Tutorial: Create Microsoft Entra users using Microsoft Entra applications
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
This article explains how to configure a service principal so it can create Microsoft Entra users in Azure SQL Database. This capability enables programmatic configuration of access management to Azure SQL resources for users and applications in your Microsoft Entra tenant.
Note
Microsoft Entra ID was previously known as Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
For more information on Microsoft Entra authentication for Azure SQL, see the article Use Microsoft Entra authentication.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Assign an identity to the logical server
- Assign the Directory Readers role to the server identity
- Register an application in Microsoft Entra ID
- Create a database user for that application's service principal in Azure SQL Database
- Create a Microsoft Entra database user with the service principal
Prerequisites
- An existing Azure SQL Database deployment. We assume you have a working SQL Database for this tutorial.
- Microsoft Entra
Global AdministratororPrivileged Role Administratorpermissions in the tenant where your SQL database resides. - The latest version of the Az.Sql PowerShell module.
- The latest version of the Microsoft.Graph PowerShell module.
Assign an identity to the logical server
Connect to Azure, specifying the Microsoft Entra tenant that hosts your SQL database. The Tenant ID can be found on the Overview page for your Microsoft Entra ID resource in the Azure portal. Copy the Tenant ID and then run the following PowerShell command:
- Replace
<TenantId>with your Tenant ID.
Connect-AzAccount -Tenant <TenantId>Record the
TenantIdfor future use in this tutorial.- Replace
Generate a system-assigned managed identity and assign it to the logical server in Azure. Execute the following PowerShell command:
- Replace
<ResourceGroupName>and<ServerName>with your resources in the Set-AzSqlServer command. If your server name ismyserver.database.windows.net, replace<ServerName>withmyserver.
Set-AzSqlServer -ResourceGroupName <ResourceGroupName> -ServerName <ServerName> -AssignIdentity- Replace
Check the server identity was successfully assigned. Execute the following PowerShell command:
- Replace
<ResourceGroupName>and<ServerName>with your resources. If your server name ismyserver.database.windows.net, replace<ServerName>withmyserver.
$xyz = Get-AzSqlServer -ResourceGroupName <ResourceGroupName> -ServerName <ServerName> $xyz.identityYour output should show you
PrincipalId,Type, andTenantId. The identity assigned is thePrincipalId.- Replace
You can also check the identity by going to the Azure portal.
- In the Microsoft Entra ID resource, go to Enterprise applications. Type in the name of your logical server. The Object ID that appears on the resource is the ID of the primary server identity.
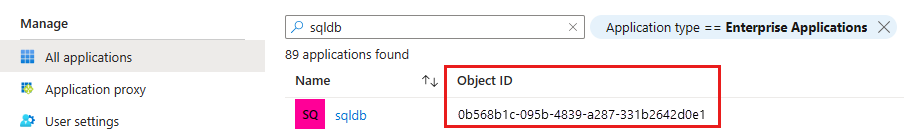
Add server identity to Directory Readers role
The server identity requires permissions to query Microsoft Entra ID for administrative functions, which includes creating Microsoft Entra users and logins, and doing group expansion to apply user permissions based on their Microsoft Entra group membership. If server identity permissions to query Microsoft Entra ID are revoked, or the server identity is deleted, Microsoft Entra authentication stops working.
Assign Microsoft Entra query permissions to the server identity by adding it to the Directory Readers role or assigning the following lower-level Microsoft Graph permissions:
Note
This script must be executed by a Microsoft Entra ID Global Administrator or a Privileged Role Administrator.
The following script grants the Microsoft Entra Directory Readers permission to an identity that represents the logical server for Azure SQL Database.
- Replace
<TenantId>with yourTenantIdgathered earlier. - Replace
<ServerName>with your logical server name. If your server name ismyserver.database.windows.net, replace<ServerName>withmyserver.
# This script grants "Directory Readers" permission to a service principal representing a logical server for Azure SQL Database
# It can be executed only by a user who is a member of the **Global Administrator** or **Privileged Role Administrator** role.
# To check if the "Directory Readers" role was granted, re-execute this script
Import-Module Microsoft.Graph.Authentication
$ServerIdentityName = "<ServerName>" # Enter your logical server name
$TenantId = "<TenantId>" # Enter your tenant ID
Connect-MgGraph -TenantId "<TenantId>" -Scopes "RoleManagement.ReadWrite.Directory,Application.Read.All"
# Get Microsoft Entra "Directory Readers" role and create if it doesn't exist
$roleName = "Directory Readers"
$role = Get-MgDirectoryRole -Filter "DisplayName eq '$roleName'"
if ($role -eq $null) {
# Instantiate an instance of the role template
$roleTemplate = Get-MgDirectoryRoleTemplate -Filter "DisplayName eq '$roleName'"
New-MgDirectoryRoleTemplate -RoleTemplateId $roleTemplate.Id
$role = Get-MgDirectoryRole -Filter "DisplayName eq '$roleName'"
}
# Get service principal for server
$roleMember = Get-MgServicePrincipal -Filter "DisplayName eq '$ServerIdentityName'"
$roleMember.Count
if ($roleMember -eq $null) {
Write-Output "Error: No service principal with name '$($ServerIdentityName)' found, make sure that ServerIdentityName parameter was entered correctly."
exit
}
if (-not ($roleMember.Count -eq 1)) {
Write-Output "Error: Multiple service principals with name '$($ServerIdentityName)'"
Write-Output $roleMember | Format-List DisplayName, Id, AppId
exit
}
# Check if service principal is already member of Directory Readers role
$isDirReader = Get-MgDirectoryRoleMember -DirectoryRoleId $role.Id -Filter "Id eq '$($roleMember.Id)'"
if ($isDirReader -eq $null) {
# Add principal to Directory Readers role
Write-Output "Adding service principal '$($ServerIdentityName)' to 'Directory Readers' role'..."
$body = @{
"@odata.id"= "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/directoryObjects/{$($roleMember.Id)}"
}
New-MgDirectoryRoleMemberByRef -DirectoryRoleId $role.Id -BodyParameter $body
Write-Output "'$($ServerIdentityName)' service principal added to 'Directory Readers' role'."
} else {
Write-Output "Service principal '$($ServerIdentityName)' is already member of 'Directory Readers' role'."
}
Note
The output from this script indicates if the identity is assigned to the Directory Readers role. You can re-run the script if you are unsure if the permission was granted.
For a similar approach on how to assign the Directory Readers role for SQL Managed Instance, see Set Microsoft Entra admin.
In production environments, a common management practice is to assign the Directory Readers role to a role-assignable group in Microsoft Entra ID. Then, group owners can add managed identities to the group. This maintains the principle of least privilege, and bypasses the need for a Global Administrator or Privileged Role Administrator to grant the Directory Readers role individually to every SQL instance. For more information on this feature, see Directory Readers role in Microsoft Entra ID for Azure SQL.
Create an application in Microsoft Entra ID
Register your applications. To register an app, you need at least the Microsoft Entra ID Application Developer role. For more information about assigning roles, see Assign user roles in Microsoft Entra ID.
This tutorial uses two service principals. The first service principal, DBOwnerApp, is used to create other users in the database. The second service principal, myapp, is the application that DBOwnerApp creates a database user for later in this tutorial.
To register your applications:
In the Azure portal, select Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations > New registration.
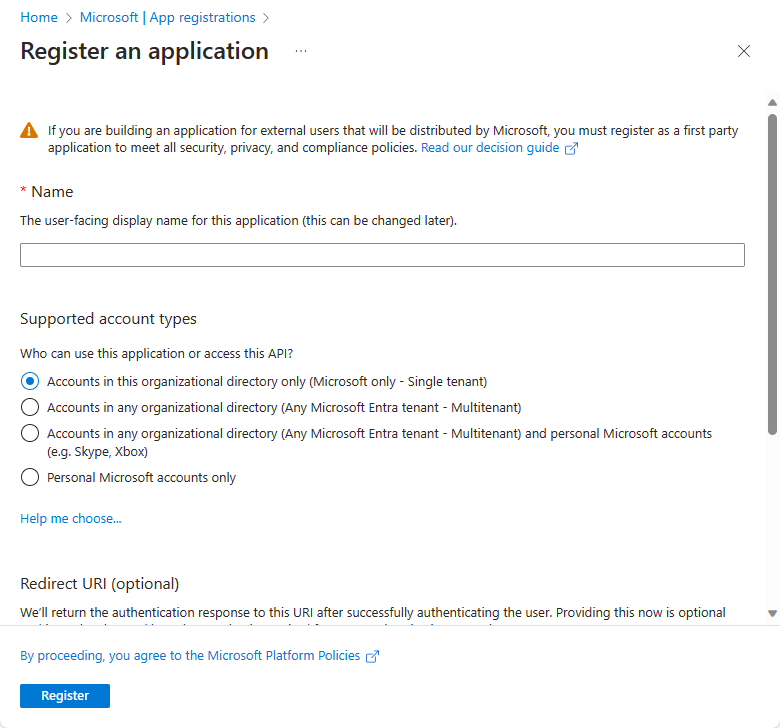
After the app registration is created, the Application (client) ID value is generated and displayed. Record this value for future use in this tutorial.
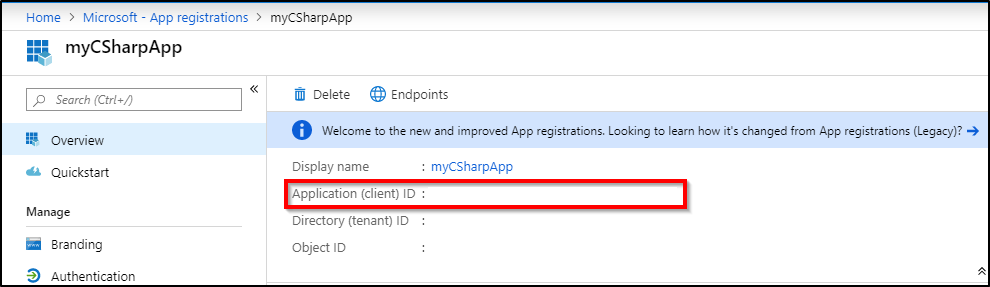
Create a client secret for the application to sign in with. Follow upload a certificate or create a secret for signing in. Record the client secret for DBOwnerApp for future use in this tutorial.
For more information, review Use the portal to create a Microsoft Entra application and service principal that can access resources.
Create the service principal user
Add the newly created service principal, DBOwnerApp, as a user in SQL Database and assign permissions to it.
Connect to your SQL Database using a Microsoft Entra identity that has permissions to create other users.
Important
Only Microsoft Entra users can create other Microsoft Entra users in Azure SQL Database. No users based on SQL authentication, including the server admin, can create a Microsoft Entra user. The Microsoft Entra admin is the only user who can initially create other Microsoft Entra users in SQL Database. After the Microsoft Entra admin has created other users, any Microsoft Entra user with proper permissions can create other Microsoft Entra users.
Create the user DBOwnerApp in the SQL Database using the following T-SQL command:
CREATE USER [DBOwnerApp] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER GOIn order to create other Microsoft Entra users, at minimum, the
ALTER ANY USERSQL permission is required. This permission is also inherited through membership indb_owner, and through assignment as the Microsoft Entra admin. The following examples demonstrate three different options to assign permissions to DBOwnerApp that allow it to create other Microsoft Entra users in the database.You can add DBOwnerApp to the
db_ownerrole with sp_addrolemember:EXEC sp_addrolemember 'db_owner', [DBOwnerApp] GOYou can assign the
ALTER ANY USERpermission to DBOwnerApp like the following T-SQL sample:GRANT ALTER ANY USER TO [DBOwnerApp] GOYou can set the DBOwnerApp as the Microsoft Entra admin. This can be done using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI commands. For more information, see Set Microsoft Entra admin.
Create a user with a service principal
Use the following script to create a Microsoft Entra service principal user myapp using the service principal DBOwnerApp:
- Replace
<TenantId>with yourTenantIdgathered earlier. - Replace
<ClientId>with yourClientIdgathered earlier. - Replace
<ClientSecret>with your client secret created earlier. - Replace
<ServerName>with your logical server name. If your server name ismyserver.database.windows.net, replace<ServerName>withmyserver. - Replace
<database name>with your SQL Database name.
# PowerShell script for creating a new SQL user called myapp using application DBOwnerApp with secret # DBOwnerApp is an admin for the server # Download latest MSAL - https://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/MSAL.PS Import-Module MSAL.PS $tenantId = "<TenantId>" # Microsoft Entra tenant ID where DBOwnerApp resides $clientId = "<ClientId>" # Application (client) ID recorded earlier for DBOwnerApp $clientSecret = "<ClientSecret>" # Client secret for DBOwnerApp $scopes = "https://database.windows.net/.default" # The endpoint $result = Get-MsalToken -RedirectUri $uri -ClientId $clientId -ClientSecret (ConvertTo-SecureString $clientSecret -AsPlainText -Force) -TenantId $tenantId -Scopes $scopes $Tok = $result.AccessToken #Write-host "token" $Tok $SQLServerName = "<ServerName>" # Logical server name $DatabaseName = "<database name>" # Azure SQL database name Write-Host "Create SQL connection string" $conn = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SQLConnection $conn.ConnectionString = "Data Source=$SQLServerName.database.windows.net;Initial Catalog=$DatabaseName;Connect Timeout=30" $conn.AccessToken = $Tok Write-host "Connect to database and execute SQL script" $conn.Open() $ddlstmt = 'CREATE USER [myapp] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;' Write-host " " Write-host "SQL DDL command" $ddlstmt $command = New-Object -TypeName System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand($ddlstmt, $conn) Write-host "results" $command.ExecuteNonQuery() $conn.Close()Alternatively, you can use the following code: Microsoft Entra service principal authentication to Azure SQL Database. Modify the script to execute the DDL statement
CREATE USER [myapp] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER. The same script can be used to create a Microsoft Entra user or group in your database.- Replace
Check if the user myapp exists in the database by executing the following command:
SELECT name, type, type_desc, CAST(CAST(sid as varbinary(16)) as uniqueidentifier) as appId FROM sys.database_principals WHERE name = 'myapp' GOYou should see a similar output:
name type type_desc appId myapp E EXTERNAL_USER 6d228f48-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Next steps
- Microsoft Entra service principal with Azure SQL
- What are managed identities for Azure resources?
- How to use managed identities for App Service and Azure Functions
- Microsoft Entra service principal authentication to SQL DB - Code Sample
- Application and service principal objects in Microsoft Entra ID
- Create an Azure service principal with Azure PowerShell
- Directory Readers role in Microsoft Entra ID for Azure SQL