Nota
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare ad accedere o modificare le directory.
L'accesso a questa pagina richiede l'autorizzazione. È possibile provare a modificare le directory.
Finestra di dialogo popup che funziona come finestra di messaggio, ma che può visualizzare informazioni aggiuntive all'utente. L'oggetto CTaskDialog include inoltre la funzionalità per raccogliere informazioni dall'utente.
Sintassi
class CTaskDialog : public CObject
Membri
Costruttori
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| CTaskDialog::CTaskDialog | Costruisce un oggetto CTaskDialog. |
Metodi
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| CTaskDialog::AddCommandControl | Aggiunge un controllo pulsante di comando all'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::AddRadioButton | Aggiunge un pulsante di opzione a CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::ClickCommandControl | Fa clic su un controllo pulsante di comando o un pulsante comune a livello di codice. |
| CTaskDialog::ClickRadioButton | Fa clic su un pulsante di opzione a livello di codice. |
| CTaskDialog::D oModal | Visualizza la CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonCount | Recupera il numero di pulsanti comuni disponibili. |
| CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonFlag | Converte un pulsante Standard di Windows nel tipo di pulsante comune associato alla CTaskDialog classe . |
| CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonId | Converte uno dei tipi di pulsante comuni associati alla CTaskDialog classe in un pulsante Standard di Windows. |
| CTaskDialog::GetOptions | Restituisce i flag di opzione per questo CTaskDialogoggetto . |
| CTaskDialog::GetSelectedCommandControlID | Restituisce il controllo pulsante di comando selezionato. |
| CTaskDialog::GetSelectedRadioButtonID | Restituisce il pulsante di opzione selezionato. |
| CTaskDialog::GetVerificationCheckboxState | Recupera lo stato della casella di controllo di verifica. |
| CTaskDialog::IsCommandControlEnabled | Determina se è abilitato un controllo pulsante di comando o un pulsante comune. |
| CTaskDialog::IsRadioButtonEnabled | Determina se un pulsante di opzione è abilitato. |
| CTaskDialog::IsSupported | Determina se il computer che esegue l'applicazione supporta .CTaskDialog |
| CTaskDialog::LoadCommandControls | Aggiunge i controlli del pulsante di comando usando i dati della tabella di stringhe. |
| CTaskDialog::LoadRadioButtons | Aggiunge pulsanti di opzione usando i dati della tabella stringa. |
| CTaskDialog::NavigateTo | Trasferisce lo stato attivo a un altro CTaskDialogoggetto . |
| CTaskDialog::OnCommandControlClick | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic su un controllo pulsante di comando. |
| CTaskDialog::OnCreate | Il framework chiama questo metodo dopo aver creato l'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::OnDestroy | Il framework chiama questo metodo immediatamente prima di distruggere .CTaskDialog |
| CTaskDialog::OnExpandButtonClick | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic sul pulsante di espansione. |
| CTaskDialog::OnHelp | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente richiede assistenza. |
| CTaskDialog::OnHyperlinkClick | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic su un collegamento ipertestuale. |
| CTaskDialog::OnInit | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando viene inizializzato .CTaskDialog |
| CTaskDialog::OnNavigatePage | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente sposta lo stato attivo per quanto riguarda i controlli in CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::OnRadioButtonClick | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente seleziona un controllo pulsante di opzione. |
| CTaskDialog::OnTimer | Il framework chiama questo metodo alla scadenza del timer. |
| CTaskDialog::OnVerificationCheckboxClick | Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic sulla casella di controllo verifica. |
| CTaskDialog::RemoveAllCommandControls | Rimuove tutti i controlli di comando da CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::RemoveAllRadioButtons | Rimuove tutti i pulsanti di opzione da CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetCommandControlOptions | Aggiorna un controllo pulsante di comando in CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtonOptions | Aggiorna un subset di pulsanti comuni da abilitare e richiedere l'elevazione del controllo dell'account utente. |
| CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtons | Aggiunge pulsanti comuni all'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetContent | Aggiorna il contenuto di CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetDefaultCommandControl | Specifica il controllo pulsante di comando predefinito. |
| CTaskDialog::SetDefaultRadioButton | Specifica il pulsante di opzione predefinito. |
| CTaskDialog::SetDialogWidth | Regola la larghezza di CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetExpansionArea | Aggiorna l'area di espansione dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetFooterIcon | Aggiorna l'icona del piè di pagina per .CTaskDialog |
| CTaskDialog::SetFooterText | Aggiorna il testo nel piè di pagina dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetMainIcon | Aggiorna l'icona principale di CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetMainInstruction | Aggiorna l'istruzione principale di CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetOptions | Configura le opzioni per .CTaskDialog |
| CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarMarquee | Configura una barra di selezione per e CTaskDialog la aggiunge alla finestra di dialogo. |
| CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarPosition | Regola la posizione dell'indicatore di stato. |
| CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarRange | Regola l'intervallo dell'indicatore di stato. |
| CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarState | Imposta lo stato della barra di stato e lo visualizza nell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::SetRadioButtonOptions | Abilita o disabilita un pulsante di opzione. |
| CTaskDialog::SetVerificationCheckbox | Imposta lo stato selezionato della casella di controllo verifica. |
| CTaskDialog::SetVerificationCheckboxText | Imposta il testo sul lato destro della casella di controllo verifica. |
| CTaskDialog::SetWindowTitle | Imposta il titolo dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::ShowDialog | Crea e visualizza un oggetto CTaskDialog. |
| CTaskDialog::TaskDialogCallback | Il framework lo chiama in risposta a vari messaggi di Windows. |
Membri dei dati
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
m_aButtons |
Matrice di controlli pulsante di comando per .CTaskDialog |
m_aRadioButtons |
Matrice di controlli pulsante di opzione per .CTaskDialog |
m_bVerified |
TRUE indica che la casella di controllo verifica è selezionata; FALSE indica che non è . |
m_footerIcon |
Icona nel piè di pagina dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
m_hWnd |
Handle della finestra per l'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
m_mainIcon |
Icona principale di CTaskDialog. |
m_nButtonDisabled |
Maschera che indica quale dei pulsanti comuni sono disabilitati. |
m_nButtonElevation |
Maschera che indica quale dei pulsanti comuni richiedono l'elevazione del controllo dell'account utente. |
m_nButtonId |
ID del controllo pulsante di comando selezionato. |
m_nCommonButton |
Maschera che indica quali pulsanti comuni vengono visualizzati in CTaskDialog. |
m_nDefaultCommandControl |
ID del controllo pulsante di comando selezionato quando CTaskDialog viene visualizzato . |
m_nDefaultRadioButton |
ID del controllo pulsante di opzione selezionato quando CTaskDialog viene visualizzato . |
m_nFlags |
Maschera che indica le opzioni per .CTaskDialog |
m_nProgressPos |
Posizione corrente per l'indicatore di stato. Il valore deve essere compreso tra m_nProgressRangeMin e m_nProgressRangeMax. |
m_nProgressRangeMax |
Valore massimo per la barra di stato. |
m_nProgressRangeMin |
Valore minimo per l'indicatore di stato. |
m_nProgressState |
Stato dell'indicatore di stato. Per altre informazioni, vedere CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarState. |
m_nRadioId |
ID del controllo pulsante di opzione selezionato. |
m_nWidth |
Larghezza dell'oggetto CTaskDialog in pixel. |
m_strCollapse |
Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata a destra della casella di espansione quando le informazioni espanse sono nascoste. |
m_strContent |
Stringa di contenuto dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
m_strExpand |
Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata a destra della casella di espansione quando vengono visualizzate le informazioni espanse. |
m_strFooter |
Piè di pagina dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
m_strInformation |
Informazioni espanse per .CTaskDialog |
m_strMainInstruction |
Istruzione principale di CTaskDialog. |
m_strTitle |
Titolo dell'oggetto CTaskDialog. |
m_strVerification |
Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata a destra della casella di controllo di verifica. |
Osservazioni:
La CTaskDialog classe sostituisce la finestra di messaggio standard di Windows e include funzionalità aggiuntive, ad esempio i nuovi controlli per raccogliere informazioni dall'utente. Questa classe si trova nella libreria MFC in Visual Studio 2010 e versioni successive. è CTaskDialog disponibile a partire da Windows Vista. Le versioni precedenti di Windows non possono visualizzare l'oggetto CTaskDialog . Usare CTaskDialog::IsSupported per determinare in fase di esecuzione se l'utente corrente può visualizzare la finestra di dialogo attività. La finestra di messaggio standard di Windows è ancora supportata.
CTaskDialog è disponibile solo quando si compila l'applicazione usando la libreria Unicode.
ha CTaskDialog due costruttori diversi. Un costruttore consente di specificare due pulsanti di comando e un massimo di sei controlli pulsante regolari. È possibile aggiungere altri pulsanti di comando dopo aver creato .CTaskDialog Il secondo costruttore non supporta pulsanti di comando, ma è possibile aggiungere un numero illimitato di controlli pulsante regolari. Per altre informazioni sui costruttori, vedere CTaskDialog::CTaskDialog.
L'immagine seguente mostra un esempio CTaskDialog per illustrare la posizione di alcuni controlli.
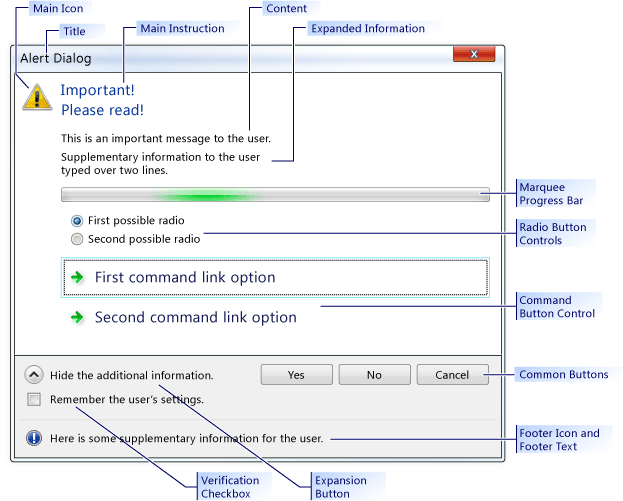
Esempio di CTaskDialog
Requisiti
Sistema operativo minimo richiesto: Windows Vista
Intestazione: afxtaskdialog.h
CTaskDialog::AddCommandControl
Aggiunge un nuovo controllo pulsante di comando all'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void AddCommandControl(
int nCommandControlID,
const CString& strCaption,
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE,
BOOL bRequiresElevation = FALSE);
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] Numero di identificazione del controllo del comando.
strCaption
[in] Stringa visualizzata dall'utente CTaskDialog . Usare questa stringa per spiegare lo scopo del comando.
bEnabled
[in] Parametro booleano che indica se il nuovo pulsante è abilitato o disabilitato.
bRequiresElevation
[in] Parametro booleano che indica se un comando richiede l'elevazione dei privilegi.
Osservazioni:
CTaskDialog Class Può visualizzare un numero illimitato di controlli pulsante di comando. Tuttavia, se un controllo CTaskDialog visualizza qualsiasi controllo pulsante di comando, può visualizzare un massimo di sei pulsanti. Se un oggetto CTaskDialog non dispone di controlli pulsante di comando, può visualizzare un numero illimitato di pulsanti.
Quando l'utente seleziona un controllo pulsante di comando, viene CTaskDialog chiuso. Se l'applicazione visualizza la finestra di dialogo utilizzando CTaskDialog::D oModal, DoModal restituisce il valore nCommandControlID del controllo pulsante di comando selezionato.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::AddRadioButton
Aggiunge un pulsante di opzione a CTaskDialog.
void CTaskDialog::AddRadioButton(
int nRadioButtonID,
const CString& strCaption,
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE);
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] Numero di identificazione del pulsante di opzione.
strCaption
[in] Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata accanto al pulsante di opzione.
bEnabled
[in] Parametro booleano che indica se il pulsante di opzione è abilitato.
Osservazioni:
I pulsanti di opzione per la classe CTaskDialog consentono di raccogliere informazioni dall'utente. Usare la funzione CTaskDialog::GetSelectedRadioButtonID per determinare il pulsante di opzione selezionato.
Non CTaskDialog richiede che i parametri nRadioButtonID siano univoci per ogni pulsante di opzione. Tuttavia, è possibile che si verifichi un comportamento imprevisto se non si usa un identificatore distinto per ogni pulsante di opzione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::ClickCommandControl
Fa clic su un controllo pulsante di comando o un pulsante comune a livello di codice.
protected:
void ClickCommandControl(int nCommandControlID) const;
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] ID comando del controllo da fare clic.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera il messaggio di Windows TDM_CLICK_BUTTON.
CTaskDialog::ClickRadioButton
Fa clic su un pulsante di opzione a livello di codice.
protected:
void ClickRadioButton(int nRadioButtonID) const;
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID del pulsante di opzione da fare clic.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera il messaggio di Windows TDM_CLICK_RADIO_BUTTON.
CTaskDialog::CTaskDialog
Crea un'istanza della classe CTaskDialog.
CTaskDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nCommonButtons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
CTaskDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast,
int nCommonButtons,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
Parametri
strContent
[in] Stringa da utilizzare per il contenuto dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
strMainInstruction
[in] Istruzione principale di CTaskDialog.
strTitle
[in] Titolo dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
nCommonButtons
[in] Maschera dei pulsanti comuni da aggiungere a CTaskDialog.
nTaskDialogOptions
[in] Set di opzioni da utilizzare per .CTaskDialog
strFooter
[in] Stringa da utilizzare come piè di pagina.
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID stringa del primo comando.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID stringa dell'ultimo comando.
Osservazioni:
Esistono due modi per aggiungere un oggetto CTaskDialog all'applicazione. Il primo modo consiste nell'usare uno dei costruttori per creare e CTaskDialog visualizzarlo usando CTaskDialog::D oModal. Il secondo modo consiste nell'usare la funzione statica CTaskDialog::ShowDialog, che consente di visualizzare un CTaskDialog oggetto senza creare in modo esplicito un CTaskDialog oggetto.
Il secondo costruttore crea controlli pulsante di comando usando i dati del file di risorse dell'applicazione. La tabella di stringhe nel file di risorse include diverse stringhe con ID stringa associati. Questo metodo aggiunge un controllo pulsante di comando per ogni voce valida nella tabella di stringhe tra nIDCommandControlsFirst e nCommandControlsLast, inclusivo. Per questi controlli pulsante di comando, la stringa nella tabella di stringhe è la didascalia del controllo e l'ID stringa è l'ID del controllo.
Per un elenco di opzioni valide, vedere CTaskDialog::SetOptions .
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::D oModal
Mostra e CTaskDialog lo rende modale.
INT_PTR DoModal (HWND hParent = ::GetActiveWindow());
Parametri
hParent
[in] Finestra padre per l'oggetto CTaskDialog.
Valore restituito
Intero che corrisponde alla selezione effettuata dall'utente.
Osservazioni:
Visualizza questa istanza di CTaskDialog. L'applicazione attende quindi che l'utente chiuda la finestra di dialogo.
Chiude CTaskDialog quando l'utente seleziona un pulsante comune, un controllo collegamento di comando o chiude .CTaskDialog Il valore restituito è l'identificatore che indica come l'utente ha chiuso la finestra di dialogo.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonCount
Recupera il numero di pulsanti comuni.
int GetCommonButtonCount() const;
Valore restituito
Numero di pulsanti comuni disponibili.
Osservazioni:
I pulsanti comuni sono i pulsanti predefiniti forniti a CTaskDialog::CTaskDialog. La classe CTaskDialog visualizza i pulsanti nella parte inferiore della finestra di dialogo.
L'elenco enumerato dei pulsanti è disponibile in CommCtrl.h.
CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonFlag
Converte un pulsante Windows standard nel tipo di pulsante comune associato alla classe CTaskDialog.
int GetCommonButtonFlag(int nButtonId) const;
Parametri
nButtonId
[in] Valore del pulsante Standard di Windows.
Valore restituito
Valore del pulsante comune corrispondente CTaskDialog . Se non è presente alcun pulsante comune corrispondente, questo metodo restituisce 0.
CTaskDialog::GetCommonButtonId
Converte uno dei tipi di pulsante comuni associati alla classe CTaskDialog in un pulsante Standard di Windows.
int GetCommonButtonId(int nFlag);
Parametri
nFlag
[in] Tipo di pulsante comune associato alla CTaskDialog classe .
Valore restituito
Valore del pulsante Standard di Windows corrispondente. Se non è presente alcun pulsante Windows corrispondente, il metodo restituisce 0.
CTaskDialog::GetOptions
Restituisce i flag di opzione per questo CTaskDialogoggetto .
int GetOptions() const;
Valore restituito
Flag per .CTaskDialog
Osservazioni:
Per altre informazioni sulle opzioni disponibili per la classe CTaskDialog, vedere CTaskDialog::SetOptions.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::GetSelectedCommandControlID
Restituisce il controllo pulsante di comando selezionato.
int GetSelectedCommandControlID() const;
Valore restituito
ID del controllo pulsante di comando attualmente selezionato.
Osservazioni:
Non è necessario usare questo metodo per recuperare l'ID del pulsante di comando selezionato dall'utente. Tale ID viene restituito da CTaskDialog::D oModal o CTaskDialog::ShowDialog.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::GetSelectedRadioButtonID
Restituisce il pulsante di opzione selezionato.
int GetSelectedRadioButtonID() const;
Valore restituito
ID del pulsante di opzione selezionato.
Osservazioni:
È possibile utilizzare questo metodo dopo che l'utente chiude la finestra di dialogo per recuperare il pulsante di opzione selezionato.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::GetVerificationCheckboxState
Recupera lo stato della casella di controllo di verifica.
BOOL GetVerificationCheckboxState() const;
Valore restituito
TRUE se la casella di controllo è selezionata, FALSE in caso contrario.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog::IsCommandControlEnabled
Determina se un controllo o un pulsante di comando è abilitato.
BOOL IsCommandControlEnabled(int nCommandControlID) const;
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] ID del controllo o del pulsante di comando da testare.
Valore restituito
TRUE se il controllo è abilitato, FALSE in caso contrario.
Osservazioni:
È possibile usare questo metodo per determinare la disponibilità di entrambi i controlli pulsante di comando e dei pulsanti comuni della CTaskDialog classe*.
Se nCommandControlID non è un identificatore valido per un pulsante comune CTaskDialog o un controllo pulsante di comando, questo metodo genera un'eccezione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::IsRadioButtonEnabled
Determina se un pulsante di opzione è abilitato.
BOOL IsRadioButtonEnabled(int nRadioButtonID) const;
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID del pulsante di opzione da testare.
Valore restituito
TRUE se il pulsante di opzione è abilitato, FALSE in caso contrario.
Osservazioni:
Se nRadioButtonID non è un identificatore valido per un pulsante di opzione, questo metodo genera un'eccezione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::IsSupported
Determina se il computer che esegue l'applicazione supporta .CTaskDialog
static BOOL IsSupported();
Valore restituito
TRUE se il computer supporta ; CTaskDialog FALSE in caso contrario.
Osservazioni:
Usare questa funzione per determinare in fase di esecuzione se il computer che esegue l'applicazione supporta la CTaskDialog classe . Se il computer non supporta CTaskDialog, è necessario fornire un altro metodo di comunicazione delle informazioni all'utente. L'applicazione si arresterà in modo anomalo se tenta di usare un CTaskDialog oggetto in un computer che non supporta la CTaskDialog classe .
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the string below with the actual message to the user
CString message("Important information to the user");
// TODO: Replace the string below with the title of this project
CString title("Project Title");
CString emptyString;
if (CTaskDialog::IsSupported())
{
CTaskDialog::ShowDialog(message, emptyString, title, 0, 0,
TDCBF_OK_BUTTON);
}
else
{
AfxMessageBox(message);
}
CTaskDialog::LoadCommandControls
Aggiunge i controlli del pulsante di comando usando i dati della tabella di stringhe.
void LoadCommandControls(
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast);
Parametri
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID stringa del primo comando.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID stringa dell'ultimo comando.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo crea controlli pulsante di comando usando i dati del file di risorse dell'applicazione. La tabella di stringhe nel file di risorse include diverse stringhe con ID stringa associati. I nuovi controlli pulsante di comando aggiunti usando questo metodo usano la stringa per la didascalia del controllo e l'ID stringa per l'ID del controllo. L'intervallo di stringhe selezionate viene fornito da nIDCommandControlsFirst e nCommandControlsLast, inclusivo. Se è presente una voce vuota nell'intervallo, il metodo non aggiunge un controllo pulsante di comando per tale voce.
Per impostazione predefinita, i nuovi controlli pulsante di comando sono abilitati e non richiedono l'elevazione dei privilegi.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::LoadRadioButtons
Aggiunge controlli pulsante di opzione utilizzando i dati della tabella stringa.
void LoadRadioButtons(
int nIDRadioButtonsFirst,
int nIDRadioButtonsLast);
Parametri
nIDRadioButtonsFirst
[in] ID stringa del primo pulsante di opzione.
nIDRadioButtonsLast
[in] ID stringa dell'ultimo pulsante di opzione.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo crea pulsanti di opzione usando i dati del file di risorse dell'applicazione. La tabella di stringhe nel file di risorse include diverse stringhe con ID stringa associati. I nuovi pulsanti di opzione aggiunti usando questo metodo usano la stringa per la didascalia del pulsante di opzione e l'ID stringa per l'ID del pulsante di opzione. L'intervallo di stringhe selezionate è fornito da nIDRadioButtonsFirst e nRadioButtonsLast, inclusivo. Se è presente una voce vuota nell'intervallo, il metodo non aggiunge un pulsante di opzione per tale voce.
Per impostazione predefinita, sono abilitati nuovi pulsanti di opzione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::NavigateTo
Trasferisce lo stato attivo a un altro CTaskDialogoggetto .
protected:
void NavigateTo(CTaskDialog& oTaskDialog) const;
Parametri
oTaskDialog
[in] Oggetto CTaskDialog che riceve lo stato attivo.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo nasconde l'oggetto corrente CTaskDialog quando viene visualizzato oTaskDialog. OTaskDialog viene visualizzato nella stessa posizione dell'oggetto correnteCTaskDialog.
CTaskDialog::OnCommandControlClick
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic su un controllo pulsante di comando.
virtual HRESULT OnCommandControlClick(int nCommandControlID);
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] ID del controllo pulsante di comando selezionato dall'utente.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnCreate
Il framework chiama questo metodo dopo aver creato l'oggetto CTaskDialog.
virtual HRESULT OnCreate();
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnDestroy
Il framework chiama questo metodo immediatamente prima di distruggere .CTaskDialog
virtual HRESULT OnDestroy();
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnExpandButtonClick
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic sul pulsante di espansione.
virtual HRESULT OnExpandButtonClicked(BOOL bExpanded);
Parametri
bExpanded
[in] Un valore diverso da zero indica che vengono visualizzate le informazioni aggiuntive; 0 indica che le informazioni aggiuntive sono nascoste.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnHelp
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente richiede assistenza.
virtual HRESULT OnHelp();
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_FALSE.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnHyperlinkClick
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic su un collegamento ipertestuale.
virtual HRESULT OnHyperlinkClick(const CString& strHref);
Parametri
strHref
[in] Stringa che rappresenta il collegamento ipertestuale.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo chiama ShellExecute prima di restituire S_OK.
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnInit
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando viene inizializzato .CTaskDialog
virtual HRESULT OnInit();
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnNavigatePage
Il framework chiama questo metodo in risposta al metodo CTaskDialog::NavigateTo .
virtual HRESULT OnNavigatePage();
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnRadioButtonClick
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente seleziona un controllo pulsante di opzione.
virtual HRESULT OnRadioButtonClick(int nRadioButtonID);
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID del controllo pulsante di opzione su cui l'utente ha fatto clic.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnTimer
Il framework chiama questo metodo alla scadenza del timer.
virtual HRESULT OnTimer(long lTime);
Parametri
lTime
[in] Tempo in millisecondi dopo la CTaskDialog creazione o il timer è stato reimpostato.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::OnVerificationCheckboxClick
Il framework chiama questo metodo quando l'utente fa clic sulla casella di controllo verifica.
virtual HRESULT OnVerificationCheckboxClick(BOOL bChecked);
Parametri
bChecked
[in] TRUE indica che la casella di controllo verifica è selezionata; FALSE indica che non lo è.
Valore restituito
L'implementazione predefinita restituisce S_OK.
Osservazioni:
Eseguire l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata per implementare un comportamento personalizzato.
CTaskDialog::RemoveAllCommandControls
Rimuove tutti i controlli del pulsante di comando da CTaskDialog.
void RemoveAllCommandControls();
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::RemoveAllRadioButtons
Rimuove tutti i pulsanti di opzione da CTaskDialog.
void RemoveAllRadioButtons();
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::SetCommandControlOptions
Aggiorna un controllo pulsante di comando in CTaskDialog.
void SetCommandControlOptions(
int nCommandControlID,
BOOL bEnabled,
BOOL bRequiresElevation = FALSE);
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] ID del controllo del comando da aggiornare.
bEnabled
[in] Parametro booleano che indica se il controllo del pulsante di comando specificato è abilitato o disabilitato.
bRequiresElevation
[in] Parametro booleano che indica se il controllo del pulsante di comando specificato richiede l'elevazione dei privilegi.
Osservazioni:
Utilizzare questo metodo per modificare se un controllo pulsante di comando è abilitato o richiede l'elevazione dei privilegi dopo l'aggiunta alla CTaskDialog classe .
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtonOptions
Aggiorna un subset di pulsanti comuni da abilitare e richiedere l'elevazione del controllo dell'account utente.
void SetCommonButtonOptions(
int nDisabledButtonMask,
int nElevationButtonMask = 0);
Parametri
nDisabledButtonMask
[in] Maschera per i pulsanti comuni da disabilitare.
nElevationButtonMask
[in] Maschera per i pulsanti comuni che richiedono l'elevazione dei privilegi.
Osservazioni:
È possibile impostare i pulsanti comuni disponibili per un'istanza della classe CTaskDialog usando il costruttore CTaskDialog::CTaskDialog e il metodo CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtons.
CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtonOptions non supporta l'aggiunta di nuovi pulsanti comuni.
Se si utilizza questo metodo per disabilitare o elevare un pulsante comune non disponibile per questo CTaskDialog, questo metodo genera un'eccezione utilizzando la macro ENSURE .
Questo metodo abilita qualsiasi pulsante disponibile per ma CTaskDialog non è presente in nDisabledButtonMask, anche se è stato disabilitato in precedenza. Questo metodo considera l'elevazione in modo simile: registra i pulsanti comuni come non richiedere l'elevazione se il pulsante comune è disponibile ma non incluso in nElevationButtonMask.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title);
// Create a button mask.
int buttons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON;
buttons |= TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON | TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON;
taskDialog.SetCommonButtons(buttons);
// Disable the close button and make the retry button require
// elevation.
taskDialog.SetCommonButtonOptions(TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON,
TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetCommonButtons
Aggiunge pulsanti comuni all'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void SetCommonButtons(
int nButtonMask,
int nDisabledButtonMask = 0,
int nElevationButtonMask = 0);
Parametri
nButtonMask
[in] Maschera dei pulsanti da aggiungere all'oggetto CTaskDialog.
nDisabledButtonMask
[in] Maschera dei pulsanti da disabilitare.
nElevationButtonMask
[in] Maschera dei pulsanti che richiedono l'elevazione.
Osservazioni:
Non è possibile chiamare questo metodo dopo la creazione della finestra di visualizzazione per questa istanza della CTaskDialog classe . In questo caso, questo metodo genera un'eccezione.
I pulsanti indicati da nButtonMask sostituiscono tutti i pulsanti comuni aggiunti in precedenza a CTaskDialog. Sono disponibili solo i pulsanti indicati in nButtonMask .
Se nDisabledButtonMask o nElevationButtonMask contengono un pulsante che non si trova in nButtonMask, questo metodo genera un'eccezione utilizzando la macro ENSURE.
Per impostazione predefinita, tutti i pulsanti comuni sono abilitati e non richiedono l'elevazione dei privilegi.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title);
// Create a button mask.
int buttons = TDCBF_OK_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON;
buttons |= TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON | TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON;
taskDialog.SetCommonButtons(buttons);
// Disable the close button and make the retry button require
// elevation.
taskDialog.SetCommonButtonOptions(TDCBF_CLOSE_BUTTON,
TDCBF_RETRY_BUTTON);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetContent
Aggiorna il contenuto di CTaskDialog.
void SetContent(const CString& strContent);
Parametri
strContent
[in] Stringa da visualizzare all'utente.
Osservazioni:
Il contenuto della CTaskDialog classe è il testo visualizzato all'utente nella sezione principale della finestra di dialogo.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetDefaultCommandControl
Specifica il controllo pulsante di comando predefinito.
void SetDefaultCommandControl(int nCommandControlID);
Parametri
nCommandControlID
[in] ID del controllo pulsante di comando che deve essere l'impostazione predefinita.
Osservazioni:
Il controllo pulsante di comando predefinito è il controllo selezionato quando CTaskDialog viene visualizzato per la prima volta all'utente.
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione se non riesce a trovare il controllo pulsante di comando specificato da nCommandControlID.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title.
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(201, L"First command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(202, L"Second command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(203, L"Third command button control");
// Show the CTaskDialog and remember how the user closed it.
int selection = taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// command button control.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// command button control.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command controls so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new command button controls.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(301,
L"New first command button control");
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(302,
L"New second command button control should require elevation",
TRUE, TRUE);
taskDialog.AddCommandControl(303,
L"New third command button control should be disabled");
// Change the default command button control
taskDialog.SetDefaultCommandControl(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsCommandControlEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetCommandControlOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedCommandControlID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the command button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllCommandControls();
taskDialog.LoadCommandControls(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::SetDefaultRadioButton
Specifica il pulsante di opzione predefinito.
void SetDefaultRadioButton(int nRadioButtonID);
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID del pulsante di opzione per l'impostazione predefinita.
Osservazioni:
Il pulsante di opzione predefinito è il pulsante selezionato quando CTaskDialog viene visualizzato per la prima volta all'utente.
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione se non riesce a trovare il pulsante di opzione specificato da nRadioButtonID.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::SetDialogWidth
Regola la larghezza di CTaskDialog.
void SetDialogWidth(int nWidth = 0);
Parametri
nWidth
[in] Larghezza della finestra di dialogo, in pixel.
Osservazioni:
Il parametro nWidth deve essere maggiore o uguale a 0. In caso contrario, questo metodo genera un'eccezione.
Se nWidth è impostato su 0, questo metodo imposta la finestra di dialogo sulle dimensioni predefinite.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetExpansionArea
Aggiorna l'area di espansione dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void SetExpansionArea(
const CString& strExpandedInformation,
const CString& strCollapsedLabel = _T(""),
const CString& strExpandedLabel = _T(""));
Parametri
strExpandedInformation
[in] Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata nel corpo principale della finestra di dialogo quando l'utente fa clic sul pulsante di espansione.
strCollapsedLabel
[in] Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata accanto al pulsante di espansione quando l'area espansa viene compressa.
strExpandedLabel
[in] Stringa CTaskDialog visualizzata accanto al pulsante di espansione quando viene visualizzata l'area espansa.
Osservazioni:
L'area di espansione della CTaskDialog classe consente di fornire informazioni aggiuntive all'utente. L'area di espansione si trova nella parte principale di CTaskDialog, che si trova immediatamente sotto il titolo e la stringa di contenuto.
CTaskDialog Quando viene visualizzato per la prima volta, non visualizza le informazioni espanse e viene inserito strCollapsedLabel accanto al pulsante di espansione. Quando l'utente fa clic sul pulsante di espansione, visualizza CTaskDialogstrExpandedInformation e modifica l'etichetta in strExpandedLabel.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetFooterIcon
Aggiorna l'icona del piè di pagina di CTaskDialog.
void SetFooterIcon(HICON hFooterIcon);
void SetFooterIcon(LPCWSTR lpszFooterIcon);
Parametri
hFooterIcon
[in] Nuova icona per .CTaskDialog
lpszFooterIcon
[in] Nuova icona per .CTaskDialog
Osservazioni:
L'icona del piè di pagina viene visualizzata nella parte inferiore della classe CTaskDialog. Può avere testo del piè di pagina associato. È possibile modificare il testo del piè di pagina con CTaskDialog::SetFooterText.
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se CTaskDialog viene visualizzato o il parametro di input è NULL.
Un CTaskDialog oggetto può accettare solo un oggetto HICON o LPCWSTR come icona del piè di pagina. Questa operazione viene configurata impostando l'opzione TDF_USE_HICON_FOOTER nel costruttore o in CTaskDialog::SetOptions. Per impostazione predefinita, è CTaskDialog configurato per l'uso LPCWSTR come tipo di input per l'icona del piè di pagina. Questo metodo genera un'eccezione se si tenta di impostare l'icona usando il tipo non appropriato.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetFooterText
Aggiorna il testo nel piè di pagina dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void SetFooterText(const CString& strFooterText);
Parametri
strFooterText
[in] Nuovo testo per il piè di pagina.
Osservazioni:
L'icona del piè di pagina viene visualizzata accanto al testo del piè di pagina nella parte inferiore di CTaskDialog. È possibile modificare l'icona del piè di pagina con CTaskDialog::SetFooterIcon.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetMainIcon
Aggiorna l'icona principale di CTaskDialog.
void SetMainIcon(HICON hMainIcon);
void SetMainIcon(LPCWSTR lpszMainIcon);
Parametri
hMainIcon
[in] Nuova icona.
lpszMainIcon
[in] Nuova icona.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se CTaskDialog viene visualizzato o il parametro di input è NULL.
Un CTaskDialog oggetto può accettare solo un oggetto HICON o LPCWSTR come icona principale. È possibile configurarla impostando l'opzione TDF_USE_HICON_MAIN nel costruttore o nel metodo CTaskDialog::SetOptions . Per impostazione predefinita, CTaskDialog è configurato per l'uso LPCWSTR come tipo di input per l'icona principale. Questo metodo genera un'eccezione se si tenta di impostare l'icona usando il tipo non appropriato.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetMainInstruction
Aggiorna l'istruzione principale di CTaskDialog.
void SetMainInstruction(const CString& strInstructions);
Parametri
strInstructions
[in] Nuova istruzione principale.
Osservazioni:
L'istruzione principale della CTaskDialog classe è il testo visualizzato all'utente in un carattere in grassetto di grandi dimensioni. Si trova nella finestra di dialogo sotto la barra del titolo.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetOptions
Configura le opzioni per .CTaskDialog
void SetOptions(int nOptionFlag);
Parametri
nOptionFlag
[in] Set di flag da utilizzare per .CTaskDialog
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo cancella tutte le opzioni correnti per .CTaskDialog Per mantenere le opzioni correnti, è necessario recuperarle prima con CTaskDialog::GetOptions e combinarle con le opzioni da impostare.
Nella tabella seguente sono elencate tutte le opzioni valide.
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | Abilita i collegamenti ipertestuali in CTaskDialog. |
| TDF_USE_HICON_MAIN | Configura l'oggetto CTaskDialog per l'uso di per HICON l'icona principale. L'alternativa consiste nell'usare un oggetto LPCWSTR. |
| TDF_USE_HICON_FOOTER | Configura l'oggetto CTaskDialog per l'uso di per HICON l'icona del piè di pagina. L'alternativa consiste nell'usare un oggetto LPCWSTR. |
| TDF_ALLOW_DIALOG_CANCELLATION | Consente all'utente di chiudere CTaskDialog utilizzando la tastiera o utilizzando l'icona nell'angolo superiore destro della finestra di dialogo, anche se il pulsante Annulla non è abilitato. Se questo flag non è impostato e il pulsante Annulla non è abilitato, l'utente non può chiudere la finestra di dialogo utilizzando ALT+F4, il tasto Escape o il pulsante di chiusura della barra del titolo. |
| TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS | Configura l'oggetto per l'uso CTaskDialog dei controlli dei pulsanti di comando. |
| TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS_NO_ICON | Configura l'oggetto per l'uso CTaskDialog dei controlli pulsante di comando senza visualizzare un'icona accanto al controllo . TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS esegue l'override di TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS_NO_ICON. |
| TDF_EXPAND_FOOTER_AREA | Indica che l'area di espansione è attualmente espansa. |
| TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT | Determina se l'area di espansione viene espansa per impostazione predefinita. |
| TDF_VERIFICATION_FLAG_CHECKED | Indica che la casella di controllo verifica è attualmente selezionata. |
| TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR | Configura per CTaskDialog visualizzare un indicatore di stato. |
| TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR | Configura l'indicatore di stato in modo che sia un indicatore di stato di selezione. Se si abilita questa opzione, è necessario impostare TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR per avere il comportamento previsto. |
| TDF_CALLBACK_TIMER | Indica che l'intervallo CTaskDialog di callback è impostato su circa 200 millisecondi. |
| TDF_POSITION_RELATIVE_TO_WINDOW | Configura l'oggetto CTaskDialog da allineare al centro rispetto alla finestra padre. Se questo flag non è abilitato, l'oggetto CTaskDialog viene centrato rispetto al monitor. |
| TDF_RTL_LAYOUT | Configura per CTaskDialog un layout di lettura da destra a sinistra. |
| TDF_NO_DEFAULT_RADIO_BUTTON | Indica che non viene selezionato alcun pulsante di opzione quando CTaskDialog viene visualizzato . |
| TDF_CAN_BE_MINIMIZED | Consente all'utente di ridurre al minimo l'oggetto CTaskDialog. Per supportare questa opzione, non CTaskDialog può essere modale. MFC non supporta questa opzione perché MFC non supporta un oggetto modeless CTaskDialog. |
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarMarquee
Configura una barra di selezione per e CTaskDialog la aggiunge alla finestra di dialogo.
void SetProgressBarMarquee(
BOOL bEnabled = TRUE,
int nMarqueeSpeed = 0);
Parametri
bEnabled
[in] TRUE per abilitare la barra di selezione; FALSE per disabilitare la barra di selezione e rimuoverla da CTaskDialog.
nMarqueeSpeed
[in] Intero che indica la velocità della barra di selezione.
Osservazioni:
La barra di selezione viene visualizzata sotto il testo principale della CTaskDialog classe.
Utilizzare nMarqueeSpeed per impostare la velocità della barra di selezione. I valori più grandi indicano una velocità più lenta. Il valore 0 per nMarqueeSpeed sposta la barra di selezione alla velocità predefinita per Windows.
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se nMarqueeSpeed è minore di 0.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarPosition
Regola la posizione dell'indicatore di stato.
void SetProgressBarPosition(int nProgressPos);
Parametri
nProgressPos
[in] Posizione per l'indicatore di stato.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se nProgressPos non è compreso nell'intervallo di barre di stato. È possibile modificare l'intervallo di barre di stato con CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarRange.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarRange
Regola l'intervallo dell'indicatore di stato.
void SetProgressBarRange(
int nRangeMin,
int nRangeMax);
Parametri
nRangeMin
[in] Limite inferiore dell'indicatore di stato.
nRangeMax
[in] Limite superiore dell'indicatore di stato.
Osservazioni:
La posizione della barra di stato è relativa a nRangeMin e nRangeMax. Ad esempio, se nRangeMin è 50 e nRangeMax è 100, una posizione di 75 è a metà strada sull'indicatore di stato. Usare CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarPosition per impostare la posizione della barra di stato.
Per visualizzare l'indicatore di stato, l'opzione TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR deve essere abilitata e TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR non deve essere abilitata. Questo metodo imposta automaticamente TDF_SHOW_PROGRESS_BAR e cancella TDF_SHOW_MARQUEE_PROGRESS_BAR. Usare CTaskDialog::SetOptions per modificare manualmente le opzioni per questa istanza della classe CTaskDialog.
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se nRangeMin non è minore di nRangeMax. Questo metodo genera anche un'eccezione se l'oggetto CTaskDialog è già visualizzato e dispone di un indicatore di stato di selezione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarState
Imposta lo stato della barra di stato e lo visualizza nell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void SetProgressBarState(int nState = PBST_NORMAL);
Parametri
nState
[in] Stato dell'indicatore di stato. Per i valori possibili, vedere la sezione Osservazioni.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se CTaskDialog è già visualizzato e ha una barra di stato di selezione.
Nella tabella seguente sono elencati i valori possibili per nState. In tutti questi casi, la barra di stato riempirà con il colore regolare fino a raggiungere la posizione di arresto designata. A quel punto cambierà colore in base allo stato.
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| PBST_NORMAL | Dopo il riempimento della barra di stato, l'oggetto CTaskDialog non modifica il colore della barra. Per impostazione predefinita, il colore normale è verde. |
| PBST_ERROR | Dopo il riempimento della barra di stato, il CTaskDialog colore della barra viene modificato nel colore dell'errore. Per impostazione predefinita, questo è rosso. |
| PBST_PAUSED | Dopo il riempimento della barra di stato, il CTaskDialog colore della barra viene modificato nel colore sospeso. Per impostazione predefinita, questo è giallo. |
È possibile impostare la posizione in cui si arresta la barra di stato con CTaskDialog::SetProgressBarPosition.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add a marquee progress bar.
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee();
taskDialog.DoModal();
// Remove the marquee bar and replace it with a standard progress bar
taskDialog.SetProgressBarMarquee(0);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarRange(0, 100);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarPosition(75);
taskDialog.SetProgressBarState();
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::SetRadioButtonOptions
Abilita o disabilita un pulsante di opzione.
void SetRadioButtonOptions(
int nRadioButtonID,
BOOL bEnabled);
Parametri
nRadioButtonID
[in] ID del controllo pulsante di opzione.
bEnabled
[in] TRUE per abilitare il pulsante di opzione; FALSE per disabilitare il pulsante di opzione.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se nRadioButtonID non è un ID valido per un pulsante di opzione.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(201, L"First option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(202, L"Second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(203, L"Third option");
taskDialog.DoModal();
int selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (selection)
{
case 201:
// TODO: Place processing here for the first
// radio button.
break;
case 202:
// TODO: Place processing here for the second
// radio button.
break;
case 203:
// TODO: Place processing here for the third
// radio button.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio buttons so that we can use the same task
// dialog with new radio buttons.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(301, L"New first option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(302, L"New second option");
taskDialog.AddRadioButton(303,
L"New third option should be disabled");
// Change the default radio button to the second option
taskDialog.SetDefaultRadioButton(302);
// Make sure the third option is disabled.
if (taskDialog.IsRadioButtonEnabled(303))
{
taskDialog.SetRadioButtonOptions(303, FALSE);
}
taskDialog.DoModal();
selection = taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID();
switch (taskDialog.GetSelectedRadioButtonID())
{
case 301:
// TODO: Place processing here for new first
// command button control.
break;
case 302:
// TODO: Place processing here for new second
// command button control.
break;
case 303:
// TODO: Place processing here for the new third
// command button control.
break;
default:
break;
}
// Remove all the radio button controls and add new ones from
// the string table resource.
taskDialog.RemoveAllRadioButtons();
taskDialog.LoadRadioButtons(1001, 1005);
CTaskDialog::SetVerificationCheckbox
Imposta lo stato selezionato della casella di controllo verifica.
void SetVerificationCheckbox(BOOL bChecked);
Parametri
bChecked
[in] TRUE per fare in modo che la casella di controllo di verifica sia selezionata quando viene visualizzato;CTaskDialog FALSE per deselezionare la casella di controllo verifica quando viene visualizzato .CTaskDialog
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog::SetVerificationCheckboxText
Imposta il testo visualizzato a destra della casella di controllo verifica.
void SetVerificationCheckboxText(CString& strVerificationText);
Parametri
strVerificationText
[in] Testo visualizzato da questo metodo accanto alla casella di controllo verifica.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo genera un'eccezione con la macro ENSURE se questa istanza della CTaskDialog classe è già visualizzata.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Add the verification checkbox and set the default state.
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckboxText(L"Remember your selection.");
taskDialog.SetVerificationCheckbox(false);
taskDialog.DoModal();
if (taskDialog.GetVerificationCheckboxState())
{
// TODO: Write settings of the task dialog to the registry
}
CTaskDialog::SetWindowTitle
Imposta il titolo dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
void SetWindowTitle(CString& strWindowTitle);
Parametri
strWindowTitle
[in] Nuovo titolo per .CTaskDialog
Osservazioni:
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the strings below with the appropriate message,
// main instruction, and dialog title
CString message("This is an important message to the user.");
CString mainInstruction("Important!\nPlease read!");
CString title("Alert Dialog");
CTaskDialog taskDialog(message, mainInstruction, title,
TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON | TDCBF_CANCEL_BUTTON);
// Setting new information to be able to reuse the dialog resource
taskDialog.SetWindowTitle(L"New title for the task dialog");
taskDialog.SetContent(L"New message to show the user.");
taskDialog.SetMainInstruction(L"Even more important!");
taskDialog.SetMainIcon(TD_ERROR_ICON);
taskDialog.SetDialogWidth(300);
// Add a footer
taskDialog.SetFooterText(L"Footer information for the dialog.");
taskDialog.SetFooterIcon(TD_INFORMATION_ICON);
// Add expansion information
taskDialog.SetExpansionArea(L"Additional information\non two lines.",
L"Click here for more information.",
L"Click here to hide the extra information.");
// Change the options to show the expanded information by default.
// It is necessary to retrieve the current options first.
int options = taskDialog.GetOptions();
options |= TDF_EXPANDED_BY_DEFAULT;
taskDialog.SetOptions(options);
taskDialog.DoModal();
CTaskDialog::ShowDialog
Crea e visualizza un oggetto CTaskDialog.
static INT_PTR ShowDialog(
const CString& strContent,
const CString& strMainInstruction,
const CString& strTitle,
int nIDCommandControlsFirst,
int nIDCommandControlsLast,
int nCommonButtons = TDCBF_YES_BUTTON | TDCBF_NO_BUTTON,
int nTaskDialogOptions = TDF_ENABLE_HYPERLINKS | TDF_USE_COMMAND_LINKS,
const CString& strFooter = _T(""));
Parametri
strContent
[in] Stringa da utilizzare per il contenuto dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
strMainInstruction
[in] Istruzione principale di CTaskDialog.
strTitle
[in] Titolo dell'oggetto CTaskDialog.
nIDCommandControlsFirst
[in] ID stringa del primo comando.
nIDCommandControlsLast
[in] ID stringa dell'ultimo comando.
nCommonButtons
[in] Maschera dei pulsanti da aggiungere all'oggetto CTaskDialog.
nTaskDialogOptions
[in] Set di opzioni da utilizzare per .CTaskDialog
strFooter
[in] Stringa da utilizzare come piè di pagina.
Valore restituito
Intero che corrisponde alla selezione effettuata dall'utente.
Osservazioni:
Questo metodo statico consente di creare un'istanza della CTaskDialog classe senza creare in modo esplicito un CTaskDialog oggetto nel codice. Poiché non è presente alcun CTaskDialog oggetto, non è possibile chiamare altri metodi di CTaskDialog se si utilizza questo metodo per visualizzare un oggetto CTaskDialog all'utente.
Questo metodo crea controlli pulsante di comando usando i dati del file di risorse dell'applicazione. La tabella di stringhe nel file di risorse include diverse stringhe con ID stringa associati. Questo metodo aggiunge un controllo pulsante di comando per ogni voce valida nella tabella di stringhe tra nIDCommandControlsFirst e nCommandControlsLast, inclusivo. Per questi controlli pulsante di comando, la stringa nella tabella di stringhe è la didascalia del controllo e l'ID stringa è l'ID del controllo.
Per un elenco di opzioni valide, vedere CTaskDialog::SetOptions .
Chiude CTaskDialog quando l'utente seleziona un pulsante comune, un controllo collegamento di comando o chiude .CTaskDialog Il valore restituito è l'identificatore che indica come l'utente ha chiuso la finestra di dialogo.
Esempio
// TODO: Replace the string below with the actual message to the user
CString message("Important information to the user");
// TODO: Replace the string below with the title of this project
CString title("Project Title");
CString emptyString;
if (CTaskDialog::IsSupported())
{
CTaskDialog::ShowDialog(message, emptyString, title, 0, 0,
TDCBF_OK_BUTTON);
}
else
{
AfxMessageBox(message);
}
CTaskDialog::TaskDialogCallback
Il framework chiama questo metodo in risposta a vari messaggi di Windows.
friend:
HRESULT TaskDialogCallback(
HWND hWnd,
UINT uNotification,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam,
LONG_PTR dwRefData);
Parametri
hwnd
[in] Handle per la m_hWnd struttura per l'oggetto CTaskDialog.
uNotification
[in] Codice di notifica che specifica il messaggio generato.
wParam
[in] Altre informazioni sul messaggio.
lParam
[in] Altre informazioni sul messaggio.
dwRefData
[in] Puntatore all'oggetto CTaskDialog a cui si applica il messaggio di callback.
Valore restituito
Dipende dal codice di notifica specifico. Per ulteriori informazioni, vedere le sezione Note.
Osservazioni:
L'implementazione predefinita di TaskDialogCallback gestisce il messaggio specifico e quindi chiama il metodo On appropriato della classe CTaskDialog. Ad esempio, in risposta al messaggio TDN_BUTTON_CLICKED, TaskDialogCallback chiama CTaskDialog::OnCommandControlClick.
I valori per wParam e lParam dipendono dal messaggio generato specifico. È possibile che uno o entrambi questi valori siano vuoti. Nella tabella seguente sono elencate le notifiche predefinite supportate e i valori di wParam e lParam . Se si esegue l'override di questo metodo in una classe derivata, è necessario implementare il codice di callback per ogni messaggio nella tabella seguente.
| Messaggio di notifica | Valore wParam | Valore lParam |
|---|---|---|
| TDN_CREATED | Non utilizzato. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_NAVIGATED | Non utilizzato. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_BUTTON_CLICKED | ID di controllo del pulsante di comando. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_HYPERLINK_CLICKED | Non utilizzato. | Struttura LPCWSTR che contiene il collegamento. |
| TDN_TIMER | Tempo in millisecondi dopo la CTaskDialog creazione o il timer è stato reimpostato. |
Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_DESTROYED | Non utilizzato. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_RADIO_BUTTON_CLICKED | ID pulsante di opzione. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_DIALOG_CONSTRUCTED | Non utilizzato. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_VERIFICATION_CLICKED | 1 se la casella di controllo è selezionata, 0 in caso contrario. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_HELP | Non utilizzato. | Non utilizzato. |
| TDN_EXPANDO_BUTTON_CLICKED | 0 se l'area di espansione è compressa; diverso da zero se viene visualizzato il testo di espansione. | Non utilizzato. |
Vedi anche
Classi
Classe CObject
Grafico della gerarchia
Procedura dettagliata: Aggiunta di CTaskDialog a un'applicazione