Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Load Testing is a fully managed load-testing service that enables you to generate high-scale load. The service simulates traffic for your applications, regardless of where they're hosted. Developers, testers, and quality assurance (QA) engineers can use it to optimize application performance, scalability, or capacity.
Quickly create a load test for your web application by using a URL, and without prior knowledge of testing tools. Azure Load Testing abstracts the complexity and infrastructure to run your load test at scale.
For more advanced load testing scenarios, you can also create a load test by uploading a test script. Azure Load Testing supports running Apache JMeter-based tests or Locust-based tests. For example, your test plan might consist of multiple application requests, you want to call non-HTTP endpoints, or you're using input data and parameters to make the test more dynamic.
If your application is hosted on Azure, Azure Load Testing collects detailed resource metrics to help you identify performance bottlenecks across your Azure application components.
To capture application performance regressions early, add your load test in your continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) workflow. Leverage test fail criteria to define and validate your application quality requirements.
Azure Load Testing enables you to test private application endpoints or applications that you host on-premises. For more information, see the scenarios for deploying Azure Load Testing in a virtual network.
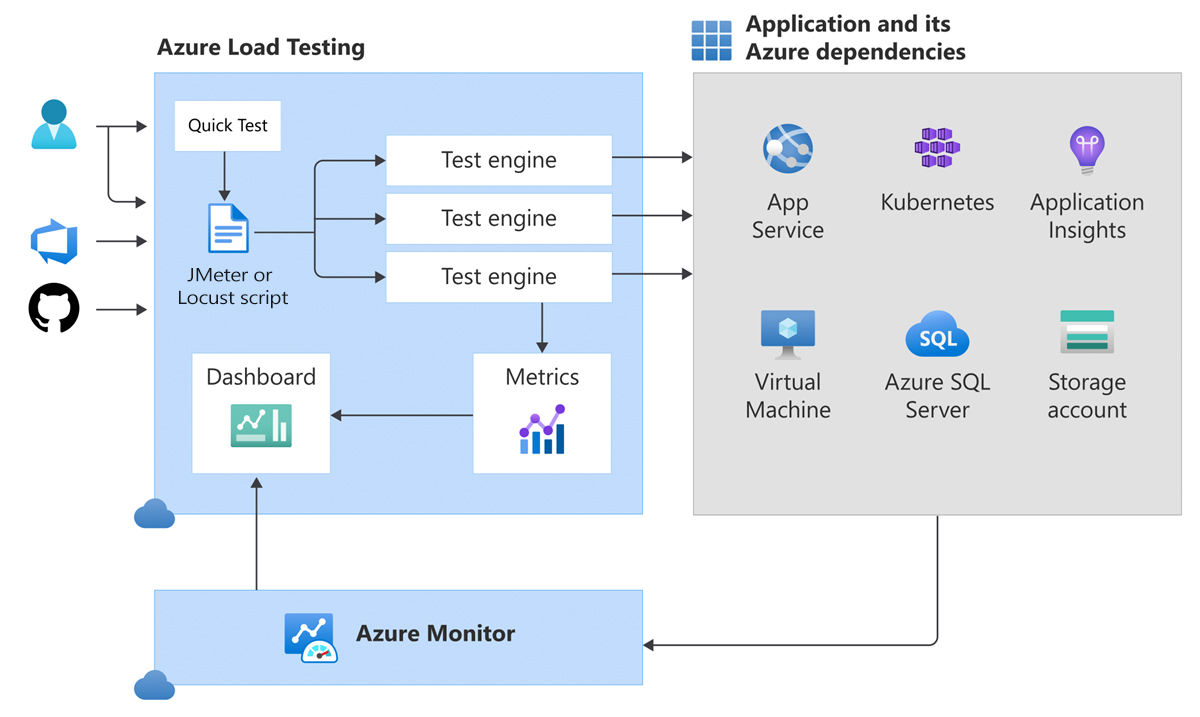
The following diagram shows an architecture overview of Azure Load Testing.
Note
The overview image shows how Azure Load Testing uses Azure Monitor to capture metrics for app components. Learn more about the supported Azure resource types.
Learn more about the key concepts for Azure Load Testing.
Usage scenarios
Azure Load Testing can use the Apache JMeter or Locust testing frameworks and supports a wide range of application types and communication protocols. The following list provides examples of supported application or endpoint types:
- Web applications, using HTTP or HTTPS
- REST APIs
- Databases via JDBC
- TCP-based endpoints
For JMeter, you can use JMeter plugins in your test script, you can load test more application types. For Locust, you can use third party extensions, Locust plugins, or any other Python libraries to extend the capabilities of Locust.
With the quick test experience you can test a single URL-based HTTP endpoint. By uploading a JMeter script, you can use all JMeter-supported communication protocols.
Azure Load Testing currently does not support other testing frameworks than Apache JMeter and Locust.
Identify performance bottlenecks by using high-scale load tests
Performance problems often remain undetected until an application is under load. You can start a high-scale load test in the Azure portal to learn sooner how your application behaves under stress. While the test is running, the Azure Load Testing dashboard provides a live update of the client and server-side metrics.
After the load test finishes, you can use the dashboard to analyze the test results and identify performance bottlenecks. For Azure-hosted applications, the dashboard shows detailed resource metrics of the Azure application components. Get started with a tutorial to identify performance bottlenecks for Azure-hosted applications.
Azure Load Testing keeps a history of test runs and allows you to visually compare multiple runs to detect performance regressions over time.
You might also download the test results for analysis in a third-party tool.
Enable automated load testing
You can integrate Azure Load Testing in your CI/CD pipeline at meaningful points during the development lifecycle. For example, you could automatically run a load test at the end of each sprint or in a staging environment to validate a release candidate build.
Get started with adding load testing to your CI/CD workflow to quickly identify performance degradation of your application under load.
In the test configuration, specify test fail criteria to catch application performance or stability regressions early in the development cycle. For example, get alerted when the average response time or the number of errors exceed a specific threshold.
Azure Load Testing will automatically stop an automated load test in response to specific error conditions. Alternately, you can also use the AutoStop listener in your Apache JMeter script. Automatically stopping safeguards you against failing tests further incurring costs, for example, because of an incorrectly configured endpoint URL. Learn how you can configure auto stop for your load test.
You can trigger Azure Load Testing from Azure Pipelines or GitHub Actions workflows, or use the Azure CLI to integrate with other CI tools.
How does Azure Load Testing work?
Azure Load Testing uses Apache JMeter or Locust for running load tests. You can use Apache JMeter plugins from https://jmeter-plugins.org or upload your own plugin code. Azure Load Testing supports all communication protocols that JMeter supports. For example, use Azure Load Testing to load test a database connection or message queue. Learn more about the supported Apache JMeter functionality.
The Azure Load Testing test engines abstract the required infrastructure for running a high-scale load test. Each test engine instance runs your test script to simulate a large number of virtual users simultaneously accessing your application endpoints. When you create a load test based on a URL (quick test), Azure Load Testing automatically generates a test script for you. To scale out the load test, you can configure the number of test engines.
You can host the application under load anywhere: in Azure, on-premises, or in other clouds. To run a load test for services that have no public endpoint, deploy Azure Load Testing in a virtual network.
During the load test, Azure Load Testing collects the following resource metrics and displays them in a dashboard:
Client-side metrics give you details reported by the test engine. These details include the number of virtual users, the request response time, or the number of requests per second.
Server-side metrics provide information about your Azure application components. Azure Load Testing integrates with Azure Monitor, including Application Insights and Container insights, to capture details from the Azure services. Depending on the type of service, different metrics are available. For example, metrics can be for the number of database reads, the type of HTTP responses, or container resource consumption.
Azure Load Testing automatically incorporates best practices for Azure networking to help make sure that your tests run securely and reliably. Load tests are automatically stopped if the application endpoints or Azure components start throttling requests.
The service automatically encrypts all data stored in your load testing resource with keys managed by Microsoft (service-managed keys). For example, this data includes your Apache JMeter or Locust test script, configuration files, and more. Alternately, you can also configure the service to use customer-managed keys.
In-region data residency
Azure Load Testing doesn't store or process customer data outside the region you deploy the service instance in.
Related content
Start using Azure Load Testing: