Firewall policy for endpoint security in Intune
Use the endpoint security Firewall policy in Intune to configure a devices built-in firewall for devices that run macOS and Windows devices.
While you can configure the same firewall settings by using Endpoint Protection profiles for device configuration, the device configuration profiles include additional categories of settings. These additional settings are unrelated to firewalls and can complicate the task of configuring only firewall settings for your environment.
Find the endpoint security policies for firewalls under Manage in the Endpoint security node of the Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Windows 10
- Windows 11
- Windows Server 2012 R2 or later (through the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security settings management scenario)
- Any supported version of macOS
Svarbu
Windows has updated how the Windows Firewall configuration service provider (CSP) enforces rules from Atomic blocks of firewall rules. The Windows Firewall CSP on a device implements the firewall rule settings from your Intune endpoint security Firewall policies. Beginning with the following versions of Windows, the updated CSP behavior now enforces an all-or-nothing application of firewall rules from each Atomic block of rules:
- Windows 11 21H2
- Windows 11 22H2
- Windows 10 21H2
On devices that run an earlier version of Windows, the CSP processes firewall rules in an Atomic block of rules, one rule (or setting) at a time. The intent is to apply all the rules in that Atomic block, or none of them. However, if the CSP encounters an issue with applying any rule from the block, the CSP stops applying subsequent rules but doesn't roll back a rule from that block that has already been applied successfully. This behavior can result in a partial deployment of firewall rules on a device.
For guidance on assigning the right level of permissions and rights to manage Intune firewall policy, see Assign-role-based-access-controls-for-endpoint-security-policy.
Platform: macOS:
- macOS firewall – Enable and configure settings for the built-in firewall on macOS.
Platform: Windows:
For information about configuring settings in the following profiles, see the Firewall configuration service provider (CSP).
Pastaba
Beginning on April 5, 2022, the Windows 10 and later platform was replaced by the Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server platform that is now named more simply as Windows.
The Windows platform supports devices communicating through Microsoft Intune or Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. These profiles also add support for the Windows Server platform which is not supported through Microsoft Intune natively.
Profiles for this new platform use the settings format as found in the Settings Catalog. Each new profile template for this new platform includes the same settings as the older profile template it replaces. With this change you can no longer create new versions of the old profiles. Your existing instances of the old profile remain available to use and edit.
Windows Firewall – Configure settings for Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. Windows Firewall provides host-based, two-way network traffic filtering for a device and can block unauthorized network traffic flowing into or out of the local device.
Windows Firewall rules - Define granular Firewall rules, including specific ports, protocols, applications and networks, and to allow or block network traffic. Each instance of this profile supports up to 150 custom rules.
Patarimas
Use of the Policy App Id setting, which is described in the MdmStore/FirewallRules/{FirewallRuleName}/PolicyAppId CSP, requires that your environment use Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC) tagging. For more information, see the following Windows Defender articles:
Windows Hyper-V Firewall Rules The Windows Hyper-V Firewall Rules template allows you to control firewall rules that will apply to specific Hyper-V containers on Windows, including applications like the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) and the Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA)
In public preview, Windows Firewall rule profiles support use of reusable settings groups for the following platforms:
- Windows 10
- Windows 11
The following firewall rule profile settings are available in reusable settings groups:
- Remote IP address ranges
- FQDN definitions and auto-resolution
When you configure a firewall rule to add one or more reusable settings groups, you’ll also configure the rules Action to define how the settings in those groups are used.
Each rule you add to the profile can include both reusable settings groups and individual settings that are added directly to the rule. However, consider using each rule for either reusable settings groups or to manage settings you add directly to the rule. This separation can help simplify future configurations or changes you might make.
Pastaba
Inbound FQDN rules aren’t natively supported. However, it’s possible to use pre-hydration scripts to generate inbound IP entries for the rule. For more information, see Windows Firewall dynamic keywords in the Windows Firewall documentation.
For prerequisites and guidance on configuring reusable groups, and then adding them to this profile, see Use reusable groups of settings with Intune policies.
Support for devices managed by Configuration Manager is in Preview.
Manage Firewall policy settings for Configuration Manager devices, when you use tenant attach.
Policy path:
- Endpoint security > Firewall
Profiles:
- Windows Firewall (ConfigMgr)
Required version of Configuration Manager:
- Configuration Manager current branch version 2006 or later, with in-console update Configuration Manager 2006 Hotfix (KB4578605)
Supported Configuration Manager device platforms:
- Windows 11 and later (x86, x64, ARM64)
- Windows 10 and later (x86, x64, ARM64)
Plan for Firewall policies to be applied to a device using only one policy. Use of a single policy instance and policy type helps avoid having two separate policies apply different configurations to the same setting, which creates conflicts. When a conflict exists between two policy instances or types of policy that manage the same setting with different values, the setting isn't sent to the device.
That form of policy conflict applies to the Windows Firewall profile, which can conflict with other Windows Firewall profiles, or a firewall configuration that’s delivered by a different policy type, like device configuration.
Windows Firewall profiles don't conflict with Windows Firewall rules profiles.
When you use Windows Firewall rules profiles, you can apply multiple rules profiles to the same device. However, when different rules exist for the same thing with different configurations, both are sent to the device and create a conflict, on that device.
- For example, if one rule blocks Teams.exe through the firewall and a second rule allows Teams.exe, both rules are delivered to the client. This result is different from conflicts created through other policies for Firewall settings.
When rules from multiple rules profiles don't conflict with each other, devices merge the rules from each profile to create a combined firewall rule configuration on the device. This behavior enables you to deploy more than the 150 rules that each individual profile supports to a device.
- For example, you have two Windows Firewall rules profiles. The first profile allows Teams.exe through the firewall. The second profile allows Outlook.exe through the firewall. When a device receives both profiles, the device is configured to allow both apps through the firewall.
The reports for Firewall policy display status details about the firewall status for your managed devices. Firewall reports support managed devices that run the following operating systems.
- Windows 10/11
Summary is the default view when you open the Firewall node. Open the Microsoft Intune admin center, and then go to Endpoint security > Firewall > Summary.
This view provides:
- An aggregate count of devices that have the firewall turned off.
- A list of your Firewall policies, including the name, type, if it's assigned, and when it was last modified.
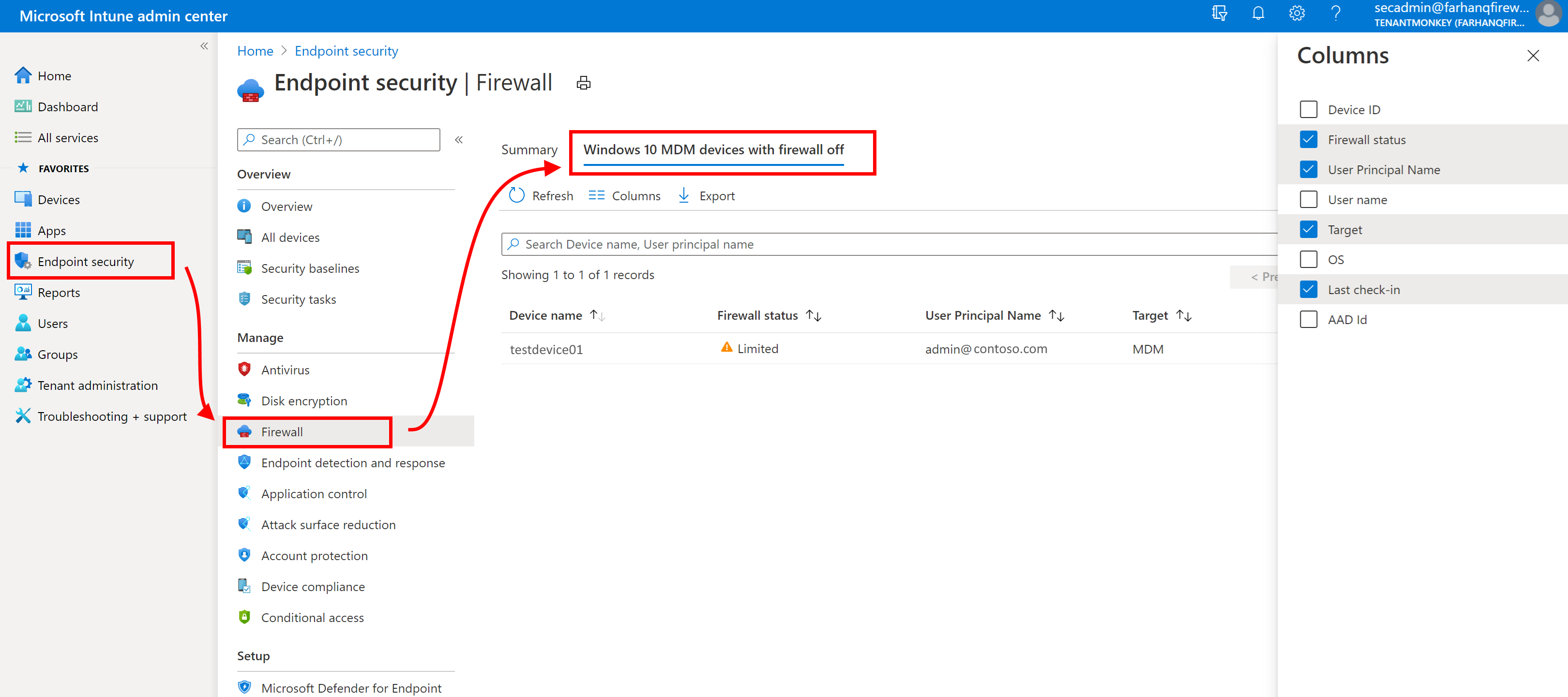
This report is located in the Endpoint security node. Open the Microsoft Intune admin center, and then go to Endpoint security > Firewall > MDM devices running Windows 10 or later with firewall off.
Data is reported through the Windows DeviceStatus CSP, and identifies each device where the Firewall is off. By default, visible details include:
- Device name
- Firewall status
- User principal name
- Target (The method of device management)
- Last check in time
This organizational report is also described in Intune Reports.
As an organizational report, this report is available from the Reports node. Open the Microsoft Intune admin center, and then go to Reports > Firewall > MDM Firewall status for Windows 10 and later.
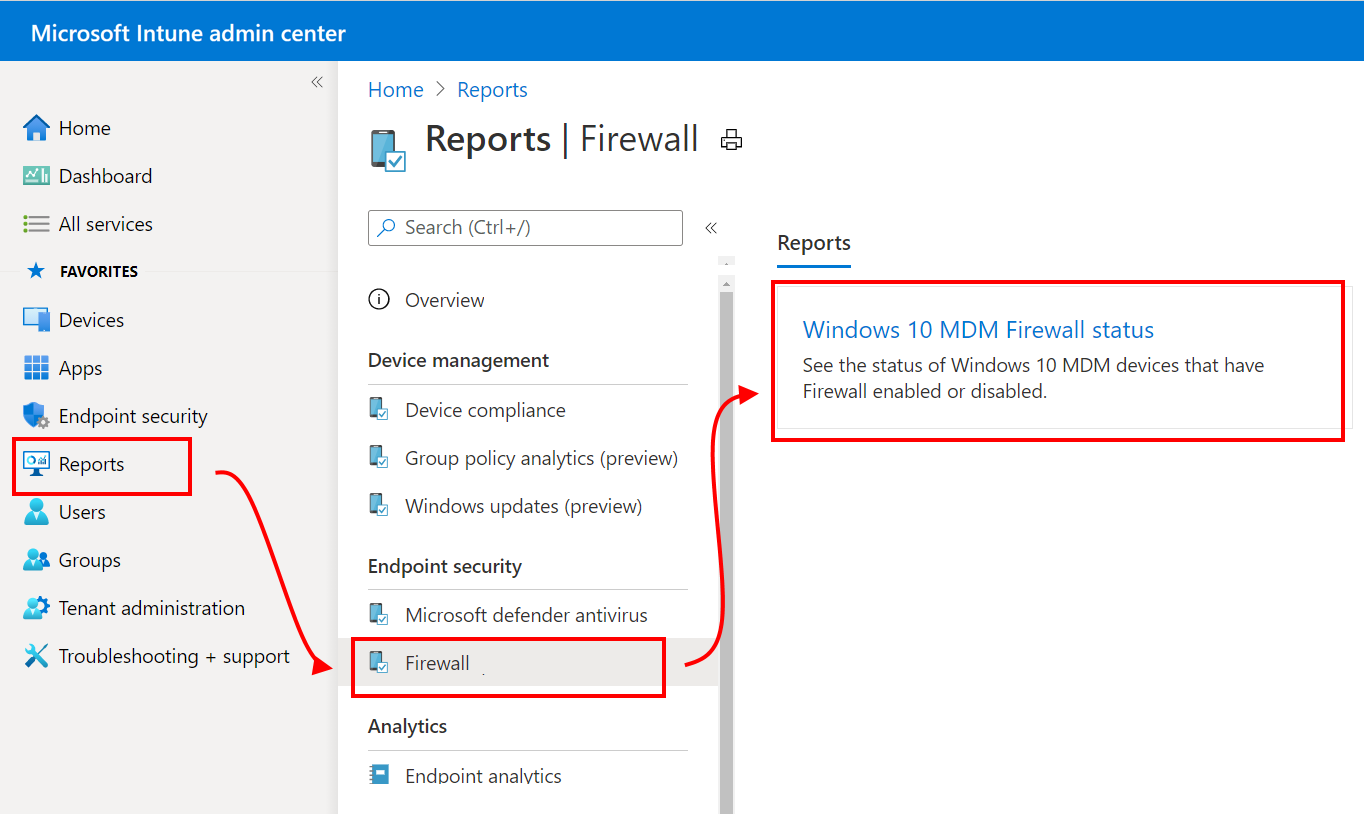
Data is reported through the Windows DeviceStatus CSP, and reports on the status of the firewall on your managed devices. You can filter returns for this report by using one or more of the status detail categories.
Status details include:
- Enabled – The firewall on, and successfully reporting.
- Disabled - The firewall is turned off.
- Limited – The firewall isn’t monitoring all networks, or some rules are turned off.
- Temporarily Disabled (default) – The firewall is temporarily not monitoring all networks
- Not applicable – The device doesn’t support firewall reporting.
You can filter returns for this report by using one or more of the status detail categories.
To learn more about Firewall rules in Intune, and how to troubleshoot common problems, see the following Intune Customer Success blog:
Additional common firewall rule issues:
Event Viewer: RemotePortRanges or LocalPortRanges "The parameter is incorrect"
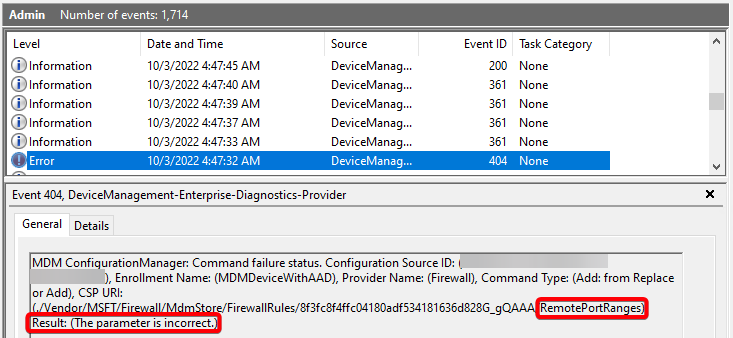
- Verify configured ranges are ascending (Example: 1-5 is correct, 5-1 will cause this error)
- Verify configured ranges are within the overall port range of 0-65535
- If either remote port ranges or local port ranges are configured in a rule, protocol must also be configured with 6 (TCP) or 17 (UDP)
Event Viewer: "...Name), Result: (The parameter is incorrect)"
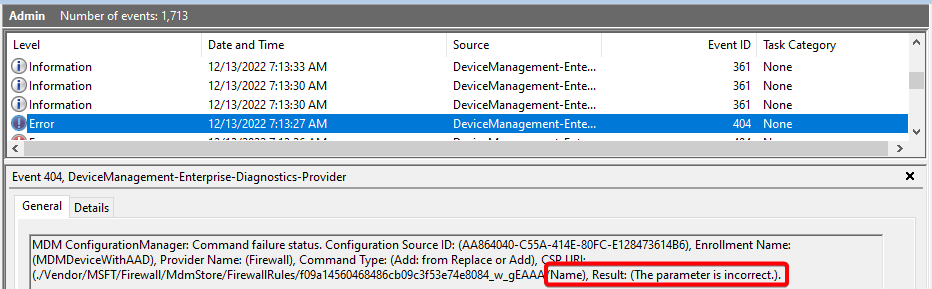
- If edge traversal is enabled in a rule, the rule direction must be set to "This rule applies to inbound traffic".
Event Viewer: "...InterfaceTypes), Result: (The parameter is incorrect)"
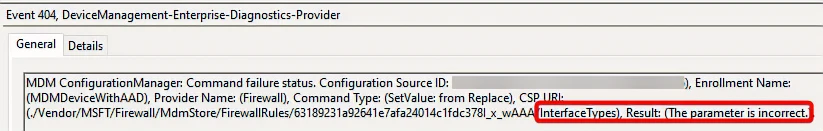
- If "All" interface type is enabled in a rule, the other interface types must not be selected.
Configure Endpoint security policies
View details for the settings in the deprecated Firewall profiles for the deprecated Windows 10 and later platform: