Nata
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti prisijungti arba pakeisti katalogus.
Norint pasiekti šį puslapį, reikalingas leidimas. Galite pabandyti pakeisti katalogus.
You can use Visual Studio Code with a set of extensions to create and manage User Data Functions. The Microsoft Fabric extension and Fabric User data functions extension for VS Code enable you to write functions locally, test them with breakpoints, and publish directly to your Fabric workspace—all within your editor.
This quickstart guides you through creating your first User Data Functions item in VS Code. You learn how to set up your environment, create a function with the default template, and understand the different views available for managing your functions.
Prerequisites
- A Fabric workspace
- Visual Studio Code
- Python 3.11
- Azure Functions Core Tools v4
- Microsoft ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server
- Microsoft Fabric extension
- Fabric User data functions extension
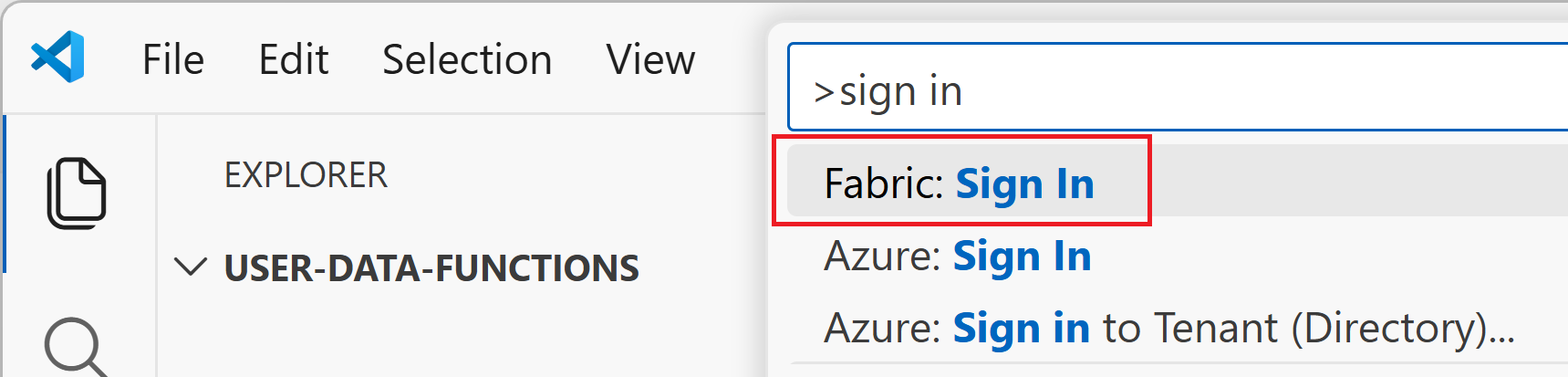
Sign in to Fabric
Before you can create or manage User Data Functions in VS Code, you need to authenticate with your Fabric account. Signing in connects VS Code to your Fabric tenant and allows the extensions to access your workspaces, view existing items, and create new resources in the cloud.
Open VS Code.
Open the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows/Linux or Cmd+Shift+P on Mac).
Enter Fabric: Sign in and select it from the list.
A browser window opens. Sign in with your Microsoft account that has access to Fabric.
After successful authentication, return to VS Code. You should see your account information in the status bar or Microsoft Fabric explorer. You can now access all the workspaces and items you have permissions for in Fabric.
Select your workspace
A workspace is a collaborative environment in Fabric where you organize and manage your items. You need to select a workspace because that's where your User Data Functions item will be created and stored.
Open the Fabric explorer view:
- In the left Activity Bar (the vertical icon bar on the far left), look for the Microsoft Fabric icon and select it.
- If you don't see it, you might need to select the "..." (More Actions) menu in the Activity Bar and select Microsoft Fabric to make it visible.
- The Fabric explorer opens in the left sidebar, showing your workspaces.
In the Fabric explorer in the left sidebar, expand your workspaces to see available workspaces.
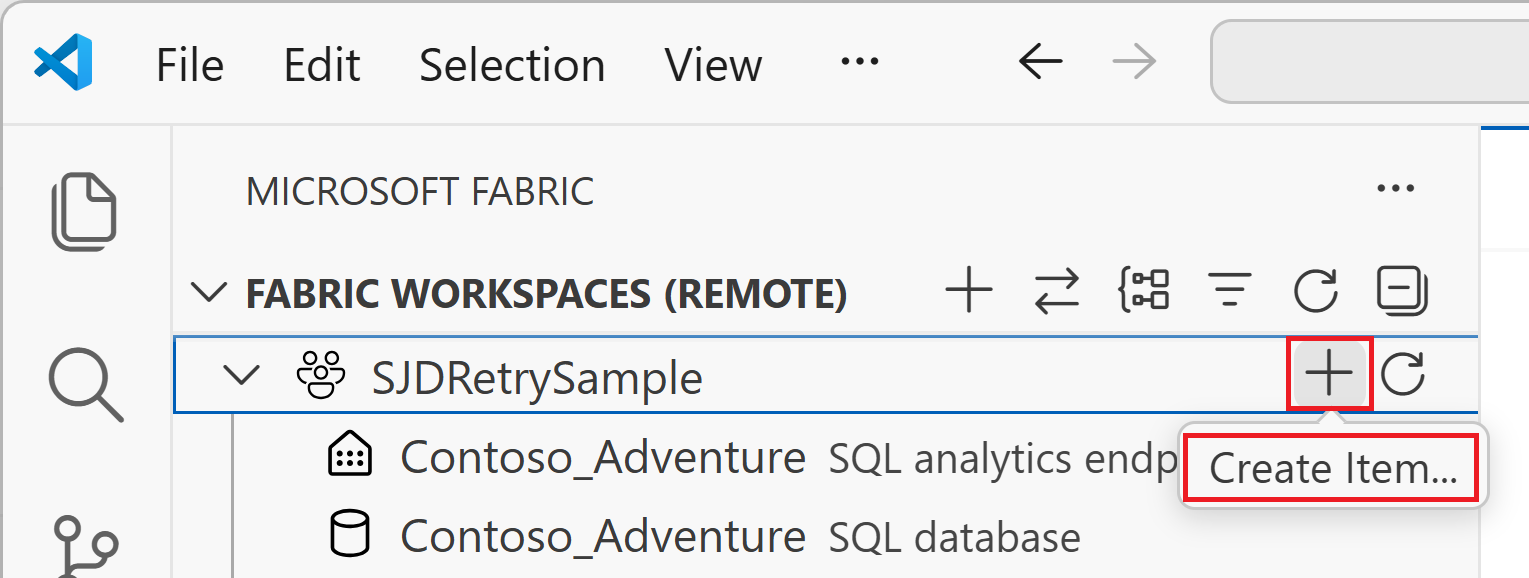
Create a user data functions item
After selecting a workspace, you create a new User Data Functions item. The Fabric User data functions extension guides you through choosing the runtime language, setting up a Python virtual environment, and configuring the project structure. When complete, you have a ready-to-use function template that you can modify or extend.
Right-click your workspace name (or select the "+" button) and then select Create new item.
In the Choose item type dialog, search for and select the User data functions item type.
Enter a name for the new user data functions item and press enter.
Select Python as the runtime language.
Choose whether to open the item in the current window or a new window.
Select the workspace where you want to create the user data functions item.
The item is created. You see the creation status in the lower right corner of VS Code.
When prompted about whether you trust the authors of the files in this folder, select Yes, I trust the authors if you want to continue.
Create a virtual environment for this user data functions item. You should see a prompt (such as Failed to find Python virtual environment ".venv", which is expected based on the setting "azureFunctions.pythonVenv".) in the lower right corner of VS Code. Select Create virtual environment.
Select the Python interpreter and runtime version. User data functions require Python Version 3.11.
Open
function_app.pyto see the defaulthello_fabricfunction. You can modify this function or add more functions.@udf.function() def hello_fabric(name: str) -> str: # Use logging to write custom logs to help trace and debug issues logging.info('Python UDF trigger function processed a request.') logging.info('Executing hello fabric function.') return f"Welcome to Fabric Functions, {name}, at {datetime.datetime.now()}!"
Write a custom function
A user data functions item contains one or many functions. You can modify the default hello_fabric function or add more functions to function_app.py. Every runnable function requires the @udf.function() decorator before the function definition. You can pass inputs for the function such as primitive data types like str, int, float, and more. Within the function, you can write your custom business logic.
For detailed information about function syntax, decorators, and programming model concepts, see Python programming model for user data functions.
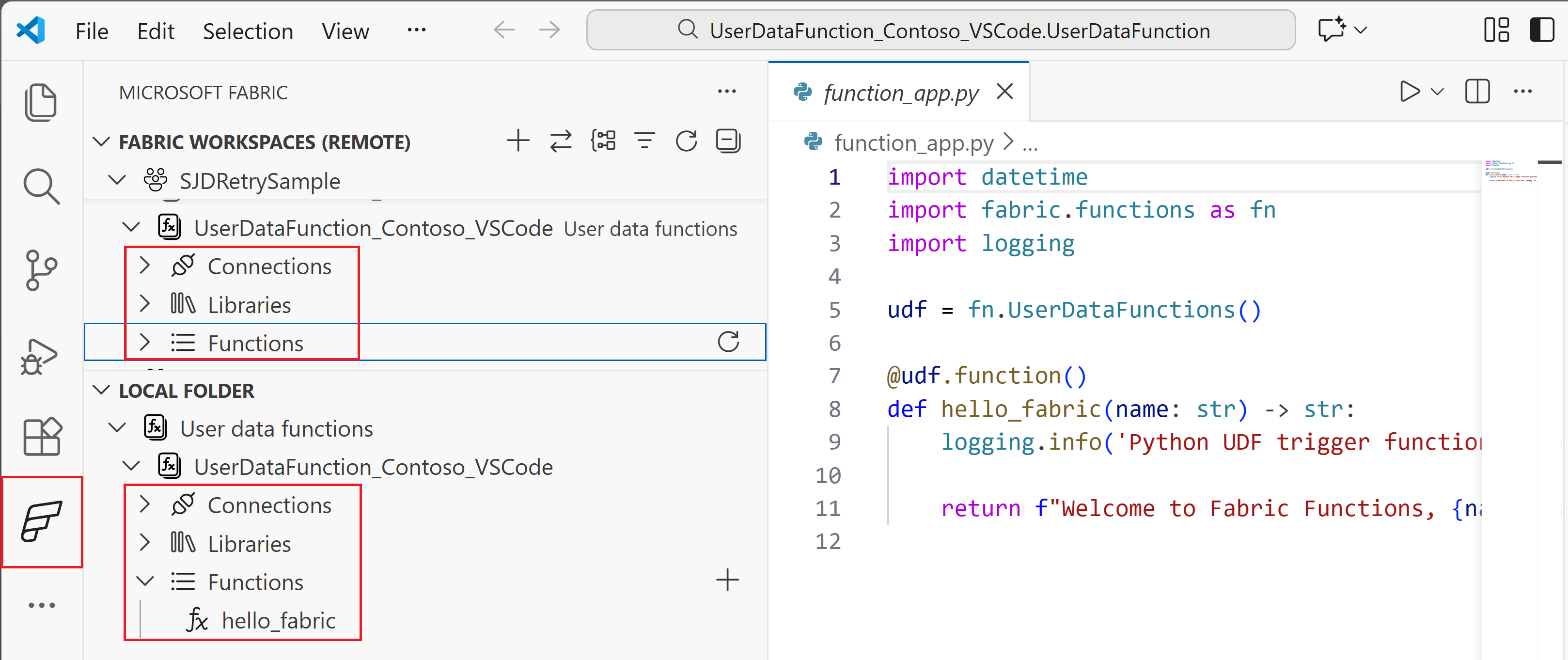
Navigating views in VS Code
In VS Code, you have three different views for working with your user data functions. Understanding these views helps you navigate between editing code files, managing local changes, and working with published functions in Fabric.
Fabric Explorer - Workspace view (remote)
To access the Fabric Explorer, select the Microsoft Fabric icon in the left Activity Bar. The Fabric explorer displays two views simultaneously in the left pane.
The top section shows your Workspace view, which contains items published to Fabric:
- Connections: View and manage data connections published to Fabric. Right-click and select Manage connections in Fabric.
- Libraries: View and manage libraries published to Fabric. Right-click and select Manage libraries in Fabric.
- Functions: View all published functions. Select a function to:
- Run and test the function in VS Code without using API testing tools
- Copy public URL if the function is publicly accessible
Fabric Explorer - Local view
The bottom section of the Fabric explorer shows your Local view, which contains items in your local development environment:
Connections: View connections in your local
local.settings.jsonfile. Select Sync connections from local.settings to refresh the list.Libraries: View libraries in your local
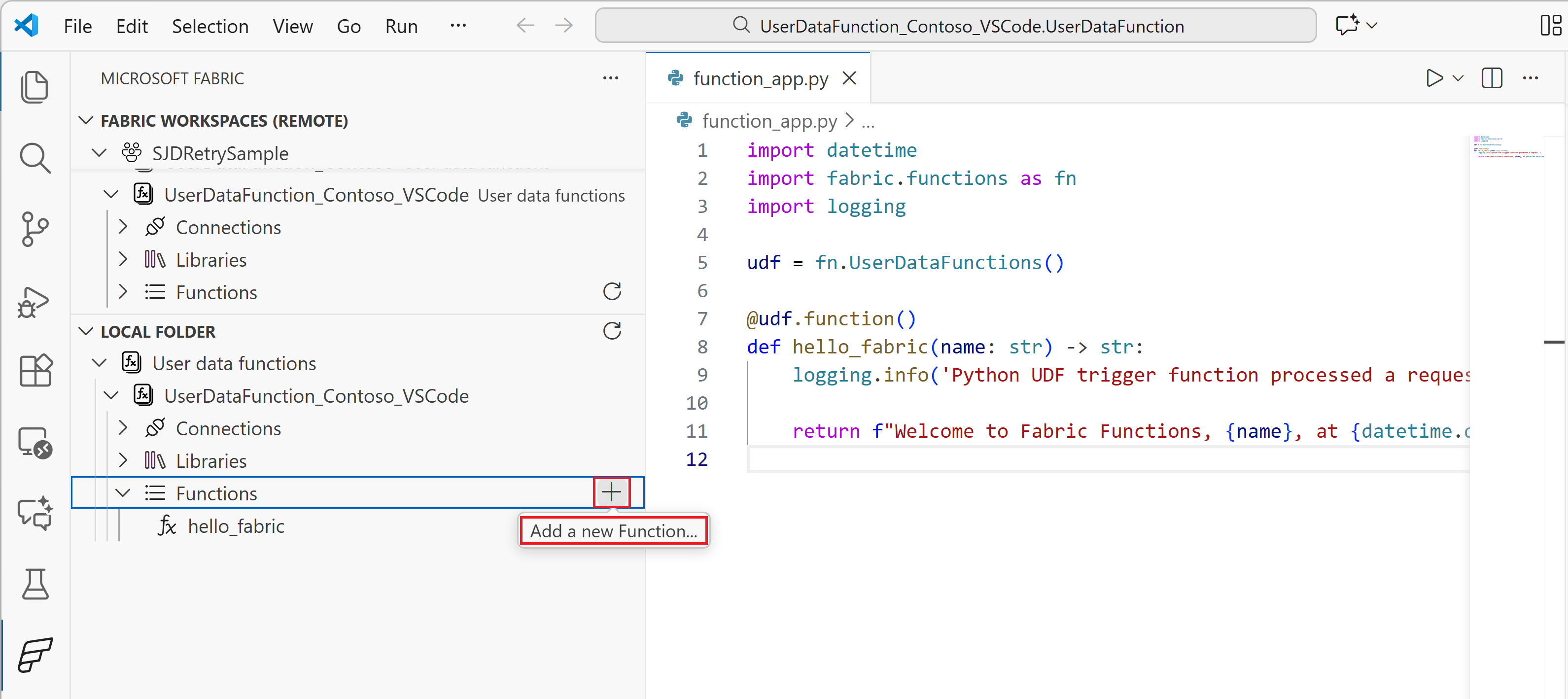
requirements.txtfile. Select Sync requirements.txt to refresh the list.Functions: Expand the Functions node to see all functions in your local
function_app.pyfile. To add a sample function:- Select the + button on the Functions node and select Add function, or
- Right-click on the Functions node and select Add function
File Explorer view
To access the standard File Explorer, select the Explorer icon (file icon) in the left Activity Bar. The File Explorer shows your project files and folders where you edit your function code and configuration files:
- function_app.py: Contains your function code with the
@udf.function()decorators - requirements.txt: Lists Python libraries for your functions
- local.settings.json: Contains local configuration and connection settings
To test your function locally, press F5 to start debugging. You can also select the function item and select Run and debug. You can add a breakpoint anywhere in your code. In debug mode, your breakpoints are hit as expected and test your code as you would test a deployed function.
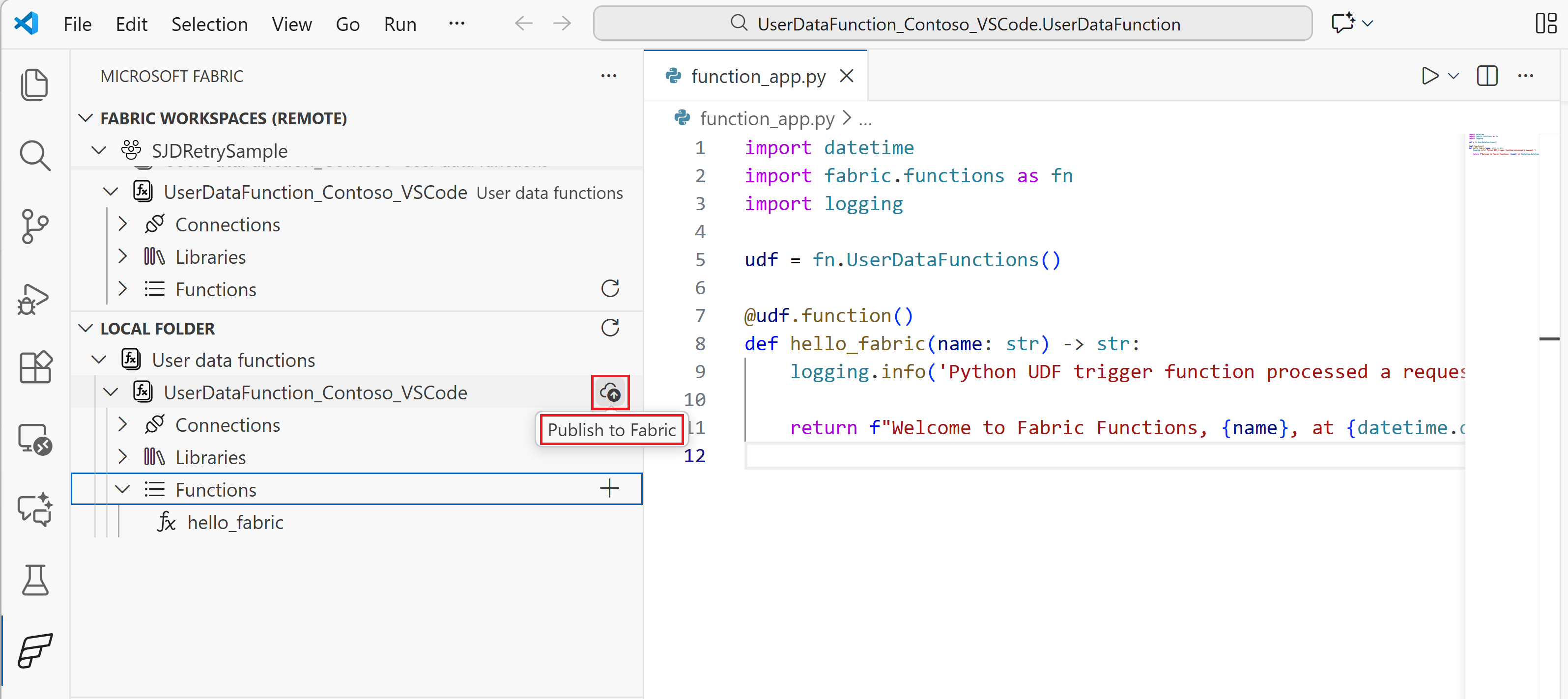
Publish to Fabric
Once you test your changes locally, you can publish the user data function to Fabric. Publishing makes your functions available in the cloud where they can be invoked by other Fabric items or external applications. It can take a few minutes to publish any changes.
To publish, locate your user data functions item node in the Fabric Explorer Local view (named with the item name you created earlier) and:
- Select the Upload to cloud button next to the item name, or
- Right-click on the user data functions item node and select Publish