Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
This article applies to Microsoft Intune features only. If you're looking for information on other features, then go to that specific documentation. For example, for Microsoft Teams devices, go to Teams Rooms on Windows and Android.
The Intune U.S. government service description is as an overview of the service offering in the Government Community Cloud (GCC) High and U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) environments.
This article lists the feature differences compared to the commercial offering of Microsoft Intune.
To learn more about Intune for GCC customers, go to EMS offers for US Government and Microsoft 365 interoperability.
Tip
For information on the US Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) accreditation and Microsoft, go to FedRAMP.
Get started with Intune for US Government GCC High and DoD
The Intune GCC High and DoD offerings are built on the Microsoft Azure Government Cloud. This cloud is designed to interoperate with Microsoft 365 GCC High and DoD environments.
For more information about Intune, and what you can do, go to Microsoft Intune securely manages identities, manages apps, and manages devices. Use this documentation as your starting point for deploying and using Microsoft Intune.
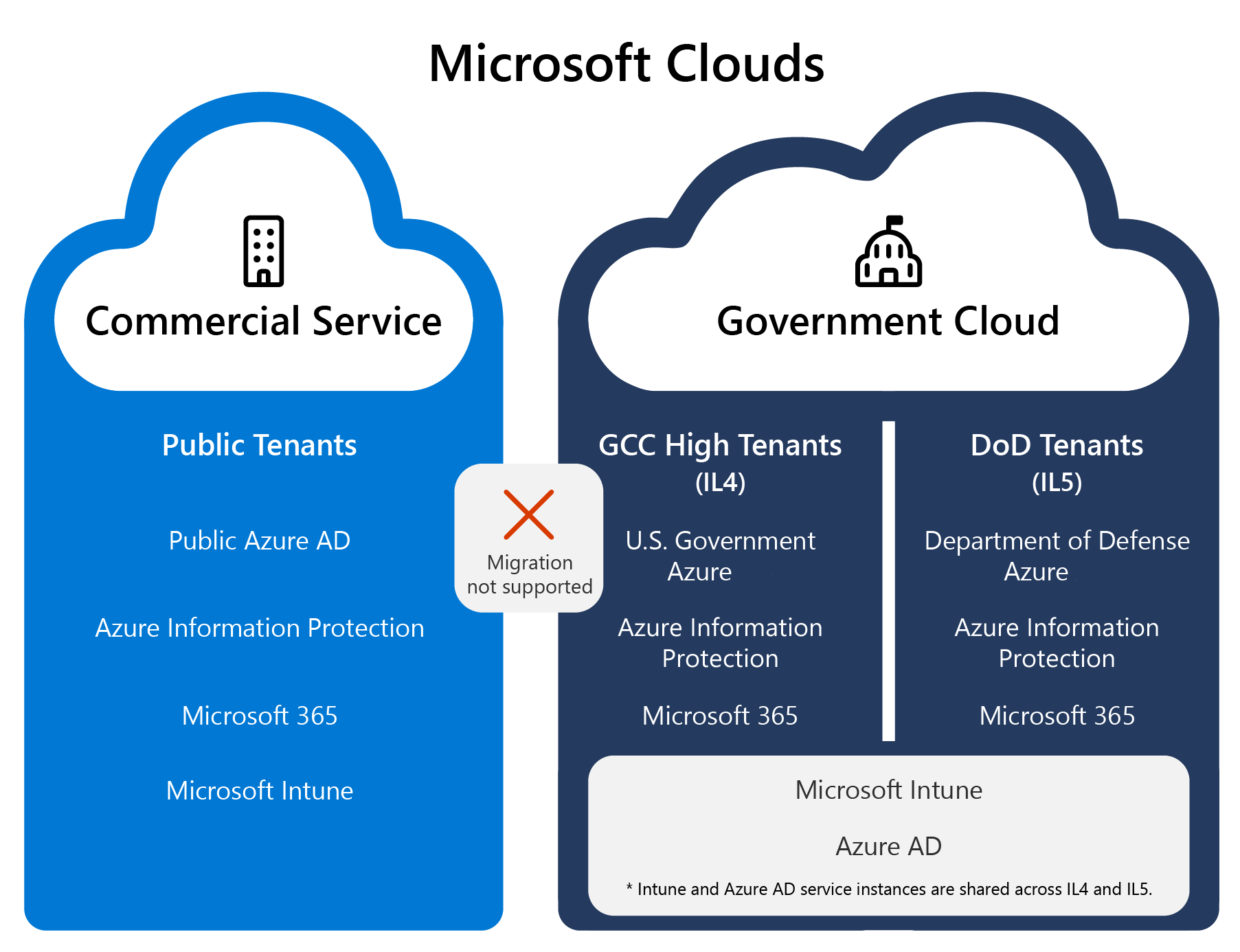
Intune has two service instances:
- Commercial service: The commercial service is available to anyone with an Intune license and is used by most Intune customers.
- Government cloud: This service is also known as GCC High or DoD. This instance is a datacenter that's physically separate from the commercial instances. The datacenter is locked down and is only used by government customers who purchase the appropriate license.
These government instances are also known as IL4 and IL5, where IL refers to Impact Level.
What you need to know
There isn't a built-in way to migrate from the commercial service to the government cloud, and vice versa. To migrate, devices need to unenroll from the current tenant, and then re-enroll to the new tenant.
This approach is similar to unenrolling from another mobile device management (MDM) service and enrolling in Intune. For more information, go to Deployment guide: Setup or move to Microsoft Intune.
In the government cloud, the Intune service instance is shared with GCC High and DoD tenants. This architecture is slightly different than other services, such as Microsoft 365 and Azure.
GCC is the same instance as Microsoft Intune in the commercial space. Other services, like Microsoft 365, have a separate GCC instance. Intune doesn't have a separate GCC instance.
So, when you see GCC in this Intune article, it refers to the commercial service. When you see GCC High or DoD, it refers to the government cloud.
GCC instances are commonly used by state and local government customers that require extra accreditation for the cloud services they use.
Intune is now Common Criteria certified and is on the National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) Product Compliance List (PCL).
To see the certification materials, go to NIAP - Product Details.
Administrators can get help locking down their Intune tenants using the Secure Technical Implementation Guide (STIG).
To get guidance from the
cyber.milwebsite, go to the STIGs Document Library (opens thepublic.cyber.milwebsite).
Feature differences in Intune GCC High and DoD
Available and supported
The following features are available and supported in Microsoft GCC High and/or DoD clouds:
| Feature | Availability |
|---|---|
| Standard MDM features | ✅ You can use app policies, device configuration profiles, compliance policies, and more. |
| Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) | ✅ Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) connectors for Android and iOS/iPadOS devices with MTD vendors that also support the GCC High environment can be used. When you sign in to a GCC High tenant, you see the connectors that are available in these environments. |
| Microsoft Defender for Endpoint security settings management | ✅ On devices onboarded to Defender but not enrolled in Intune, you can use Intune endpoint security policies to manage Defender security settings. This support extends to the US Government Community Cloud (GCC), US Government Community High (GCC High), and Department of Defense (DoD) environments. For more information on this feature, go to Defender for Endpoint security settings management. |
| Platform support | ✅ You can use the same operating systems - Android, Android Open Source Project (AOSP), iOS/iPadOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows. - Android (AOSP): There are some device restrictions. For more information, go to Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune - AOSP. - Linux: Generally available (GA) in February 2024. |
| Remote Help | ✅ Remote Help is supported in GCC on Android, macOS, and Windows devices. Remote Help is not supported in GCC High or DoD. For more information on this feature, go to Remote Help in Microsoft Intune. |
| Windows Autopilot device preparation | ✅ Some features are available now, such as user-driven deployments, and some are still in the planning phase. For more information on the recent changes to Windows Autopilot device preparation, go to Blog: Windows deployment with the next generation of Windows Autopilot. To get started with Windows Autopilot device preparation, go to Windows Autopilot Device Preparation overview. |
| Log Analytics | ✅ You can send Intune log data to Azure Storage, Event Hubs, or Log Analytics. For more information on this feature, go to Send log data to storage, event hubs, or log analytics from Intune. |
| Microsoft Intune Plan 2 and Microsoft Intune Suite |
For more information on these plans, go to Use Intune Suite add-on capabilities. The following Plan 2 features support the GCC High and DoD environments: - Microsoft Tunnel for Mobile Application Management - Firmware-over-the-air update - Specialty devices management The following Microsoft Intune Suite features support the GCC High and DoD environments: - Endpoint Privilege Management - Advanced Analytics |
In the planning phase
The following features are currently not available and aren't supported in GCC High and DoD clouds. Planning is underway to support these features for GCC High and DoD. If ETAs are available, then they're listed.
| Feature | Availability |
|---|---|
| Expedited updates | For more information on this feature, go to Expedite Windows quality updates in Microsoft Intune. |
| Feature updates | For more information on this feature, go to Feature updates for Windows in Intune. |
| Windows Autopilot | The following features are in the planning phase: - Customize out-of-box experience (OOBE) and rename devices during provisioning based on organizational structure - Self-deploying and pre-provisioning mode - More admin-specified configurations delivered before allowing desktop access. - Enhanced optional desktop onboarding experience inside the Windows Company Portal app - The ability to associate a device with a tenant. For information about Windows Autopilot, go to Windows Autopilot overview. |
| Delivery Optimization for Win32 Apps | For more information on the Delivery Optimization feature in Windows, go to What is Delivery Optimization?. |
| BIOS configuration policies on Windows | For more information on this feature, go to Use BIOS configuration profiles on Windows devices in Microsoft Intune. |
Not available
The following features aren't available and won't be supported for GCC High and DoD:
| Feature | Availability |
|---|---|
| Chrome OS Connector | ❌ |
| Microsoft Store for Business | ❌ |
| On-premises Exchange Connector | ❌ |
| Windows Subscription Activation | ❌ |
| TeamViewer connector or TeamViewer feature |
❌ |
Next steps
To learn more about Intune and how to get started, go to the Microsoft Intune planning guide.