BackgroundWorker 类
定义
重要
一些信息与预发行产品相关,相应产品在发行之前可能会进行重大修改。 对于此处提供的信息,Microsoft 不作任何明示或暗示的担保。
在单独的线程上执行操作。
public ref class BackgroundWorker : IDisposablepublic ref class BackgroundWorker : System::ComponentModel::Componentpublic class BackgroundWorker : IDisposablepublic class BackgroundWorker : System.ComponentModel.Componenttype BackgroundWorker = class
interface IDisposabletype BackgroundWorker = class
inherit ComponentPublic Class BackgroundWorker
Implements IDisposablePublic Class BackgroundWorker
Inherits Component- 继承
-
BackgroundWorker
- 继承
- 实现
示例
下面的代码示例演示 类的 BackgroundWorker 基础知识,这些基础知识用于异步执行耗时的操作。 下图显示了输出的示例。
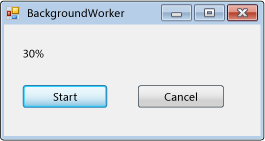
若要尝试此代码,请创建Windows 窗体应用程序。 添加名为 Label 的resultLabel控件,并添加两Button个名为 和 cancelAsyncButton的startAsyncButton控件。 为这两个按钮创建 Click 事件处理程序。 在工具箱的“ 组件 ”选项卡中,添加名为 BackgroundWorker 的 backgroundWorker1组件。 为 BackgroundWorker创建 DoWork、 ProgressChanged和 RunWorkerCompleted 事件处理程序。 在窗体的代码中,将现有代码替换为以下代码。
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace BackgroundWorkerSimple
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
}
private void startAsyncButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (backgroundWorker1.IsBusy != true)
{
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync();
}
}
private void cancelAsyncButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation == true)
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync();
}
}
// This event handler is where the time-consuming work is done.
private void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
BackgroundWorker worker = sender as BackgroundWorker;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (worker.CancellationPending == true)
{
e.Cancel = true;
break;
}
else
{
// Perform a time consuming operation and report progress.
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500);
worker.ReportProgress(i * 10);
}
}
}
// This event handler updates the progress.
private void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
resultLabel.Text = (e.ProgressPercentage.ToString() + "%");
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the background operation.
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Cancelled == true)
{
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled!";
}
else if (e.Error != null)
{
resultLabel.Text = "Error: " + e.Error.Message;
}
else
{
resultLabel.Text = "Done!";
}
}
}
}
Imports System.ComponentModel
Public Class Form1
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = True
backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True
End Sub
Private Sub startAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles startAsyncButton.Click
If backgroundWorker1.IsBusy <> True Then
' Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync()
End If
End Sub
Private Sub cancelAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles cancelAsyncButton.Click
If backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True Then
' Cancel the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync()
End If
End Sub
' This event handler is where the time-consuming work is done.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_DoWork(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.DoWork
Dim worker As BackgroundWorker = CType(sender, BackgroundWorker)
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 10
If (worker.CancellationPending = True) Then
e.Cancel = True
Exit For
Else
' Perform a time consuming operation and report progress.
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(500)
worker.ReportProgress(i * 10)
End If
Next
End Sub
' This event handler updates the progress.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As ProgressChangedEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged
resultLabel.Text = (e.ProgressPercentage.ToString() + "%")
End Sub
' This event handler deals with the results of the background operation.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) Handles backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted
If e.Cancelled = True Then
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled!"
ElseIf e.Error IsNot Nothing Then
resultLabel.Text = "Error: " & e.Error.Message
Else
resultLabel.Text = "Done!"
End If
End Sub
End Class
下面的代码示例演示如何使用 BackgroundWorker 类异步执行耗时的操作。 下图显示了输出的示例。
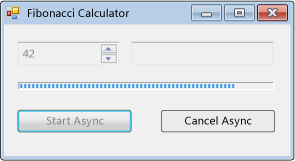
该操作计算所选的斐波纳契数,在计算过程中报告进度更新,并允许取消挂起的计算。
#using <System.Drawing.dll>
#using <System.dll>
#using <System.Windows.Forms.dll>
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Collections;
using namespace System::ComponentModel;
using namespace System::Drawing;
using namespace System::Threading;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
public ref class FibonacciForm: public System::Windows::Forms::Form
{
private:
int numberToCompute;
int highestPercentageReached;
System::Windows::Forms::NumericUpDown^ numericUpDown1;
System::Windows::Forms::Button^ startAsyncButton;
System::Windows::Forms::Button^ cancelAsyncButton;
System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar^ progressBar1;
System::Windows::Forms::Label ^ resultLabel;
System::ComponentModel::BackgroundWorker^ backgroundWorker1;
public:
FibonacciForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
numberToCompute = highestPercentageReached = 0;
InitializeBackgoundWorker();
}
private:
// Set up the BackgroundWorker object by
// attaching event handlers.
void InitializeBackgoundWorker()
{
backgroundWorker1->DoWork += gcnew DoWorkEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_DoWork );
backgroundWorker1->RunWorkerCompleted += gcnew RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted );
backgroundWorker1->ProgressChanged += gcnew ProgressChangedEventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged );
}
void startAsyncButton_Click( System::Object^ /*sender*/, System::EventArgs^ /*e*/ )
{
// Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel->Text = String::Empty;
// Disable the UpDown control until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this->numericUpDown1->Enabled = false;
// Disable the Start button until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this->startAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
// Enable the Cancel button while
// the asynchronous operation runs.
this->cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = true;
// Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = (int)numericUpDown1->Value;
// Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0;
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1->RunWorkerAsync( numberToCompute );
}
void cancelAsyncButton_Click( System::Object^ /*sender*/, System::EventArgs^ /*e*/ )
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
this->backgroundWorker1->CancelAsync();
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler is where the actual,
// potentially time-consuming work is done.
void backgroundWorker1_DoWork( Object^ sender, DoWorkEventArgs^ e )
{
// Get the BackgroundWorker that raised this event.
BackgroundWorker^ worker = dynamic_cast<BackgroundWorker^>(sender);
// Assign the result of the computation
// to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
// object. This is will be available to the
// RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e->Result = ComputeFibonacci( safe_cast<Int32>(e->Argument), worker, e );
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the
// background operation.
void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted( Object^ /*sender*/, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs^ e )
{
// First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
if ( e->Error != nullptr )
{
MessageBox::Show( e->Error->Message );
}
else
if ( e->Cancelled )
{
// Next, handle the case where the user cancelled
// the operation.
// Note that due to a race condition in
// the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
// flag may not have been set, even though
// CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel->Text = "Cancelled";
}
else
{
// Finally, handle the case where the operation
// succeeded.
resultLabel->Text = e->Result->ToString();
}
// Enable the UpDown control.
this->numericUpDown1->Enabled = true;
// Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton->Enabled = true;
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler updates the progress bar.
void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged( Object^ /*sender*/, ProgressChangedEventArgs^ e )
{
this->progressBar1->Value = e->ProgressPercentage;
}
// This is the method that does the actual work. For this
// example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
// reports progress as it does its work.
long ComputeFibonacci( int n, BackgroundWorker^ worker, DoWorkEventArgs ^ e )
{
// The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
// Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
if ( (n < 0) || (n > 91) )
{
throw gcnew ArgumentException( "value must be >= 0 and <= 91","n" );
}
long result = 0;
// Abort the operation if the user has cancelled.
// Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
// CancellationPending to true just after the
// last invocation of this method exits, so this
// code will not have the opportunity to set the
// DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
// that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
// not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
// event handler. This is a race condition.
if ( worker->CancellationPending )
{
e->Cancel = true;
}
else
{
if ( n < 2 )
{
result = 1;
}
else
{
result = ComputeFibonacci( n - 1, worker, e ) + ComputeFibonacci( n - 2, worker, e );
}
// Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
int percentComplete = (int)((float)n / (float)numberToCompute * 100);
if ( percentComplete > highestPercentageReached )
{
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete;
worker->ReportProgress( percentComplete );
}
}
return result;
}
void InitializeComponent()
{
this->numericUpDown1 = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::NumericUpDown;
this->startAsyncButton = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button;
this->cancelAsyncButton = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Button;
this->resultLabel = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::Label;
this->progressBar1 = gcnew System::Windows::Forms::ProgressBar;
this->backgroundWorker1 = gcnew System::ComponentModel::BackgroundWorker;
(dynamic_cast<System::ComponentModel::ISupportInitialize^>(this->numericUpDown1))->BeginInit();
this->SuspendLayout();
//
// numericUpDown1
//
this->numericUpDown1->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 16, 16 );
array<Int32>^temp0 = {91,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Maximum = System::Decimal( temp0 );
array<Int32>^temp1 = {1,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Minimum = System::Decimal( temp1 );
this->numericUpDown1->Name = "numericUpDown1";
this->numericUpDown1->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 80, 20 );
this->numericUpDown1->TabIndex = 0;
array<Int32>^temp2 = {1,0,0,0};
this->numericUpDown1->Value = System::Decimal( temp2 );
//
// startAsyncButton
//
this->startAsyncButton->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 16, 72 );
this->startAsyncButton->Name = "startAsyncButton";
this->startAsyncButton->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 120, 23 );
this->startAsyncButton->TabIndex = 1;
this->startAsyncButton->Text = "Start Async";
this->startAsyncButton->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::startAsyncButton_Click );
//
// cancelAsyncButton
//
this->cancelAsyncButton->Enabled = false;
this->cancelAsyncButton->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 153, 72 );
this->cancelAsyncButton->Name = "cancelAsyncButton";
this->cancelAsyncButton->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 119, 23 );
this->cancelAsyncButton->TabIndex = 2;
this->cancelAsyncButton->Text = "Cancel Async";
this->cancelAsyncButton->Click += gcnew System::EventHandler( this, &FibonacciForm::cancelAsyncButton_Click );
//
// resultLabel
//
this->resultLabel->BorderStyle = System::Windows::Forms::BorderStyle::Fixed3D;
this->resultLabel->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 112, 16 );
this->resultLabel->Name = "resultLabel";
this->resultLabel->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 160, 23 );
this->resultLabel->TabIndex = 3;
this->resultLabel->Text = "(no result)";
this->resultLabel->TextAlign = System::Drawing::ContentAlignment::MiddleCenter;
//
// progressBar1
//
this->progressBar1->Location = System::Drawing::Point( 18, 48 );
this->progressBar1->Name = "progressBar1";
this->progressBar1->Size = System::Drawing::Size( 256, 8 );
this->progressBar1->Step = 2;
this->progressBar1->TabIndex = 4;
//
// backgroundWorker1
//
this->backgroundWorker1->WorkerReportsProgress = true;
this->backgroundWorker1->WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
//
// FibonacciForm
//
this->ClientSize = System::Drawing::Size( 292, 118 );
this->Controls->Add( this->progressBar1 );
this->Controls->Add( this->resultLabel );
this->Controls->Add( this->cancelAsyncButton );
this->Controls->Add( this->startAsyncButton );
this->Controls->Add( this->numericUpDown1 );
this->Name = "FibonacciForm";
this->Text = "Fibonacci Calculator";
(dynamic_cast<System::ComponentModel::ISupportInitialize^>(this->numericUpDown1))->EndInit();
this->ResumeLayout( false );
}
};
[STAThread]
int main()
{
Application::Run( gcnew FibonacciForm );
}
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace BackgroundWorkerExample
{
public class FibonacciForm : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private int numberToCompute = 0;
private int highestPercentageReached = 0;
private System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown numericUpDown1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button startAsyncButton;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button cancelAsyncButton;
private System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar progressBar1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label resultLabel;
private System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker backgroundWorker1;
public FibonacciForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeBackgroundWorker();
}
// Set up the BackgroundWorker object by
// attaching event handlers.
private void InitializeBackgroundWorker()
{
backgroundWorker1.DoWork +=
new DoWorkEventHandler(backgroundWorker1_DoWork);
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted +=
new RunWorkerCompletedEventHandler(
backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted);
backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged +=
new ProgressChangedEventHandler(
backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged);
}
private void startAsyncButton_Click(System.Object sender,
System.EventArgs e)
{
// Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel.Text = String.Empty;
// Disable the UpDown control until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this.numericUpDown1.Enabled = false;
// Disable the Start button until
// the asynchronous operation is done.
this.startAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
// Enable the Cancel button while
// the asynchronous operation runs.
this.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = true;
// Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = (int)numericUpDown1.Value;
// Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0;
// Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(numberToCompute);
}
private void cancelAsyncButton_Click(System.Object sender,
System.EventArgs e)
{
// Cancel the asynchronous operation.
this.backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync();
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler is where the actual,
// potentially time-consuming work is done.
private void backgroundWorker1_DoWork(object sender,
DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
// Get the BackgroundWorker that raised this event.
BackgroundWorker worker = sender as BackgroundWorker;
// Assign the result of the computation
// to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
// object. This is will be available to the
// RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e.Result = ComputeFibonacci((int)e.Argument, worker, e);
}
// This event handler deals with the results of the
// background operation.
private void backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted(
object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
// First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
if (e.Error != null)
{
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.Message);
}
else if (e.Cancelled)
{
// Next, handle the case where the user canceled
// the operation.
// Note that due to a race condition in
// the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
// flag may not have been set, even though
// CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled";
}
else
{
// Finally, handle the case where the operation
// succeeded.
resultLabel.Text = e.Result.ToString();
}
// Enable the UpDown control.
this.numericUpDown1.Enabled = true;
// Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton.Enabled = true;
// Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
}
// This event handler updates the progress bar.
private void backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged(object sender,
ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
this.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage;
}
// This is the method that does the actual work. For this
// example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
// reports progress as it does its work.
long ComputeFibonacci(int n, BackgroundWorker worker, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
// The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
// Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
if ((n < 0) || (n > 91))
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n");
}
long result = 0;
// Abort the operation if the user has canceled.
// Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
// CancellationPending to true just after the
// last invocation of this method exits, so this
// code will not have the opportunity to set the
// DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
// that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
// not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
// event handler. This is a race condition.
if (worker.CancellationPending)
{
e.Cancel = true;
}
else
{
if (n < 2)
{
result = 1;
}
else
{
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1, worker, e) +
ComputeFibonacci(n - 2, worker, e);
}
// Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
int percentComplete =
(int)((float)n / (float)numberToCompute * 100);
if (percentComplete > highestPercentageReached)
{
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete;
worker.ReportProgress(percentComplete);
}
}
return result;
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.numericUpDown1 = new System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown();
this.startAsyncButton = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.cancelAsyncButton = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.resultLabel = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.progressBar1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar();
this.backgroundWorker1 = new System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker();
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.numericUpDown1)).BeginInit();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// numericUpDown1
//
this.numericUpDown1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(16, 16);
this.numericUpDown1.Maximum = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
91,
0,
0,
0});
this.numericUpDown1.Minimum = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
1,
0,
0,
0});
this.numericUpDown1.Name = "numericUpDown1";
this.numericUpDown1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 20);
this.numericUpDown1.TabIndex = 0;
this.numericUpDown1.Value = new System.Decimal(new int[] {
1,
0,
0,
0});
//
// startAsyncButton
//
this.startAsyncButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(16, 72);
this.startAsyncButton.Name = "startAsyncButton";
this.startAsyncButton.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(120, 23);
this.startAsyncButton.TabIndex = 1;
this.startAsyncButton.Text = "Start Async";
this.startAsyncButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.startAsyncButton_Click);
//
// cancelAsyncButton
//
this.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = false;
this.cancelAsyncButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(153, 72);
this.cancelAsyncButton.Name = "cancelAsyncButton";
this.cancelAsyncButton.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(119, 23);
this.cancelAsyncButton.TabIndex = 2;
this.cancelAsyncButton.Text = "Cancel Async";
this.cancelAsyncButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.cancelAsyncButton_Click);
//
// resultLabel
//
this.resultLabel.BorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle.Fixed3D;
this.resultLabel.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(112, 16);
this.resultLabel.Name = "resultLabel";
this.resultLabel.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(160, 23);
this.resultLabel.TabIndex = 3;
this.resultLabel.Text = "(no result)";
this.resultLabel.TextAlign = System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter;
//
// progressBar1
//
this.progressBar1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(18, 48);
this.progressBar1.Name = "progressBar1";
this.progressBar1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(256, 8);
this.progressBar1.Step = 2;
this.progressBar1.TabIndex = 4;
//
// backgroundWorker1
//
this.backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = true;
this.backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true;
//
// FibonacciForm
//
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(292, 118);
this.Controls.Add(this.progressBar1);
this.Controls.Add(this.resultLabel);
this.Controls.Add(this.cancelAsyncButton);
this.Controls.Add(this.startAsyncButton);
this.Controls.Add(this.numericUpDown1);
this.Name = "FibonacciForm";
this.Text = "Fibonacci Calculator";
((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize)(this.numericUpDown1)).EndInit();
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new FibonacciForm());
}
}
}
Imports System.Collections
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Public Class FibonacciForm
Inherits System.Windows.Forms.Form
Private numberToCompute As Integer = 0
Private highestPercentageReached As Integer = 0
Private numericUpDown1 As System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
Private WithEvents startAsyncButton As System.Windows.Forms.Button
Private WithEvents cancelAsyncButton As System.Windows.Forms.Button
Private progressBar1 As System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
Private resultLabel As System.Windows.Forms.Label
Private WithEvents backgroundWorker1 As System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
Public Sub New()
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Sub startAsyncButton_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles startAsyncButton.Click
' Reset the text in the result label.
resultLabel.Text = [String].Empty
' Disable the UpDown control until
' the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = False
' Disable the Start button until
' the asynchronous operation is done.
Me.startAsyncButton.Enabled = False
' Enable the Cancel button while
' the asynchronous operation runs.
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = True
' Get the value from the UpDown control.
numberToCompute = CInt(numericUpDown1.Value)
' Reset the variable for percentage tracking.
highestPercentageReached = 0
' Start the asynchronous operation.
backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerAsync(numberToCompute)
End Sub
Private Sub cancelAsyncButton_Click( _
ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) _
Handles cancelAsyncButton.Click
' Cancel the asynchronous operation.
Me.backgroundWorker1.CancelAsync()
' Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
' This event handler is where the actual work is done.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_DoWork( _
ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.DoWork
' Get the BackgroundWorker object that raised this event.
Dim worker As BackgroundWorker = _
CType(sender, BackgroundWorker)
' Assign the result of the computation
' to the Result property of the DoWorkEventArgs
' object. This is will be available to the
' RunWorkerCompleted eventhandler.
e.Result = ComputeFibonacci(e.Argument, worker, e)
End Sub
' This event handler deals with the results of the
' background operation.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_RunWorkerCompleted( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.RunWorkerCompleted
' First, handle the case where an exception was thrown.
If (e.Error IsNot Nothing) Then
MessageBox.Show(e.Error.Message)
ElseIf e.Cancelled Then
' Next, handle the case where the user canceled the
' operation.
' Note that due to a race condition in
' the DoWork event handler, the Cancelled
' flag may not have been set, even though
' CancelAsync was called.
resultLabel.Text = "Canceled"
Else
' Finally, handle the case where the operation succeeded.
resultLabel.Text = e.Result.ToString()
End If
' Enable the UpDown control.
Me.numericUpDown1.Enabled = True
' Enable the Start button.
startAsyncButton.Enabled = True
' Disable the Cancel button.
cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
End Sub
' This event handler updates the progress bar.
Private Sub backgroundWorker1_ProgressChanged( _
ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As ProgressChangedEventArgs) _
Handles backgroundWorker1.ProgressChanged
Me.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage
End Sub
' This is the method that does the actual work. For this
' example, it computes a Fibonacci number and
' reports progress as it does its work.
Function ComputeFibonacci( _
ByVal n As Integer, _
ByVal worker As BackgroundWorker, _
ByVal e As DoWorkEventArgs) As Long
' The parameter n must be >= 0 and <= 91.
' Fib(n), with n > 91, overflows a long.
If n < 0 OrElse n > 91 Then
Throw New ArgumentException( _
"value must be >= 0 and <= 91", "n")
End If
Dim result As Long = 0
' Abort the operation if the user has canceled.
' Note that a call to CancelAsync may have set
' CancellationPending to true just after the
' last invocation of this method exits, so this
' code will not have the opportunity to set the
' DoWorkEventArgs.Cancel flag to true. This means
' that RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs.Cancelled will
' not be set to true in your RunWorkerCompleted
' event handler. This is a race condition.
If worker.CancellationPending Then
e.Cancel = True
Else
If n < 2 Then
result = 1
Else
result = ComputeFibonacci(n - 1, worker, e) + _
ComputeFibonacci(n - 2, worker, e)
End If
' Report progress as a percentage of the total task.
Dim percentComplete As Integer = _
CSng(n) / CSng(numberToCompute) * 100
If percentComplete > highestPercentageReached Then
highestPercentageReached = percentComplete
worker.ReportProgress(percentComplete)
End If
End If
Return result
End Function
Private Sub InitializeComponent()
Me.numericUpDown1 = New System.Windows.Forms.NumericUpDown
Me.startAsyncButton = New System.Windows.Forms.Button
Me.cancelAsyncButton = New System.Windows.Forms.Button
Me.resultLabel = New System.Windows.Forms.Label
Me.progressBar1 = New System.Windows.Forms.ProgressBar
Me.backgroundWorker1 = New System.ComponentModel.BackgroundWorker
CType(Me.numericUpDown1, System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize).BeginInit()
Me.SuspendLayout()
'
'numericUpDown1
'
Me.numericUpDown1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(16, 16)
Me.numericUpDown1.Maximum = New Decimal(New Integer() {91, 0, 0, 0})
Me.numericUpDown1.Minimum = New Decimal(New Integer() {1, 0, 0, 0})
Me.numericUpDown1.Name = "numericUpDown1"
Me.numericUpDown1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(80, 20)
Me.numericUpDown1.TabIndex = 0
Me.numericUpDown1.Value = New Decimal(New Integer() {1, 0, 0, 0})
'
'startAsyncButton
'
Me.startAsyncButton.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(16, 72)
Me.startAsyncButton.Name = "startAsyncButton"
Me.startAsyncButton.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(120, 23)
Me.startAsyncButton.TabIndex = 1
Me.startAsyncButton.Text = "Start Async"
'
'cancelAsyncButton
'
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Enabled = False
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(153, 72)
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Name = "cancelAsyncButton"
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(119, 23)
Me.cancelAsyncButton.TabIndex = 2
Me.cancelAsyncButton.Text = "Cancel Async"
'
'resultLabel
'
Me.resultLabel.BorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.BorderStyle.Fixed3D
Me.resultLabel.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(112, 16)
Me.resultLabel.Name = "resultLabel"
Me.resultLabel.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(160, 23)
Me.resultLabel.TabIndex = 3
Me.resultLabel.Text = "(no result)"
Me.resultLabel.TextAlign = System.Drawing.ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter
'
'progressBar1
'
Me.progressBar1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(18, 48)
Me.progressBar1.Name = "progressBar1"
Me.progressBar1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(256, 8)
Me.progressBar1.TabIndex = 4
'
'backgroundWorker1
'
Me.backgroundWorker1.WorkerReportsProgress = True
Me.backgroundWorker1.WorkerSupportsCancellation = True
'
'FibonacciForm
'
Me.ClientSize = New System.Drawing.Size(292, 118)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.progressBar1)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.resultLabel)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.cancelAsyncButton)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.startAsyncButton)
Me.Controls.Add(Me.numericUpDown1)
Me.Name = "FibonacciForm"
Me.Text = "Fibonacci Calculator"
CType(Me.numericUpDown1, System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize).EndInit()
Me.ResumeLayout(False)
End Sub
<STAThread()> _
Shared Sub Main()
Application.Run(New FibonacciForm)
End Sub
End Class
注解
类 BackgroundWorker 允许在单独的专用线程上运行操作。 下载和数据库事务等耗时的操作可能会导致用户界面 (UI) 在运行时似乎已停止响应。 当你需要响应式 UI 并且遇到与此类操作相关的长时间延迟时,类 BackgroundWorker 提供了一个方便的解决方案。
若要在后台执行耗时的操作,请创建 并 BackgroundWorker 侦听报告操作进度的事件,并在操作完成时发出信号。 可以通过编程方式创建 ,BackgroundWorker也可以从工具箱的“组件”选项卡将其拖到窗体上。 如果在Windows 窗体 Designer中创建 BackgroundWorker ,它将出现在组件托盘中,其属性将显示在属性窗口中。
若要设置后台操作,请为 DoWork 事件添加事件处理程序。 在此事件处理程序中调用耗时的操作。 若要启动操作,请调用 RunWorkerAsync。 若要接收进度更新通知,请 ProgressChanged 处理 事件。 若要在操作完成时接收通知,请 RunWorkerCompleted 处理 事件。
注意
必须小心不要在事件处理程序中 DoWork 操作任何用户界面对象。 而是通过 ProgressChanged 和 RunWorkerCompleted 事件与用户界面通信。
BackgroundWorker 事件不会跨 AppDomain 边界封送。 不要使用 BackgroundWorker 组件在多个 AppDomain中执行多线程操作。
如果后台操作需要参数,请使用参数调用 RunWorkerAsync 。 在事件处理程序中 DoWork ,可以从 属性中提取 参数 DoWorkEventArgs.Argument 。
有关 BackgroundWorker 的详细信息,请参阅如何:在后台运行操作。
构造函数
| BackgroundWorker() |
初始化 BackgroundWorker 类的新实例。 |
属性
| CancellationPending |
获取一个值,指示应用程序是否已请求取消后台操作。 |
| CanRaiseEvents |
获取一个指示组件是否可以引发事件的值。 (继承自 Component) |
| Container |
获取包含 IContainer 的 Component。 (继承自 Component) |
| DesignMode |
获取一个值,用以指示 Component 当前是否处于设计模式。 (继承自 Component) |
| Events |
获取附加到此 Component 的事件处理程序的列表。 (继承自 Component) |
| IsBusy |
获取一个值,指示 BackgroundWorker 是否正在运行异步操作。 |
| Site | (继承自 Component) |
| WorkerReportsProgress |
获取或设置一个值,该值指示 BackgroundWorker 能否报告进度更新。 |
| WorkerSupportsCancellation |
获取或设置一个值,该值指示 BackgroundWorker 是否支持异步取消。 |
方法
事件
| Disposed |
在通过调用 Dispose() 方法释放组件时发生。 (继承自 Component) |
| DoWork |
调用 RunWorkerAsync() 时发生。 |
| ProgressChanged |
调用 ReportProgress(Int32) 时发生。 |
| RunWorkerCompleted |
当后台操作已完成、被取消或引发异常时发生。 |
