重要 API: Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls.Frame 類別、 Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls.Page 類別、 Windows.UI.Xaml.Navigation 命名空間、 OnNavigatedTo
若要在應用程式中實作向後流覽,請將返回按鈕放在應用程式 UI 左上角。 用戶預期返回按鈕會巡覽至應用程式瀏覽歷程記錄中的上一個位置。 根據預設, Frame 控件會記錄其 BackStack 和 ForwardStack 中的瀏覽動作。 不過,您可以修改哪些瀏覽動作會新增至瀏覽歷程記錄。
對於擁有多個頁面的大部分應用程式,建議您使用 NavigationView 控件來提供應用程式的瀏覽架構。 它適應各種螢幕大小,並支援 頂端 和 左側 瀏覽樣式。 如果您的應用程式使用 NavigationView 控制件,那麼您就可以使用 NavigationView 的內建返回按鈕。
備註
當您實作導覽而不使用 NavigationView 控件時,應該使用本文中的指導方針和範例。 如果您使用 NavigationView,此資訊會提供實用的背景知識,但您應該使用 NavigationView 文章中的特定指引和範例
返回按鈕
若要建立返回按鈕,請使用具有樣式的 Button 控件 NavigationBackButtonNormalStyle ,並將按鈕放在應用程式 UI 左上角(如需詳細資訊,請參閱下面的 XAML 程式代碼範例)。
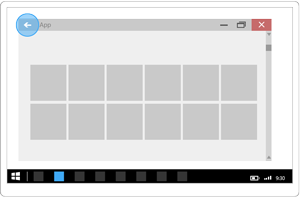
![應用程式 UI 左上角的 [上一頁] 按鈕](images/navigation/back-enabled.png)
<Page>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Button x:Name="BackButton"
Style="{StaticResource NavigationBackButtonNormalStyle}"
IsEnabled="{x:Bind Frame.CanGoBack, Mode=OneWay}"
ToolTipService.ToolTip="Back"/>
</Grid>
</Page>
如果您的應用程式有頂端 CommandBar,請將 Button 控件放在 CommandBar.Content 區域中。
<Page>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<CommandBar>
<CommandBar.Content>
<Button x:Name="BackButton"
Style="{StaticResource NavigationBackButtonNormalStyle}"
IsEnabled="{x:Bind Frame.CanGoBack, Mode=OneWay}"
ToolTipService.ToolTip="Back"
VerticalAlignment="Top"/>
</CommandBar.Content>
<AppBarButton Icon="Delete" Label="Delete"/>
<AppBarButton Icon="Save" Label="Save"/>
</CommandBar>
</Grid>
</Page>
為了減少應用程式中 UI 元素的移動,當返回堆疊中沒有任何項目時,請顯示已停用的返回按鈕(IsEnabled="{x:Bind Frame.CanGoBack, Mode=OneWay}")。 不過,如果您預期應用程式永遠不會有後台堆疊,則完全不需要顯示 [上一頁] 按鈕。

針對不同的裝置和輸入進行優化
此向後瀏覽設計指導方針適用於所有裝置,但如果您針對不同的尺寸和輸入方法優化,您的使用者將會受益。 我們建議處理下列事件(除了返回按鈕 Click 之外),以支援最常見的返回瀏覽輸入。
| 事件 | 輸入 |
|---|---|
| 核心調度器.加速鍵激活 | Alt+左箭頭 VirtualKey.GoBack |
| SystemNavigationManager.BackRequested | Windows + Backspace、 遊戲控制器 B 按鈕 平板電腦模式返回按鈕, 硬體返回按鈕 |
| CoreWindow.PointerPressed | VirtualKey.XButton1 (如在一些滑鼠上找到的返回按鈕。) |
程式碼範例
本節示範如何使用各種輸入來處理返回流覽。
上一頁按鈕和返回導航
您至少必須處理返回按鈕 Click 事件,並提供程式碼來執行返回流覽。 當backstack是空的時,您也應該停用返回按鈕。
此範例程式代碼示範如何使用返回按鈕來實作向後瀏覽行為。 程式碼會回應按鈕 點擊 事件來進行導覽。 [上一頁] 按鈕在 OnNavigatedTo 方法中被啟用或停用,此方法在流覽至新頁面時被呼叫。
代碼顯示為 MainPage,但您應將該代碼新增到每個支援返回功能的頁面。 若要避免重複,您可以將導覽相關程式代碼放在 App 程式代碼後置頁面中的 App.xaml.* 類別中。
<!-- MainPage.xaml -->
<Page x:Class="AppName.MainPage">
...
<Button x:Name="BackButton" Click="BackButton_Click"
Style="{StaticResource NavigationBackButtonNormalStyle}"
IsEnabled="{x:Bind Frame.CanGoBack, Mode=OneWay}"
ToolTipService.ToolTip="Back"/>
...
<Page/>
後置程式碼
// MainPage.xaml.cs
private void BackButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
App.TryGoBack();
}
// App.xaml.cs
//
// Add this method to the App class.
public static bool TryGoBack()
{
Frame rootFrame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
if (rootFrame.CanGoBack)
{
rootFrame.GoBack();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// MainPage.h
#include "App.h"
namespace winrt::AppName::implementation
{
struct MainPage : MainPageT<MainPage>
{
MainPage();
void MainPage::BackButton_Click(IInspectable const&, RoutedEventArgs const&)
{
App::TryGoBack();
}
};
}
// App.h
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Core.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.System.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Input.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.h"
using namespace winrt;
using namespace Windows::Foundation;
using namespace Windows::UI::Core;
using namespace Windows::UI::Input;
using namespace Windows::UI::Xaml;
using namespace Windows::UI::Xaml::Controls;
struct App : AppT<App>
{
App();
// ...
// Perform back navigation if possible.
static bool TryGoBack()
{
Frame rootFrame{ nullptr };
auto content = Window::Current().Content();
if (content)
{
rootFrame = content.try_as<Frame>();
if (rootFrame.CanGoBack())
{
rootFrame.GoBack();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
支援存取金鑰
鍵盤支援是確保應用程式適用於具有不同技能、能力和期望的使用者不可或缺的一項。 我們建議您支援前進和返回導覽的加速鍵,因為依賴這些鍵的用戶會預期兩者。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱 鍵盤互動 和 鍵盤快捷鍵。
向前和向後瀏覽的常見快速鍵是 Alt+向右鍵(正向)和 Alt+向左鍵(返回)。 要支援這些鍵進行導覽,請處理 CoreDispatcher.AcceleratorKeyActivated 事件。 您處理直接在視窗上的事件(而不是頁面上的元素),讓應用程式不論哪個元素處於焦點狀態,都能回應快捷鍵。
將程式代碼新增至 App 類別,以支援快捷鍵和向前導航,如下所示。 (這假設先前支援返回按鈕的程式代碼已經新增。您可以在程式代碼範例一節結尾看到所有 App 程式代碼。
// App.xaml.cs
// Add event handler in OnLaunched.
protected override void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == null)
{
// ...
// rootFrame.NavigationFailed += OnNavigationFailed;
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// Listen to the window directly so the app responds
// to accelerator keys regardless of which element has focus.
Window.Current.CoreWindow.Dispatcher.AcceleratorKeyActivated +=
CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated;
// ...
}
}
// ...
// Add this code after the TryGoBack method added previously.
// Perform forward navigation if possible.
private bool TryGoForward()
{
Frame rootFrame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
if (rootFrame.CanGoForward)
{
rootFrame.GoForward();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Invoked on every keystroke, including system keys such as Alt key combinations.
// Used to detect keyboard navigation between pages even when the page itself
// doesn't have focus.
private void CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated(CoreDispatcher sender, AcceleratorKeyEventArgs e)
{
// When Alt+Left are pressed navigate back.
// When Alt+Right are pressed navigate forward.
if (e.EventType == CoreAcceleratorKeyEventType.SystemKeyDown
&& (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Left || e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Right)
&& e.KeyStatus.IsMenuKeyDown == true
&& !e.Handled)
{
if (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Left)
{
e.Handled = TryGoBack();
}
else if (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Right)
{
e.Handled = TryGoForward();
}
}
}
// App.cpp
void App::OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs const& e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == nullptr)
{
// ...
// rootFrame.NavigationFailed({ this, &App::OnNavigationFailed });
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// Listen to the window directly so the app responds
// to accelerator keys regardless of which element has focus.
Window::Current().CoreWindow().Dispatcher().
AcceleratorKeyActivated({ this, &App::CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated });
// ...
}
}
// App.h
struct App : AppT<App>
{
App();
// ...
// Add this code after the TryGoBack method added previously.
private:
// Perform forward navigation if possible.
bool TryGoForward()
{
Frame rootFrame{ nullptr };
auto content = Window::Current().Content();
if (content)
{
rootFrame = content.try_as<Frame>();
if (rootFrame.CanGoForward())
{
rootFrame.GoForward();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Invoked on every keystroke, including system keys such as Alt key combinations.
// Used to detect keyboard navigation between pages even when the page itself
// doesn't have focus.
void CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated(CoreDispatcher const& /* sender */, AcceleratorKeyEventArgs const& e)
{
// When Alt+Left are pressed navigate back.
// When Alt+Right are pressed navigate forward.
if (e.EventType() == CoreAcceleratorKeyEventType::SystemKeyDown
&& (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Left || e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Right)
&& e.KeyStatus().IsMenuKeyDown
&& !e.Handled())
{
if (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Left)
{
e.Handled(TryGoBack());
}
else if (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Right)
{
e.Handled(TryGoForward());
}
}
}
};
處理系統備份要求
Windows 裝置提供各種方式,讓系統可以將返回流覽要求傳遞至您的應用程式。 一些常見的方式是遊戲板上的 B 按鈕、Windows 鍵 + Backspace 鍵快捷方式,或平板電腦模式中的系統返回按鈕;可用的確切選項取決於裝置。
您可以註冊 SystemNavigationManager.BackRequested 事件的接聽程式,以支援從硬體和軟體系統備份密鑰提供的系統備份要求。
以下是新增至 App 類別的程式代碼,以支援系統提供的返回請求。 (這假設先前支援返回按鈕的程式代碼已經新增。您可以在程式代碼範例一節結尾看到所有 App 程式代碼。
// App.xaml.cs
// Add event handler in OnLaunced.
protected override void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == null)
{
// ...
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// ... (Previously added code.)
// Add support for system back requests.
SystemNavigationManager.GetForCurrentView().BackRequested
+= System_BackRequested;
// ...
}
}
// ...
// Handle system back requests.
private void System_BackRequested(object sender, BackRequestedEventArgs e)
{
if (!e.Handled)
{
e.Handled = TryGoBack();
}
}
// App.cpp
void App::OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs const& e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == nullptr)
{
// ...
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// ... (Previously added code.)
// Add support for system back requests.
SystemNavigationManager::GetForCurrentView().
BackRequested({ this, &App::System_BackRequested });
// ...
}
}
// App.h
struct App : AppT<App>
{
App();
// ...
private:
// ...
// Handle system back requests.
void System_BackRequested(IInspectable const& /* sender */, BackRequestedEventArgs const& e)
{
if (!e.Handled())
{
e.Handled(TryGoBack());
}
}
};
向後相容性的系統返回操作
先前,UWP app 使用 SystemNavigationManager.AppViewBackButtonVisibility 來顯示或隱藏系統返回按鈕以進行向後流覽。 (此按鈕會引發 SystemNavigationManager.BackRequested 事件。此 API 將繼續受到支援,以確保回溯相容性,但我們不再建議使用 AppViewBackButtonVisibility公開的 [上一頁] 按鈕。 相反地,您應該提供您自己的應用程式內返回按鈕,如本文所述。
如果您繼續使用 AppViewBackButtonVisibility,那麼系統 UI 會在標題欄內顯示系統返回按鈕。 (返回按鈕的外觀和用戶互動與之前的版本保持不變。)
處理滑鼠導航按鈕
某些滑鼠提供用於向前和返回瀏覽的硬體瀏覽按鈕。 您可以透過處理 CoreWindow.PointerPressed 事件,來支持這些滑鼠按鈕,並檢查 IsXButton1Pressed (back)或 IsXButton2Pressed (forward)的狀態。
以下是新增至 類別以支援 App 滑鼠按鈕瀏覽的程序代碼。 (這假設先前支援返回按鈕的程式代碼已經新增。您可以在程式代碼範例一節結尾看到所有 App 程式代碼。
// App.xaml.cs
// Add event handler in OnLaunced.
protected override void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == null)
{
// ...
// Add support for system back requests.
// ... (Previously added code.)
// Add support for mouse navigation buttons.
Window.Current.CoreWindow.PointerPressed += CoreWindow_PointerPressed;
// ...
}
}
// ...
// Handle mouse back button.
private void CoreWindow_PointerPressed(CoreWindow sender, PointerEventArgs e)
{
// For this event, e.Handled arrives as 'true'.
if (e.CurrentPoint.Properties.IsXButton1Pressed)
{
e.Handled = !TryGoBack();
}
else if (e.CurrentPoint.Properties.IsXButton2Pressed)
{
e.Handled = !TryGoForward();
}
}
// App.cpp
void App::OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs const& e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == nullptr)
{
// ...
// Add support for system back requests.
// ... (Previously added code.)
// Add support for mouse navigation buttons.
Window::Current().CoreWindow().
PointerPressed({ this, &App::CoreWindow_PointerPressed });
// ...
}
}
// App.h
struct App : AppT<App>
{
App();
// ...
private:
// ...
// Handle mouse forward and back buttons.
void CoreWindow_PointerPressed(CoreWindow const& /* sender */, PointerEventArgs const& e)
{
// For this event, e.Handled arrives as 'true'.
if (e.CurrentPoint().Properties().IsXButton1Pressed())
{
e.Handled(!TryGoBack());
}
else if (e.CurrentPoint().Properties().IsXButton2Pressed())
{
e.Handled(!TryGoForward());
}
}
};
所有新增至 App 類別的程式代碼
// App.xaml.cs
//
// (Add event handlers in OnLaunched override.)
protected override void OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == null)
{
// ...
// rootFrame.NavigationFailed += OnNavigationFailed;
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// Listen to the window directly so the app responds
// to accelerator keys regardless of which element has focus.
Window.Current.CoreWindow.Dispatcher.AcceleratorKeyActivated +=
CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated;
// Add support for system back requests.
SystemNavigationManager.GetForCurrentView().BackRequested
+= System_BackRequested;
// Add support for mouse navigation buttons.
Window.Current.CoreWindow.PointerPressed += CoreWindow_PointerPressed;
// ...
}
}
// ...
// (Add these methods to the App class.)
public static bool TryGoBack()
{
Frame rootFrame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
if (rootFrame.CanGoBack)
{
rootFrame.GoBack();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Perform forward navigation if possible.
private bool TryGoForward()
{
Frame rootFrame = Window.Current.Content as Frame;
if (rootFrame.CanGoForward)
{
rootFrame.GoForward();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Invoked on every keystroke, including system keys such as Alt key combinations.
// Used to detect keyboard navigation between pages even when the page itself
// doesn't have focus.
private void CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated(CoreDispatcher sender, AcceleratorKeyEventArgs e)
{
// When Alt+Left are pressed navigate back.
// When Alt+Right are pressed navigate forward.
if (e.EventType == CoreAcceleratorKeyEventType.SystemKeyDown
&& (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Left || e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Right)
&& e.KeyStatus.IsMenuKeyDown == true
&& !e.Handled)
{
if (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Left)
{
e.Handled = TryGoBack();
}
else if (e.VirtualKey == VirtualKey.Right)
{
e.Handled = TryGoForward();
}
}
}
// Handle system back requests.
private void System_BackRequested(object sender, BackRequestedEventArgs e)
{
if (!e.Handled)
{
e.Handled = TryGoBack();
}
}
// Handle mouse back button.
private void CoreWindow_PointerPressed(CoreWindow sender, PointerEventArgs e)
{
// For this event, e.Handled arrives as 'true'.
if (e.CurrentPoint.Properties.IsXButton1Pressed)
{
e.Handled = !TryGoBack();
}
else if (e.CurrentPoint.Properties.IsXButton2Pressed)
{
e.Handled = !TryGoForward();
}
}
// App.cpp
void App::OnLaunched(LaunchActivatedEventArgs const& e)
{
// ...
// Do not repeat app initialization when the Window already has content,
// just ensure that the window is active
if (rootFrame == nullptr)
{
// ...
// rootFrame.NavigationFailed({ this, &App::OnNavigationFailed });
// Add support for accelerator keys.
// Listen to the window directly so the app responds
// to accelerator keys regardless of which element has focus.
Window::Current().CoreWindow().Dispatcher().
AcceleratorKeyActivated({ this, &App::CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated });
// Add support for system back requests.
SystemNavigationManager::GetForCurrentView().
BackRequested({ this, &App::System_BackRequested });
// Add support for mouse navigation buttons.
Window::Current().CoreWindow().
PointerPressed({ this, &App::CoreWindow_PointerPressed });
// ...
}
}
// App.h
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Core.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.System.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Input.h"
#include "winrt/Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.h"
using namespace winrt;
using namespace Windows::Foundation;
using namespace Windows::UI::Core;
using namespace Windows::UI::Input;
using namespace Windows::UI::Xaml;
using namespace Windows::UI::Xaml::Controls;
struct App : AppT<App>
{
App();
// ...
// Perform back navigation if possible.
static bool TryGoBack()
{
Frame rootFrame{ nullptr };
auto content = Window::Current().Content();
if (content)
{
rootFrame = content.try_as<Frame>();
if (rootFrame.CanGoBack())
{
rootFrame.GoBack();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
// Perform forward navigation if possible.
bool TryGoForward()
{
Frame rootFrame{ nullptr };
auto content = Window::Current().Content();
if (content)
{
rootFrame = content.try_as<Frame>();
if (rootFrame.CanGoForward())
{
rootFrame.GoForward();
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Invoked on every keystroke, including system keys such as Alt key combinations.
// Used to detect keyboard navigation between pages even when the page itself
// doesn't have focus.
void CoreDispatcher_AcceleratorKeyActivated(CoreDispatcher const& /* sender */, AcceleratorKeyEventArgs const& e)
{
// When Alt+Left are pressed navigate back.
// When Alt+Right are pressed navigate forward.
if (e.EventType() == CoreAcceleratorKeyEventType::SystemKeyDown
&& (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Left || e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Right)
&& e.KeyStatus().IsMenuKeyDown
&& !e.Handled())
{
if (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Left)
{
e.Handled(TryGoBack());
}
else if (e.VirtualKey() == Windows::System::VirtualKey::Right)
{
e.Handled(TryGoForward());
}
}
}
// Handle system back requests.
void System_BackRequested(IInspectable const& /* sender */, BackRequestedEventArgs const& e)
{
if (!e.Handled())
{
e.Handled(TryGoBack());
}
}
// Handle mouse forward and back buttons.
void CoreWindow_PointerPressed(CoreWindow const& /* sender */, PointerEventArgs const& e)
{
// For this event, e.Handled arrives as 'true'.
if (e.CurrentPoint().Properties().IsXButton1Pressed())
{
e.Handled(!TryGoBack());
}
else if (e.CurrentPoint().Properties().IsXButton2Pressed())
{
e.Handled(!TryGoForward());
}
}
};
繼續中
當使用者切換至另一個應用程式並返回您的應用程式時,建議您返回瀏覽歷程記錄中的最後一頁。