Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable, cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) that delivers an intelligent and comprehensive solution for SIEM and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR). Microsoft Sentinel provides cyberthreat detection, investigation, response, and proactive hunting, with a bird's-eye view across your enterprise.
Microsoft Sentinel also natively incorporates proven Azure services, like Log Analytics and Logic Apps, and enriches your investigation and detection with AI. It uses both Microsoft's threat intelligence stream and also enables you to bring your own threat intelligence.
Use Microsoft Sentinel to alleviate the stress of increasingly sophisticated attacks, increasing volumes of alerts, and long resolution time frames. This article highlights the key capabilities in Microsoft Sentinel.
Microsoft Sentinel inherits the Azure Monitor tamper-proofing and immutability practices. While Azure Monitor is an append-only data platform, it includes provisions to delete data for compliance purposes.
This service supports Azure Lighthouse, which lets service providers sign in to their own tenant to manage subscriptions and resource groups that customers have delegated.
Enable out of the box security content
Microsoft Sentinel provides security content packaged in SIEM solutions that enable you to ingest data, monitor, alert, hunt, investigate, respond, and connect with different products, platforms, and services.
For more information, see About Microsoft Sentinel content and solutions.
Collect data at scale
Collect data across all users, devices, applications, and infrastructure, both on-premises and in multiple clouds.
The following table highlights the key capabilities in Microsoft Sentinel for data collection.
| Capability | Description | Get started |
|---|---|---|
| Out of the box data connectors | Many connectors are packaged with SIEM solutions for Microsoft Sentinel and provide real-time integration. These connectors include Microsoft sources and Azure sources like Microsoft Entra ID, Azure Activity, Azure Storage, and more. Out of the box connectors are also available for the broader security and applications ecosystems for non-Microsoft solutions. You can also use common event format, Syslog, or REST-API to connect your data sources with Microsoft Sentinel. |
Microsoft Sentinel data connectors |
| Custom connectors | Microsoft Sentinel supports ingesting data from some sources without a dedicated connector. If you're unable to connect your data source to Microsoft Sentinel using an existing solution, create your own data source connector. | Resources for creating Microsoft Sentinel custom connectors. |
| Data normalization | Microsoft Sentinel uses both query time and ingestion time normalization to translate various sources into a uniform, normalized view. | Normalization and the Advanced Security Information Model (ASIM) |
Detect threats
Detect previously undetected threats, and minimize false positives using Microsoft's analytics and unparalleled threat intelligence.
The following table highlights the key capabilities in Microsoft Sentinel for threat detection.
| Capacity | Description | Get started |
|---|---|---|
| Analytics | Helps you reduce noise and minimize the number of alerts you have to review and investigate. Microsoft Sentinel uses analytics to group alerts into incidents. Use the out of the box analytic rules as-is, or as a starting point to build your own rules. Microsoft Sentinel also provides rules to map your network behavior and then look for anomalies across your resources. These analytics connect the dots, by combining low fidelity alerts about different entities into potential high-fidelity security incidents. | Detect threats out-of-the-box |
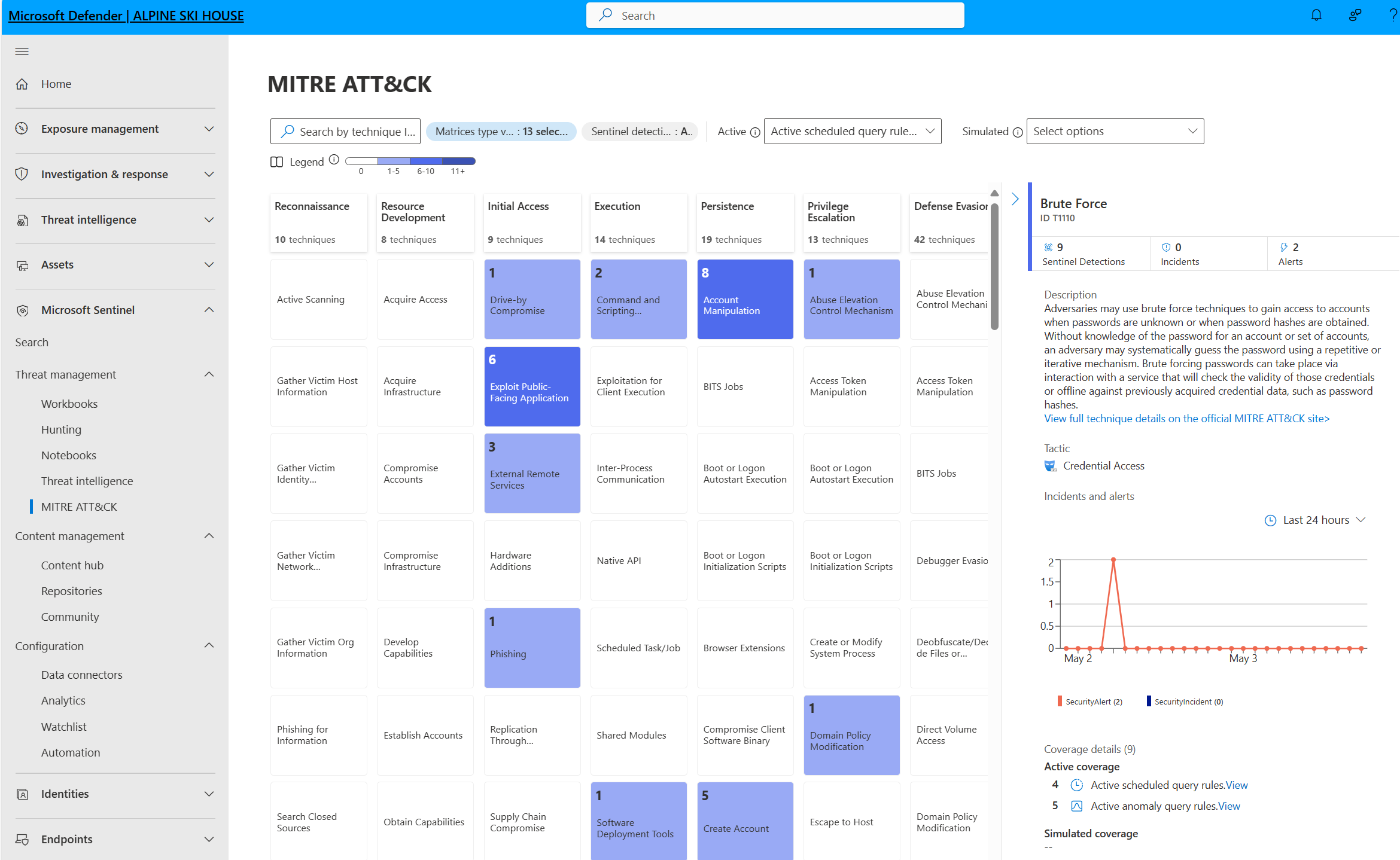
| MITRE ATT&CK coverage | Microsoft Sentinel analyzes ingested data, not only to detect threats and help you investigate, but also to visualize the nature and coverage of your organization's security status based on the tactics and techniques from the MITRE ATT&CK® framework. | Understand security coverage by the MITRE ATT&CK® framework |
| Threat intelligence | Integrate numerous sources of threat intelligence into Microsoft Sentinel to detect malicious activity in your environment and provide context to security investigators for informed response decisions. | Threat intelligence in Microsoft Sentinel |
| Watchlists | Correlate data from a data source you provide, a watchlist, with the events in your Microsoft Sentinel environment. For example, you might create a watchlist with a list of high-value assets, terminated employees, or service accounts in your environment. Use watchlists in your search, detection rules, threat hunting, and response playbooks. | Watchlists in Microsoft Sentinel |
| Workbooks | Create interactive visual reports by using workbooks. Microsoft Sentinel comes with built-in workbook templates that allow you to quickly gain insights across your data as soon as you connect a data source. Or, create your own custom workbooks. | Visualize collected data. |
Investigate threats
Investigate threats with artificial intelligence, and hunt for suspicious activities at scale, tapping into years of cyber security work at Microsoft.
The following table highlights the key capabilities in Microsoft Sentinel for threat investigation.
| Feature | Description | Get started |
|---|---|---|
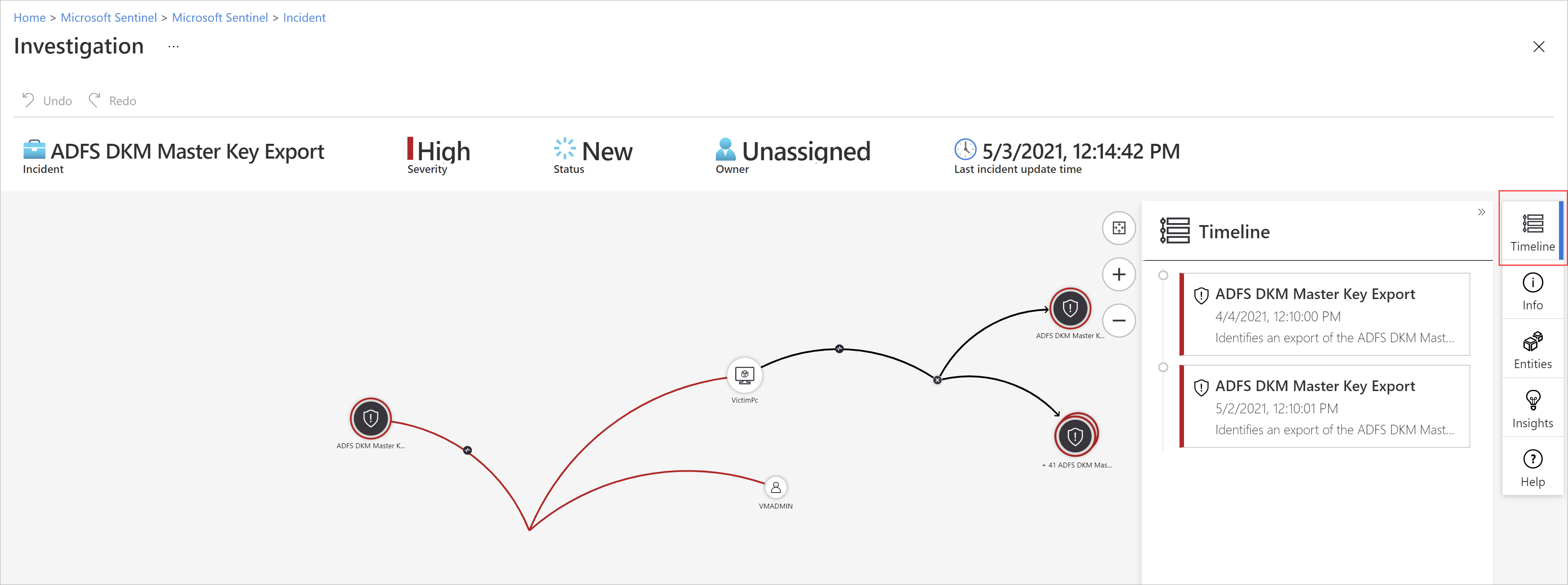
| Incidents | Microsoft Sentinel deep investigation tools help you to understand the scope and find the root cause of a potential security threat. You can choose an entity on the interactive graph to ask interesting questions for a specific entity, and drill down into that entity and its connections to get to the root cause of the threat. | Navigate and investigate incidents in Microsoft Sentinel |
| Hunts | Microsoft Sentinel's powerful hunting search-and-query tools, based on the MITRE framework, enable you to proactively hunt for security threats across your organization’s data sources, before an alert is triggered. Create custom detection rules based on your hunting query. Then, surface those insights as alerts to your security incident responders. | Threat hunting in Microsoft Sentinel |
| Notebooks | Microsoft Sentinel supports Jupyter notebooks in Azure Machine Learning workspaces, including full libraries for machine learning, visualization, and data analysis. Use notebooks in Microsoft Sentinel to extend the scope of what you can do with Microsoft Sentinel data. For example: - Perform analytics that aren't built in to Microsoft Sentinel, such as some Python machine learning features. - Create data visualizations that aren't built in to Microsoft Sentinel, such as custom timelines and process trees. - Integrate data sources outside of Microsoft Sentinel, such as an on-premises data set. |
Jupyter notebooks with Microsoft Sentinel hunting capabilities |
Respond to incidents rapidly
Automate your common tasks and simplify security orchestration with playbooks that integrate with Azure services and your existing tools. Microsoft Sentinel's automation and orchestration provides a highly extensible architecture that enables scalable automation as new technologies and threats emerge.
Playbooks in Microsoft Sentinel are based on workflows built in Azure Logic Apps. For example, if you use the ServiceNow ticketing system, use Azure Logic Apps to automate your workflows and open a ticket in ServiceNow each time a particular alert or incident is generated.
The following table highlights the key capabilities in Microsoft Sentinel for threat response.
| Feature | Description | Get started |
|---|---|---|
| Automation rules | Centrally manage the automation of incident handling in Microsoft Sentinel by defining and coordinating a small set of rules that cover different scenarios. | Automate threat response in Microsoft Sentinel with automation rules |
| Playbooks | Automate and orchestrate your threat response by using playbooks, which are a collection of remediation actions. Run a playbook on-demand or automatically in response to specific alerts or incidents, when triggered by an automation rule. To build playbooks with Azure Logic Apps, choose from a constantly expanding gallery of connectors for various services and systems like ServiceNow, Jira, and more. These connectors allow you to apply any custom logic in your workflow. |
Automate threat response with playbooks in Microsoft Sentinel List of all Logic App connectors |
Microsoft Sentinel in the Azure portal retirement timeline
Microsoft Sentinel is generally available in the Microsoft Defender portal, including for customers without Microsoft Defender XDR or an E5 license. This means that you can use Microsoft Sentinel in the Defender portal even if you aren't using other Microsoft Defender services.
Starting in July 2026, Microsoft Sentinel will be supported in the Defender portal only, and any remaining customers using the Azure portal will be automatically redirected.
If you're currently using Microsoft Sentinel in the Azure portal, we recommend that you start planning your transition to the Defender portal now to ensure a smooth transition and take full advantage of the unified security operations experience offered by Microsoft Defender.
For more information, see:
- Microsoft Sentinel in the Microsoft Defender portal
- Transition your Microsoft Sentinel environment to the Defender portal
- Planning your move to Microsoft Defender portal for all Microsoft Sentinel customers (blog)