Nóta
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað aðskrá þig inn eða breyta skráasöfnum.
Aðgangur að þessari síðu krefst heimildar. Þú getur prófað að breyta skráasöfnum.
This article demonstrates a Java Spring Boot web app that signs in users and obtains an access token for calling Microsoft Graph. It uses the Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java for authentication, authorization, and token acquisition. It uses Microsoft Graph SDK for Java to obtain data from Graph.
The following diagram shows the topology of the app:
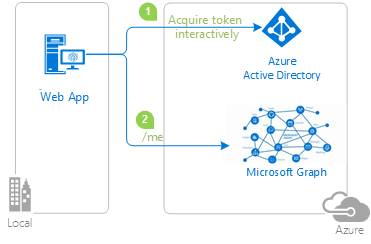
The app uses the Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java to obtain an access token for Microsoft Graph from Microsoft Entra ID. The access token proves that the user is authorized to access the Microsoft Graph API endpoint as defined in the scope.
Prerequisites
- JDK version 15. This sample was developed on a system with Java 15, but it might be compatible with other versions.
- Maven 3
- Java Extension Pack for Visual Studio Code is recommended for running this sample in Visual Studio Code.
- A Microsoft Entra ID tenant. For more information, see How to get a Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- A user account in your Microsoft Entra ID tenant. This sample doesn't work with a personal Microsoft account. Therefore, if you signed in to the Azure portal with a personal account and you don't have a user account in your directory, you need to create one now.
- Visual Studio Code
- Azure Tools for Visual Studio Code
Recommendations
- Some familiarity with the Spring Framework.
- Some familiarity with Linux/OSX terminal.
- jwt.ms for inspecting your tokens.
- Fiddler for monitoring your network activity and troubleshooting.
- Follow the Microsoft Entra Blog to stay up-to-date with the latest developments.
Set up the sample
The following sections show you how to set up the sample application.
Clone or download the sample repository
To clone the sample, open a Bash window and use the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/ms-identity-msal-java-samples.git
cd 4-spring-web-app/2-Authorization-I/call-graph
Alternatively, navigate to the ms-identity-msal-java-samples repository, then download it as a .zip file and extract it to your hard drive.
Important
To avoid file path length limitations on Windows, clone or extract the repository into a directory near the root of your hard drive.
Register the sample applications with your Microsoft Entra ID tenant
There's one project in this sample. The following sections show you how to register the app using the Azure portal.
Choose the Microsoft Entra ID tenant where you want to create your applications
To choose your tenant, use the following steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
If your account is present in more than one Microsoft Entra ID tenant, select your profile in the corner of the Azure portal, and then select Switch directory to change your session to the desired Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
Register the app (java-spring-webapp-call-graph)
To register the app, use the following steps:
Navigate to the Azure portal and select Microsoft Entra ID.
Select App Registrations on the navigation pane, then select New registration.
In the Register an application page that appears, enter the following application registration information:
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name for display to users of the app - for example,
java-spring-webapp-call-graph. - Under Supported account types, select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
- In the Redirect URI (optional) section, select Web in the combo-box and enter the following redirect URI:
http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/.
- In the Name section, enter a meaningful application name for display to users of the app - for example,
Select Register to create the application.
On the app's registration page, find and copy the Application (client) ID value to use later. You use this value in your app's configuration file or files.
On the app's registration page, select Certificates & secrets on the navigation pane to open the page where you can generate secrets and upload certificates.
In the Client secrets section, select New client secret.
Type a description - for example, app secret.
Select one of the available durations: In 1 year, In 2 years, or Never Expires.
Select Add. The generated value is displayed.
Copy and save the generated value for use in later steps. You need this value for your code's configuration files. This value isn't displayed again, and you can't retrieve it by any other means. So, be sure to save it from the Azure portal before you navigate to any other screen or pane.
On the app's registration page, select the API permissions pane on the navigation pane to open the page for access to the APIs that your application needs.
Select Add permissions, and then ensure that the Microsoft APIs tab is selected.
In the Commonly used Microsoft APIs section, select Microsoft Graph.
In the Delegated permissions section, select User.Read from the list. Use the search box if necessary.
Select Add permissions.
Configure the app (java-spring-webapp-call-graph) to use your app registration
Use the following steps to configure the app:
Note
In the following steps, ClientID is the same as Application ID or AppId.
Open the project in your IDE.
Open the src\main\resources\application.yml file.
Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Tenant_ID_Hereand replace the existing value with your Microsoft Entra tenant ID.Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Client_ID_Hereand replace the existing value with the application ID orclientIdof thejava-spring-webapp-call-graphapp copied from the Azure portal.Find the placeholder
Enter_Your_Client_Secret_Hereand replace the existing value with the value you saved during the creation ofjava-spring-webapp-call-graphcopied from the Azure portal.
Run the sample
The following sections show you how to deploy the sample to Azure Container Apps.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account. If you don't have one, create a free account. You need the
ContributororOwnerpermission on the Azure subscription to proceed. For more information, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal. - The Azure CLI.
- The Azure Container Apps CLI extension, version
0.3.47or higher. To install the latest version, use theaz extension add --name containerapp --upgrade --allow-previewcommand. - The Java Development Kit, version 17 or higher.
- Maven.
Prepare the Spring project
Use the following steps to prepare the project:
Use the following Maven command to build the project:
mvn clean verifyRun the sample project locally by using the following command:
mvn spring-boot:run
Setup
To sign in to Azure from the CLI, run the following command and follow the prompts to complete the authentication process.
az login
To ensure you're running the latest version of the CLI, run the upgrade command.
az upgrade
Next, install or update the Azure Container Apps extension for the CLI.
If you receive errors about missing parameters when you run az containerapp commands in Azure CLI, be sure you have the latest version of the Azure Container Apps extension installed.
az extension add --name containerapp --upgrade
Note
Starting in May 2024, Azure CLI extensions no longer enable preview features by default. To access Container Apps preview features, install the Container Apps extension with --allow-preview true.
az extension add --name containerapp --upgrade --allow-preview true
Now that the current extension or module is installed, register the Microsoft.App and Microsoft.OperationalInsights namespaces.
Note
Azure Container Apps resources have migrated from the Microsoft.Web namespace to the Microsoft.App namespace. Refer to Namespace migration from Microsoft.Web to Microsoft.App in March 2022 for more details.
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.App
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.OperationalInsights
Create the Azure Container Apps environment
Now that your Azure CLI setup is complete, you can define the environment variables that are used throughout this article.
Define the following variables in your bash shell.
export RESOURCE_GROUP="ms-identity-containerapps"
export LOCATION="canadacentral"
export ENVIRONMENT="env-ms-identity-containerapps"
export API_NAME="ms-identity-api"
export JAR_FILE_PATH_AND_NAME="./target/ms-identity-spring-boot-webapp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"
Create a resource group.
az group create \
--name $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--location $LOCATION \
Create an environment with an auto-generated Log Analytics workspace.
az containerapp env create \
--name $ENVIRONMENT \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--location $LOCATION
Show the default domain of the container app environment. Note down this domain to use in later sections.
az containerapp env show \
--name $ENVIRONMENT \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--query properties.defaultDomain
Prepare the app for deployment
When you deploy your application to Azure Container Apps, your redirect URL changes to the redirect URL of your deployed app instance in Azure Container Apps. Use the following steps to change these settings in your application.yml file:
Navigate to your app's src\main\resources\application.yml file and change the value of
post-logout-redirect-urito your deployed app's domain name, as shown in the following example. Be sure to replace<API_NAME>and<default-domain-of-container-app-environment>with your actual values. For example, with the default domain for your Azure Container App environment from the previous step andms-identity-apifor your app name, you would usehttps://ms-identity-api.<default-domain>for thepost-logout-redirect-urivalue.post-logout-redirect-uri: https://<API_NAME>.<default-domain-of-container-app-environment>After saving this file, use the following command to rebuild your app:
mvn clean package
Important
The application.yml file of the application currently holds the value of your client secret in the client-secret parameter. It isn't good practice to keep this value in this file. You might also be taking a risk if you commit the file to a Git repository. For the recommended approach, see Manage secrets in Azure Container Apps.
Update your Microsoft Entra ID app registration
Because the redirect URI changes to your deployed app on Azure Container Apps, you also need to change the redirect URI in your Microsoft Entra ID app registration. Use the following steps to make this change:
Navigate to the Microsoft identity platform for developers App registrations page.
Use the search box to search for your app registration - for example,
java-servlet-webapp-authentication.Open your app registration by selecting its name.
Select Authentication from the menu.
In the Web - Redirect URIs section, select Add URI.
Fill out the URI of your app, appending
/login/oauth2/code/- for example,https://<containerapp-name>.<default domain of container app environment>/login/oauth2/code/.Select Save.
Deploy the app
Deploy the JAR package to Azure Container Apps.
Note
If necessary, you can specify the JDK version in the Java build environment variables. For more information, see Build environment variables for Java in Azure Container Apps.
Now you can deploy your WAR file with the az containerapp up CLI command.
az containerapp up \
--name $API_NAME \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--location $LOCATION \
--environment $ENVIRONMENT \
--artifact <JAR_FILE_PATH_AND_NAME> \
--ingress external \
--target-port 8080 \
--query properties.configuration.ingress.fqdn
Note
The default JDK version is 17. If you need to change the JDK version for compatibility with your application, you can use the --build-env-vars BP_JVM_VERSION=<YOUR_JDK_VERSION> argument to adjust the version number.
For more build environment variables, see Build environment variables for Java in Azure Container Apps.
Validate the app
In this example, the containerapp up command includes the --query properties.configuration.ingress.fqdn argument, which returns the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), also known as the app's URL. Use the following steps to check the app's logs to investigate any deployment issue:
Access the output application URL from the Outputs page of the Deployment section.
From the navigation pane of the Azure Container Apps instance Overview page, select Logs to check the app's logs.
Explore the sample
Use the following steps to explore the sample:
- Notice the signed-in or signed-out status displayed at the center of the screen.
- Select the context-sensitive button in the corner. This button reads Sign In when you first run the app. Alternatively, select token details or call graph. Because this page is protected and requires authentication, you're automatically redirected to the sign-in page.
- On the next page, follow the instructions and sign in with an account in the Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
- On the consent screen, notice the scopes that are being requested.
- Upon successful completion of the sign-in flow, you should be redirected to the home page - which shows the sign in status - or one of the other pages, depending on which button triggered your sign-in flow.
- Notice that the context-sensitive button now says Sign out and displays your username.
- If you're on the home page, select ID Token Details to see some of the ID token's decoded claims.
- Select Call Graph to make a call to Microsoft Graph's /me endpoint and see a selection of the user details obtained.
- Use the button in the corner to sign out. The status page reflects the new state.
About the code
This sample demonstrates how to use Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java to sign in users into your Microsoft Entra ID tenant and obtain an access token for calling Microsoft Graph. The sample also makes use of the Spring Oauth2 Client and Spring Web boot starters.
Contents
The following table shows the contents of the sample project folder:
| File/folder | Description |
|---|---|
| pom.xml | Application dependencies. |
| src/main/resources/templates/ | Thymeleaf Templates for UI. |
| src/main/resources/application.yml | Application and Microsoft Entra ID Boot Starter Library Configuration. |
| src/main/java/com/microsoft/azuresamples/msal4j/msidentityspringbootwebapp/ | This directory contains the main application entry point, controller, and config classes. |
| .../MsIdentitySpringBootWebappApplication.java | Main class. |
| .../SampleController.java | Controller with endpoint mappings. |
| .../SecurityConfig.java | Security configuration - for example, which routes require authentication. |
| .../Utilities.java | Utility class - for example, filter ID token claims. |
| CHANGELOG.md | List of changes to the sample. |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Guidelines for contributing to the sample. |
| LICENSE | The license for the sample. |
ID token claims
To extract token details, the app makes use of Spring Security's AuthenticationPrincipal and OidcUser object in a request mapping, as shown in the following example. See the Sample Controller for the full details of how this app makes use of ID token claims.
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.oidc.user.OidcUser;
import org.springframework.security.core.annotation.AuthenticationPrincipal;
//...
@GetMapping(path = "/some_path")
public String tokenDetails(@AuthenticationPrincipal OidcUser principal) {
Map<String, Object> claims = principal.getIdToken().getClaims();
}
Sign-in and sign-out links
For sign-in, the app makes a request to the Microsoft Entra ID sign-in endpoint automatically configured by Microsoft Entra ID Spring Boot Starter client library for Java, as shown in the following example:
<a class="btn btn-success" href="/oauth2/authorization/azure">Sign In</a>
For sign-out, the app makes a POST request to the logout endpoint, as shown in the following example:
<form action="#" th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input class="btn btn-warning" type="submit" value="Sign Out" />
</form>
Authentication-dependent UI elements
The app has some simple logic in the UI template pages for determining content to display based on whether the user is authenticated, as shown in the following example using Spring Security Thymeleaf tags:
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
this content only shows to authenticated users
</div>
<div sec:authorize="isAnonymous()">
this content only shows to not-authenticated users
</div>
Protect routes with AADWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
By default, the app protects the ID Token Details and Call Graph pages so that only signed-in users can access them. The app configures these routes from the app.protect.authenticated property from the application.yml file. To configure your app's specific requirements, you can extend AADWebSecurityConfigurationAdapter in one of your classes. For an example, see this app's SecurityConfig class, shown in the following code:
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends AADWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Value( "${app.protect.authenticated}" )
private String[] protectedRoutes;
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// use required configuration form AADWebSecurityAdapter.configure:
super.configure(http);
// add custom configuration:
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers(protectedRoutes).authenticated() // limit these pages to authenticated users (default: /token_details, /call_graph)
.antMatchers("/**").permitAll(); // allow all other routes.
}
}
Call graph
When the user navigates to /call_graph, the application creates an instance of the GraphServiceClient using an Oauth2AuthorizedClient or graphAuthorizedClient that the Microsoft Entra ID boot starter prepared. The app asks the GraphServiceClient to call the /me endpoint and displays details for the current signed-in user. GraphServiceClient is from the Microsoft Graph SDK for Java, v3.
The Oauth2AuthorizedClient must be prepared with the correct scopes. See the application.yml file and the following Scopes section. The Oauth2AuthorizedClient is used to surface the access token and place it in the Authorization header of GraphServiceClient requests, as shown in the following example:
//see SampleController.java
@GetMapping(path = "/call_graph")
public String callGraph(@RegisteredOAuth2AuthorizedClient("graph") OAuth2AuthorizedClient graphAuthorizedClient) {
// See the Utilities.graphUserProperties() method for the full example of the following operation:
GraphServiceClient graphServiceClient = Utilities.getGraphServiceClient(graphAuthorizedClient);
User user = graphServiceClient.me().buildRequest().get();
return user.displayName;
}
The following example from the application.yml file shows the scopes requested:
# see application.yml file
authorization-clients:
graph:
# Specifies the Microsoft Graph scopes that your app needs access to:
scopes: https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read
Scopes
Scopes tell Microsoft Entra ID the level of access that the application is requesting. For the Microsoft Graph scopes requested by this application, see application.yml.
By default, the application sets the scopes value to https://graph.microsoft.com/User.Read. The User.Read scope is for accessing the information of the current signed-in user from the /me endpoint. Valid requests to the /me endpoint must contain the User.Read scope.
When a user signs in, Microsoft Entra ID presents a consent dialogue to the user based on the scopes requested by the application. If the user consents to one or more scopes and obtains a token, the scopes-consented-to are encoded into the resulting access token.
In this app, the graphAuthorizedClient surfaces the access token that proves which the scopes the user consented to. The app uses this token to create an instance of GraphServiceClient that handles Graph requests.
Using GraphServiceClient.me().buildRequest().get(), a request is built and made to https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/me. The access token is placed in the Authorization header of the request.
More information
- Microsoft identity platform documentation
- Overview of Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL)
- Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform
- Quickstart: Configure a client application to access web APIs
- Understanding Microsoft Entra ID application consent experiences
- Understand user and admin consent
- Application and service principal objects in Microsoft Entra ID
- National Clouds
- MSAL code samples
- Azure Active Directory Spring Boot Starter client library for Java
- Microsoft Authentication Library for Java (MSAL4J)
- MSAL4J Wiki
- ID tokens
- Access tokens in the Microsoft identity platform
For more information about how OAuth 2.0 protocols work in this scenario and other scenarios, see Authentication Scenarios for Microsoft Entra ID.
