpRequest, context: InvocationContext): Promise<HttpResponseInit> {
context.log(`Http function processed request for url "${request.url}"`);
const name = request.query.get('name') || (await request.text()) || 'world';
return { body: `Hello, ${name}!` };
}
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET', 'POST'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
handler: httpTrigger1,
});
以下示例显示了 HTTP 触发的 JavaScript 函数。 该函数在查询字符串或 name正文中查找参数。
const { app } = require('@azure/functions');
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET', 'POST'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
handler: async (request, context) => {
context.log(`Http function processed request for url "${request.url}"`);
const name = request.query.get('name') || (await request.text()) || 'world';
return { body: `Hello, ${name}!` };
},
});
以下示例演示 function.json 文件中的一个触发器绑定和一个 PowerShell 函数。 该函数在查询字符串或 HTTP 请求的正文中查找 name 参数。
{
"bindings": [
{
"authLevel": "function",
"type": "httpTrigger",
"direction": "in",
"name": "Request",
"methods": [
"get",
"post"
]
},
{
"type": "http",
"direction": "out",
"name": "Response"
}
]
}
using namespace System.Net
# Input bindings are passed in via param block.
param($Request, $TriggerMetadata)
# Write to the Azure Functions log stream.
Write-Host "PowerShell HTTP trigger function processed a request."
# Interact with query parameters or the body of the request.
$name = $Request.Query.Name
if (-not $name) {
$name = $Request.Body.Name
}
$body = "This HTTP triggered function executed successfully. Pass a name in the query string or in the request body for a personalized response."
if ($name) {
$body = "Hello, $name. This HTTP triggered function executed successfully."
}
# Associate values to output bindings by calling 'Push-OutputBinding'.
Push-OutputBinding -Name Response -Value ([HttpResponseContext]@{
StatusCode = [HttpStatusCode]::OK
Body = $body
})
此示例是 HTTP 触发的函数,它使用 HTTP 流 返回分块响应数据。 可以使用这些功能来支持诸如通过管道发送事件数据以实时可视化或检测大量数据中的异常并提供即时通知等场景。
import time
import azure.functions as func
from azurefunctions.extensions.http.fastapi import Request, StreamingResponse
app = func.FunctionApp(http_auth_level=func.AuthLevel.FUNCTION)
def generate_sensor_data():
"""Generate real-time sensor data."""
for i in range(10):
# Simulate temperature and humidity readings
temperature = 20 + i
humidity = 50 + i
yield f"data: {{'temperature': {temperature}, 'humidity': {humidity}}}\n\n"
time.sleep(1)
@app.route(route="stream", methods=[func.HttpMethod.GET])
async def stream_sensor_data(req: Request) -> StreamingResponse:
"""Endpoint to stream real-time sensor data."""
return StreamingResponse(generate_sensor_data(), media_type="text/event-stream")
有关详细信息,包括如何在项目中启用 HTTP 流,请参阅 HTTP 流。
此示例演示触发器绑定和使用该绑定的 Python 函数。 该函数在查询字符串或 HTTP 请求的正文中查找 name 参数。
import azure.functions as func
import logging
app = func.FunctionApp()
@app.function_name(name="HttpTrigger1")
@app.route(route="hello", auth_level=func.AuthLevel.ANONYMOUS)
def test_function(req: func.HttpRequest) -> func.HttpResponse:
logging.info('Python HTTP trigger function processed a request.')
return func.HttpResponse(
"This HTTP triggered function executed successfully.",
status_code=200
)
特性
独立工作器模型和进程内模型均使用 HttpTriggerAttribute 来定义触发器绑定。 C# 脚本改用 function.json 配置文件,如 C# 脚本指南中所述。
在独立工作器模型函数应用中,HttpTriggerAttribute 支持以下参数:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AuthLevel | 确定请求中需要提供的密钥(如果有),以便调用此函数。 有关支持的值,请参阅授权级别。 |
| 方法 | HTTP Methods的数组,该函数将响应此Methods。 如果未指定,该函数将响应所有 HTTP Methods。 请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
| 路由 | 定义路由模板,控制函数将响应的请求 URL。 如果未提供任何值,则默认值为 <functionname>。 有关详细信息,请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
修饰符
仅适用于 Python v2 编程模型。
对于使用修饰器定义的 Python v2 函数,触发器的以下属性在 route 修饰器中定义,这将添加 HttpTrigger 和 HttpOutput 绑定:
| properties | 说明 |
|---|---|
route |
http 终结点的路由。 如果为 None,则将它设置为函数名称(如果存在)或用户定义的 python 函数名称。 |
trigger_arg_name |
HttpRequest 的自变量名称。 默认值为“req”。 |
binding_arg_name |
HttpResponse 的自变量名称。 默认值为“$return”。 |
methods |
函数响应的 HTTP 方法的元组。 |
auth_level |
确定请求中需要提供的密钥(如果有),以便调用此函数。 |
对于使用 function.json 定义的 Python 函数,请参阅“配置”部分。
配置
仅适用于 Python v1 编程模型。
下表说明了可以在传递给 options 方法的 app.http() 对象上设置的属性。
| properties | 说明 |
|---|---|
| authLevel | 确定请求中需要提供的密钥(如果有),以便调用此函数。 有关支持的值,请参阅授权级别。 |
| methods | HTTP Methods的数组,该函数将响应此Methods。 如果未指定,该函数将响应所有 HTTP Methods。 请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
| route | 定义路由模板,控制函数将响应的请求 URL。 如果未提供任何值,则默认值为 <functionname>。 有关详细信息,请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
下表说明了在 function.json 文件中设置的触发器配置属性,这些属性因运行时版本而异。
下表解释了在 function.json 文件中设置的绑定配置属性。
| “function.json”属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 必需 - 必须设置为 httpTrigger。 |
| 方向 | 必需 - 必须设置为 in。 |
| 名字 | 必需 - 在请求或请求正文的函数代码中使用的变量名称。 |
| authLevel | 确定请求中需要提供的密钥(如果有),以便调用此函数。 有关支持的值,请参阅授权级别。 |
| methods | HTTP Methods的数组,该函数将响应此Methods。 如果未指定,该函数将响应所有 HTTP Methods。 请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
| route | 定义路由模板,控制函数将响应的请求 URL。 如果未提供任何值,则默认值为 <functionname>。 有关详细信息,请参阅自定义 HTTP 终结点。 |
使用情况
本部分详细介绍如何配置 HTTP 触发器函数绑定。
HttpTrigger 注释应该应用于以下类型之一的Methods参数:
- HttpRequestMessage<T>。
- 任意的本机 Java 类型,例如 int、String、byte[]。
- 使用可选的可为 null 的值。
- 任何普通旧 Java 对象 (POJO) 类型。
有效负载
触发器输入类型声明为以下类型之一:
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| HttpRequest |
使用此类型要求应用在 .NET Isolated 中配置 ASP.NET Core 集成。 这为你提供了对请求对象和整体 HttpContext 的完全访问权限。 |
| HttpRequestData | 请求对象的投影。 |
| 自定义类型 | 当请求正文是 JSON 时,运行时会尝试分析它以设置对象属性。 |
当触发器参数为 HttpRequestData 或 HttpRequest 类型时,也可以使用 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Http.FromBodyAttribute 将自定义类型绑定到其他参数。 使用此属性需要 Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Extensions.Http 版本 3.1.0 或更高版本。 此类型与 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc 中的类似属性不同。 使用 ASP.NET Core 集成时,需要完全限定的引用或 using 语句。 此示例演示如何使用属性来仅获取正文内容,同时仍可使用 ASP.NET Core 集成来访问完整的 HttpRequest:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker;
namespace AspNetIntegration
{
public class BodyBindingHttpTrigger
{
[Function(nameof(BodyBindingHttpTrigger))]
public IActionResult Run([HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Anonymous, "post")] HttpRequest req,
[Microsoft.Azure.Functions.Worker.Http.FromBody] Person person)
{
return new OkObjectResult(person);
}
}
public record Person(string Name, int Age);
}
自定义 HTTP 终结点
默认情况下,创建 HTTP 触发器的函数时,可通过以下格式的路由对该函数进行寻址:
https://<APP_NAME>.azurewebsites.net/api/<FUNCTION_NAME>
在 HTTP 触发器的输入绑定中,可以使用可选 route 属性自定义此路由。 可以将任何 Web API 路由约束与参数配合使用。
以下函数代码接受路由中的两个参数(category 和 id),并同时使用这两个参数写入响应。
[Function("HttpTrigger1")]
public static HttpResponseData Run([HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "get", "post",
Route = "products/{category:alpha}/{id:int?}")] HttpRequestData req, string category, int? id,
FunctionContext executionContext)
{
var logger = executionContext.GetLogger("HttpTrigger1");
logger.LogInformation("C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
var message = String.Format($"Category: {category}, ID: {id}");
var response = req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK);
response.Headers.Add("Content-Type", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
response.WriteString(message);
return response;
}
路由参数使用 route 注释的 HttpTrigger 设置进行定义。 以下函数代码接受路由中的两个参数(category 和 id),并同时使用这两个参数写入响应。
package com.function;
import java.util.*;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation.*;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.*;
public class HttpTriggerJava {
public HttpResponseMessage<String> HttpTrigger(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req",
methods = {"get"},
authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.FUNCTION,
route = "products/{category:alpha}/{id:int}") HttpRequestMessage<String> request,
@BindingName("category") String category,
@BindingName("id") int id,
final ExecutionContext context) {
String message = String.format("Category %s, ID: %d", category, id);
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK).body(message).build();
}
}
例如,以下 TypeScript 代码使用两个参数(route 和 category)定义了 HTTP 触发器的 id 属性。 该示例会从请求中读取参数,并在响应中返回参数的值。
import { app, HttpRequest, HttpResponseInit, InvocationContext } from '@azure/functions';
export async function httpTrigger1(request: HttpRequest, context: InvocationContext): Promise<HttpResponseInit> {
const category = request.params.category;
const id = request.params.id;
return { body: `Category: ${category}, ID: ${id}` };
}
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
route: 'products/{category:alpha}/{id:int?}',
handler: httpTrigger1,
});
例如,以下 JavaScript 代码使用两个参数(route 和 category)定义了 HTTP 触发器的 id 属性。 该示例会从请求中读取参数,并在响应中返回参数的值。
const { app } = require('@azure/functions');
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
route: 'products/{category:alpha}/{id:int?}',
handler: async (request, context) => {
const category = request.params.category;
const id = request.params.id;
return { body: `Category: ${category}, ID: ${id}` };
},
});
例如,以下代码使用两个参数(route 和 category)定义了 HTTP 触发器的 id 属性:
可将 function.json 文件中声明的路由参数作为 对象的属性进行访问。
$Category = $Request.Params.category
$Id = $Request.Params.id
$Message = "Category:" + $Category + ", ID: " + $Id
Push-OutputBinding -Name Response -Value ([HttpResponseContext]@{
StatusCode = [HttpStatusCode]::OK
Body = $Message
})
函数执行上下文是通过声明为 func.HttpRequest 的参数公开的。 此实例允许函数访问数据路由参数、查询字符串值和允许返回 HTTP 响应的Methods。
定义后,可以通过调用 route_params Methods将路由参数提供给函数。
import logging
import azure.functions as func
def main(req: func.HttpRequest) -> func.HttpResponse:
category = req.route_params.get('category')
id = req.route_params.get('id')
message = f"Category: {category}, ID: {id}"
return func.HttpResponse(message)
通过此配置,现在可以通过以下路由对该函数进行寻址,而不是通过原始路由寻址。
https://<APP_NAME>.azurewebsites.net/api/products/electronics/357
此配置使得函数代码可以支持地址中的两个参数:“category”和“ID”。 有关如何在 URL 中标记化路由参数的更多信息,请参阅 ASP.NET Core 中的路由。
默认情况下,所有函数路由的前缀均为 api。 还可以使用 extensions.http.routePrefix 文件中的 属性自定义或删除前缀。 以下示例通过将空字符串用于 host.json 文件中的前缀删除 api 路由前缀。
{
"extensions": {
"http": {
"routePrefix": ""
}
}
}
使用路由参数
定义了函数的 route 模式的路由参数可用于每个绑定。 例如,如果将某个路由定义为 "route": "products/{id}",则表存储绑定可以在绑定配置中使用 {id} 参数的值。
下面的配置演示如何将 {id} 参数传递到绑定的 rowKey。
import { app, HttpRequest, HttpResponseInit, input, InvocationContext } from '@azure/functions';
const tableInput = input.table({
connection: 'MyStorageConnectionAppSetting',
partitionKey: 'products',
tableName: 'products',
rowKey: '{id}',
});
export async function httpTrigger1(request: HttpRequest, context: InvocationContext): Promise<HttpResponseInit> {
return { jsonBody: context.extraInputs.get(tableInput) };
}
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
route: 'products/{id}',
extraInputs: [tableInput],
handler: httpTrigger1,
});
const { app, input } = require('@azure/functions');
const tableInput = input.table({
connection: 'MyStorageConnectionAppSetting',
partitionKey: 'products',
tableName: 'products',
rowKey: '{id}',
});
app.http('httpTrigger1', {
methods: ['GET'],
authLevel: 'anonymous',
route: 'products/{id}',
extraInputs: [tableInput],
handler: async (request, context) => {
return { jsonBody: context.extraInputs.get(tableInput) };
},
});
{
"type": "table",
"direction": "in",
"name": "product",
"partitionKey": "products",
"tableName": "products",
"rowKey": "{id}"
}
使用路由参数时,会自动为函数创建 invoke_URL_template。 你的客户端可以使用 URL 模板来了解在使用 URL 调用函数时需要在 URL 中传递的参数。 在 Azure 门户中导航到某个 HTTP 触发的函数,然后选择“获取函数 URL”。
可以通过用于invoke_URL_template或获取函数的 Azure 资源管理器 API 以编程方式访问 。
HTTP 流
现在,可以在 Node.js v4 函数应用中流式传输对 HTTP 终结点的请求以及来自该终结点的响应。 有关详细信息,请参阅 HTTP 流式传输。
HTTP 流
Python 中的 HTTP 流支持让你可以使用函数中启用的 FastAPI 请求和响应 API 从 HTTP 终结点接受和返回数据。 这些 API 使主机能够将 HTTP 消息中的数据作为块进行处理,而不必将整个消息读入内存。
先决条件
- Azure Functions 运行时版本 4.34.1 或更高版本。
- Python 版本 3.8 或支持的更高版本。
启用 HTTP 流
默认已禁用 HTTP 流。 需要在应用程序设置中启用此功能,并更新代码以使用 FastAPI 包。 请注意,启用 HTTP 流时,函数应用将默认使用 HTTP 流式处理,原始 HTTP 功能将不起作用。
将
azurefunctions-extensions-http-fastapi扩展包添加到项目的requirements.txt文件中,其中至少应包括以下包:azure-functions azurefunctions-extensions-http-fastapi将以下代码添加到项目的
function_app.py文件中,将导入 FastAPI 扩展:from azurefunctions.extensions.http.fastapi import Request, StreamingResponse部署到 Azure 时,请在函数应用中添加以下应用程序设置:
"PYTHON_ENABLE_INIT_INDEXING": "1"在本地运行时,还需要将同样的设置添加到
local.settings.json项目文件。
HTTP 流示例
启用 HTTP 流式处理功能后,可以创建通过 HTTP 流式传输数据的函数。
以下示例是一个 HTTP 触发的函数,用于实时接收和处理来自客户端的流数据。 它演示了流式上传功能,此功能对于处理连续数据流和处理 IoT 设备中的事件数据等场景非常有用。
import azure.functions as func
from azurefunctions.extensions.http.fastapi import JSONResponse, Request
app = func.FunctionApp(http_auth_level=func.AuthLevel.FUNCTION)
@app.route(route="streaming_upload", methods=[func.HttpMethod.POST])
async def streaming_upload(req: Request) -> JSONResponse:
"""Handle streaming upload requests."""
# Process each chunk of data as it arrives
async for chunk in req.stream():
process_data_chunk(chunk)
# Once all data is received, return a JSON response indicating successful processing
return JSONResponse({"status": "Data uploaded and processed successfully"})
def process_data_chunk(chunk: bytes):
"""Process each data chunk."""
# Add custom processing logic here
pass
调用 HTTP 流
必须使用 HTTP 客户端库来对函数的 FastAPI 终结点进行流式调用。 你使用的客户端工具或浏览器可能不支持原生流媒体,或者仅能返回首个数据块。
可以使用如下所示的客户端脚本将流式处理数据发送到 HTTP 终结点:
import httpx # Be sure to add 'httpx' to 'requirements.txt'
import asyncio
async def stream_generator(file_path):
chunk_size = 2 * 1024 # Define your own chunk size
with open(file_path, 'rb') as file:
while chunk := file.read(chunk_size):
yield chunk
print(f"Sent chunk: {len(chunk)} bytes")
async def stream_to_server(url, file_path):
timeout = httpx.Timeout(60.0, connect=60.0)
async with httpx.AsyncClient(timeout=timeout) as client:
response = await client.post(url, content=stream_generator(file_path))
return response
async def stream_response(response):
if response.status_code == 200:
async for chunk in response.aiter_raw():
print(f"Received chunk: {len(chunk)} bytes")
else:
print(f"Error: {response}")
async def main():
print('helloworld')
# Customize your streaming endpoint served from core tool in variable 'url' if different.
url = 'http://localhost:7071/api/streaming_upload'
file_path = r'<file path>'
response = await stream_to_server(url, file_path)
print(response)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
重要
对 Python 的 HTTP 流支持已正式发布,并且仅支持 Python v2 编程模型。
使用客户端标识
如果函数应用使用应用服务身份验证/授权,则可通过代码查看有关已验证身份的客户端的信息。 此信息以平台注入的请求标头的形式提供。
还可从绑定数据中读取此信息。
注意
目前只能在 .NET 语言中访问经过身份验证的客户端信息。 Functions 运行时 1.x 版本也不支持此操作。
有关经身份验证的客户端的信息作为 ClaimsPrincipal 提供,后者作为请求上下文的一部分提供,如以下示例所示:
经过身份验证的用户通过 HTTP 标头提供。
授权级别
授权级别是一个字符串值,指示访问函数终结点所需的授权密钥的类型。 对于 HTTP 触发的函数,授权级别可以是下列值之一:
| 级别值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 匿名 | 无需提供访问密钥。 |
| 函数 | 需要提供函数特定的密钥来访问终结点。 |
| 管理 | 需要提供主密钥来访问终结点。 |
未显式设置级别时,授权默认为 function 级别。
函数访问密钥
Functions 允许你使用访问密钥来加大函数终结点的访问难度。 除非 HTTP 触发的函数的授权级别设置为 anonymous,否则请求中必须包含访问密钥。 有关详细信息,请参阅在 Azure Functions 中使用访问密钥。
访问密钥授权
大多数 HTTP 触发器模板要求在请求中提供访问密钥。 因此,HTTP 请求通常类似于以下 URL:
https://<APP_NAME>.azurewebsites.net/api/<FUNCTION_NAME>?code=<API_KEY>
在容器中运行的函数应用使用容器主机的域。 有关 Azure 容器应用中托管的示例 HTTP 终结点,请参阅 此容器应用托管文章中的示例。
可将该密钥包含在名为 code 的查询字符串变量中,如上所述。 也可以将它包含在 x-functions-key HTTP 标头中。 密钥的值可以为任意为函数定义的函数密钥,也可以为任意主机密钥。
可以允许不需要密钥的匿名请求。 也可要求使用主密钥。 可使用绑定 JSON 中的 authLevel 属性更改默认授权级别。
注意
在本地运行函数时,不管指定的授权级别设置为何,都会禁用授权。 发布到 Azure 后,将强制执行触发器中的 authLevel 设置。 在容器中本地运行时,仍然需要使用密钥。
Webhook
注意
Webhook 模式仅适用于 1.x 版 Functions 运行时。 进行此更改是为了提高 2.x 及更高版本中 HTTP 触发器的性能。
在 1.x 版中,Webhook 模板为 Webhook 有效负载提供了另一项验证。 在 2.x 及更高版本中,基本 HTTP 触发器仍正常工作,且是针对 Webhook 的推荐Methods。
WebHook 类型
如果函数支持 Webhook,则 webHookType 绑定属性指示此类型,该类型还决定支持的有效负载。 Webhook 类型可以是以下值之一:
| 类型值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
genericJson |
常规用途 Webhook 终结点,不包含特定提供程序的逻辑。 此设置会将请求限制为仅请求使用 HTTP POST 以及内容类型为 application/json。 |
github |
该函数响应 GitHub Webhook。 不要将 authLevel 属性与 GitHub Webhook 配合使用。 |
slack |
该函数响应 Slack Webhook。 不要对 Slack Webhook 使用 authLevel 属性。 |
设置 webHookType 属性时,另请不要在绑定上设置 methods 属性。
GitHub Webhook
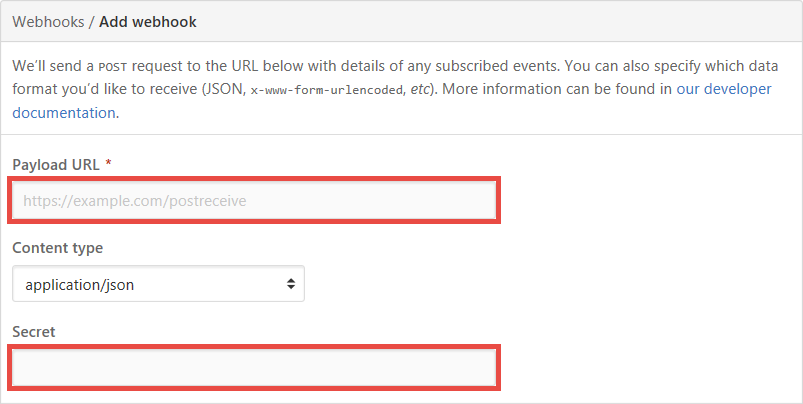
要响应 GitHub webhook,首先请创建包含 HTTP 触发器的函数,并将 webHookType 属性设置为 。 然后将其 URL 和 API 密钥复制到 GitHub 存储库的“添加 Webhook”页。
Slack Webhook
Slack webhook 为用户生成令牌,而非让用户指定它,所以必须使用 Slack 中的令牌配置特定于函数的密钥。 请参阅授权密钥。
Webhook 和密钥
Webhook 授权由属于 HTTP 触发器的 webhook 接收器组件处理,其机制因 webhook 类型而异。 每种机制都依赖于一个密钥。 默认情况下,使用名为“default”的函数密钥。 要使用其他密钥,请将 webhook 提供程序配置为使用以下方式之一的请求发送密钥名称:
-
查询字符串:提供程序通过
clientid查询字符串参数(例如,https://<APP_NAME>.azurewebsites.net/api/<FUNCTION_NAME>?clientid=<KEY_NAME>)传递密钥名称。 -
请求标头:提供程序通过
x-functions-clientid标头传递密钥名称。
调用 HTTP 触发器
可以使用 HTTP 客户端调用 HTTP 触发的函数。 本节中的示例使用 curl,但可以使用任何 HTTP 客户端工具来保护数据。 有关详细信息,请参阅 HTTP 测试工具。
需要发出的请求在代码的本地版本与 Azure 中托管时可能有所不同。 默认情况下,使用 Azure Functions Core Tools 运行项目时,将删除访问密钥授权要求。 但是,托管时,你配置的任何要求仍将强制实施。
在本地调用
Azure Functions Core Tools 为函数应用注册终结点localhost,可用于调用函数。 在应用程序启动期间,正在使用的特定端口将显示在控制台中。 输出还列出了可用的函数,并且对于每个 HTTP 触发的函数,输出还包括函数的路由模板。
使用此信息构造要提供给 API 客户端的 URL。 还需要指定函数所需的任何标头、参数和请求正文信息。 以下示例使用 JSON 正文发送 HTTP POST 请求:
curl --request POST http://localhost:7071/api/Function1 --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"message":"test data"}'
在 Azure 中调用
调用 Azure 中托管的 HTTP 触发的函数时,需要考虑网络配置。 HTTP 客户端必须对应用具有网络访问权限,因此,如果启用了 入站网络限制 ,则客户端可能需要位于虚拟网络或特定 IP 范围内。 域配置确定需要用于请求的基本 URL。
注意
新创建的函数应用可以生成使用命名约定 <app-name>-<random-hash>.<region>.azurewebsites.net的唯一默认主机名。 示例为 myapp-ds27dh7271aah175.westus-01.azurewebsites.net。 现有应用名称保持不变。
有关详细信息,请参阅 有关创建具有唯一默认主机名的应用的博客文章。
除非在触发器定义中选择了匿名 授权级别 ,否则请求可能还需要 包含访问密钥。
以下示例使用函数正文发送 HTTP POST 请求,包括查询字符串中的访问密钥:
curl --request POST "https://<your-function-app-base-url>/api/Function1?code=<your-function-key>" --header "Content-Type: application/json" --data '{"message":"test data"}'
内容类型
将二进制文件和窗体数据传递给非 C# 函数需要使用适当的 content-type 标头。 支持的内容类型包括 octet-stream(适用于二进制数据)和多部分类型。
已知问题
在非 C# 函数中,使用 content-type image/jpeg 发送的请求会导致向函数传递 string 值。 在这种情况下,可以手动将 string 值转换为字节数组以访问原始二进制数据。
限制
根据 主机中定义的设置,HTTP 请求大小和 URL 长度都受到限制。 有关详细信息,请参阅服务限制。
如果使用 HTTP 触发器的函数未在 230 秒内完成,Azure 负载均衡器将超时并返回 HTTP 502 错误。 该函数将继续运行,但将无法返回 HTTP 响应。 对于长时间运行的函数,我们建议你遵循异步模式,并返回可以 ping 通请求状态的位置。 有关函数可以运行多长时间的信息,请参阅缩放和托管 - 消耗计划。